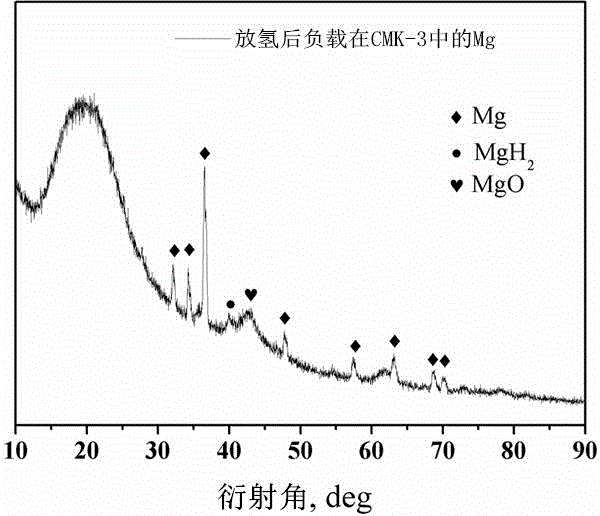
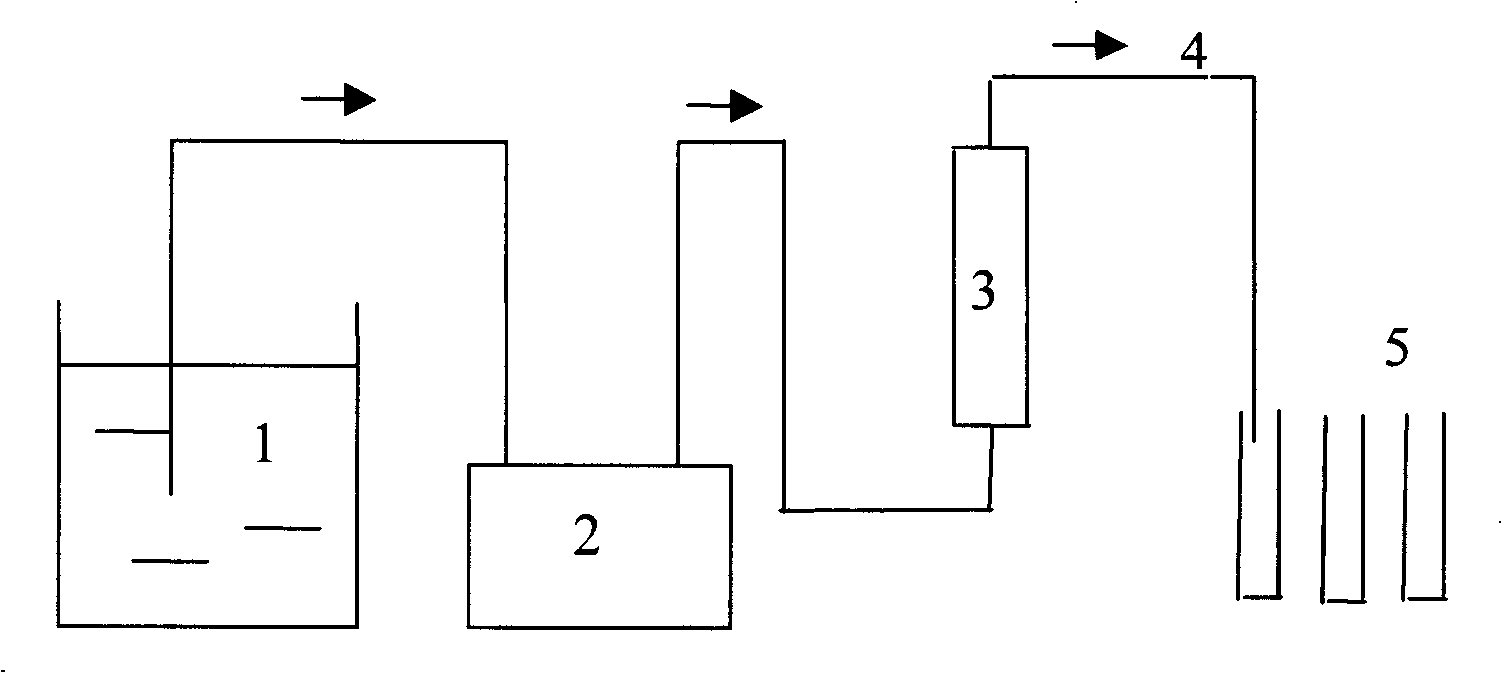
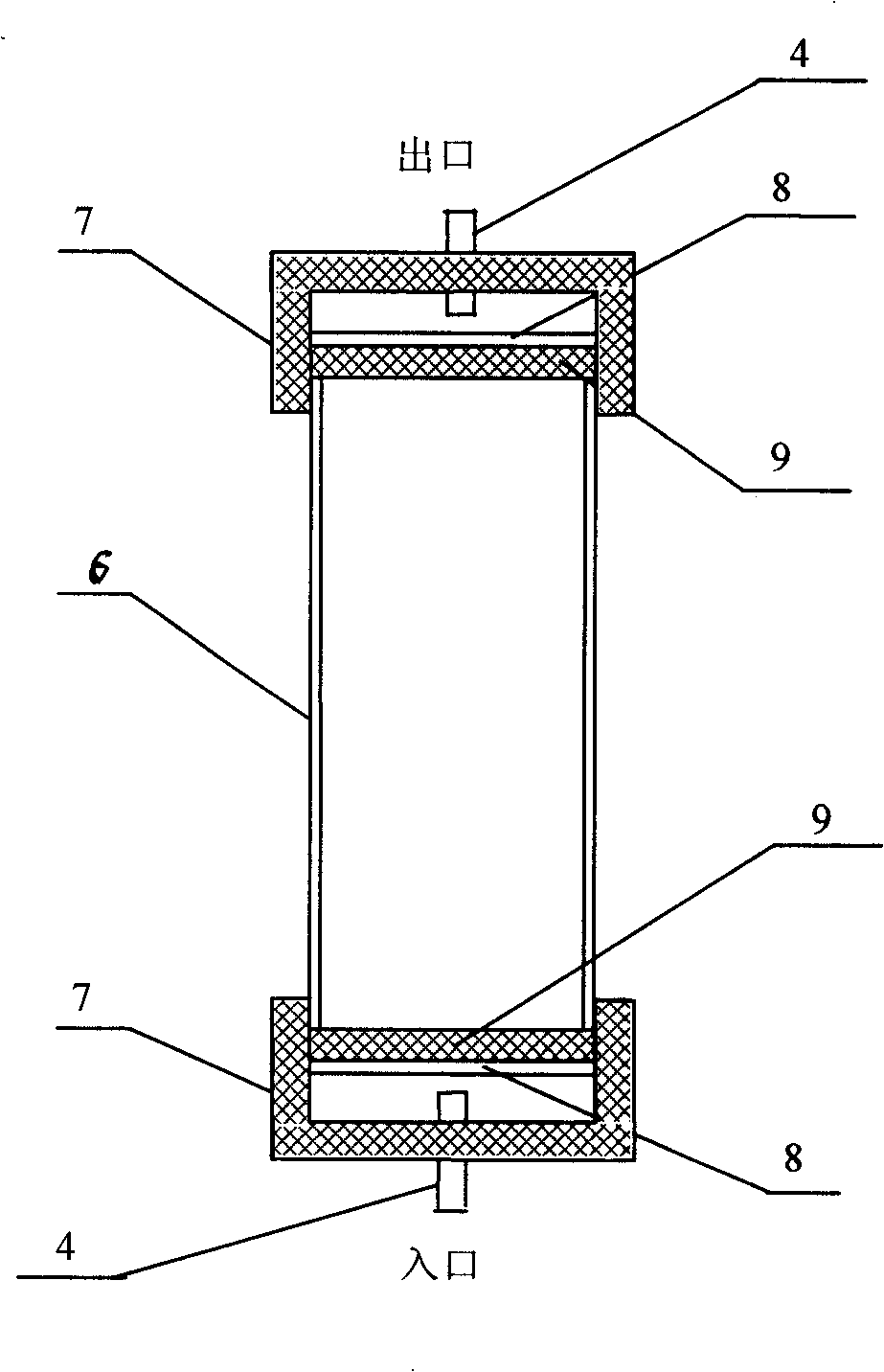
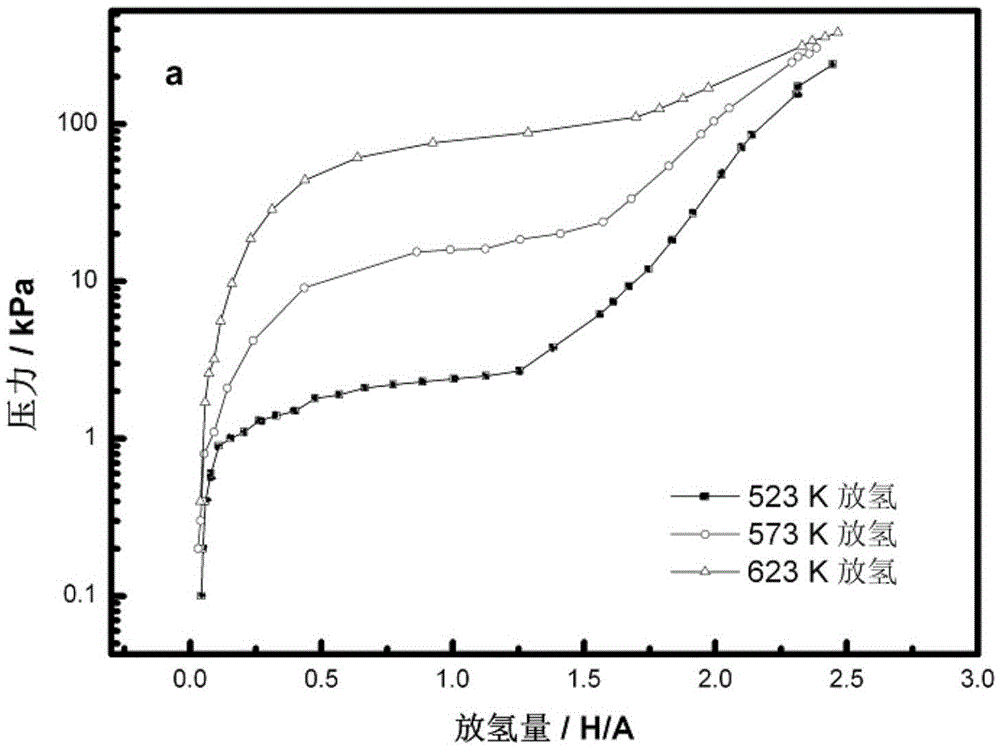
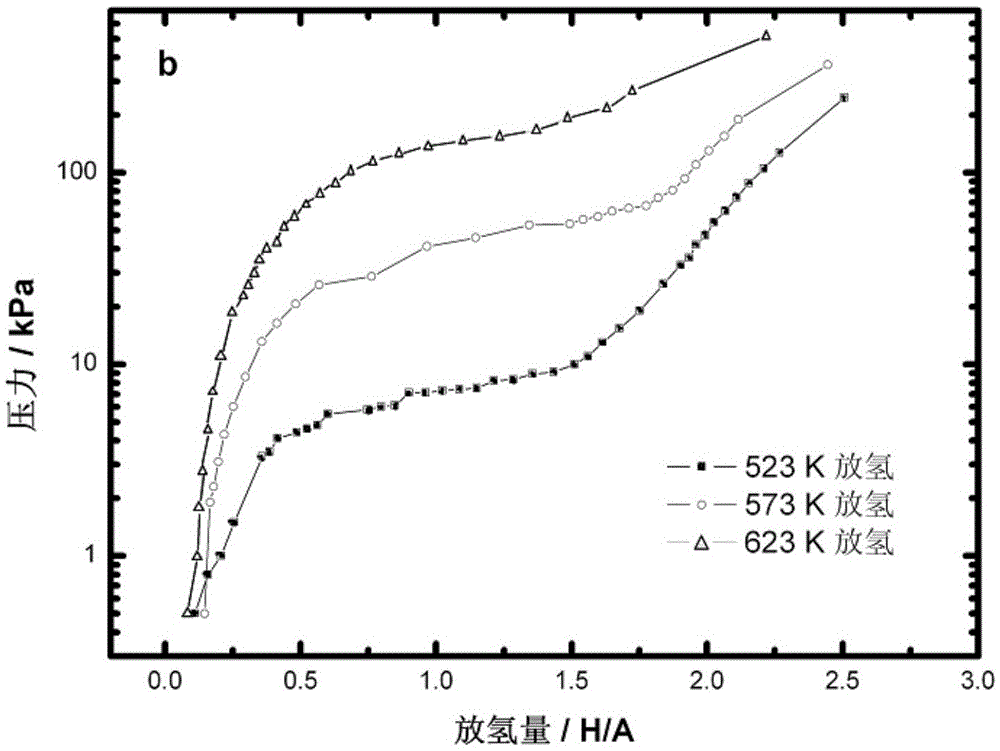
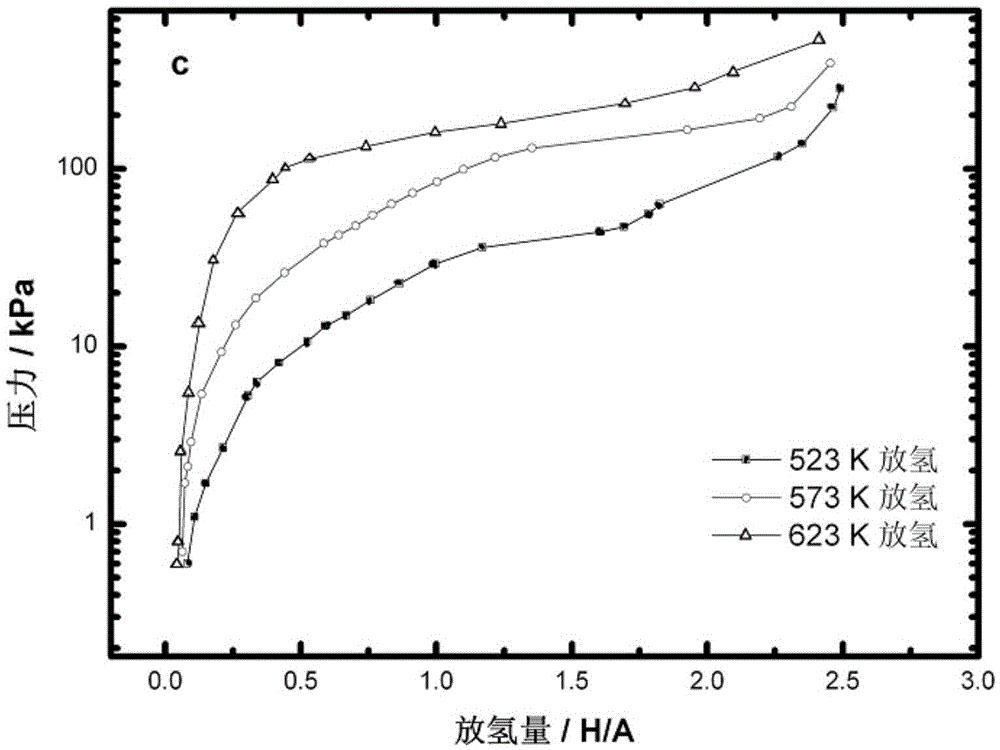
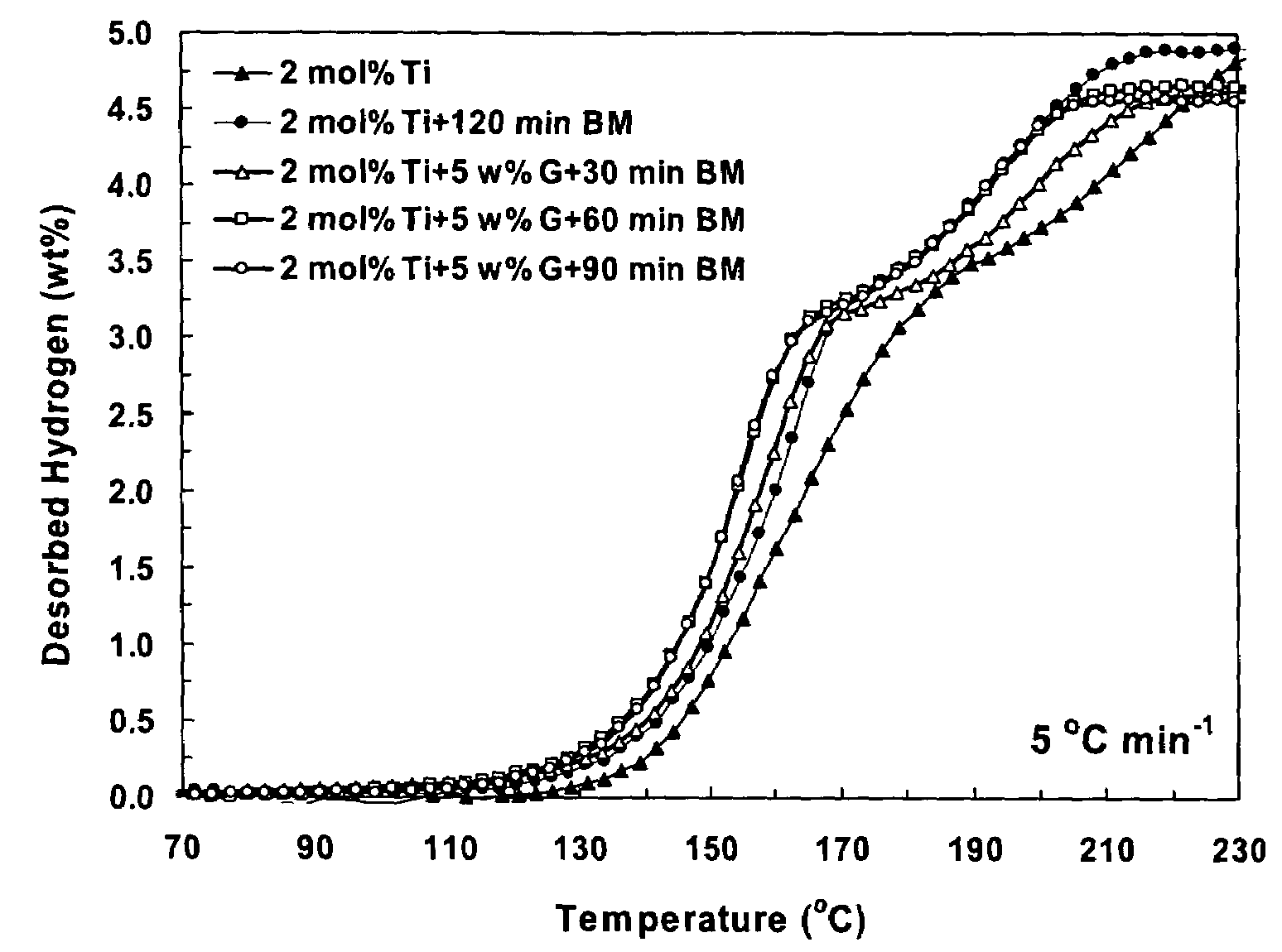
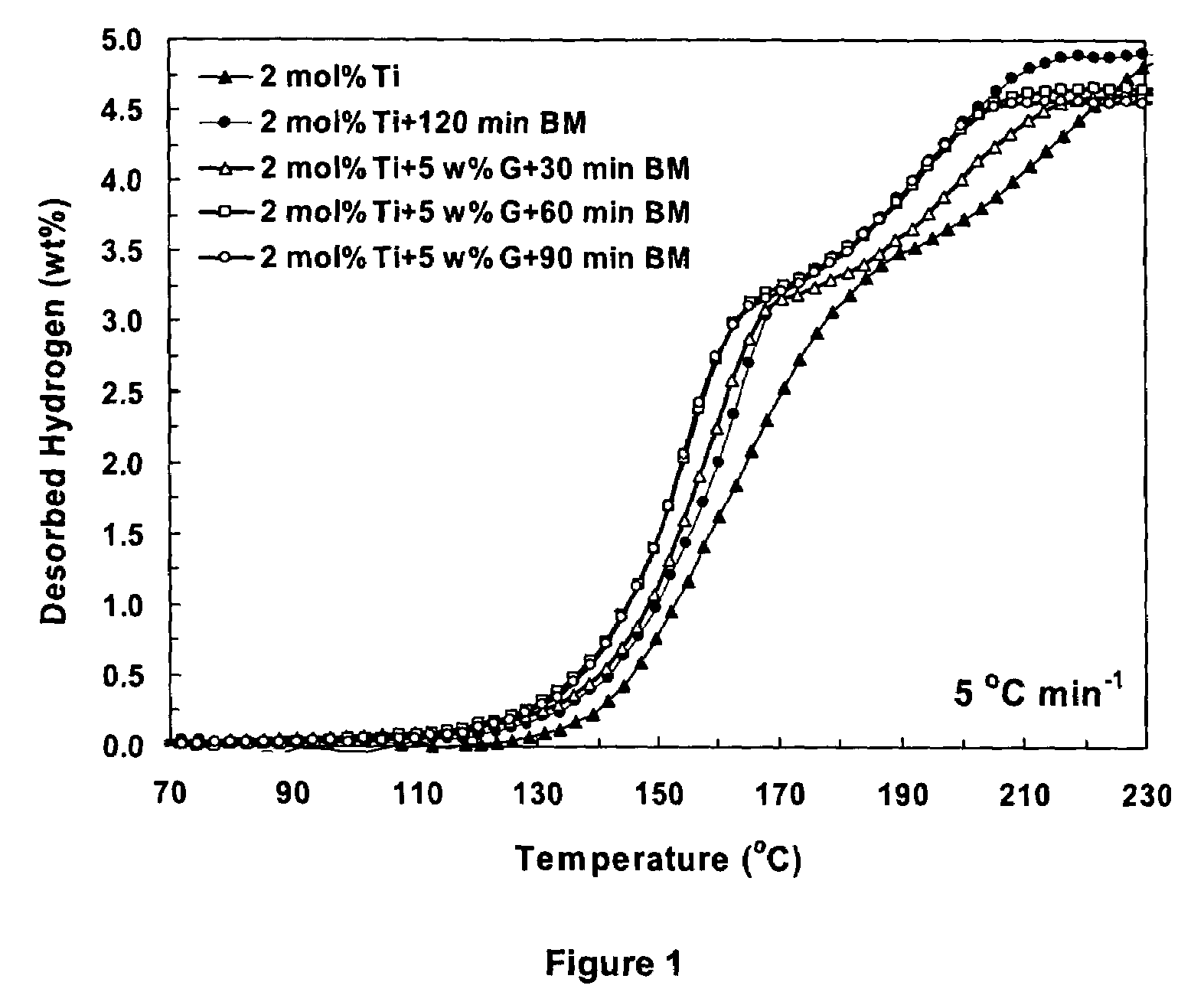
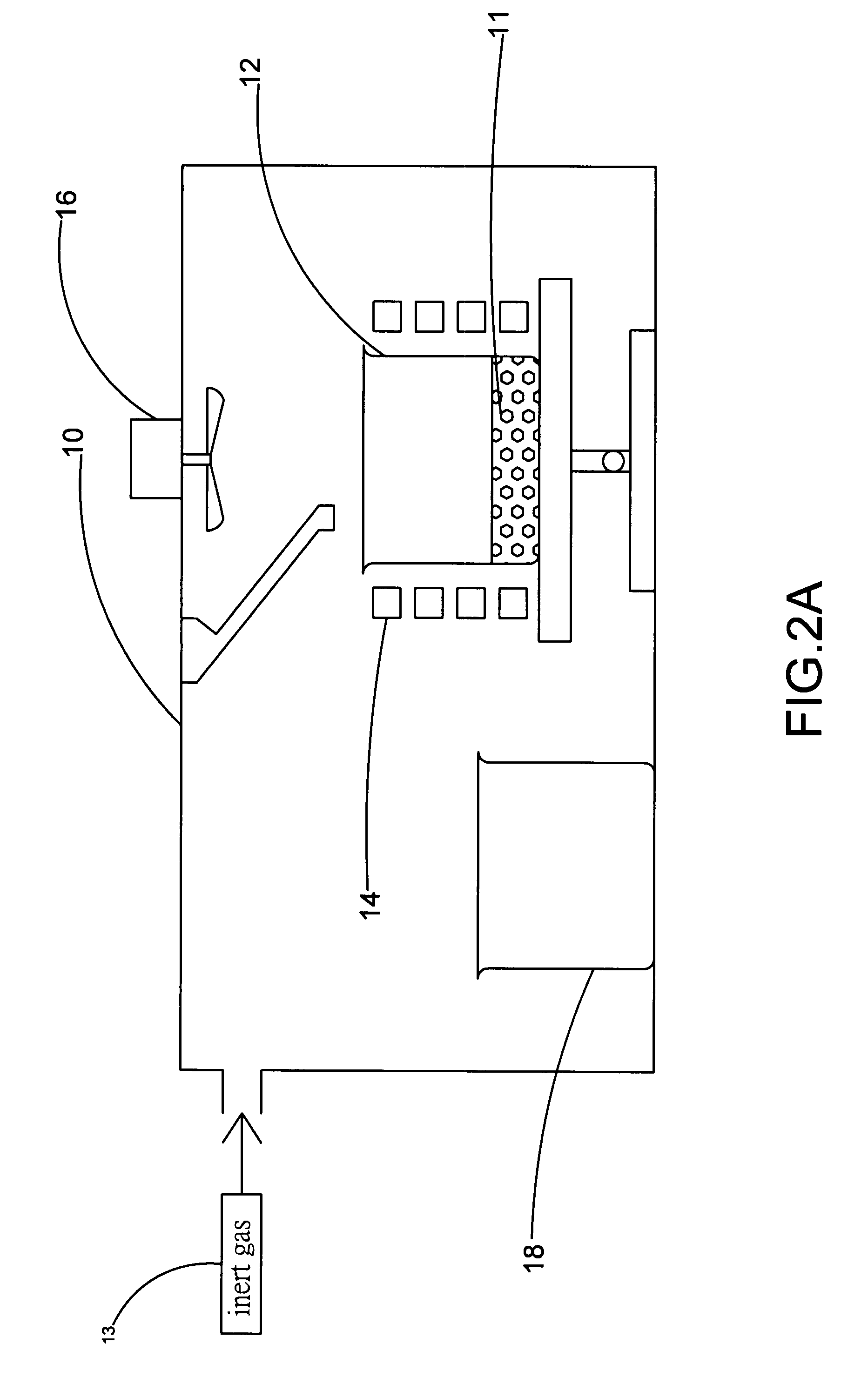
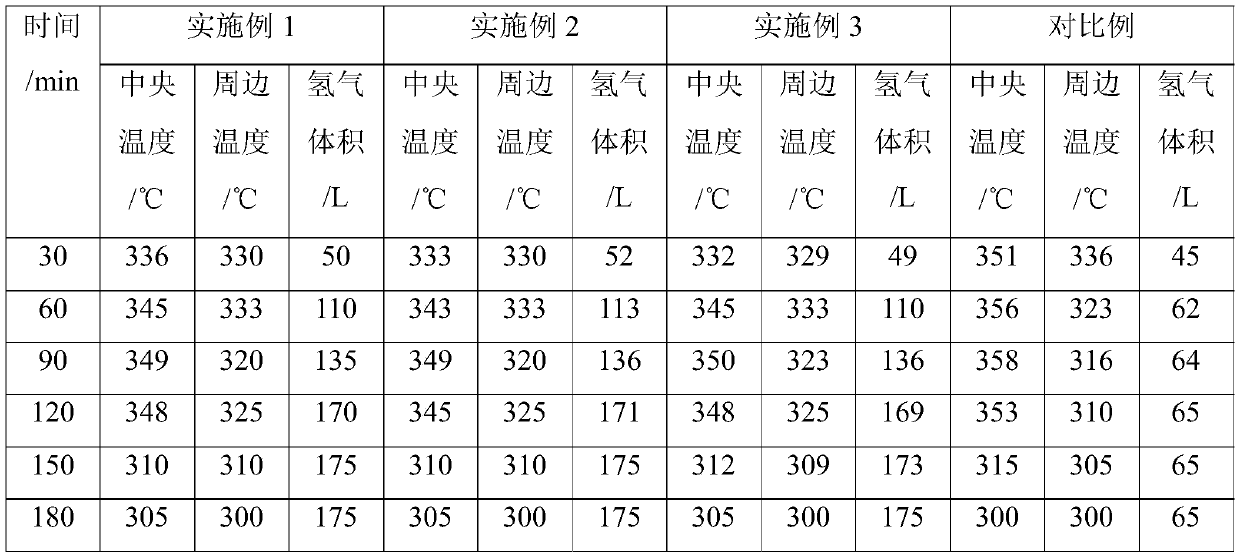
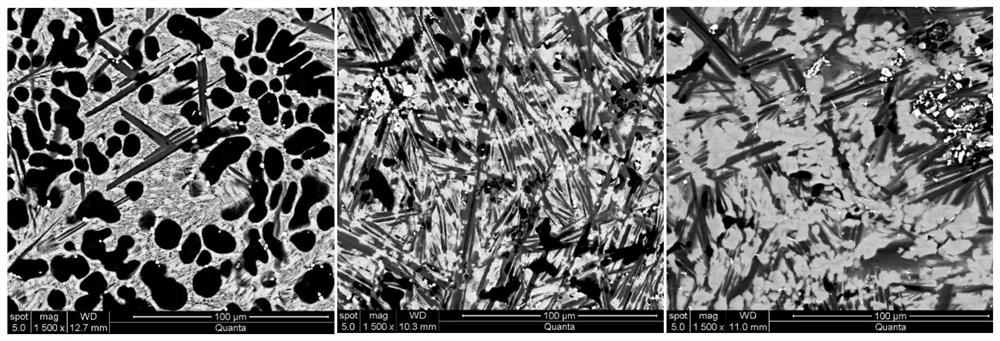
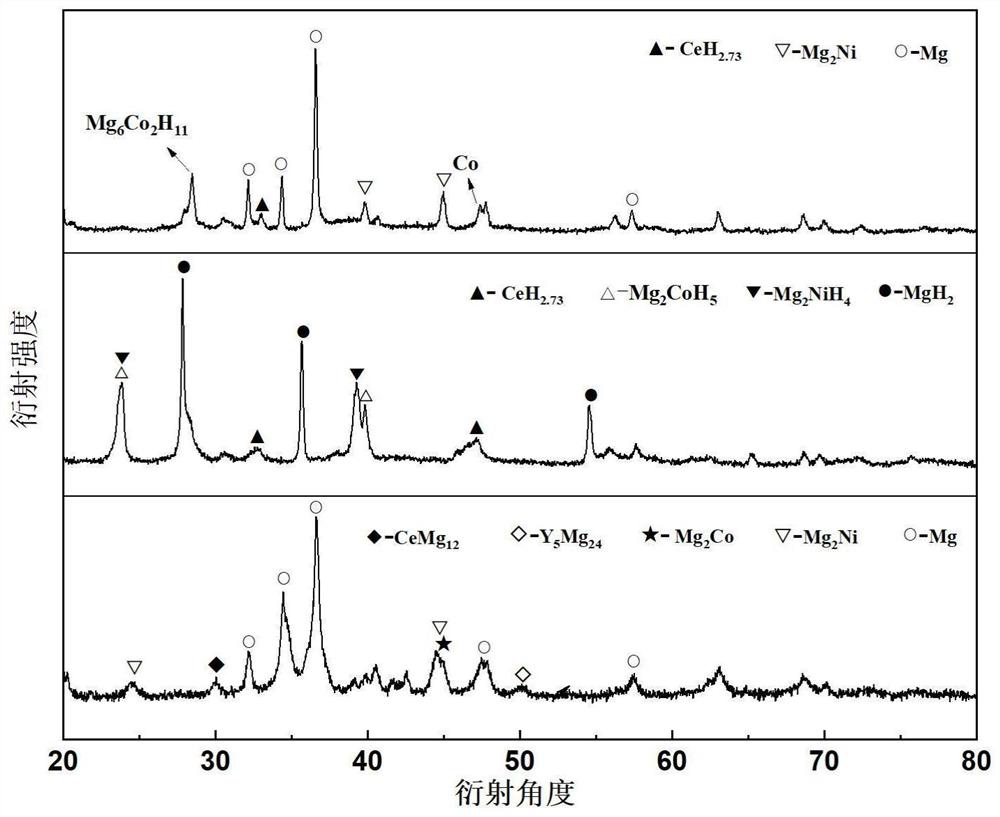
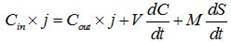Patents
Literature
35 results about "Desorption kinetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
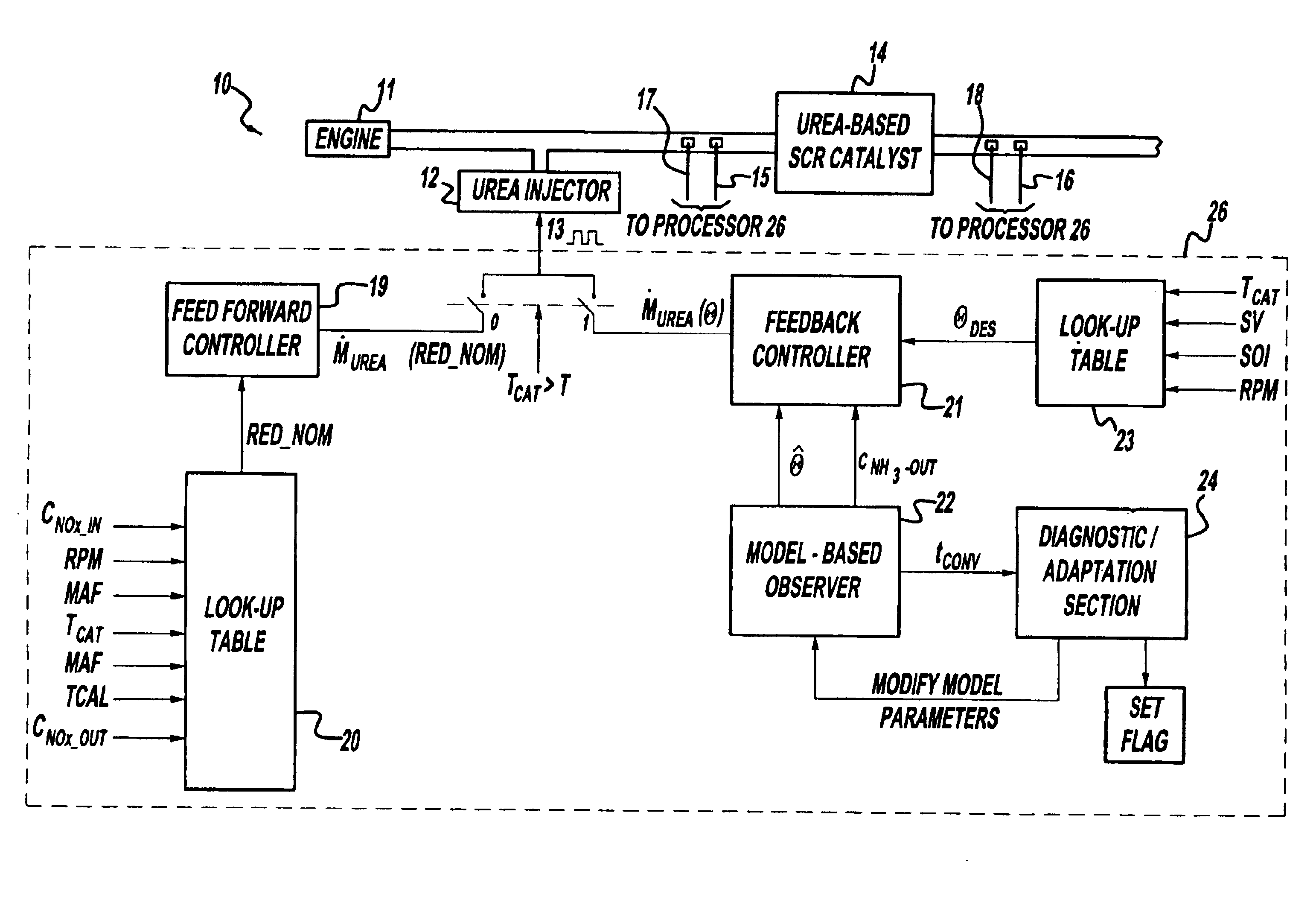
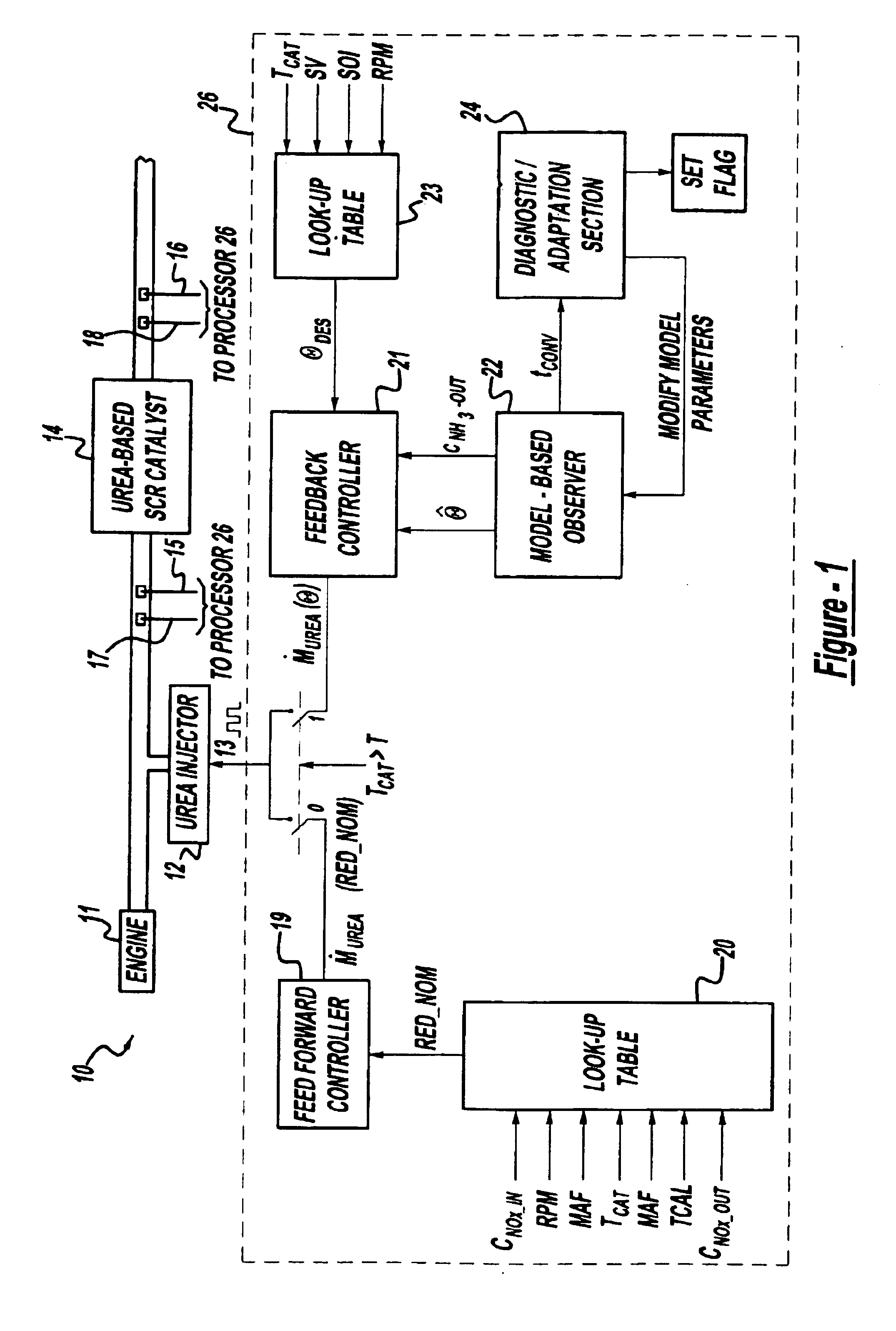
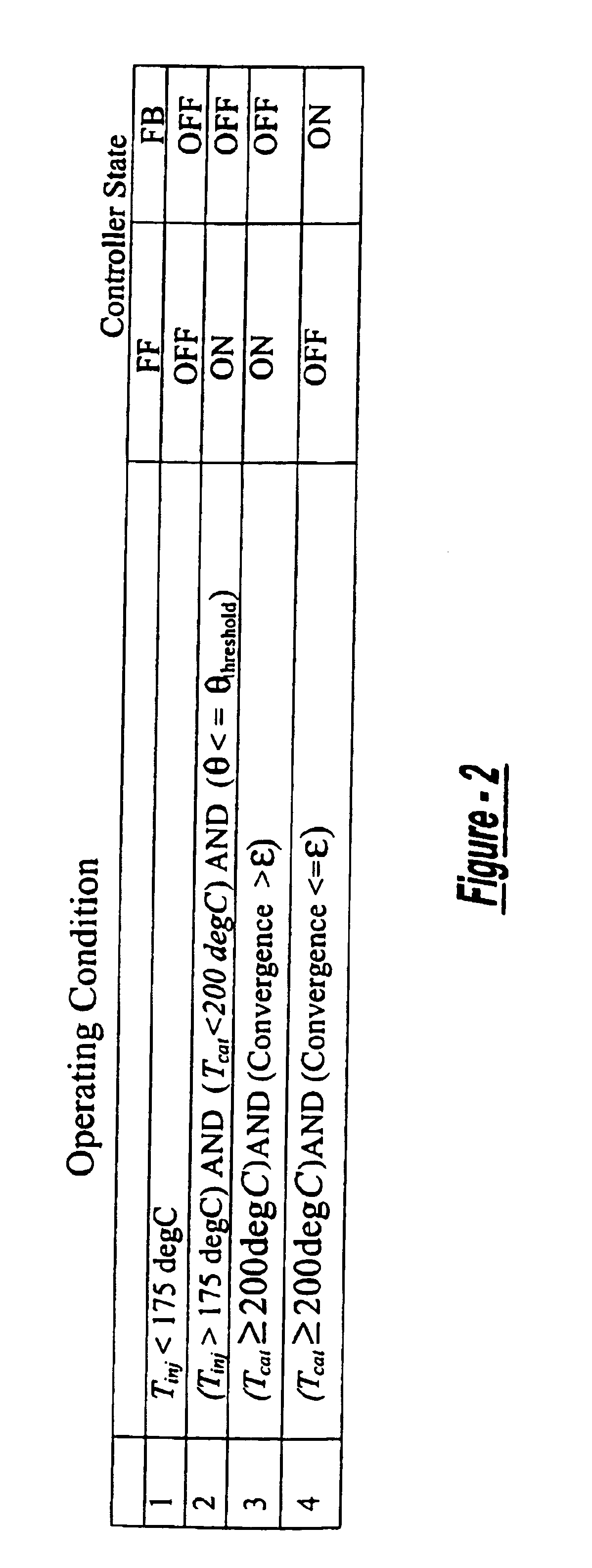
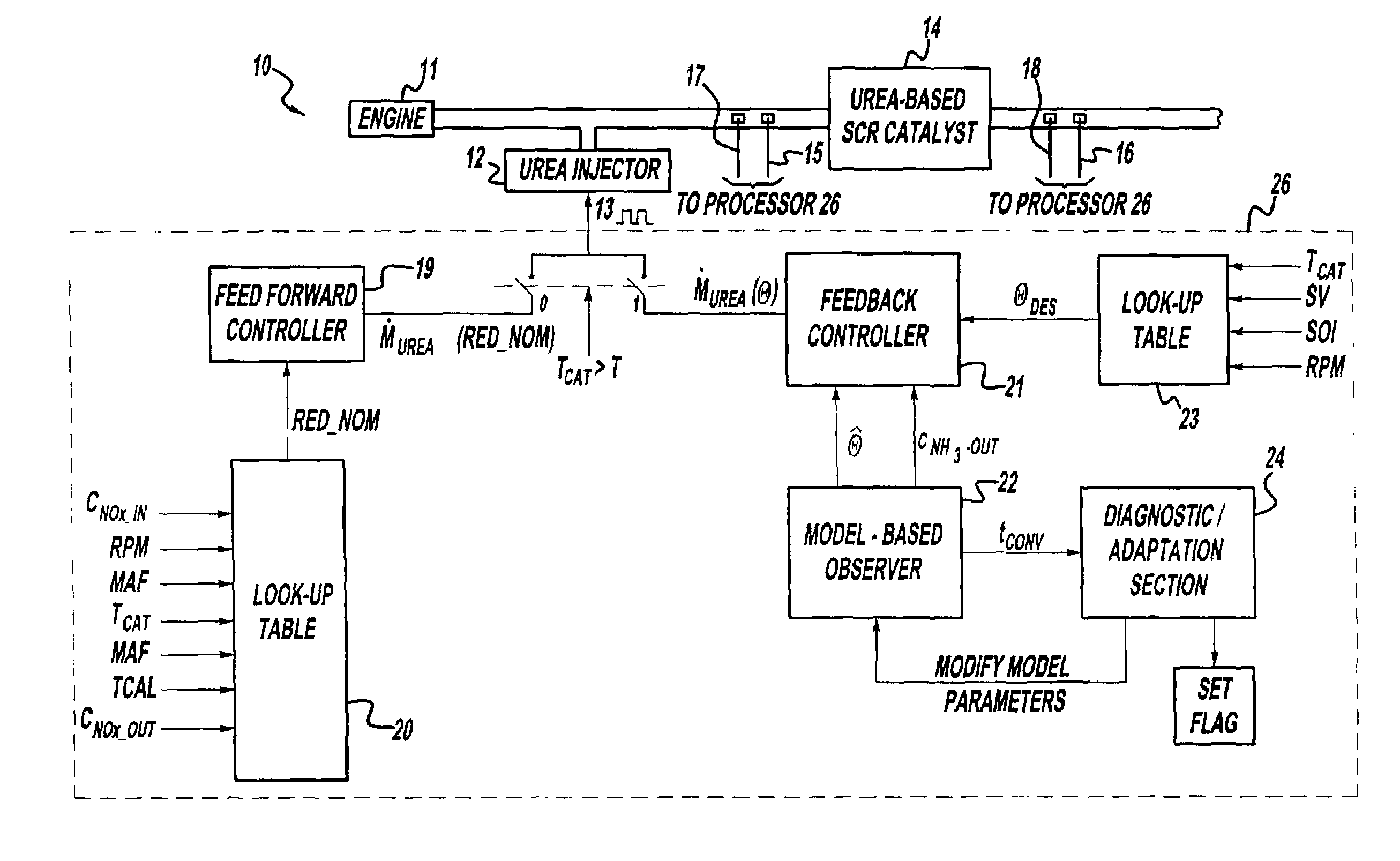
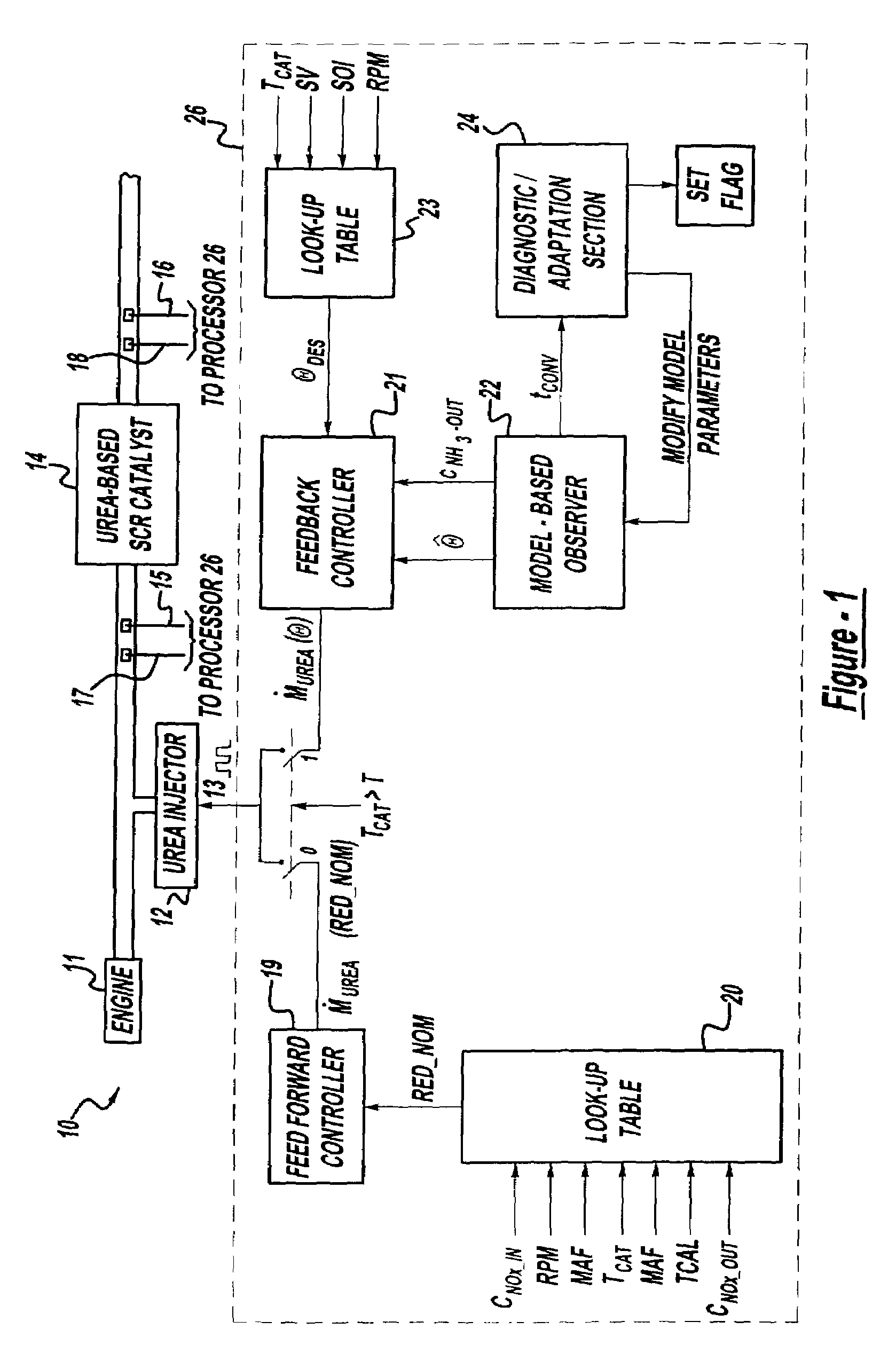
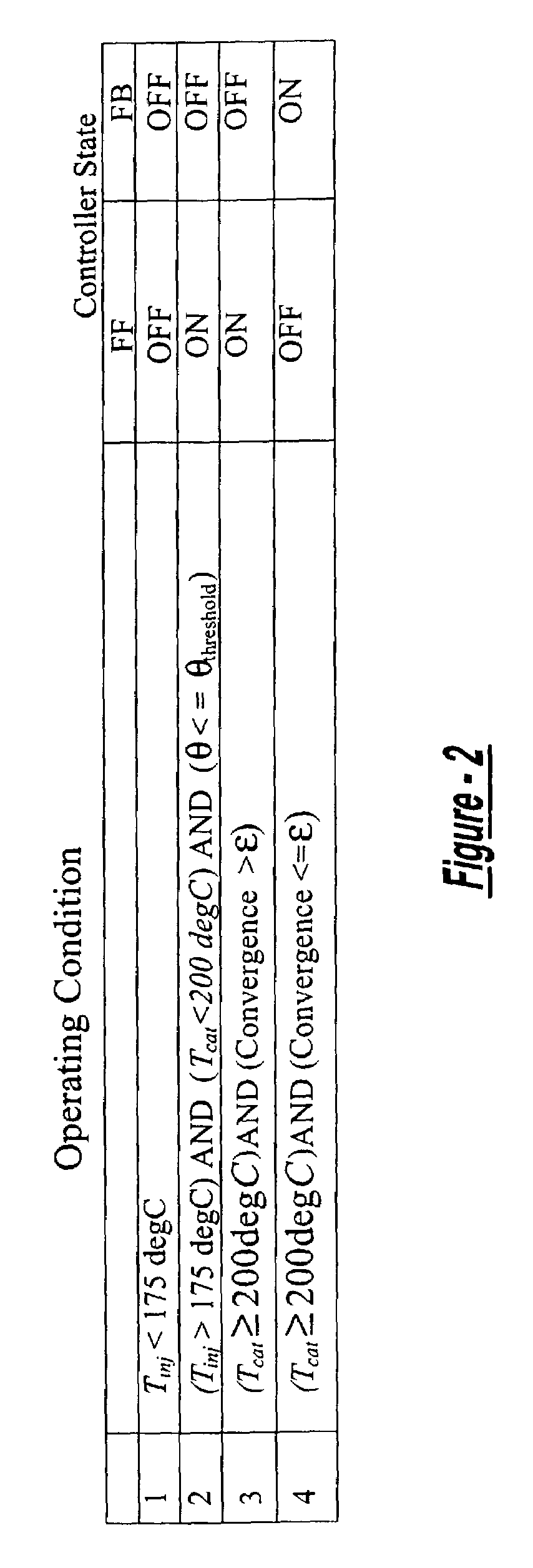
InactiveUS7093427B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesAuxillariesDynamic modelsAmmonia storage
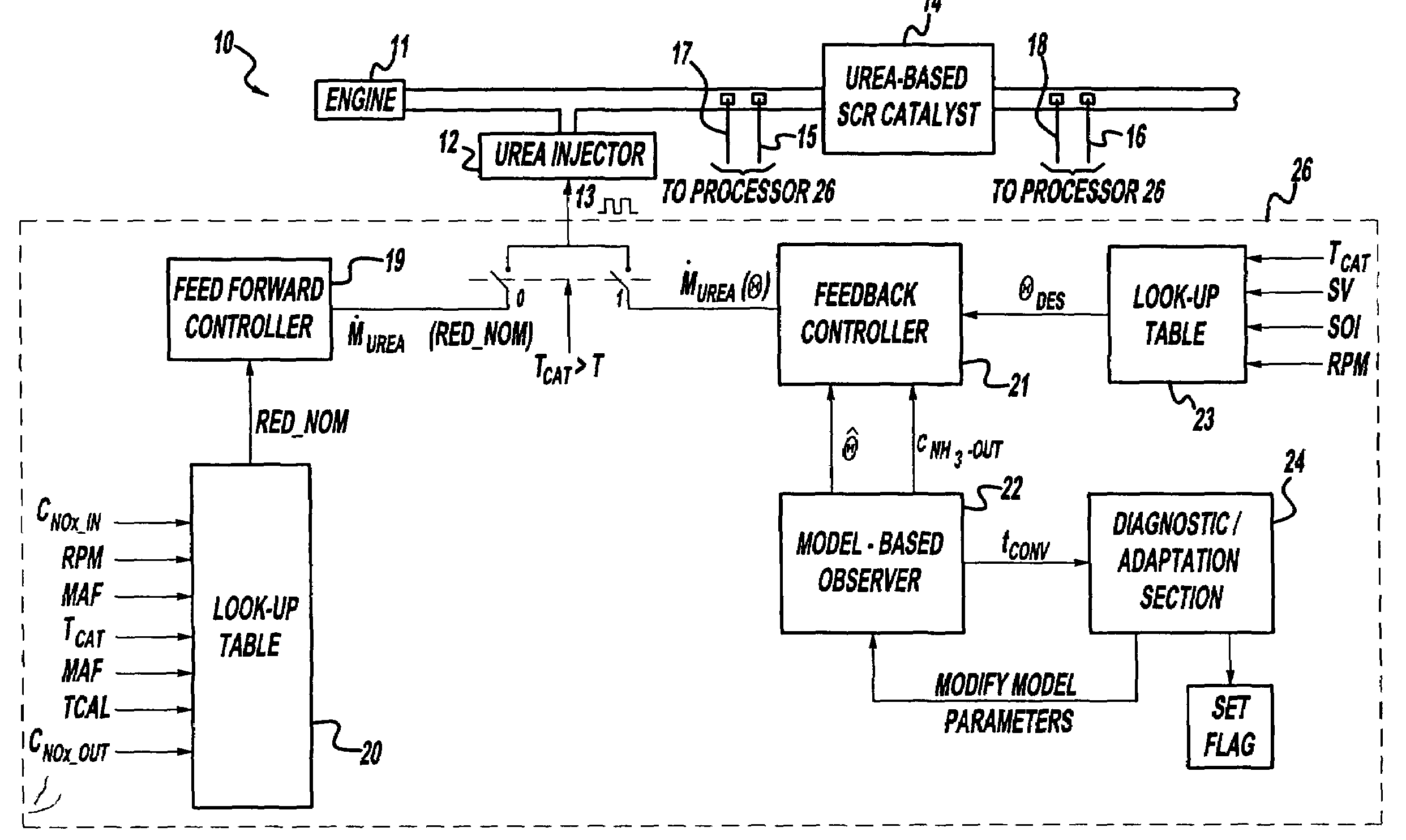
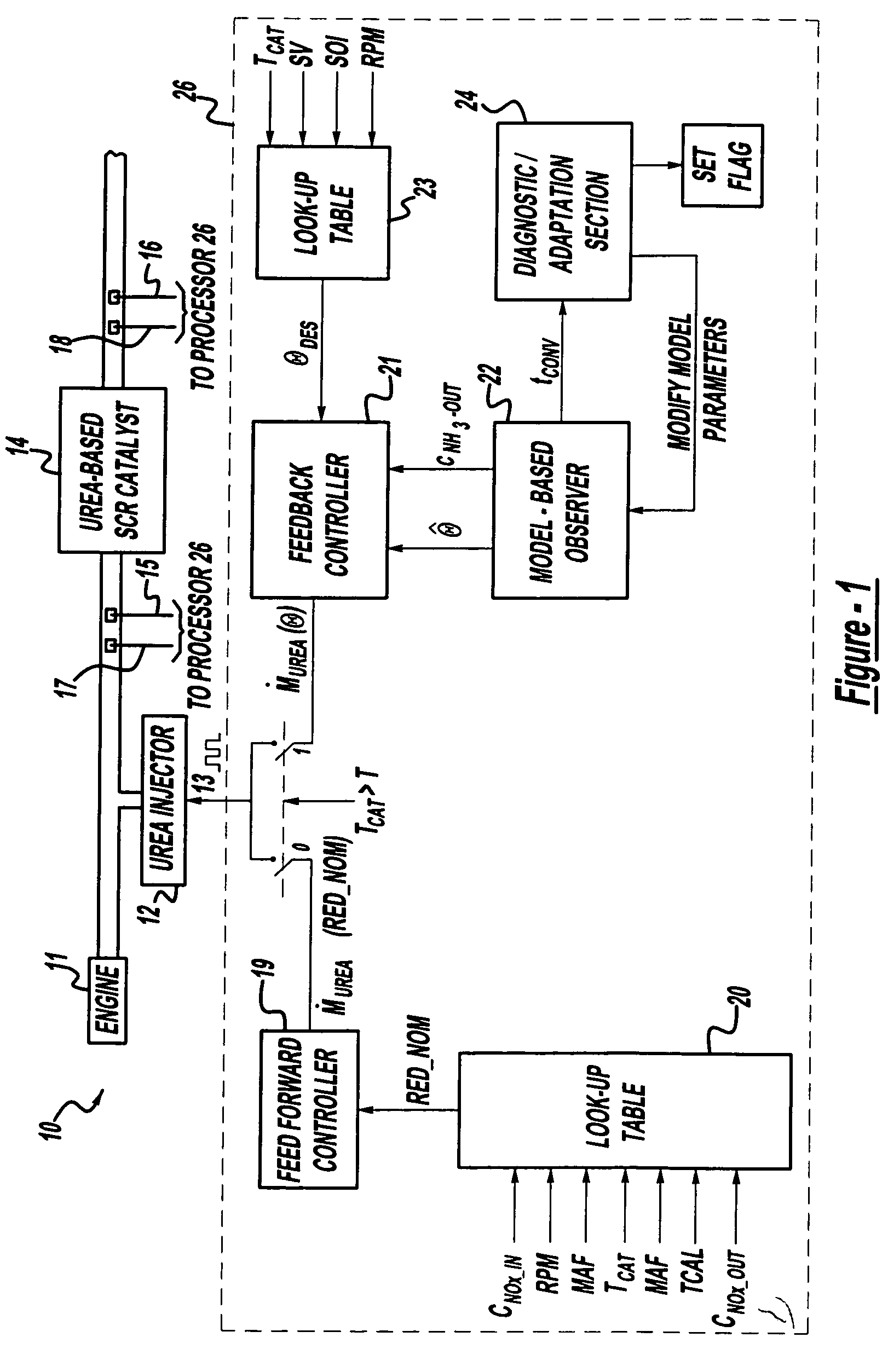
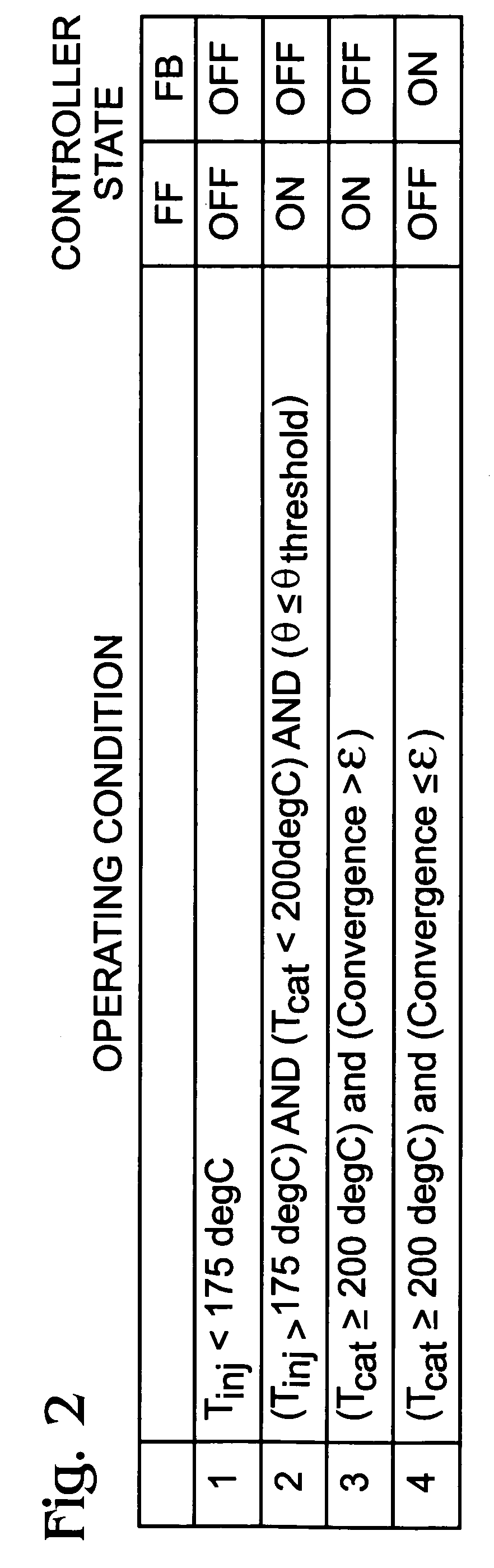
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as sulfur poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
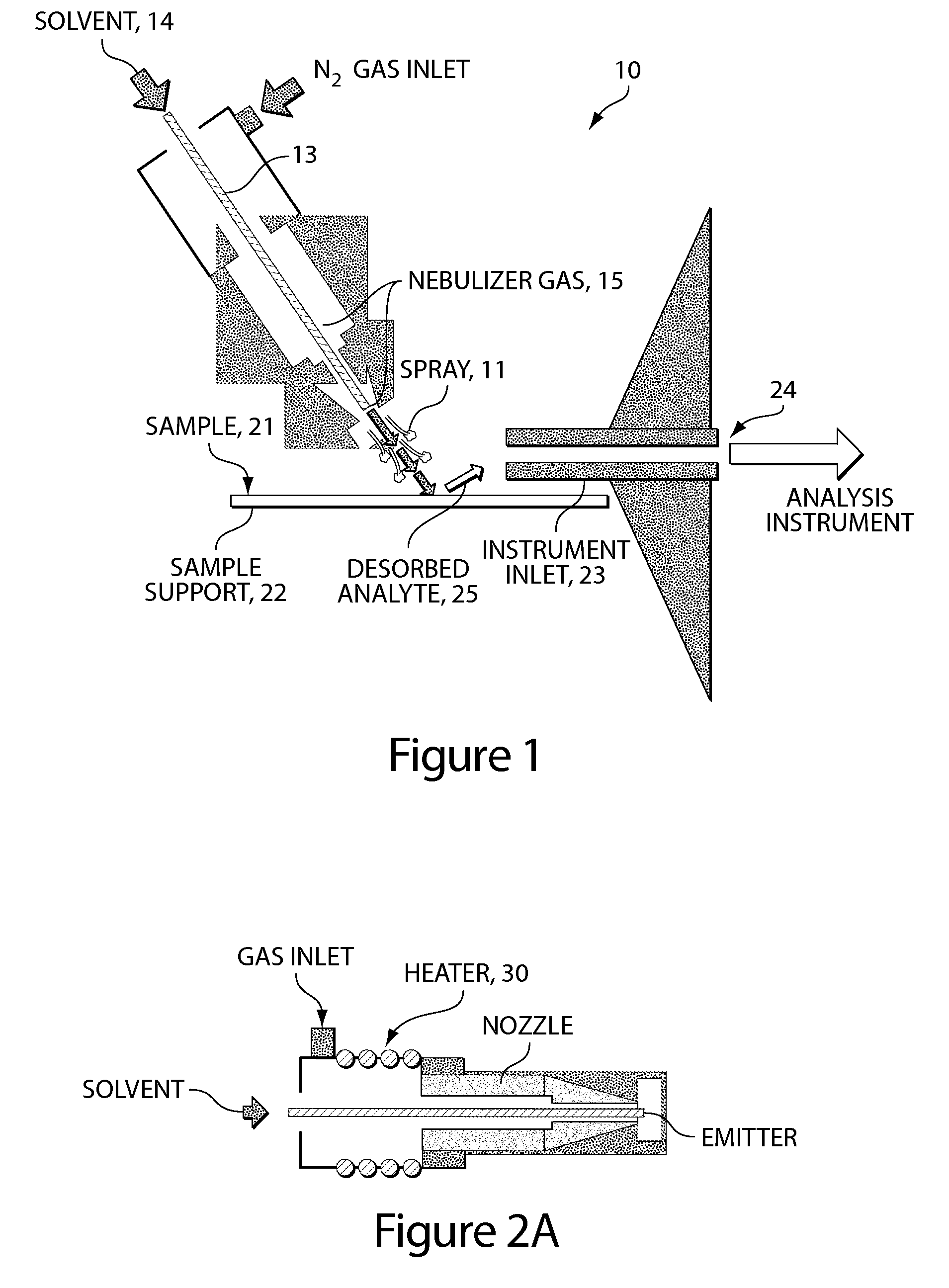
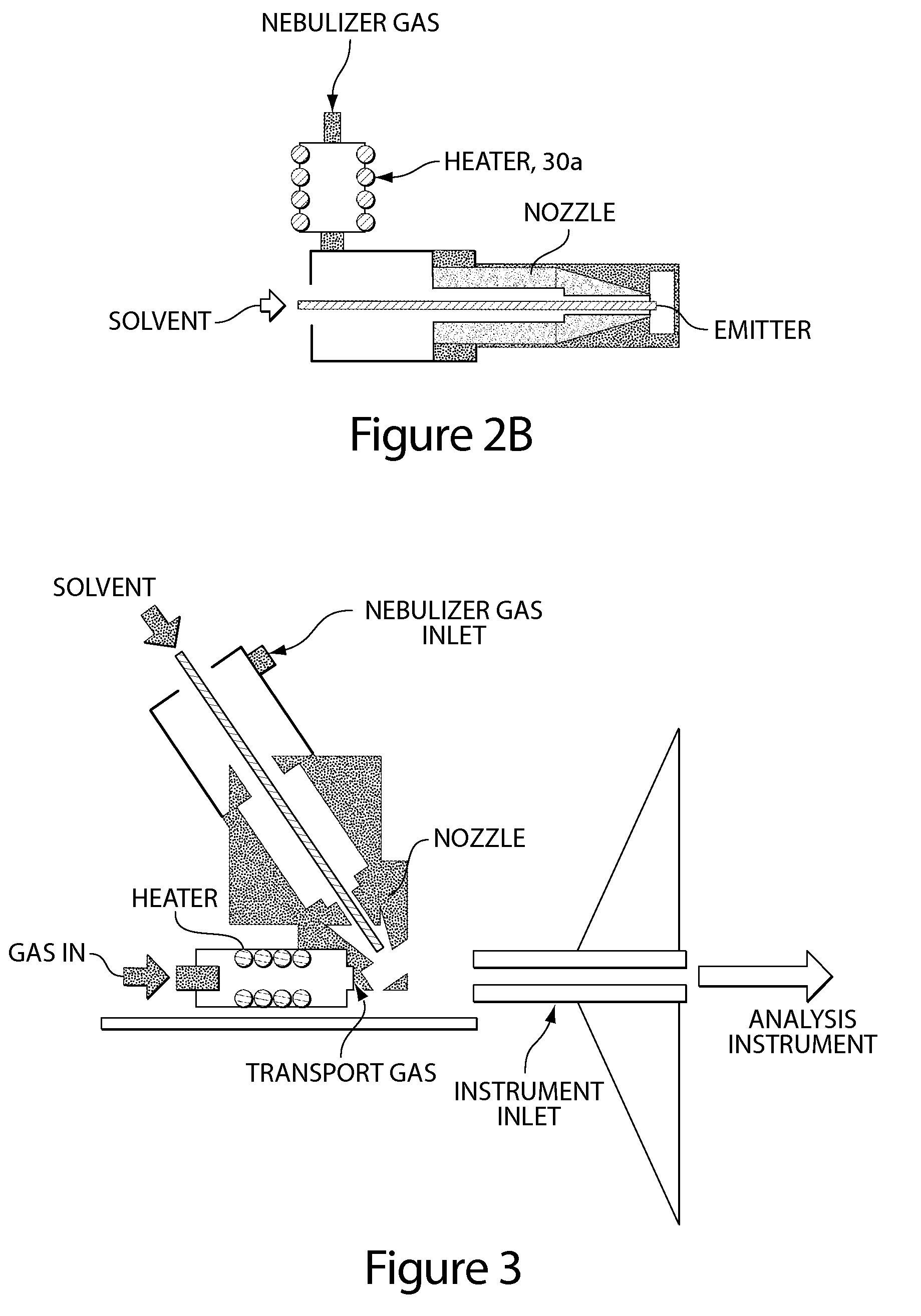
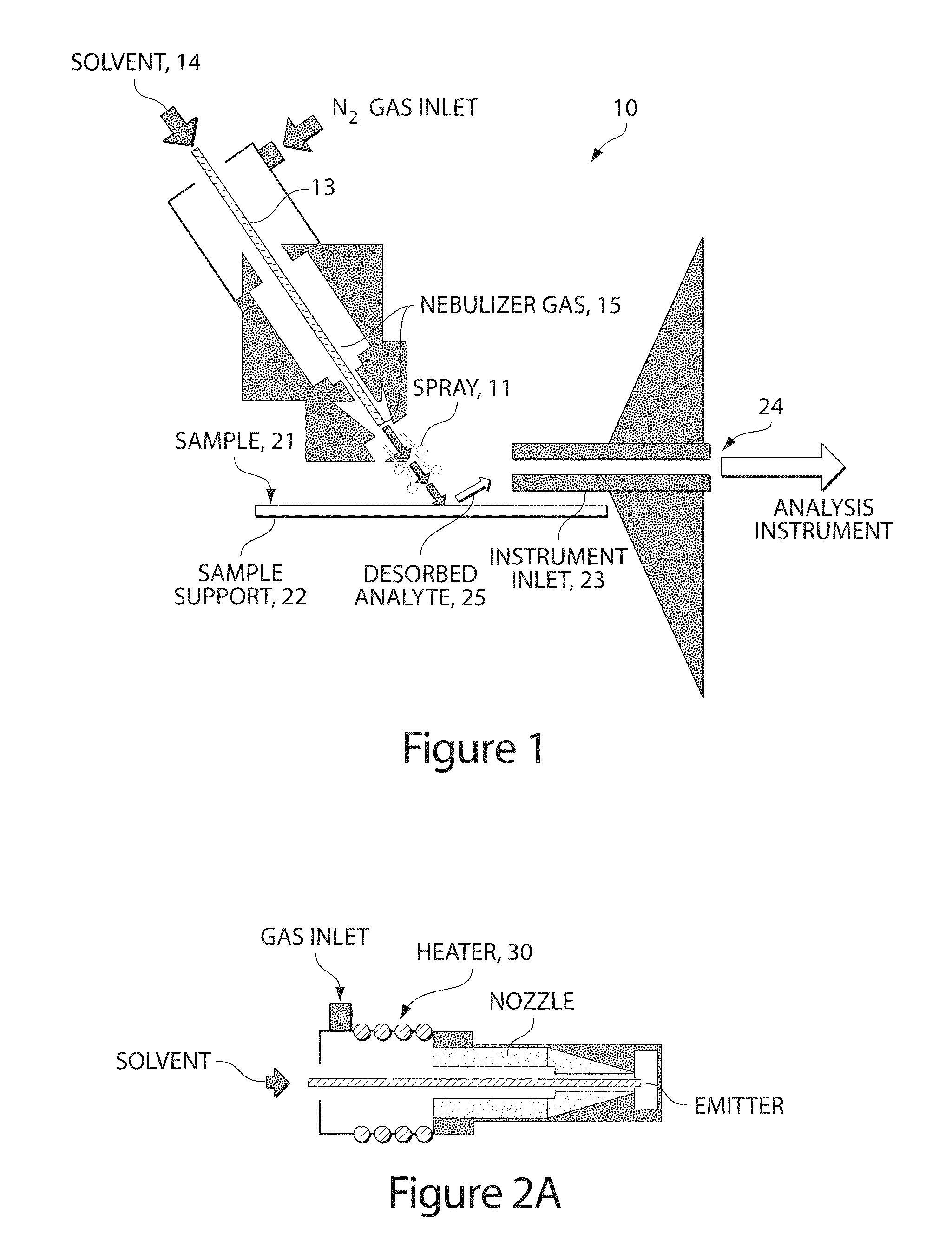
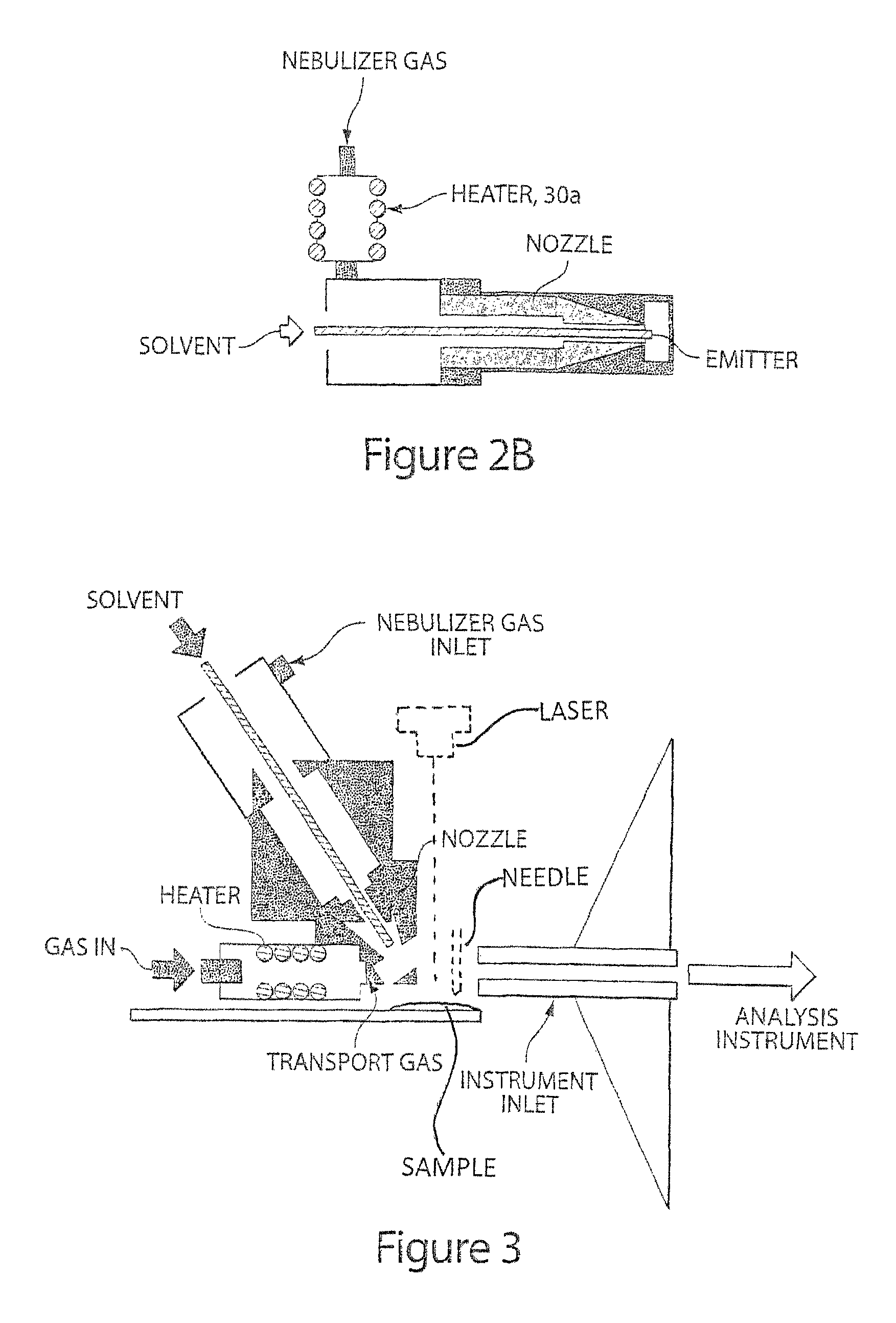
Method and apparatus for embedded heater for desorption and ionization of analytes
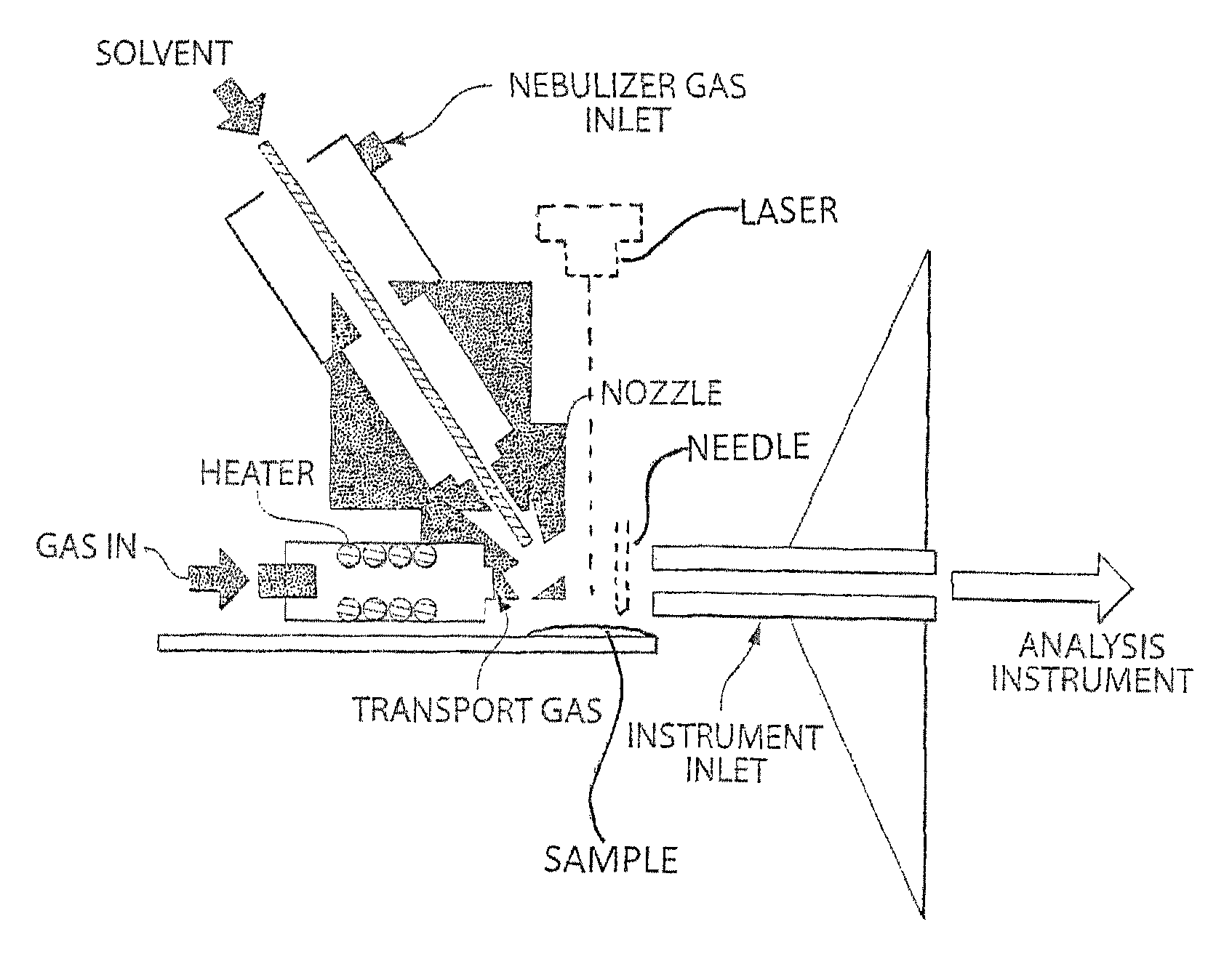
ActiveUS20100078550A1Enhance spot resolutionSmall sizeTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionDesolvationInstrumentation
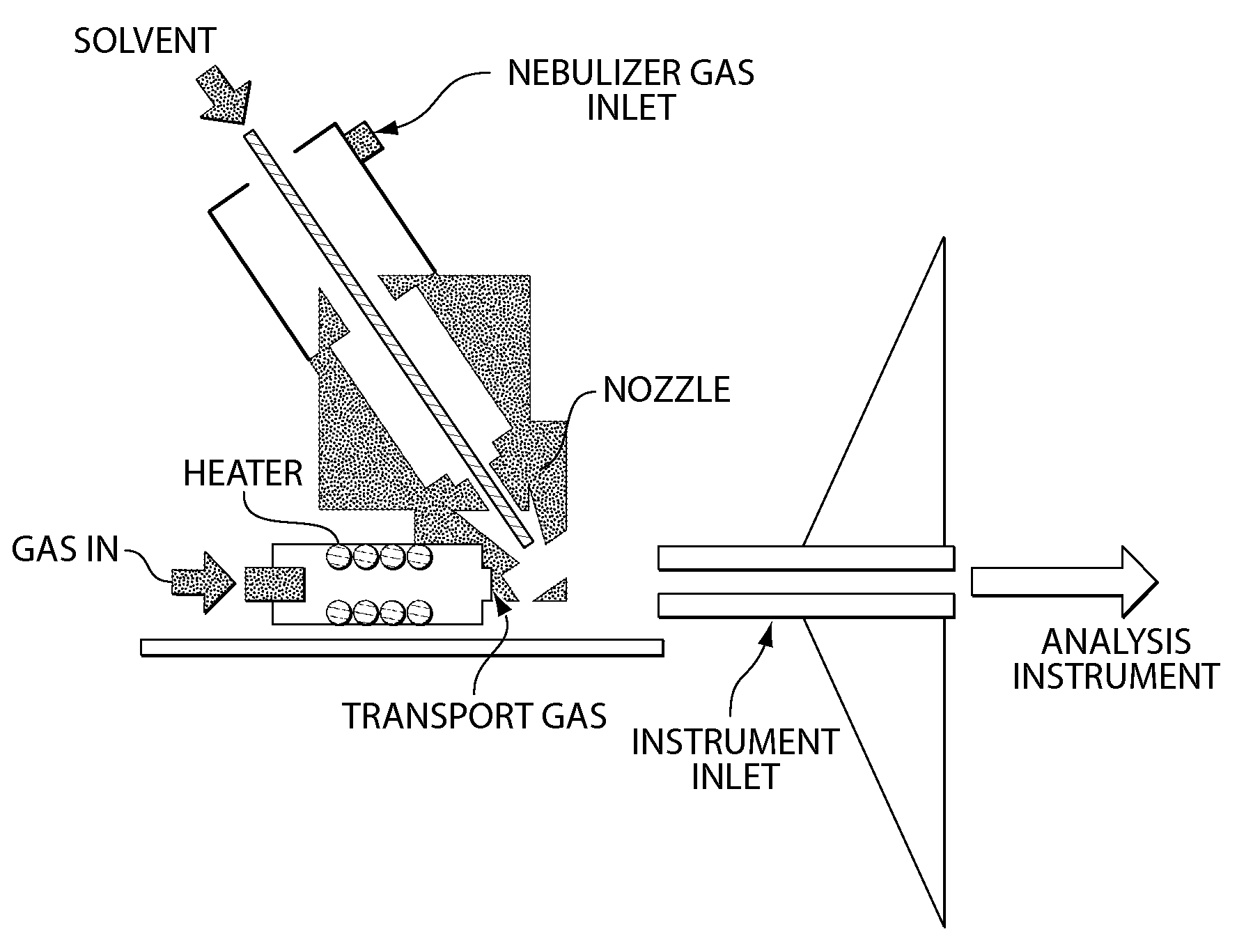
A heated DESI spray device provides improved resolution or control of analyte desorption at a target locus on a sample. Heating controls spot size and enhances resolution in an imaging mode without impairing signal level. Additionally or alternatively the heated DESI spray may control desorption kinetics of a target analyte or otherwise control analyte discrimination in detection mode. One embodiment of the DESI spray is heated by heating nebulizing gas that accompanies the electrosprayed solvent. Another embodiment heats a separate