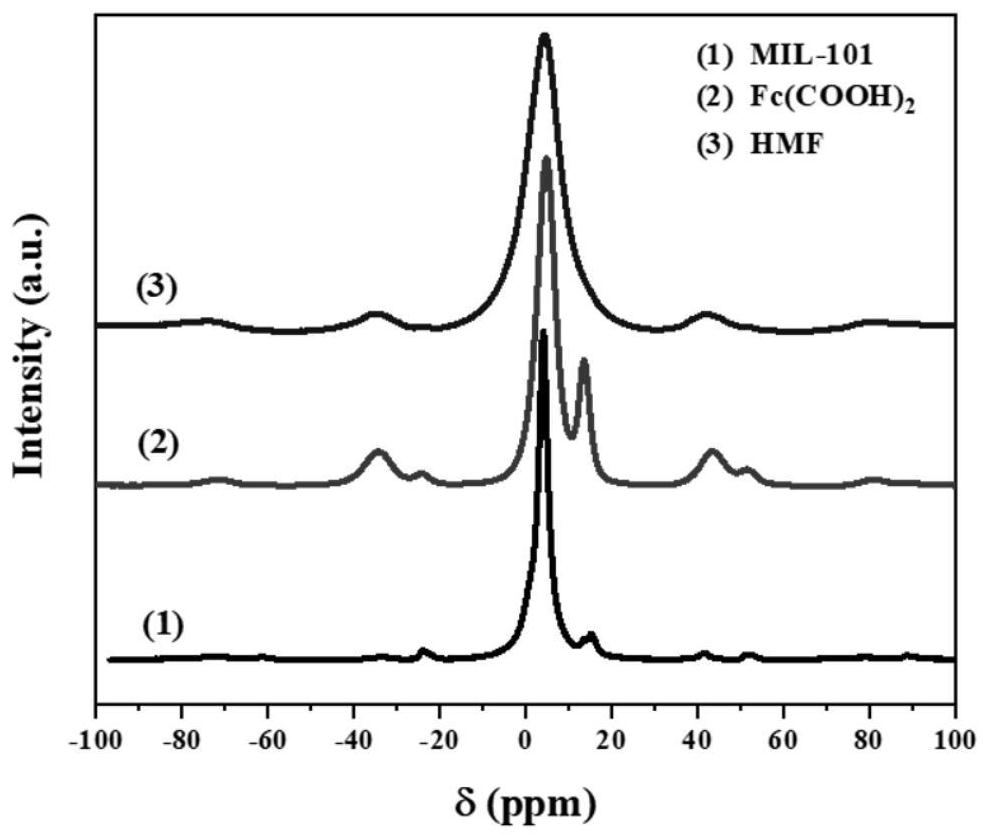
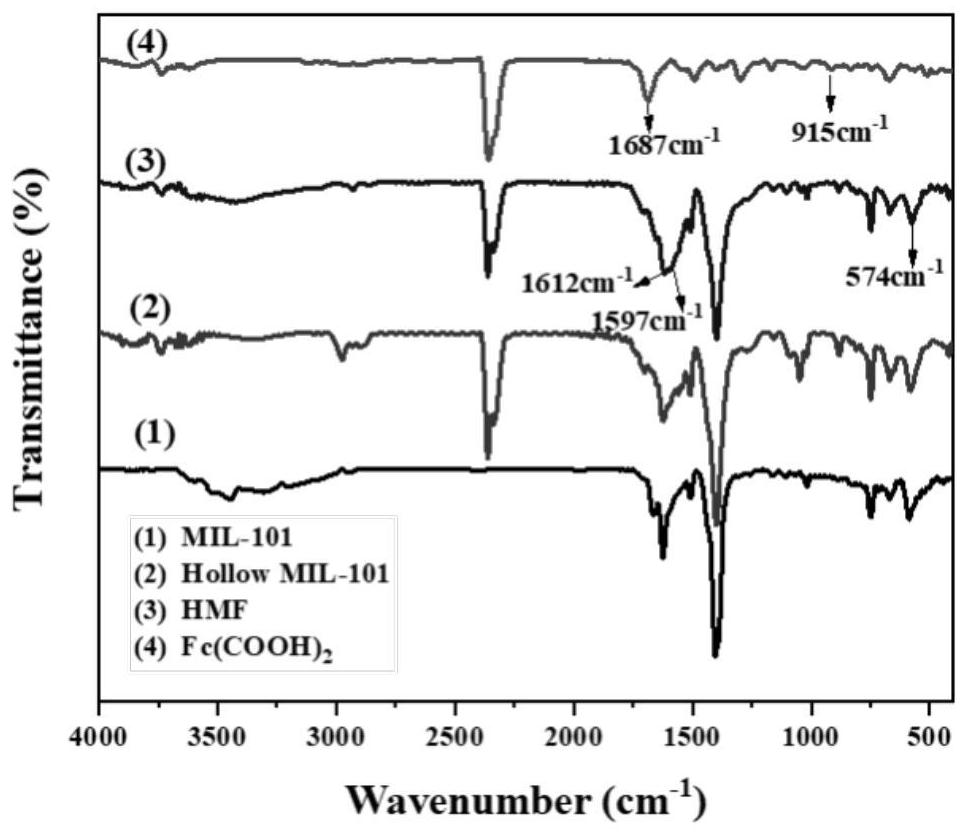
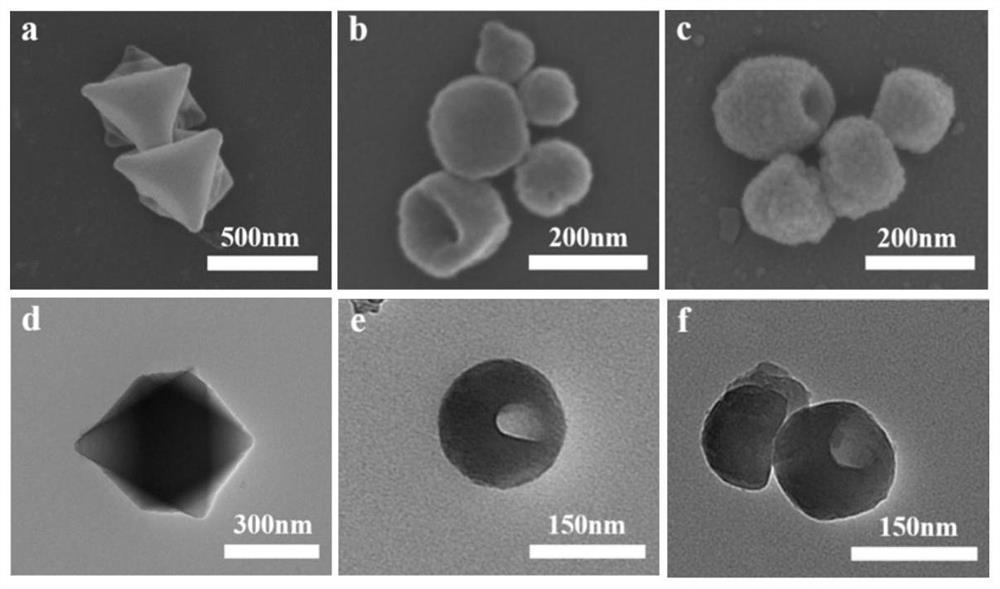
Ligand-exchanged hollow MIL-101 metal organic framework material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A metal-organic framework and ligand exchange technology, applied in the field of materials science, can solve problems such as accumulation of toxic substances, and achieve the effect of improving the total adsorption capacity and the water vapor adsorption capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] (1) Weigh chromium nitrate nonahydrate (0.8g) and terephthalic acid (0.22g) in a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, then add deionized water (20ml) for ultrasonic dispersion for 10min, and then place it in a reactor It was sealed and reacted in a preheated oven at 180°C for 4 hours. After cooling, the product was centrifuged (10000rpm, 10min) and washed with N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF) and deionized water, respectively. Three times, MIL-101 metal-organic framework materials were obtained.
[0054] (2) The above MIL-101 was redispersed in deionized water (40ml), then acetic acid (2ml) was added and dispersed uniformly by ultrasonic, then the suspension was transferred to a polytetrafluoroethylene liner and sealed, placed in a preheated The reaction was carried out at 180°C for 4 hours in an oven. After cooling, the product was centrifuged (10000rpm, 10min), washed three times with DMF and deionized water, and finally vacuum-dried at 80°C for 12 hours to obtain a hollow MIL-...
Embodiment 2 and 3