gas stream that transports or directs desorbed material to the ion aperture of an analysis instrument. Heating may reduce size of primary droplets, alter the impact dynamics or the energy delivered by the spray to the surface, reduce size of secondary droplets and / or assure desolvation, improve species selectivity or otherwise affect sampling and enhance the ion signal level.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS6993900B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageDynamic models
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS6981368B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesDynamic modelsAmmonia storage
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Hydrogen storage material and process using graphite additive with metal-doped complex hydrides
InactiveUS20050032641A1Improved hydrogen storage kineticsImproves rehydrogenationMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenGraphiteChemistry
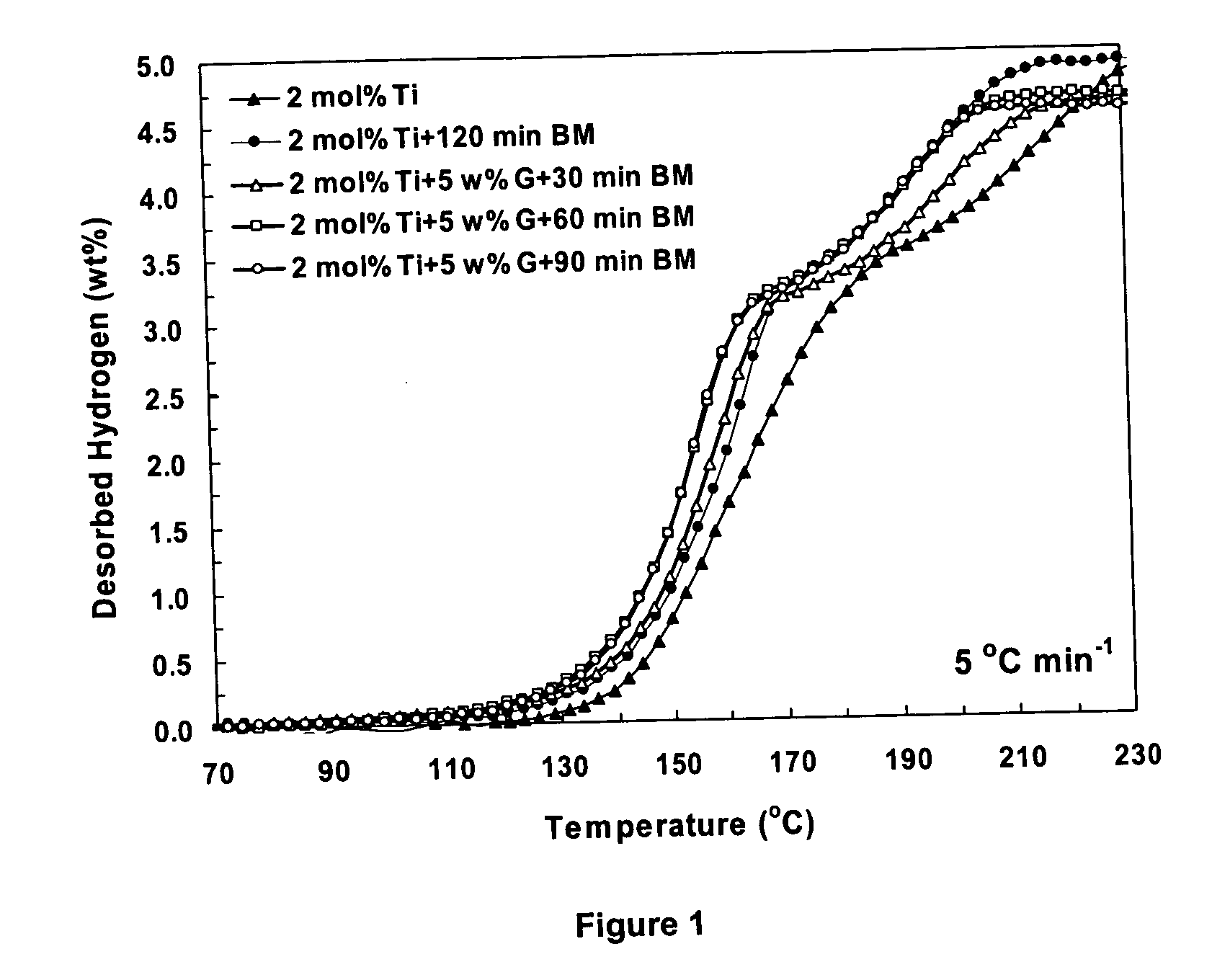
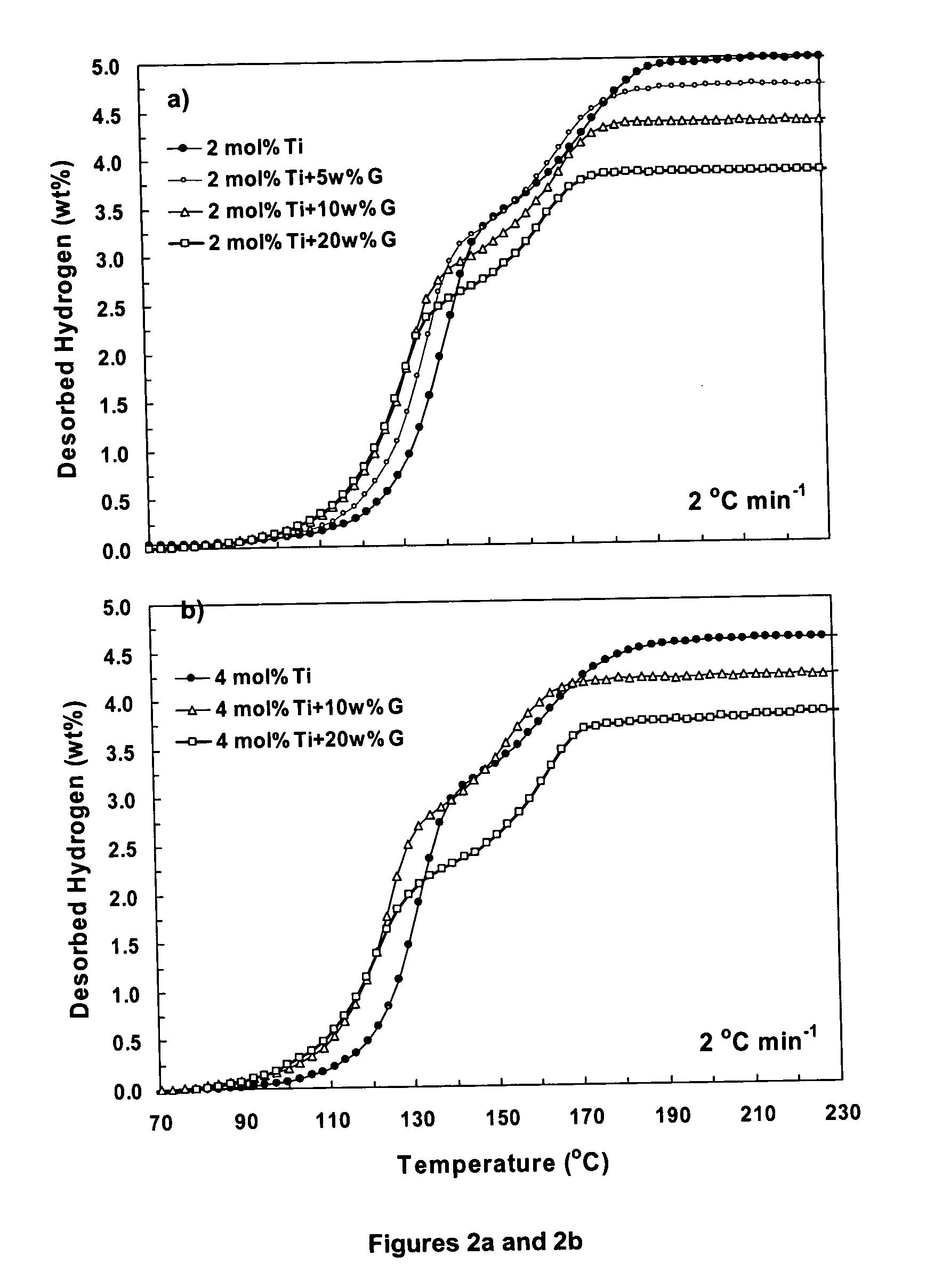
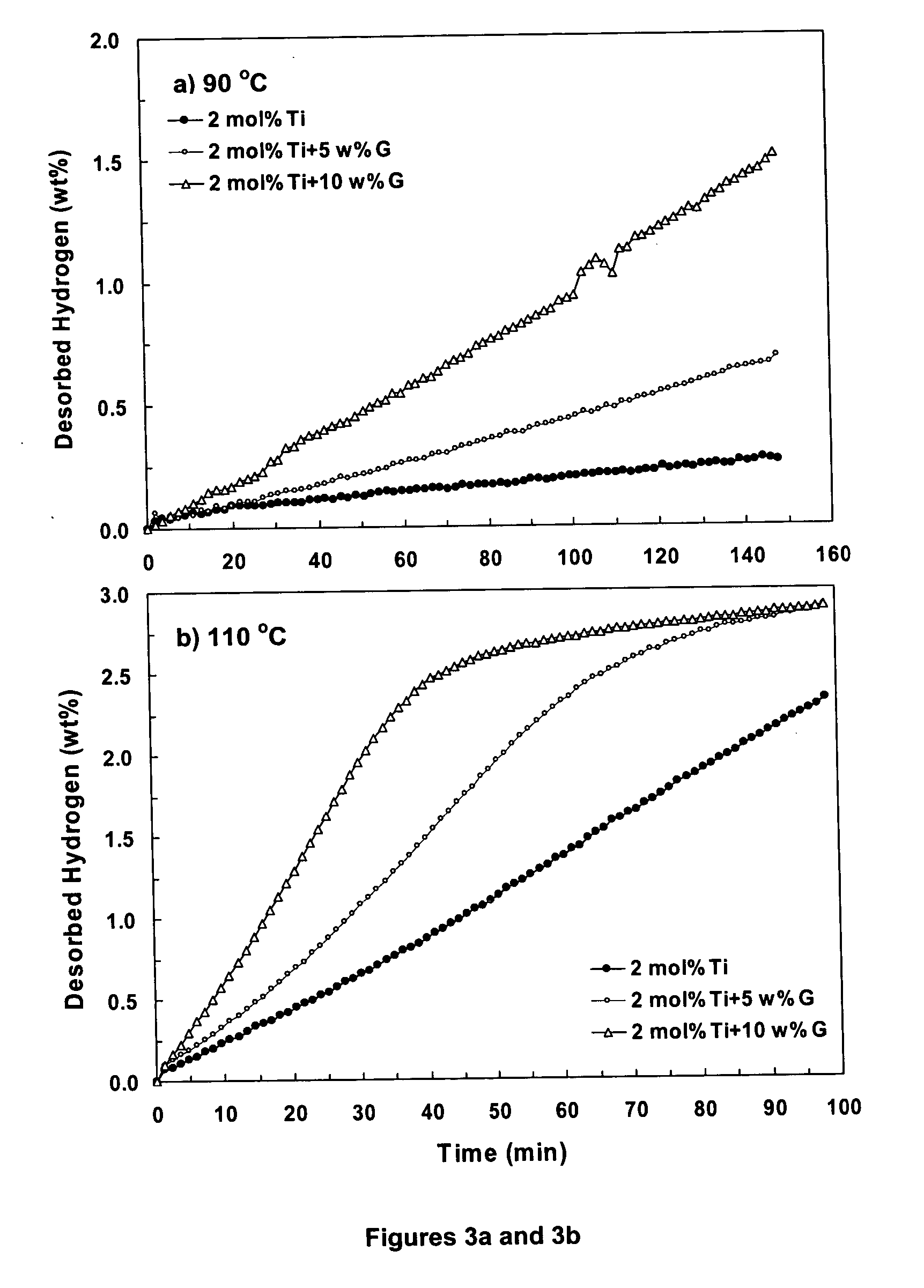
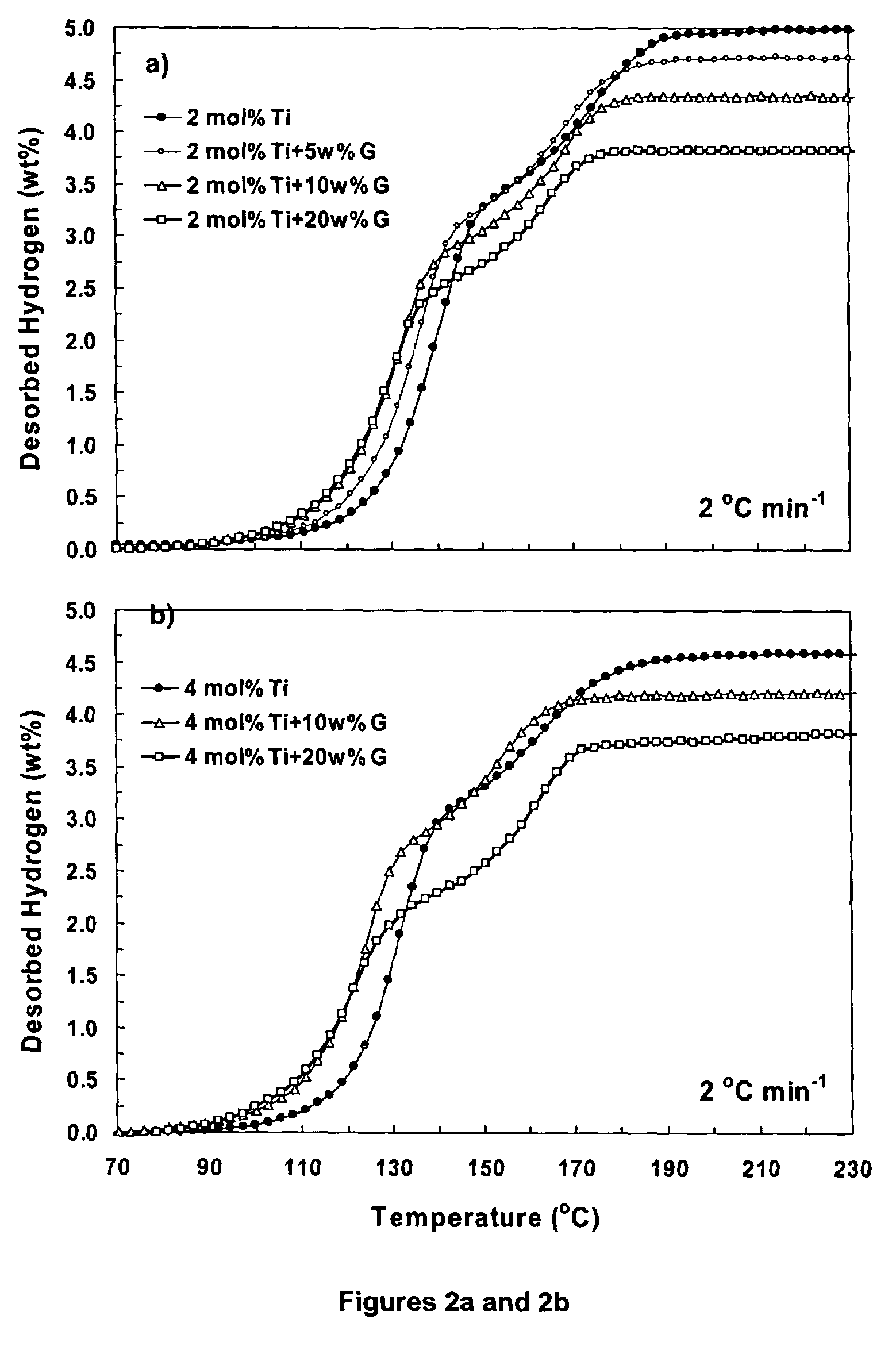
A hydrogen storage material having improved hydrogen absorbtion and desorption kinetics is provided by adding graphite to a complex hydride such as a metal-doped alanate, i.e., NaAlH4. The incorporation of graphite into the complex hydride significantly enhances the rate of hydrogen absorbtion and desorption and lowers the desorption temperature needed to release stored hydrogen.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS +1
Method and apparatus for embedded heater for desorption and ionization of analytes
ActiveUS8203117B2Small sizeHigh resolutionSamplingSamples introduction/extractionAnalyteImage resolution
A heated DESI spray device provides improved resolution or control of analyte desorption at a target locus on a sample. Heating controls spot size and enhances resolution in an imaging mode without impairing signal level. Additionally or alternatively the heated DESI spray may control desorption kinetics of a target analyte or otherwise control analyte discrimination in detection mode. One embodiment of the DESI spray is heated by heating nebulizing gas that accompanies the electrosprayed solvent. Another embodiment heats a separate gas stream that transports or directs desorbed material to the ion aperture of an analysis instrument. Heating may reduce size of primary droplets, alter the impact dynamics or the energy delivered by the spray to the surface, reduce size of secondary droplets and / or assure desolvation, improve species selectivity or otherwise affect sampling and enhance the ion signal level.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
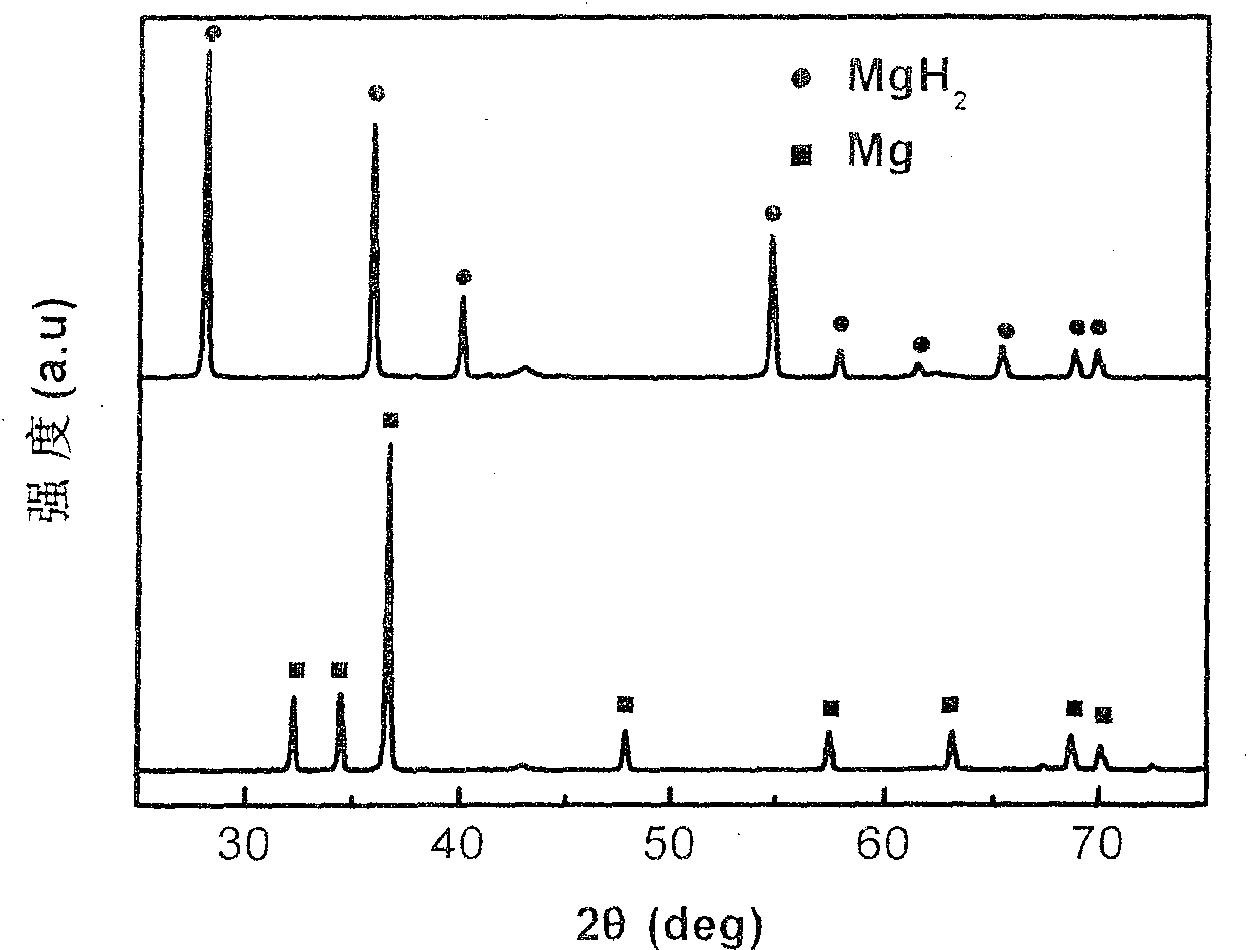
Method for preparing nanometer limited range magnesium-based hydrogen storage material
InactiveCN104649229AImprove mechanical propertiesLow costAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesDispersityNew energy
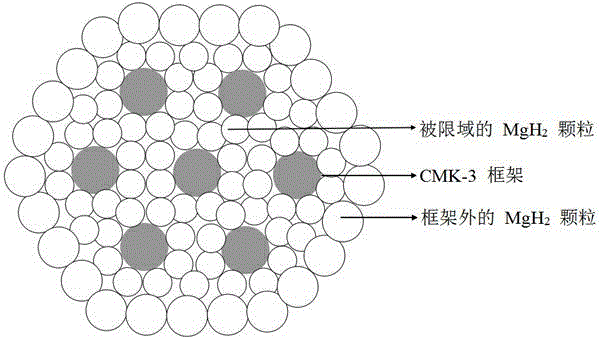
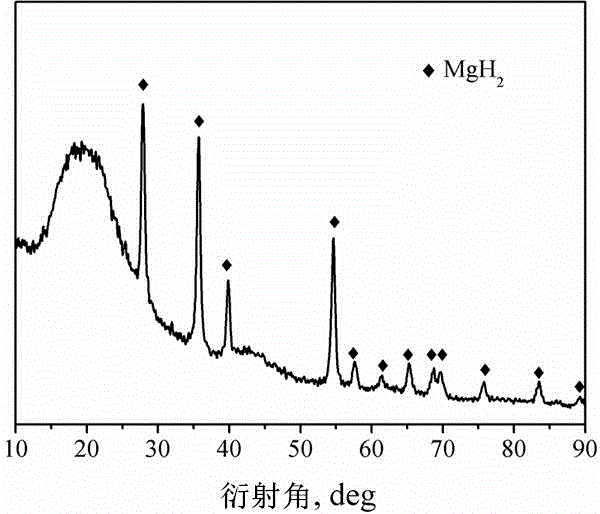
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nanometer limited range magnesium-based hydrogen storage material. The nanometer limited range method belongs to the technical field of new energy materials. The method is characterized in that the hydrogen storage material is formed by loading magnesium hydride (MgH2) in nanopores of a mesoporous framework material. The method comprises the following steps: dipping dibutyl magnesium (MgBu2) and a mesoporous framework material, replacing MgBu2 with MgH2 loaded inside and outside the nanopores of the mesoporous framework material in a high-pressure reactor under high temperature and high pressure, washing MgH2 loaded outside the pores away by using pentane, drying, thereby obtaining the material. The nanometer limited range magnesium-based hydrogen storage material prepared by the method can release hydrogen at room temperature and has excellent properties in hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics and hydrogen desorption thermodynamics. The method disclosed by the invention is easy to operate and high in synthesis speed and the prepared material is high in dispersity; therefore, the method has ideal application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Device for soil heavy metal adsorption /desorption kinetic procedure research
InactiveCN101261250AAvoid the phenomenon of resorptionEnsure consistencyComponent separationPeristaltic pumpSoil heavy metals