[0076] (1) Weigh chromium nitrate nonahydrate (0.8g) and terephthalic acid (0.22g) in a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, then add deionized water (20ml) for ultrasonic dispersion for 10min, and then place it in a reactor It was sealed and reacted in a preheated oven at 180°C for 4 hours. After cooling, the product was centrifuged (10000rpm, 10min) and washed with N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF) and deionized water, respectively. Three times, MIL-101 metal-organic framework materials were obtained.
[0077] (2) The above MIL-101 was redispersed in deionized water (40ml), then acetic acid (2ml) was added and dispersed uniformly by ultrasonic, then the suspension was transferred to a polytetrafluoroethylene liner and sealed, placed in a preheated The reaction was carried out at 180°C for 3 hours in an oven. After cooling, the product was centrifuged (10000rpm, 10min), washed three times with DMF and deionized water, and finally vacuum-dried at 80°C for 12 hours to obtain a hollow MIL-...
Embodiment 4 and 5
[0080] (1) Weigh chromium nitrate nonahydrate (0.8g) and terephthalic acid (0.22g) in a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, then add deionized water (20ml) for ultrasonic dispersion for 10min, and then place it in a reactor It was sealed and reacted in a preheated oven at 180°C for 4 hours. After cooling, the product was centrifuged (10000rpm, 10min) and washed with N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF) and deionized water, respectively. Three times, MIL-101 metal-organic framework materials were obtained.
[0081] (2) The above MIL-101 was redispersed in deionized water (40ml), then acetic acid (2ml) was added and dispersed uniformly by ultrasonic, then the suspension was transferred to a polytetrafluoroethylene liner and sealed, placed in a preheated The reaction was carried out at 180°C for 3 hours in an oven. After cooling, the product was centrifuged (10000rpm, 10min), washed three times with DMF and deionized water, and finally vacuum-dried at 80°C for 12 hours to obtain a hollow MIL-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com