The invention relates to a research on soil heavy metal absorption / desorption action, in particular to a device used for researching the soil heavy metal absorption / desorption dynamic process, which is sequentially formed by a sampling liquid storage container, a multi-channel peristaltic pump, an exchange column and an effluent automatic adaptor which are connected in series by pipelines. The research can avoid the phenomenon of heavy metal re-absorption and make better simulation on natural conditions so as to research the soil heavy metal absorption / desorption dynamic process.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metal oxide and porous material composite hydrogen storage material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110963461AAccelerate the rate of hydrogenationSmall particle sizeHydrogenHydrogen adsorptionHigh surface area
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrogen storage materials and particularly relates to a metal oxide and porous material composite hydrogen storage material and a preparation method thereof. The metal oxide and porous material composite hydrogen storage material is formed by compounding magnesium hydride, a porous material and a metal oxide, and the weight ratio of the magnesium hydride to the porous material to the metal oxide is (100-10): (5-0.1): (1-0.05). The magnesium hydride is taken as a base material, and metal oxide particles are mixed and grinded to obtain an activated magnesium hydride material; and the obtained activated magnesium hydride material is mixed with the porous material, and ball milling or compression is carried out to obtain the composite hydrogen storage material. According to the material and the preparation method, nanoscale metal oxide particles are added and compounded with the porous material, so that the hydrogenation speed of magnesium-based composite powder in the hydrogen charging ball milling process can be increased, and meanwhile, the hydrogen storage material has good characteristics in the aspects of hydrogen adsorption and desorption kinetics in combination with the properties such as excellent pore channels and high surface area of the porous material.
Owner:世能氢电科技有限公司 +1
AB type hydrogen storage alloy used for storing tritium and preparation method of AB type hydrogen storage alloy
InactiveCN105568110AEnhanced resistance to disproportionation caused by hydrogen (tritium)Improve cycle lifeDisproportionationHydrogen absorption
The invention provides an AB type hydrogen storage alloy used for storing tritium and a preparation method of the AB type hydrogen storage alloy, and relates to the technical field of hydrogen storage alloy. The general formula of components of the AB type hydrogen storage alloy used for storing the tritium is Zr1-xTixCo1-yFey, wherein the x is greater than or equal to 0.1 but smaller than or equal to 0.4, and the y is greater than or equal to 0.1 but smaller than or equal to 0.2. The hydrogen storage alloy provided by the invention has good hydrogen-induced disproportionation resistance, and excellent hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics performance and indoor-temperature hydride balance pressure, and the preparation method of the hydrogen storage alloy is simple, easy to implement and high in preparation efficiency and practicability.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Hydrogen storage material and process using graphite additive with metal-doped complex hydrides
InactiveUS7384574B2Improved hydrogen storage kineticsImproves rehydrogenationMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenGraphiteHydride
A hydrogen storage material having improved hydrogen absorbtion and desorption kinetics is provided by adding graphite to a complex hydride such as a metal-doped alanate, i.e., NaAlH4. The incorporation of graphite into the complex hydride significantly enhances the rate of hydrogen absorbtion and desorption and lowers the desorption temperature needed to release stored hydrogen.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS +1
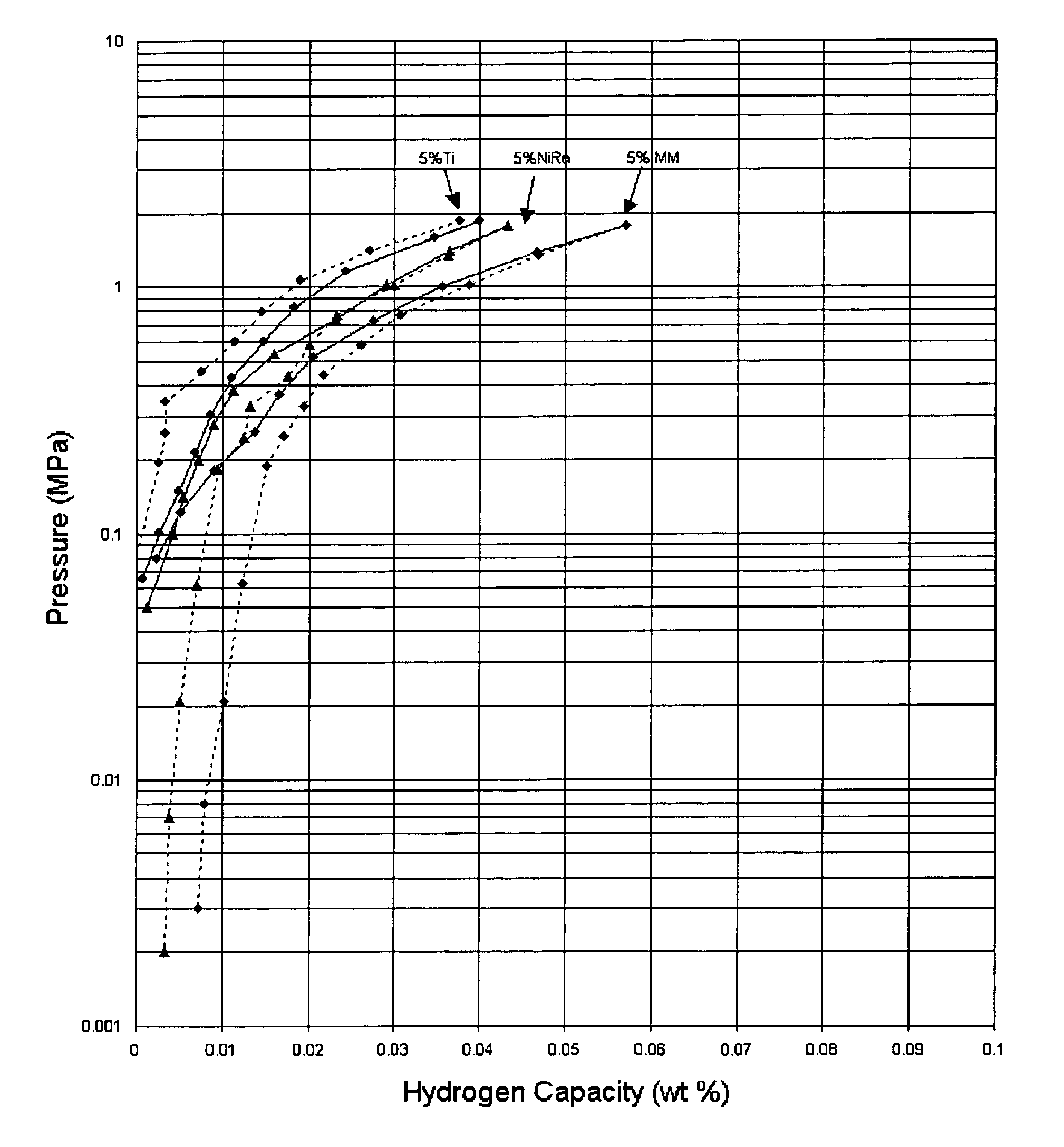
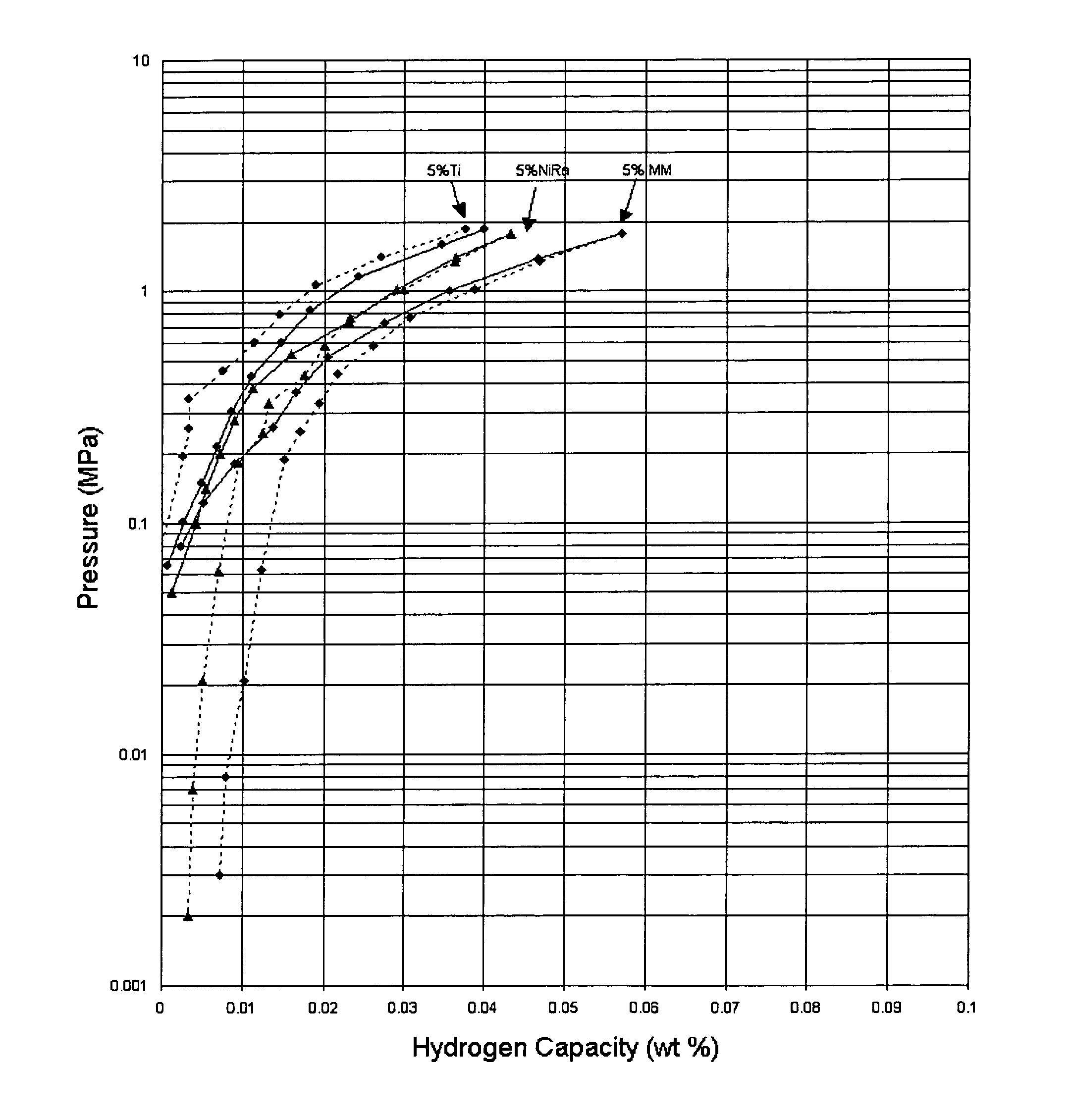
High capacity hydrogen storage material based on catalyzed alanates
A complex aluminum hydride doped with a catalytic material adapted to increase the kinetics of hydrogen absorption / desorption of the aluminum hydride without reducing the hydrogen storage capacity of the aluminum hydride.
Owner:TEXACO OVONIC FUEL CELL
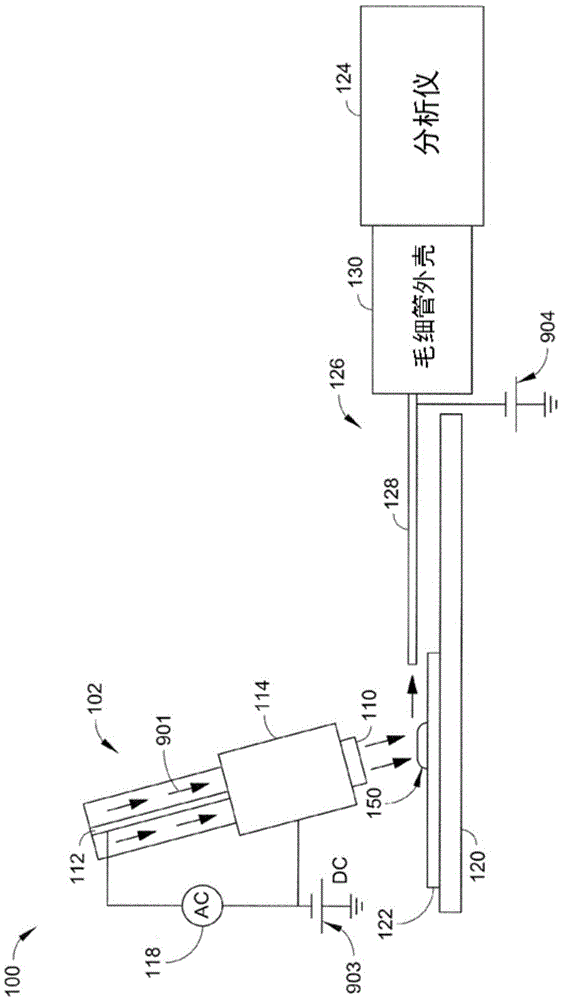
In situ chemical transformation and ionization of inorganic perchlorates on surfaces
ActiveCN105531577AWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationChemical reactionAnalyte
A method for providing in situ chemical transformation and ionization of a portion (e.g., inorganic oxidizer) of a sample via an analyte detection system is disclosed herein. The method includes introducing a gas into an ionization source of the analyte detection system via an inlet. The method further includes generating ions within the ionization source and directing the gas and generated ions through and out of the ionization source and to the sample. The sample is located proximal to the ionization source in an ambient environment. The ions chemically react with the sample and desorb and ionize an analyte from the sample, the analyte being generated from the inorganic oxidizer, the desorbed analyte having a lower melting point and / or better desorption kinetics than the inorganic oxidizer. The method further includes receiving the desorbed analyte via an analyzer of the analyte detection system.
Owner:SMITHS DETECTION MONTREAL
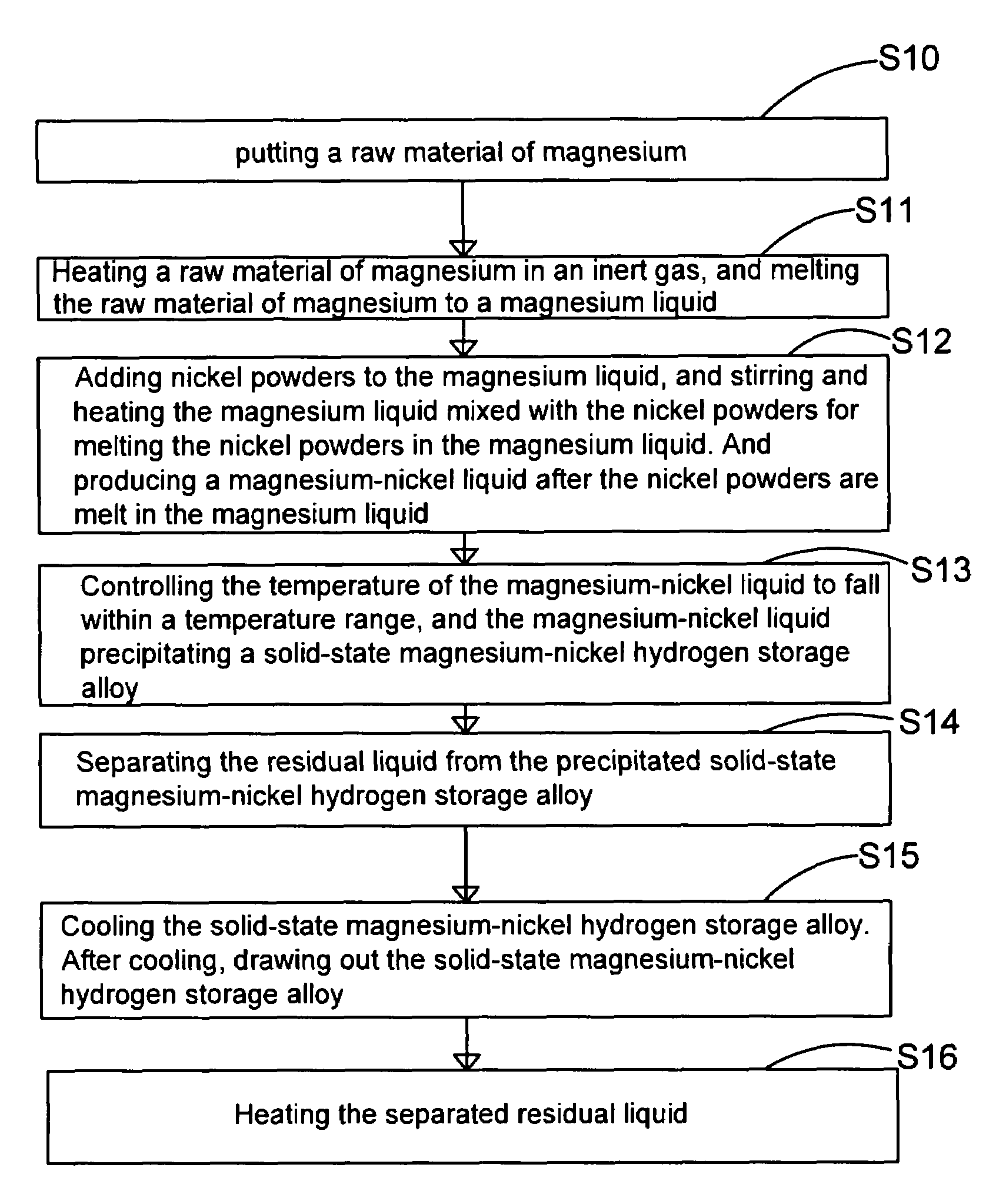
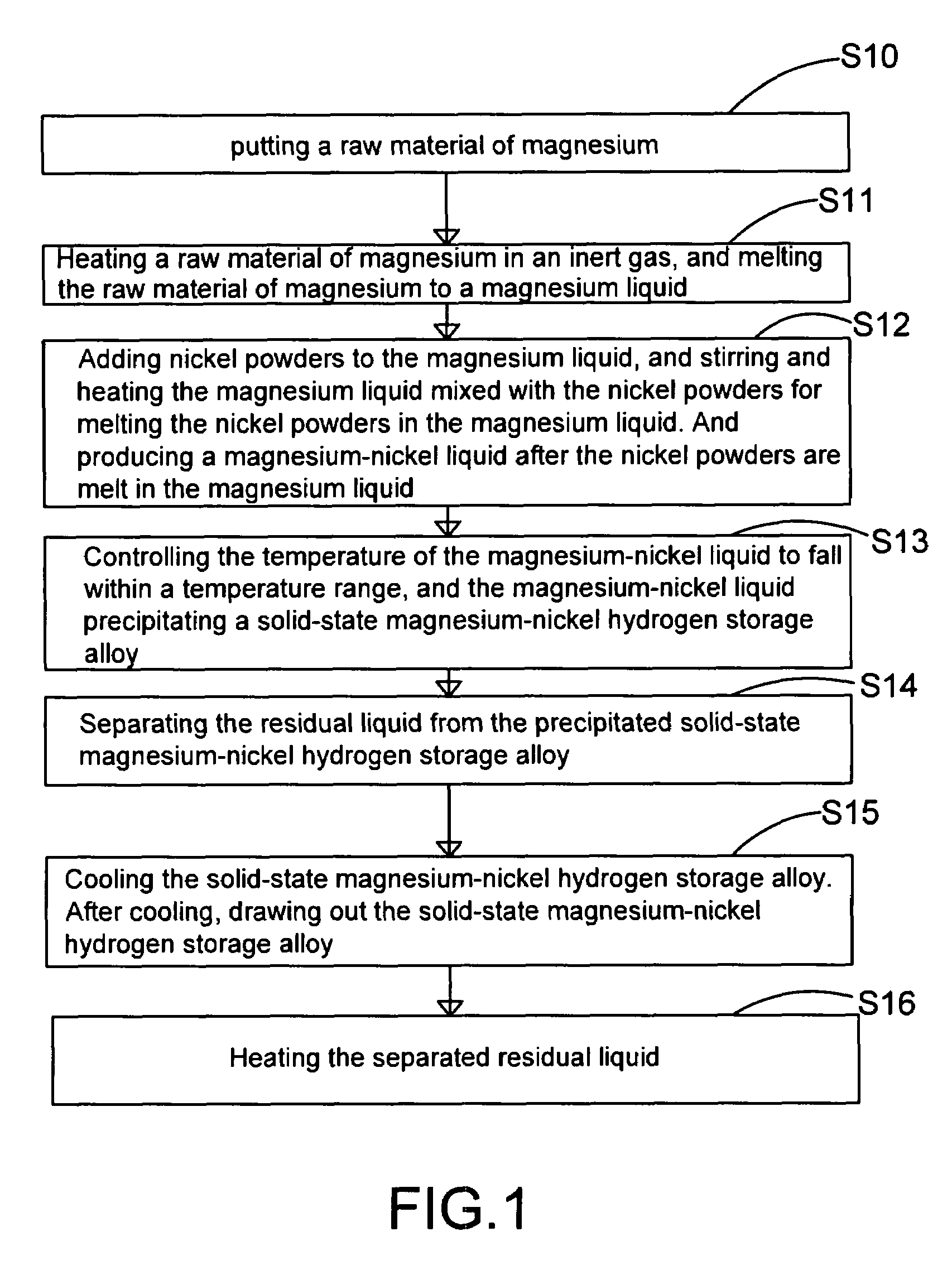
Method and apparatus for manufacturing high-purity hydrogen storage alloy Mg.sub.2Ni
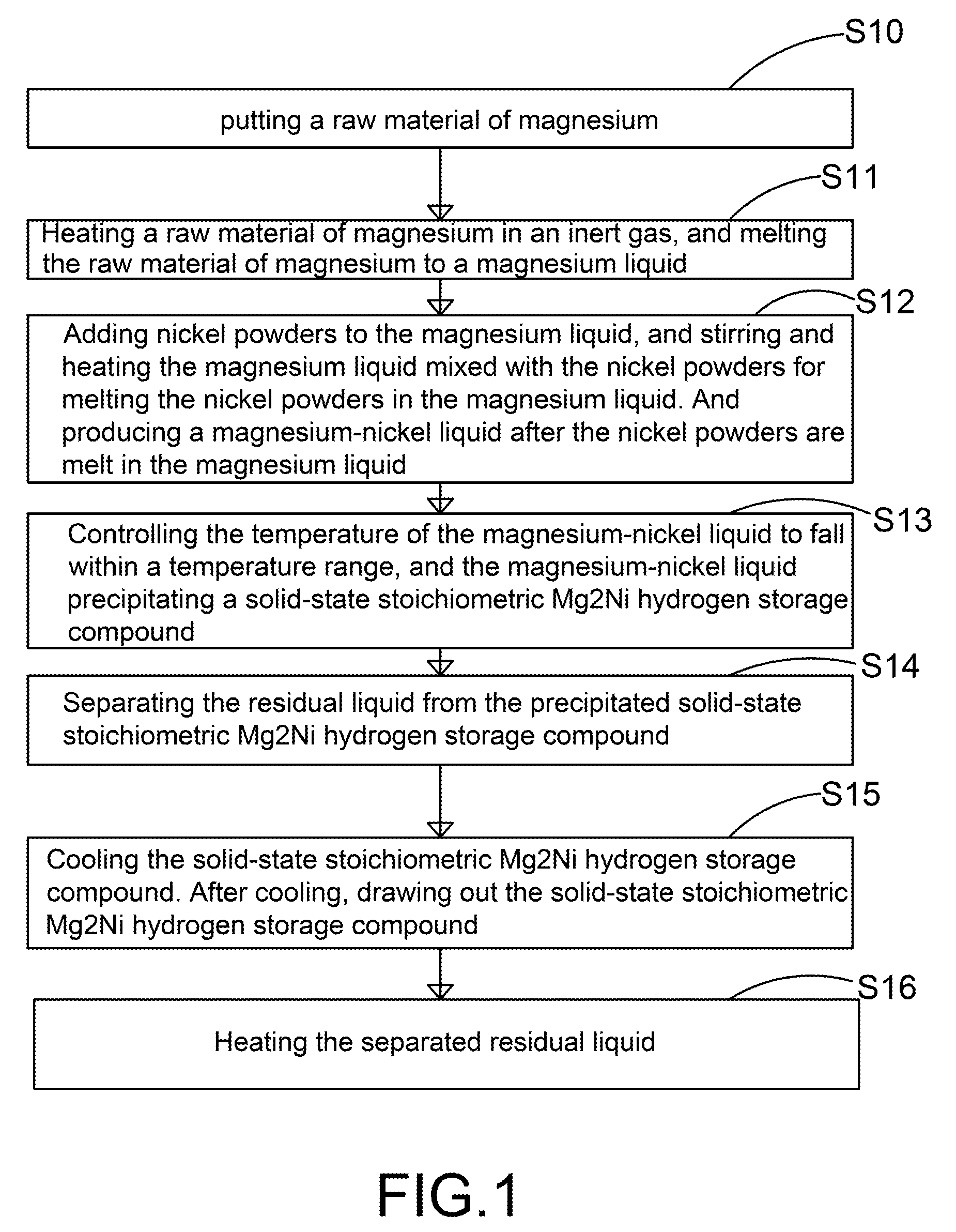
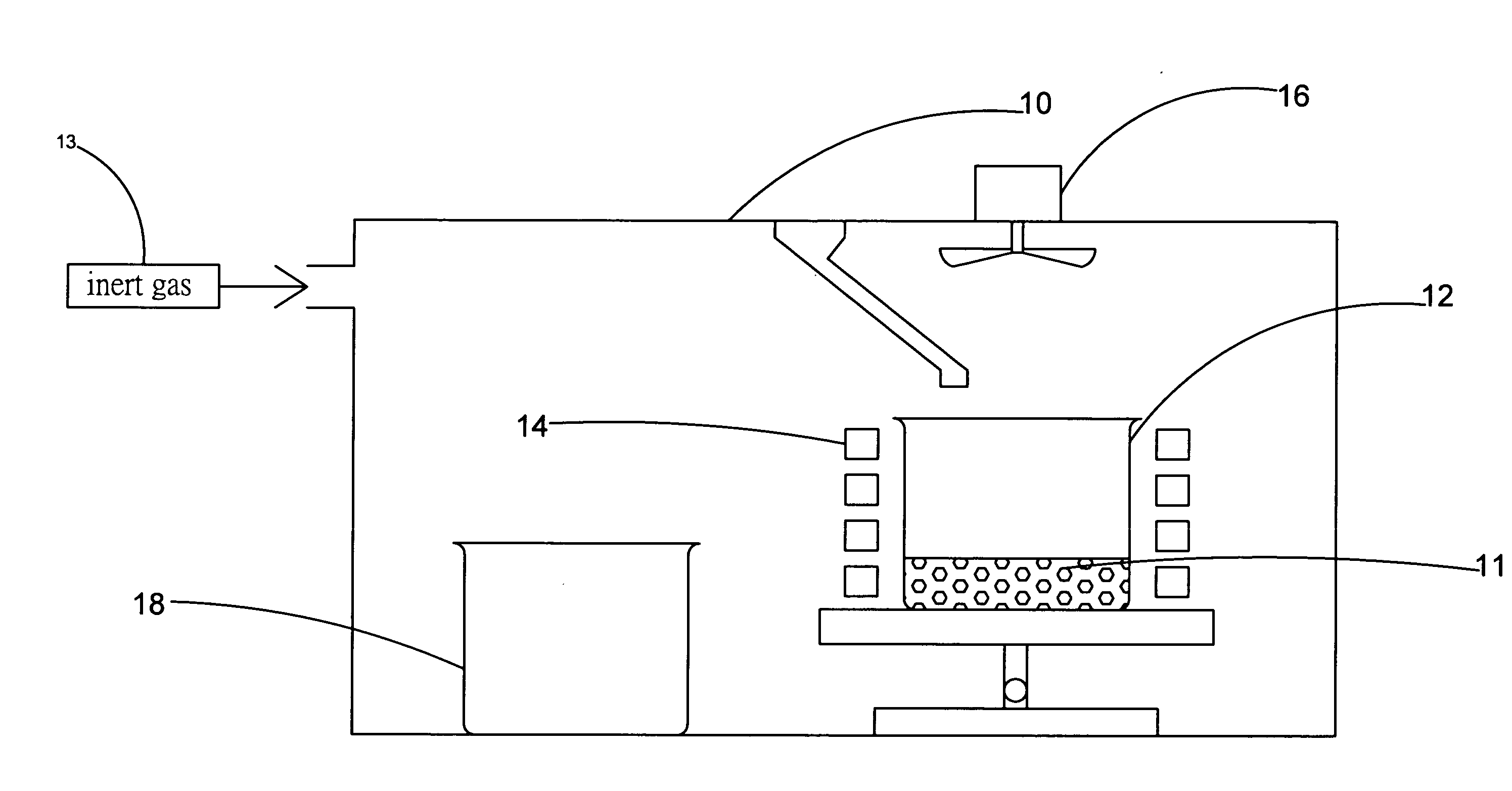
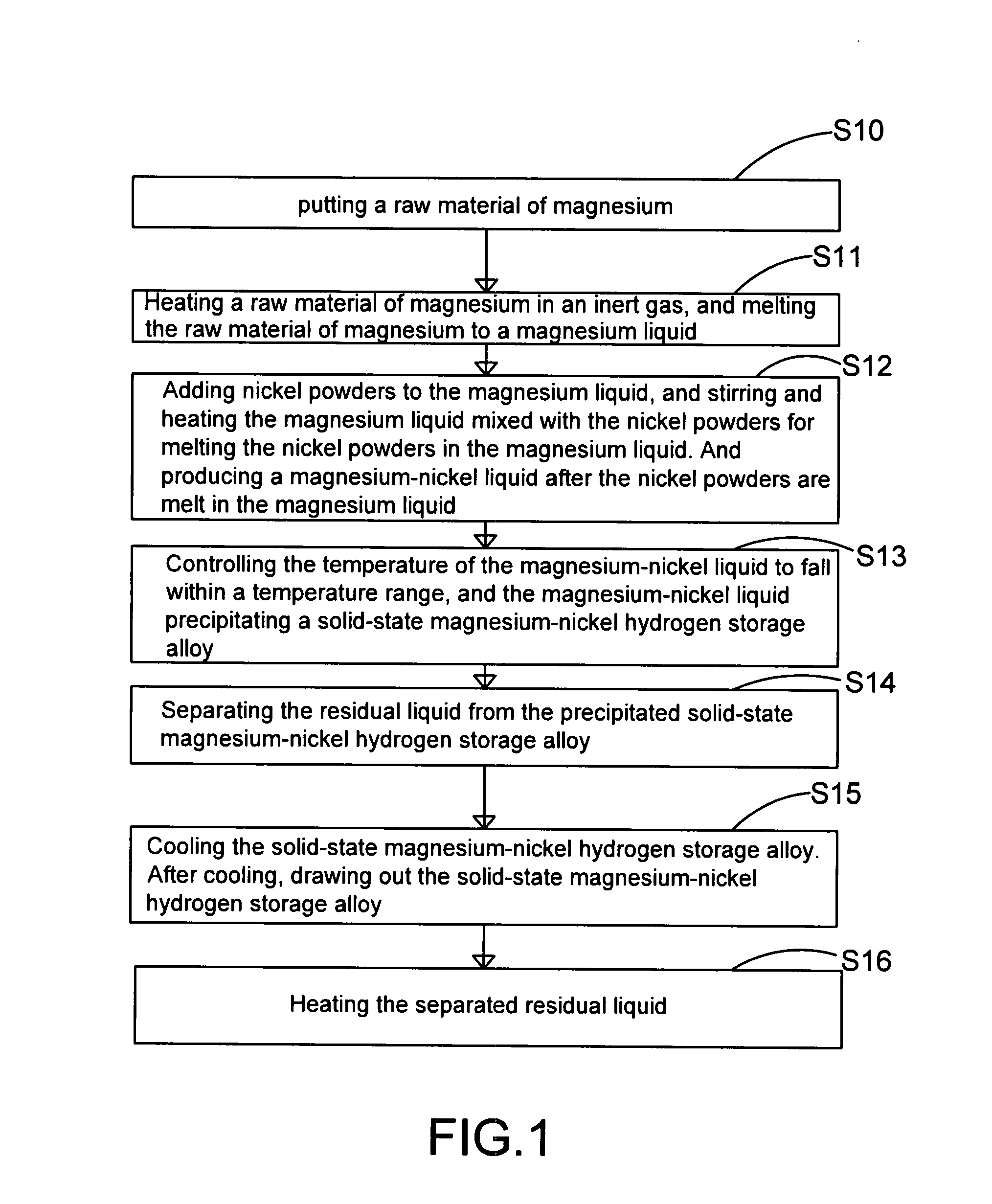
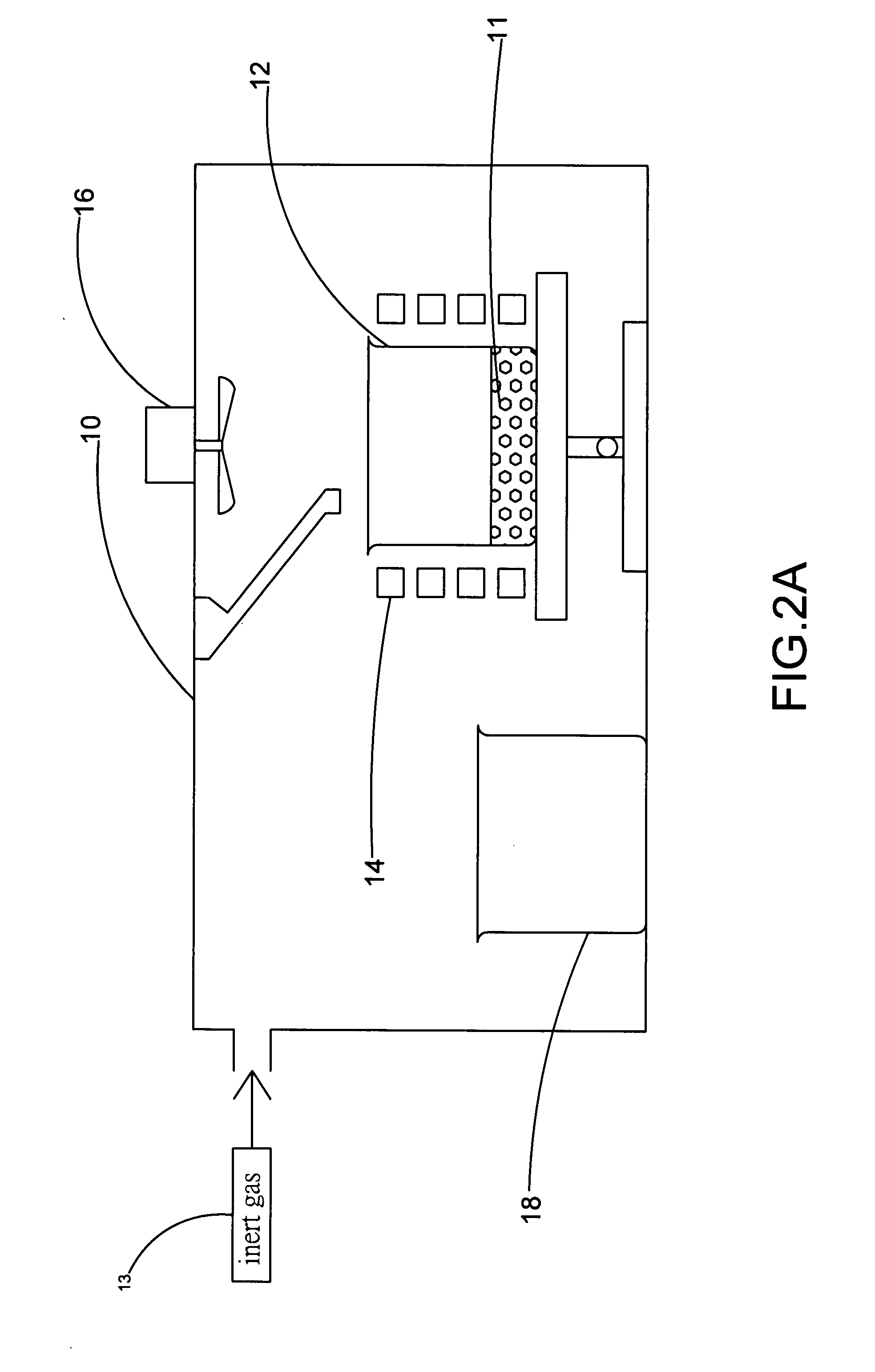
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing high-purity hydrogen storage alloy Mg2Ni applicable to industry and capable of manufacturing continuously. First, raw materials of magnesium-nickel with weight percentage of nickel between 23.5 and 50.2 are heated, melt, and mixed uniformly. Cool the magnesium-nickel liquid and control the temperature to be above the solidification temperature and below the liquification temperature in the phase diagram of magnesium-nickel. By making advantage of segregation principle in phase diagrams, solid-state high-purity γ-phase Mg2Ni hydrogen storage alloy is given. Then high-purity γ-phase Mg2Ni hydrogen storage alloy with atomic ratio of 2:1, no other phases, and with excellent hydrogen absorption-desorption dynamics is given.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Magnesium hydride hydrogen storage composite material containing porous material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110980636AExcellent channelLarge specific surface areaReversible hydrogen uptakeGraphiteUltimate tensile strength
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic porous materials, and particularly relates to a magnesium hydride hydrogen storage composite material containing a porous material and a preparation method thereof. The magnesium hydride hydrogen storage composite material containing the porous material is formed by compounding magnesium hydride and the porous material, the weight ratio ofthe magnesium hydride to the porous material is (0.1-1.2): 1, the porous material is one or more of graphite, SiO2 or Al2O3, and The method comprises the following steps: mixing the magnesium hydridewith the porous material; and compressing the mixture to form the magnesium hydride hydrogen storage composite material. According to the invention, the porous material with adjustable aperture is used as a carrier, so that the hydrogen storage performance of magnesium hydride is combined with excellent pore channels, high specific surface area and the like of the porous material, and the hydrogenstorage material has good characteristics in the aspects of hydrogen adsorption and desorption kinetics. The hydrogen storage material is compositely formed in a compression mode, the hydrogen storage density per unit volume can be improved, and the mechanical strength is improved.
Owner:世能氢电科技有限公司 +1
High-performance high-capacity hydrogen storage alloy for fuel cell and preparation method of hydrogen storage alloy
ActiveCN112048651APrevent volatilizationInhibition of solid solutionReactant parameters controlFuel cellsChemical composition
The invention relates to a high-performance high-capacity hydrogen storage alloy for a fuel cell and a preparation method of the hydrogen storage alloy. The chemical composition of the hydrogen storage alloy is expressed as Mg80+x(Ce, Y)a(Ni, Co)b according to an atomic ratio, wherein x is greater than or equal to 0 and less than and equal to 15, a is greater than or equal to 0 and less than and equal to 10, and b is greater than or equal to 5 and less than and equal to 20; and a+b is greater than or equal to 5 and less than and equal to 20. The alloy has a double-platform collaboration mechanism. According to the preparation method, a 3+1 metallurgy method, a two-step smelting method and a one-step ball milling method are adopted, volatilization of magnesium is effectively inhibited, theuniformity of alloy components is guaranteed, meanwhile, solid solution of Mg-Ni and Mg-Co compounds is avoided, and two single magnesium compounds can be generated. After repeated hydrogenation, an Mg2Ni / Mg2NiH4 cycle with high platform pressure and an Mg6Co2H11 / Mg2CoH5 cycle with low platform pressure are formed. The Mg / MgH2 is induced to preferentially nucleate by double platforms, so that themechanical properties are improved, and the reaction temperature is reduced. The hydrogen absorption capacity of the hydrogen storage alloy is larger than 5 wt.%, and the hydrogen storage alloy has fast hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics and is expected to become a solid hydrogen source of the fuel cell.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
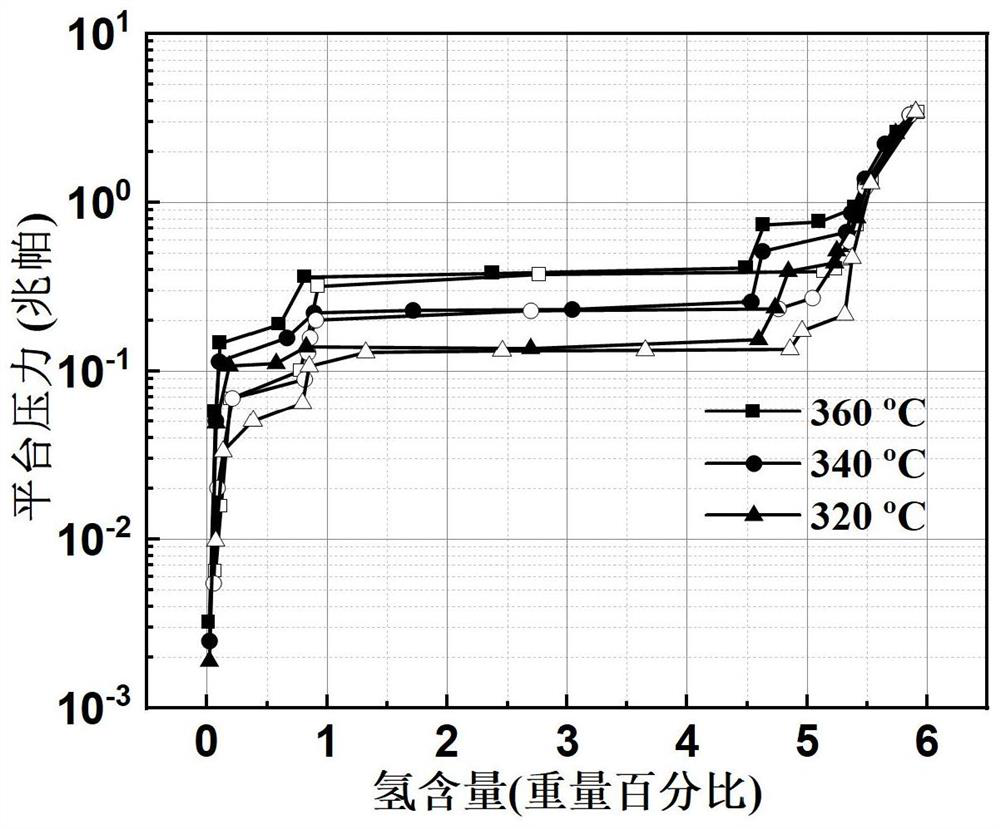
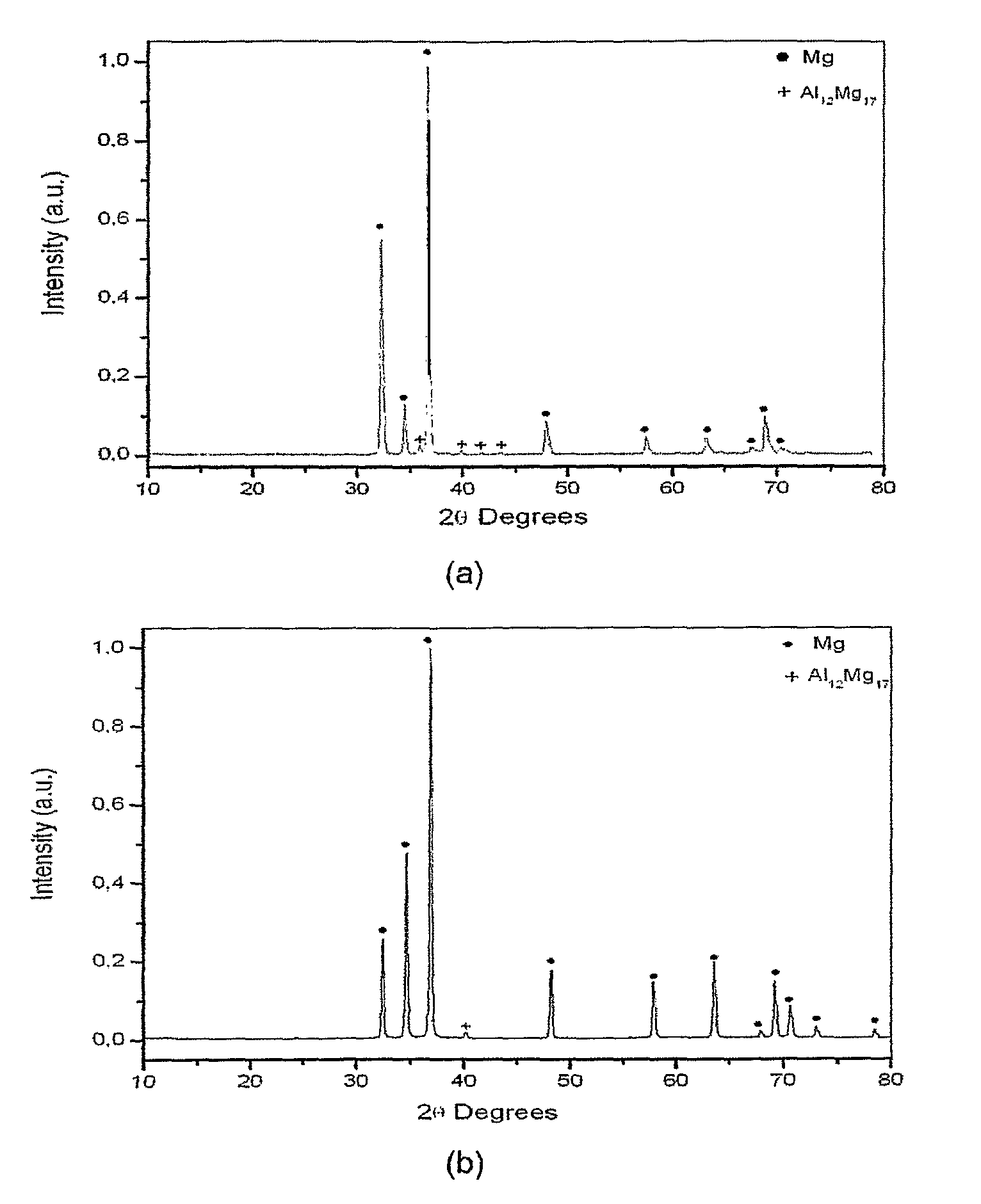
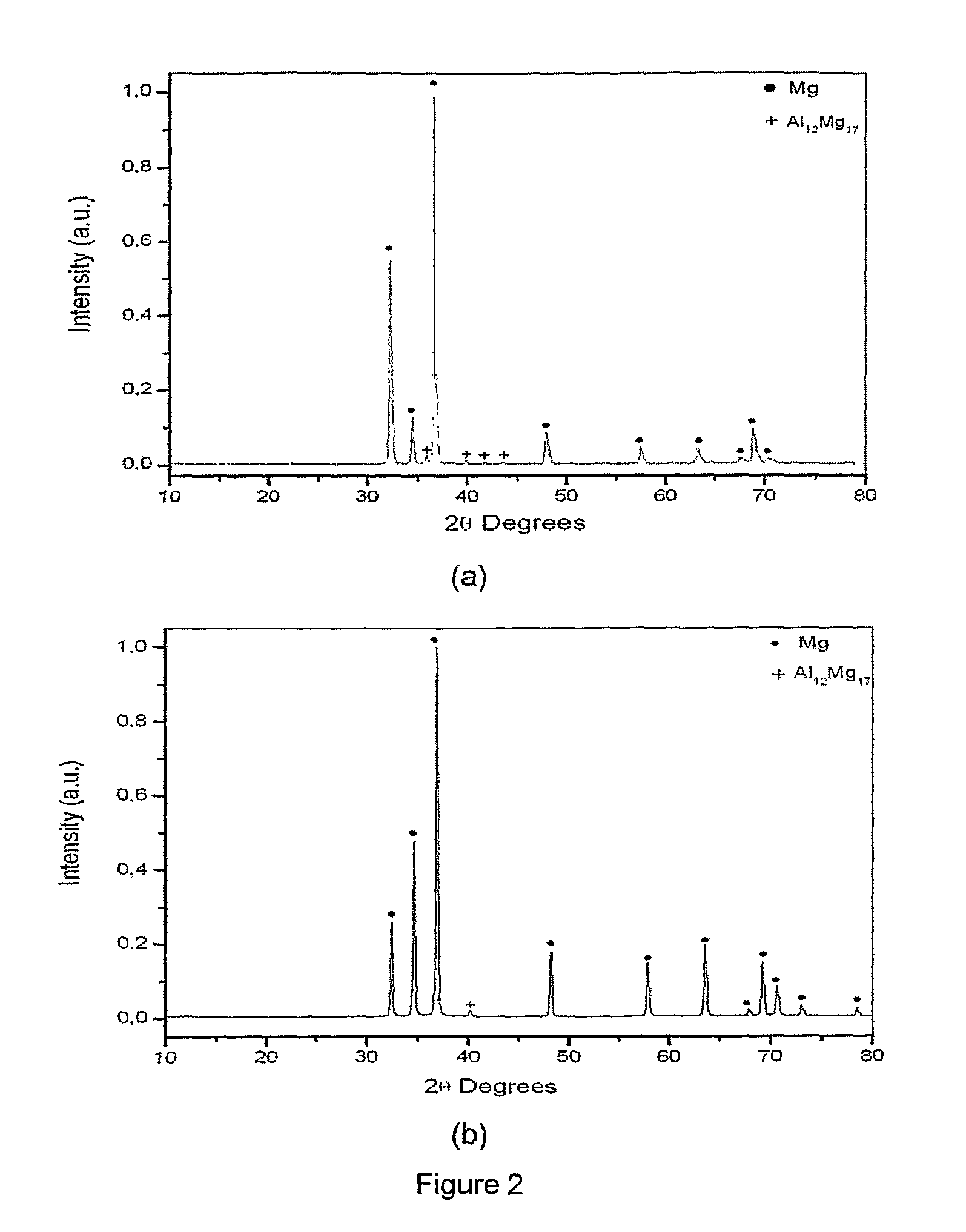
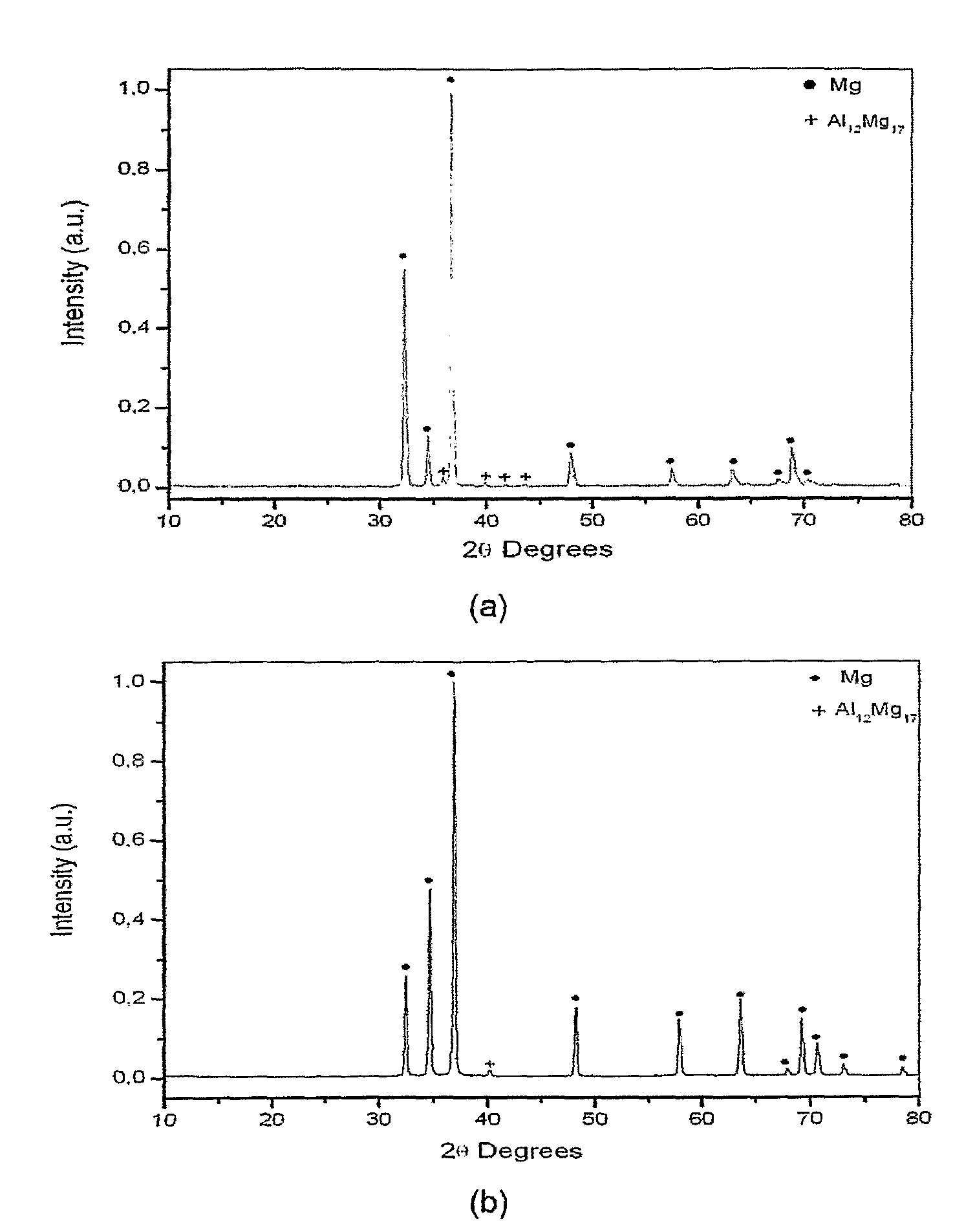
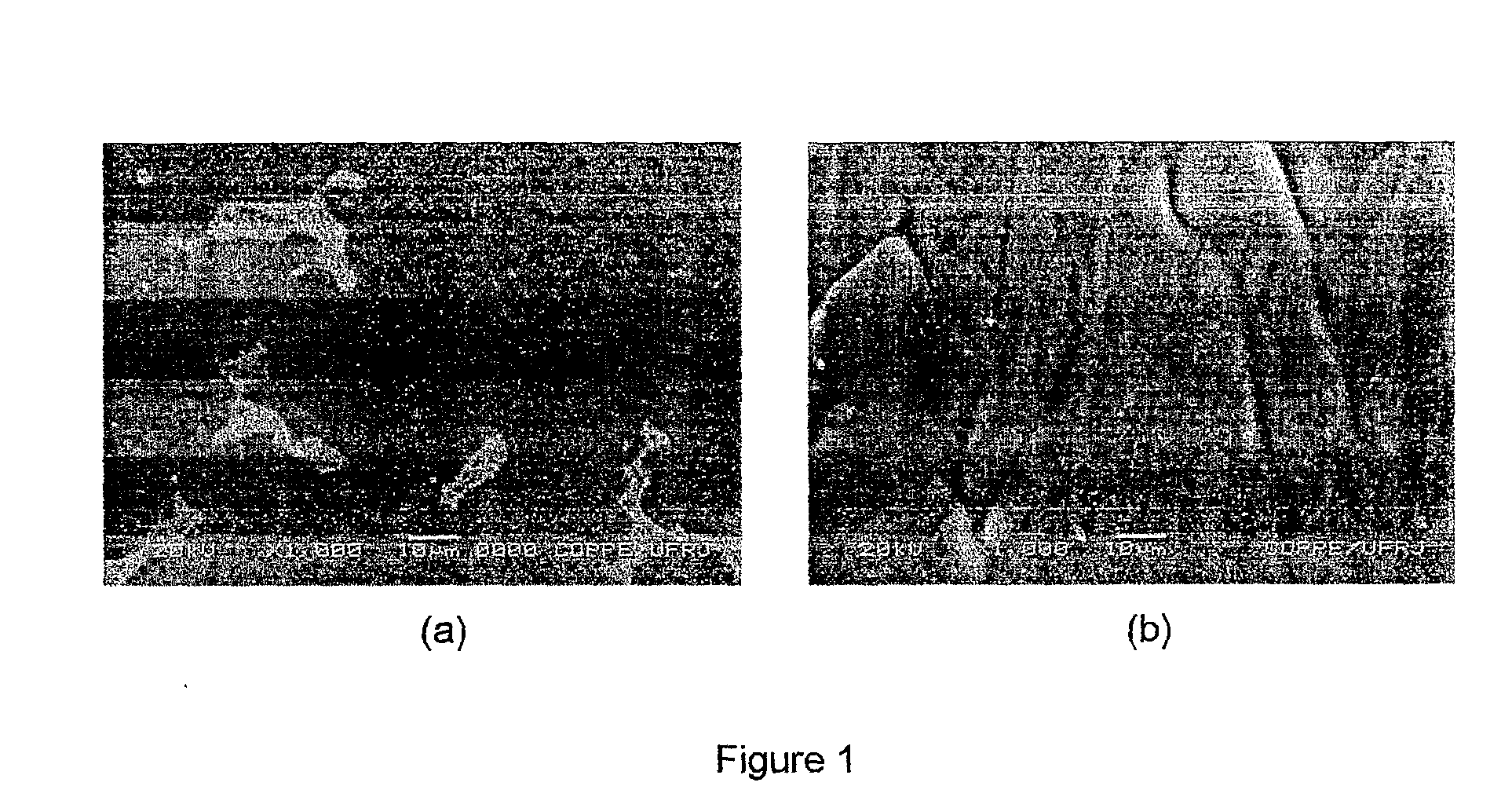
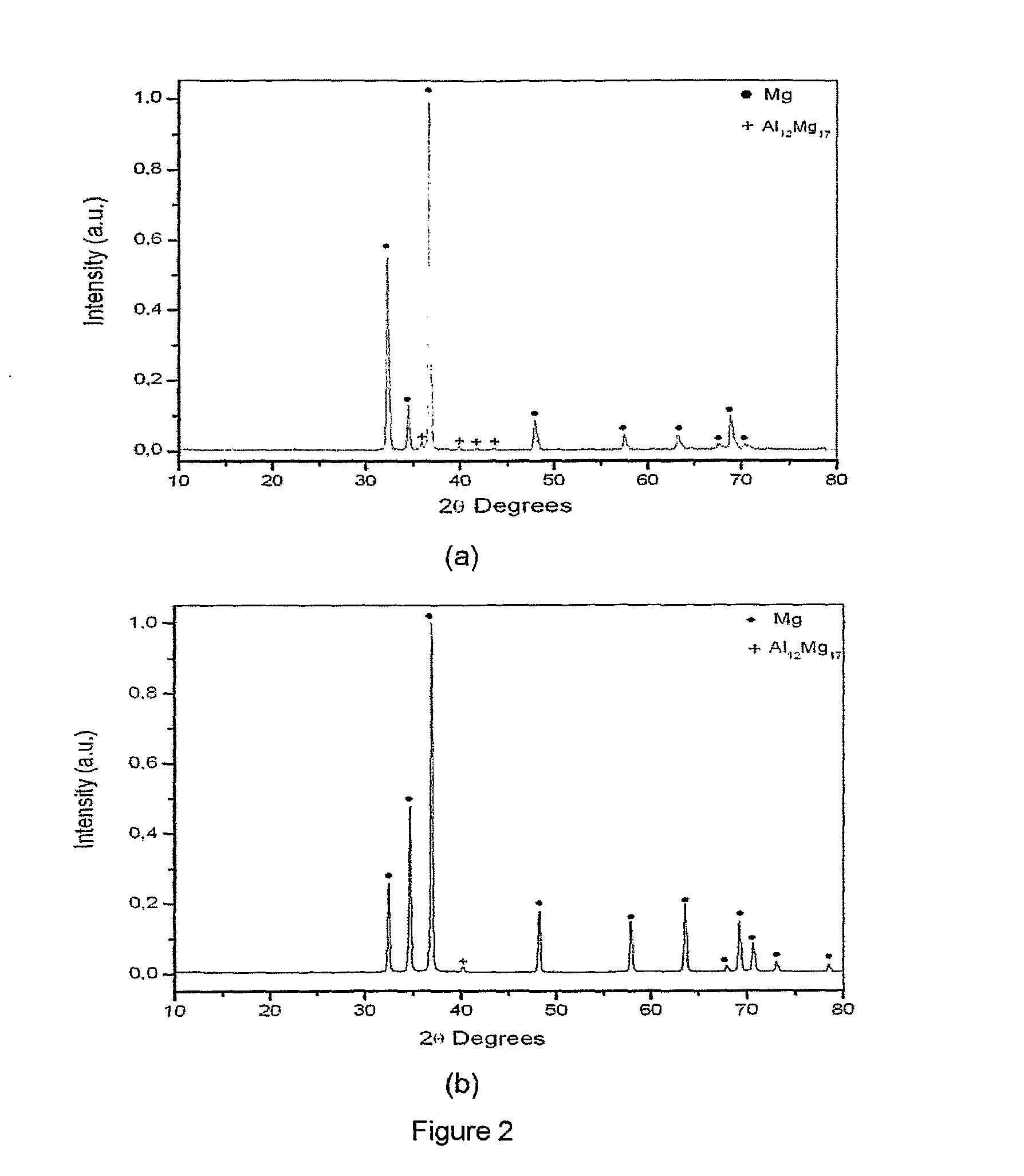
Magnesium based-alloys for hydrogen storage
Magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloys with addition of transition and rare earth elements were produced by conventional induction melting and by rapid solidification. The magnesium based-alloys of this invention posses reversible hydrogen storage capacities ranging from 3 to over 6 wt. %, and excellent performance on the hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics.
Owner:COORDENACAO DE PROGRAMAS DE POS GRADUACAO DE ENGENHARIA
Magnesium Based-Alloys for Hydrogen Storage
Magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloys with addition of transition and rare earth elements were produced by conventional induction melting and by rapid solidification. The magnesium based-alloys of this invention posses reversible hydrogen storage capacities ranging from 3 to over 6 wt. %, and excellent performance on the hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics.
Owner:COORDENACAO DE PROGRAMAS DE POS GRADUACAO DE ENGENHARIA
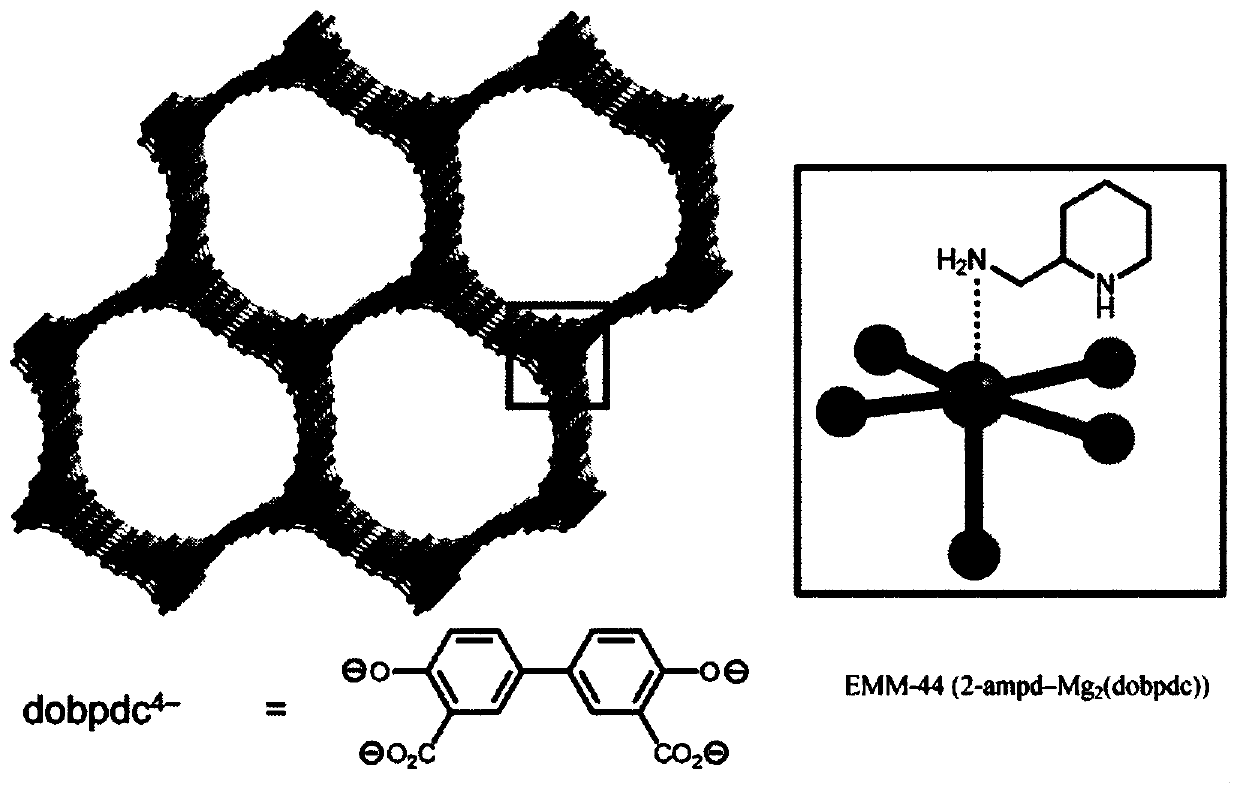
Metal organic frameworks appended with cyclic diamines for carbon dioxide capture
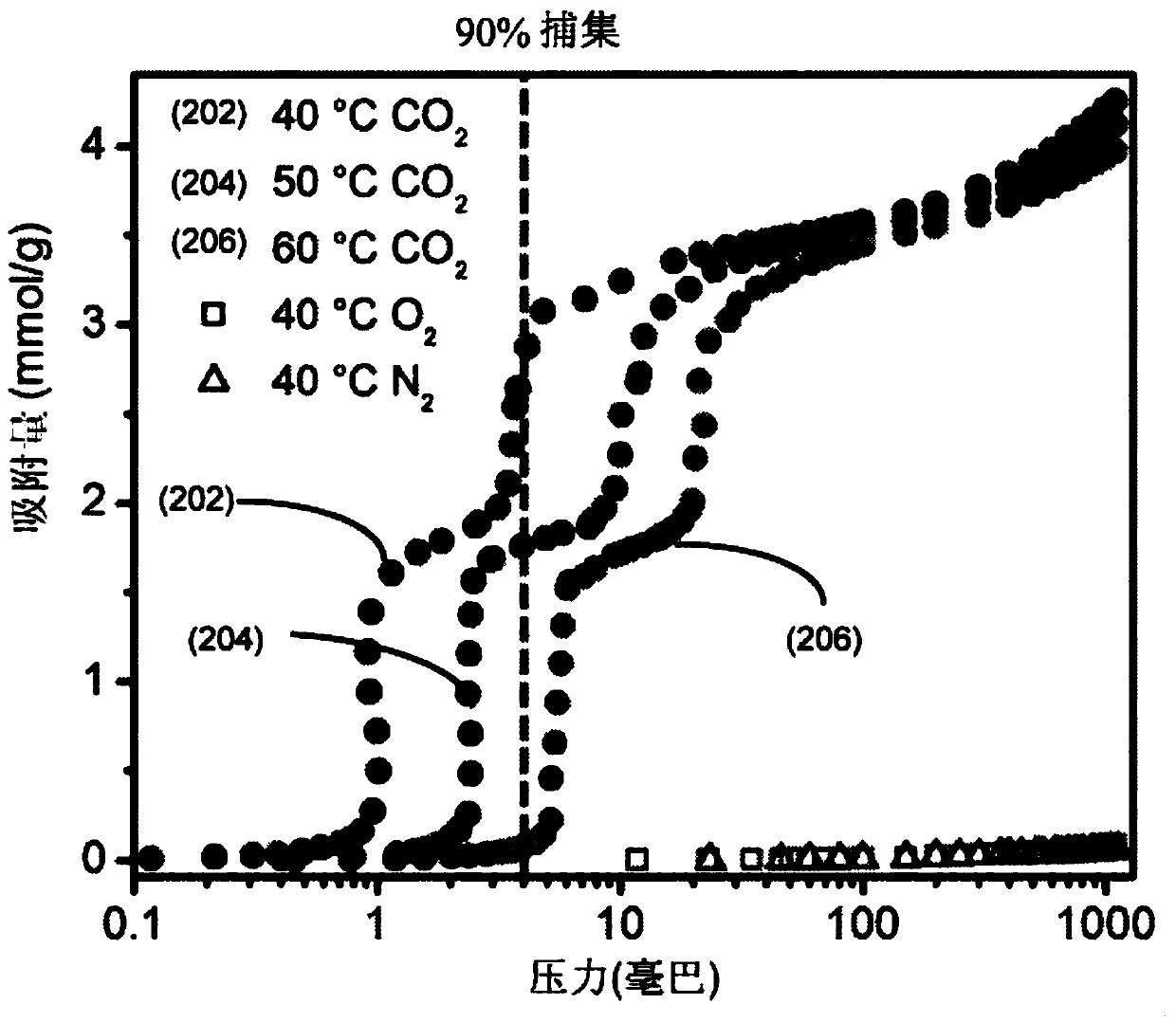
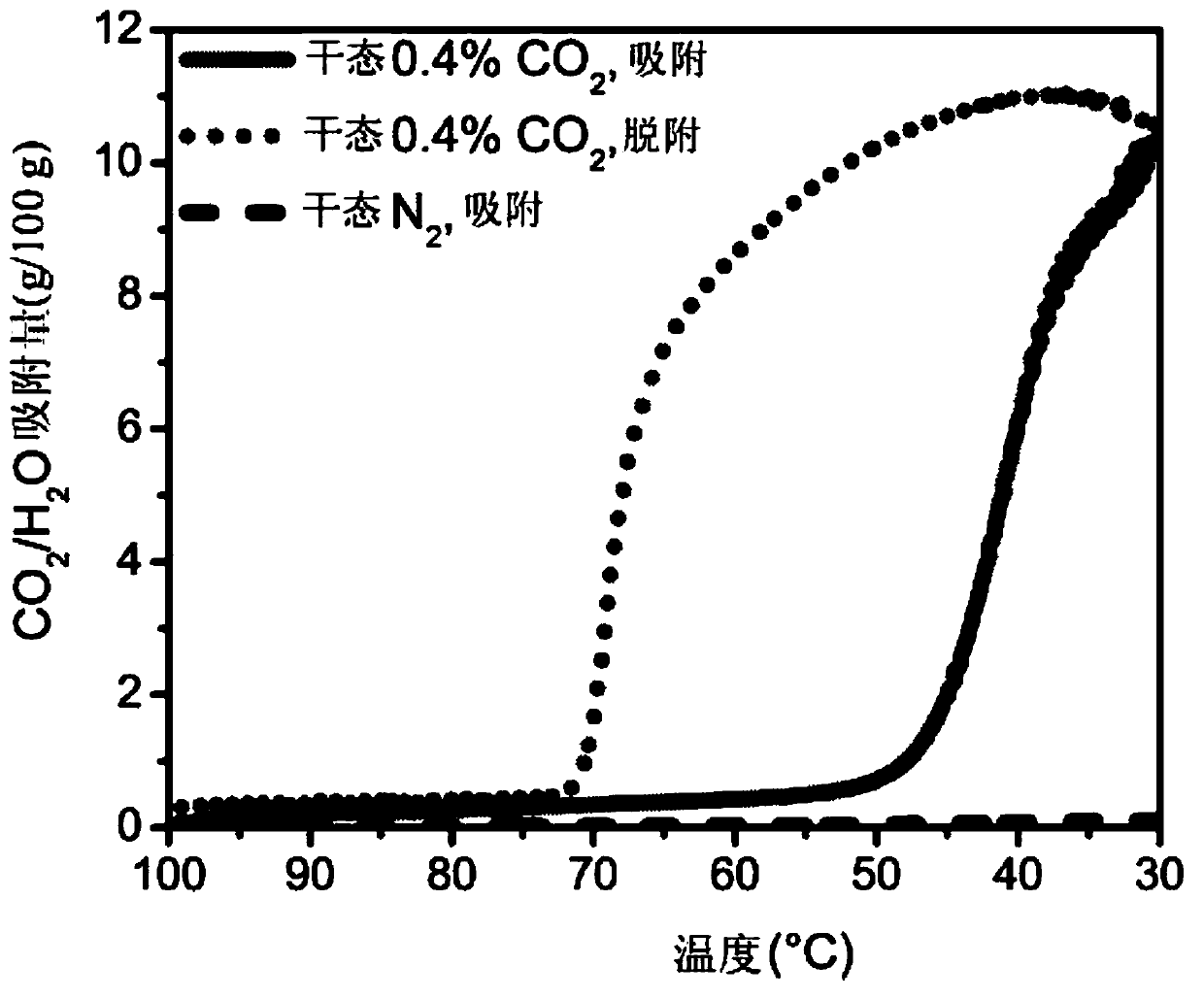
Achieving the selective and reversible adsorption of CO2 from humid, low partial pressures streams such as the flue gas resulting from the combustion of natural gas in combined cycle power plants (4%CO2) is challenging due to the need for high thermal, oxidative, and hydrolytic stability as well as moderate regeneration conditions to reduce the energy of adsorption / desorption cycling. Appending cyclic primary, secondary diamines, exemplified by 2-(aminomethyl)piperidine (2-ampd), to the metal-organic frameworks Mg2(dobpdc) (dobpdc4- = 4,4-dioxidobiphenyl-3,3-dicarboxylate), Mg2(dotpdc) (dotpdc4- = 4,4''-dioxido-[1,1':4',1''-terphenyl]-3,3''-dicarboxylate) or Mg2(pc-dobpdc) (pc-dobpdc4- = dioxidobiphenyl-4,4'-dicarboxylate) produces adsorbents of the classes EMM-44, EMM-45, and EMM-46, respectively, that display step-shaped adsorption of CO2 at the partial pressures required for 90% capture from natural gas flue gas at temperatures up to or exceeding 60 DEG C. Using a cyclic diamine inplace of a diamine functionalized with bulky alkyl groups enables fast adsorption / desorption kinetics with sharp CO2 adsorption and desorption steps.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
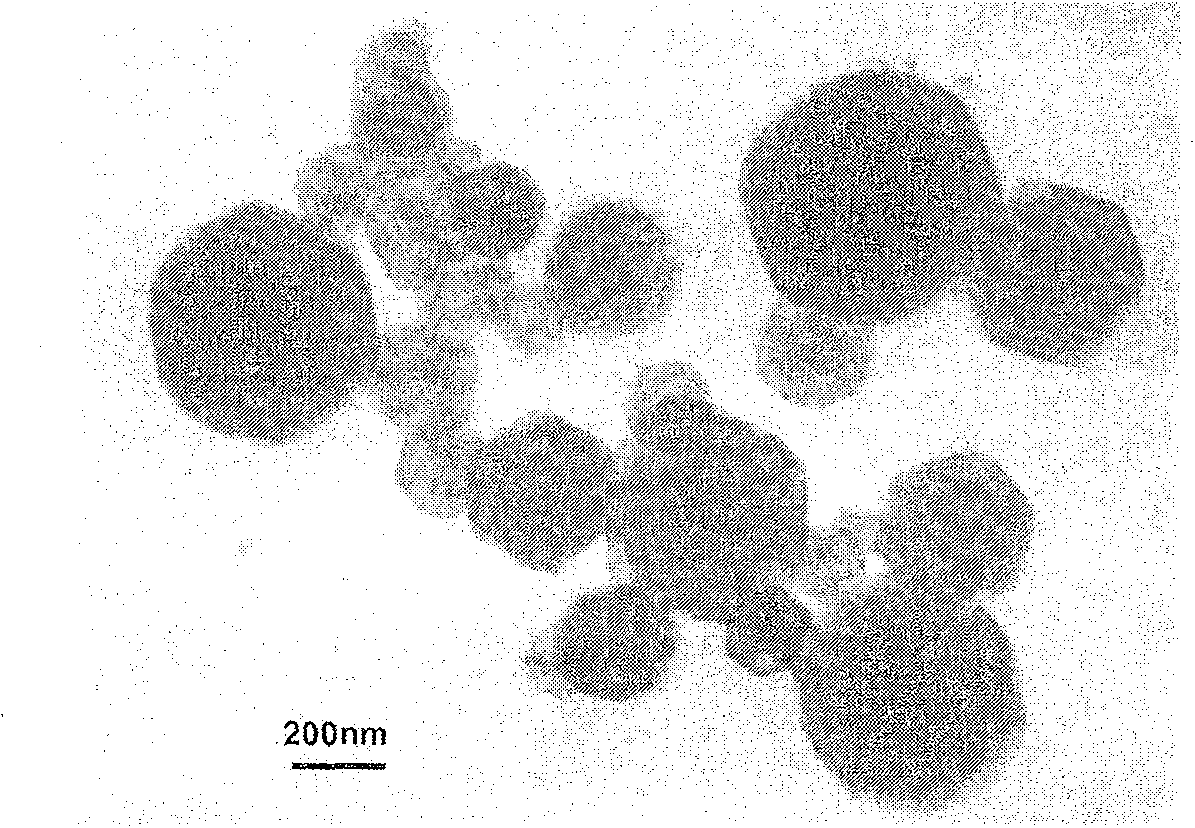
Magnesium hydride nano particle and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN100554142CLarge specific surface areaShorten the diffusion distanceAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesNanoparticleHydrogen absorption
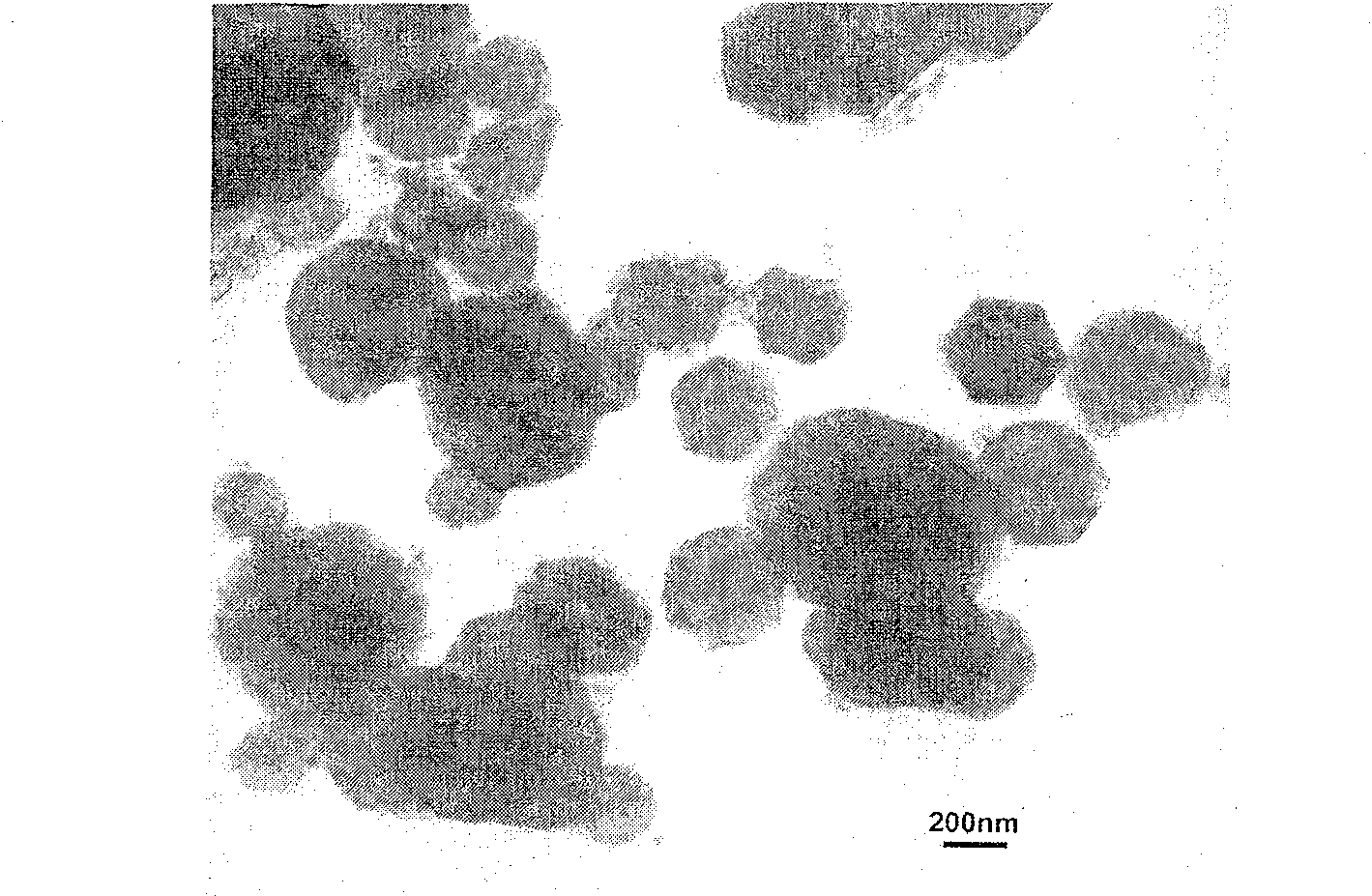
The invention discloses a magnesium hydride nano particle material, a preparation method and application thereof. The method of electric arc heating is used to prepare nano-sized magnesium powder, and then hydrogenated to obtain MgH2 particle products with a particle size of 50-600nm. The nano-scale MgH2 particle of the present invention has high purity, and has excellent kinetic properties of hydrogen absorption and desorption when used as a hydrogen storage material, so it has extremely important application value and broad application prospects in the field of hydrogen storage technology.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
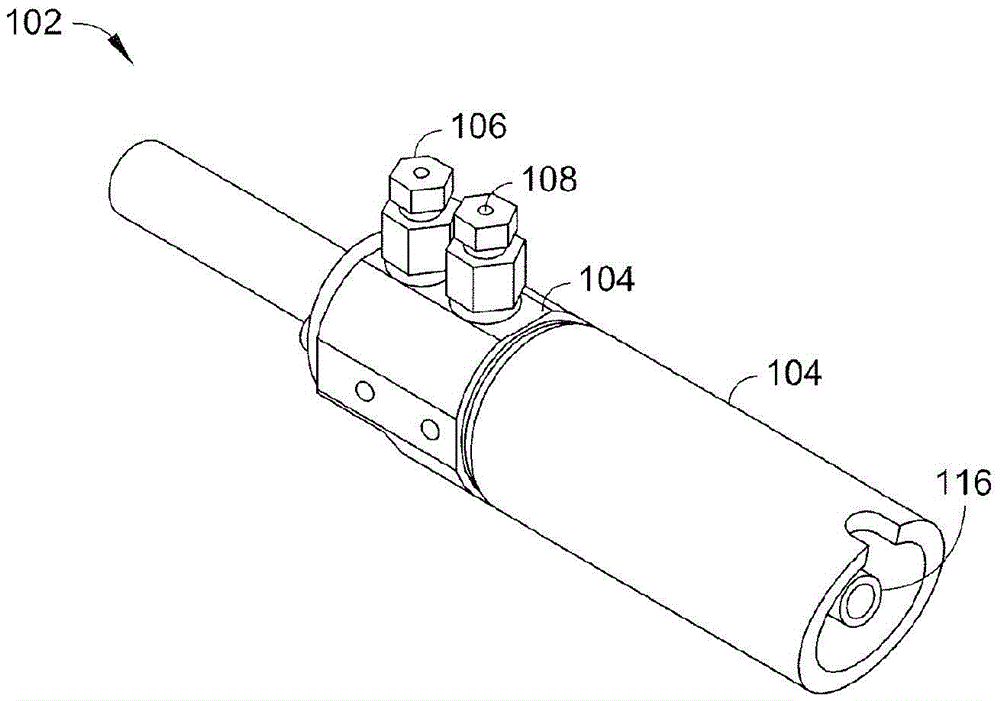
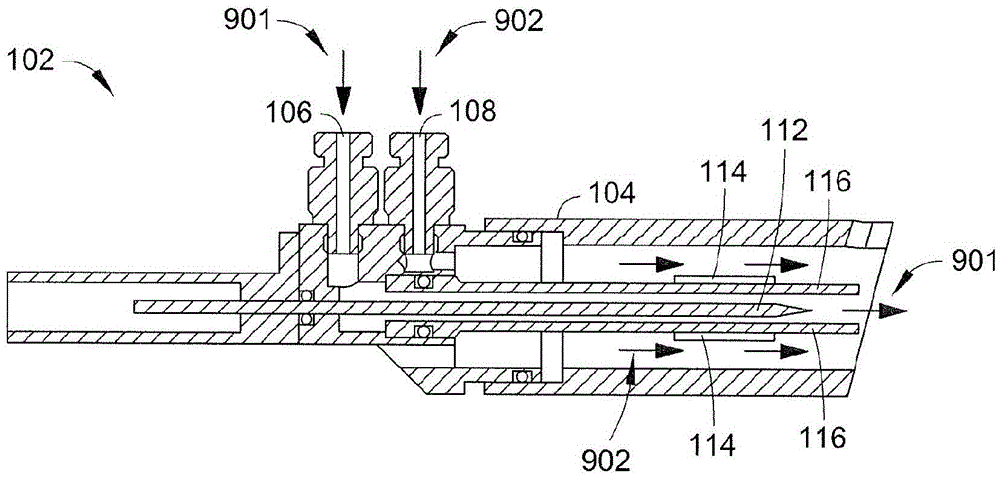
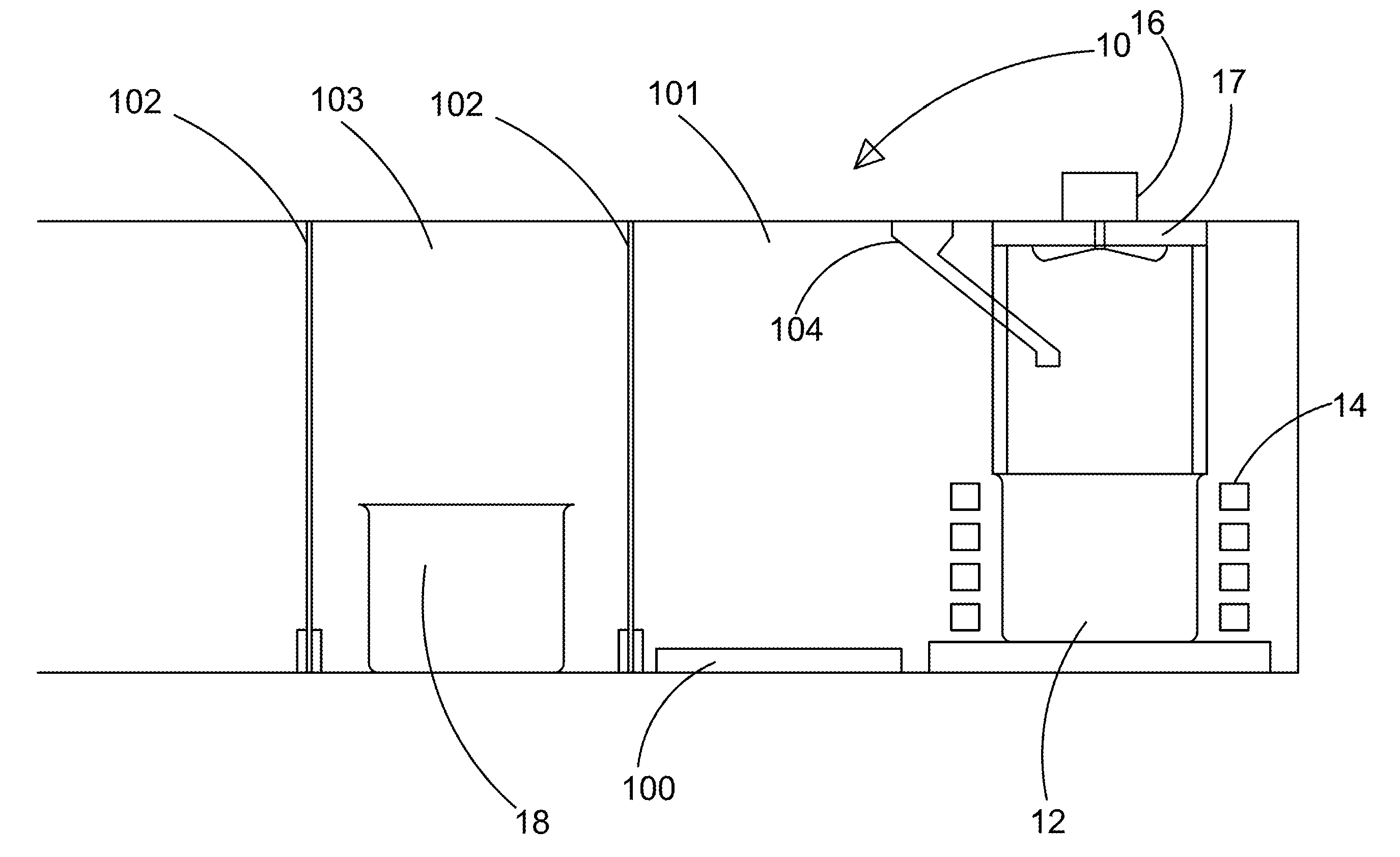
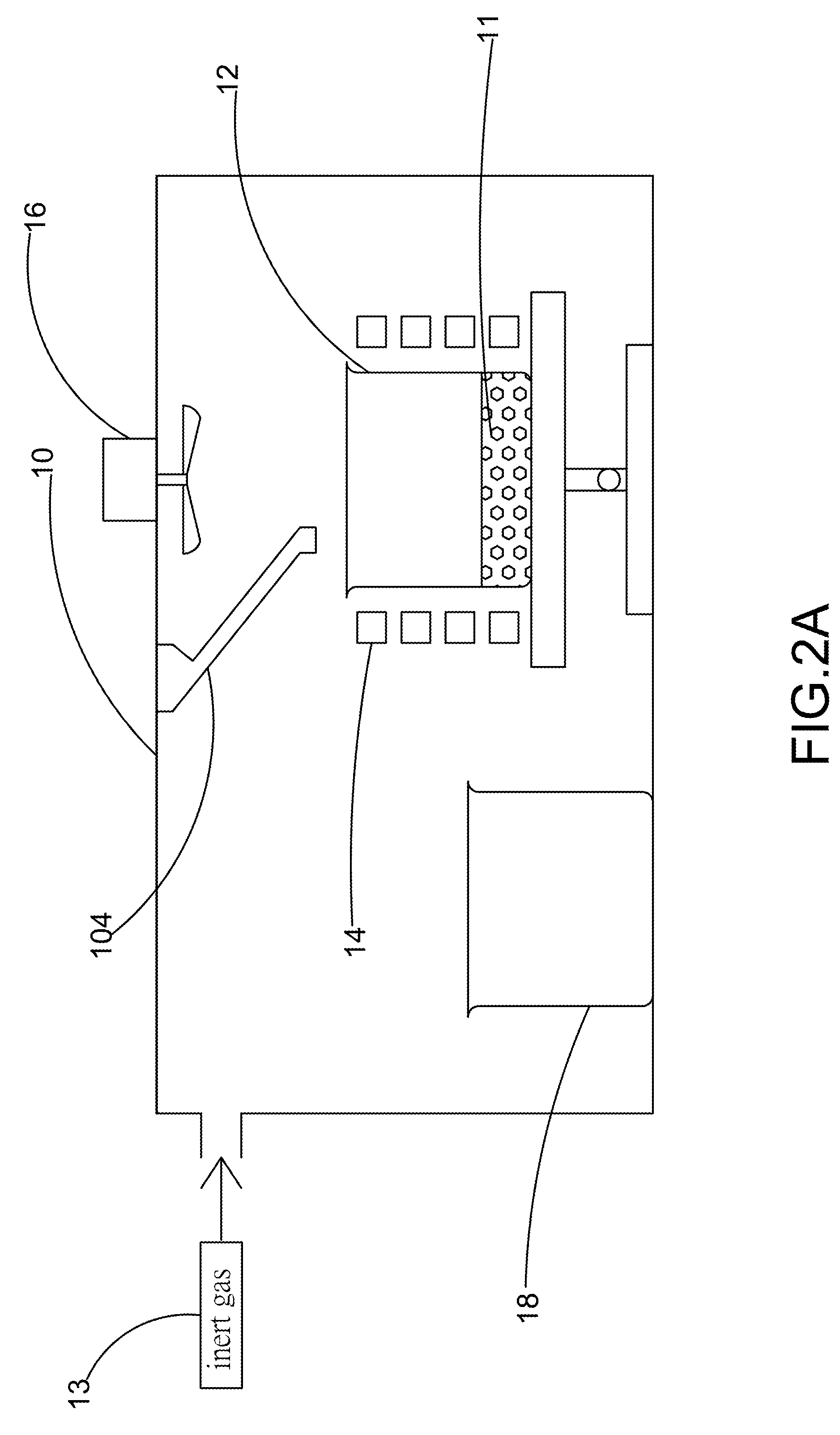
Apparatus for Continuously Manufacturing Stoichiometric Mg2Ni Hydrogen Storage Compound
The present invention provides an apparatus for manufacturing stoichiometric Mg2Ni compound applicable to industry and capable of manufacturing continuously. The apparatus mainly comprises: a vacuum chamber, comprising a material feeding tube; a first crucible, set in the vacuum chamber; a heating device, set on the first crucible; a stirring device, set in the vacuum chamber, and above the first crucible; and a second crucible, set in the vacuum chamber, and on one side of the first crucible. The present invention also discloses a method to manufacture stoichiometric γ-phase Mg2Ni hydrogen storage compound. Through this apparatus and method, the residual waste magnesium-rich liquid in the crucible is poured to another independent crucible, and switch with the position of the crucible originally containing the γ-phase Mg2Ni hydrogen storage compound. Then, new raw materials of magnesium and nickel are added and heated. Repeat the smelt steps described above continuously, and a continuous manufacturing method is introduced. After the original crucible is cooled, the solid substances at the bottom of the crucible can be tapped down without further special treatments. Then stoichiometric γ-phase Mg2Ni hydrogen storage compound with an exactly atomic ratio of 2:1, without other phases, and with excellent hydrogen absorption-desorption dynamics is given.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for manufacturing high-purity hydrogen storage alloy Mg2Ni
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for manufacturing high-purity hydrogen storage alloy Mg2Ni applicable to industry and capable of manufacturing continuously. First, raw materials of magnesium-nickel with weight percentage of nickel between 23.5 and 50.2 are heated, melt, and mixed uniformly. Cool the magnesium-nickel liquid and control the temperature to be above the solidification temperature and below the liquification temperature in the phase diagram of magnesium-nickel. By making advantage of segregation principle in phase diagrams, solid-state high-purity γ-phase Mg2Ni hydrogen storage alloy is given. The residual waste magnesium-rich liquid in the crucible is poured to another independent crucible, and switch with the position of the crucible originally containing the γ-phase Mg2Ni hydrogen storage alloy. Then, new raw materials of magnesium and nickel are added and heated. Repeat the smelt steps described above continuously, and a continuous manufacturing method is introduced. After the original crucible is cooled, the solid substances at the bottom of the crucible can be tapped down without further special treatments. Then high-purity γ-phase Mg2Ni hydrogen storage alloy with atomic ratio of 2:1, no other phases, and with excellent hydrogen absorption-desorption dynamics is given.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
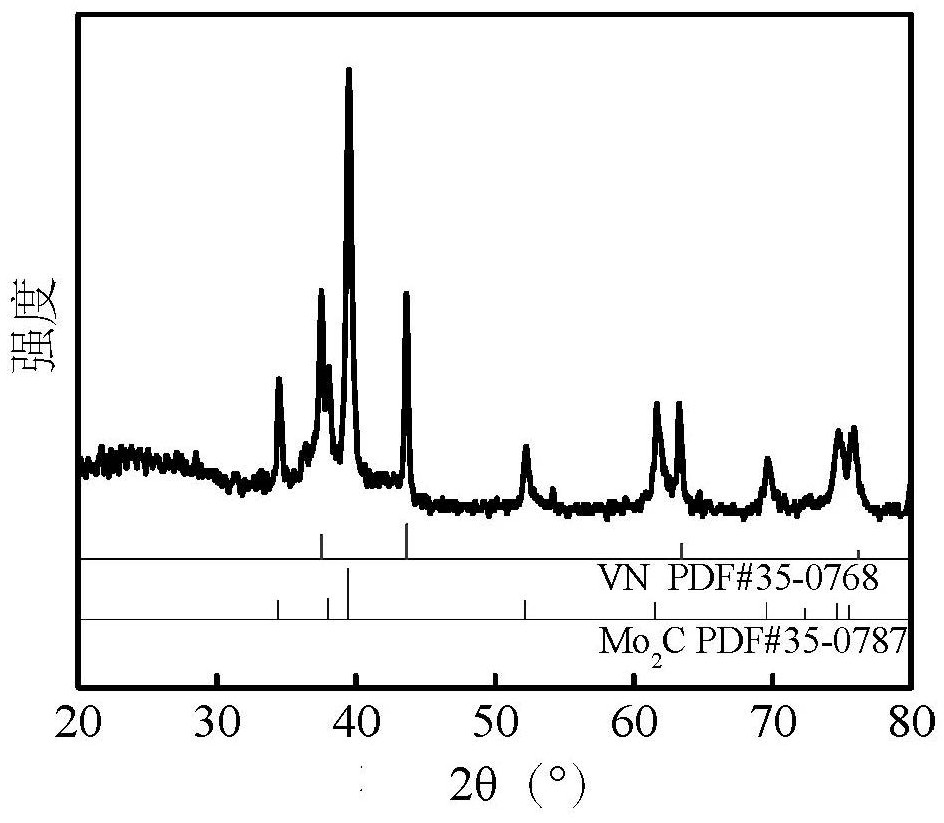
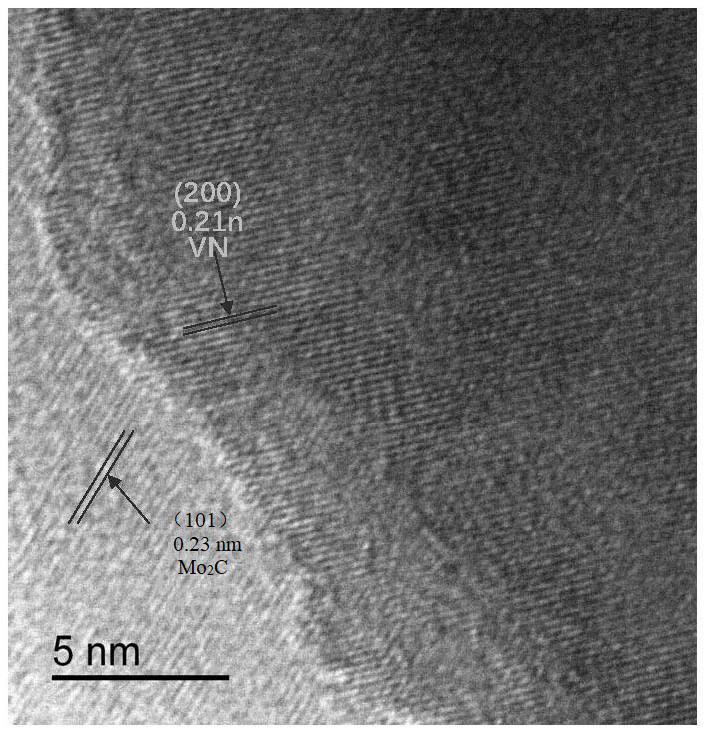
Efficient vanadium nitride/molybdenum carbide heterojunction hydrogen production electrocatalyst and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114645283AImprove conductivityImprove adsorption capacityLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectrodesPtru catalystMolybdenum carbide
The invention discloses an efficient vanadium nitride / molybdenum carbide heterojunction hydrogen production electrocatalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The electrocatalyst has a heterojunction structure formed by coupling VN and Mo2C, wherein the mass ratio of VN to Mo2C is (20: 1)-(50: 1). According to the catalyst, nano VN and Mo2C are coupled to form a VN / Mo2C heterojunction, so that active centers are increased, the balance of H < + > adsorption / H2 desorption kinetics is facilitated, and the activity of the catalyst is improved to a great extent.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
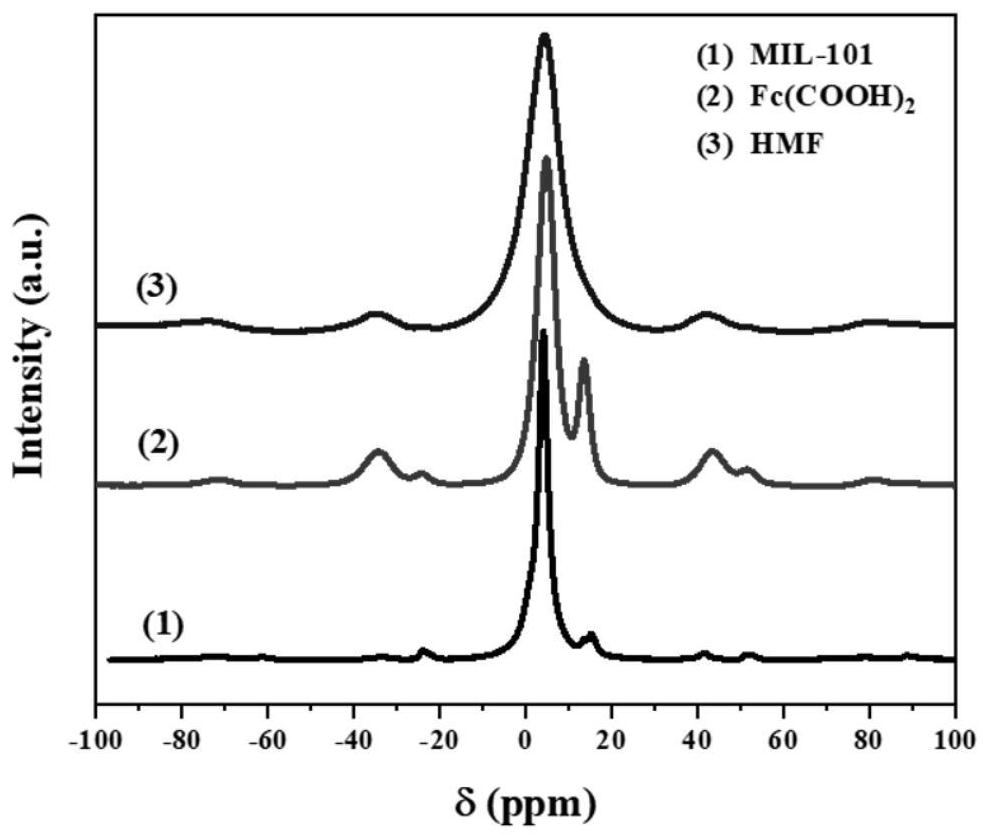
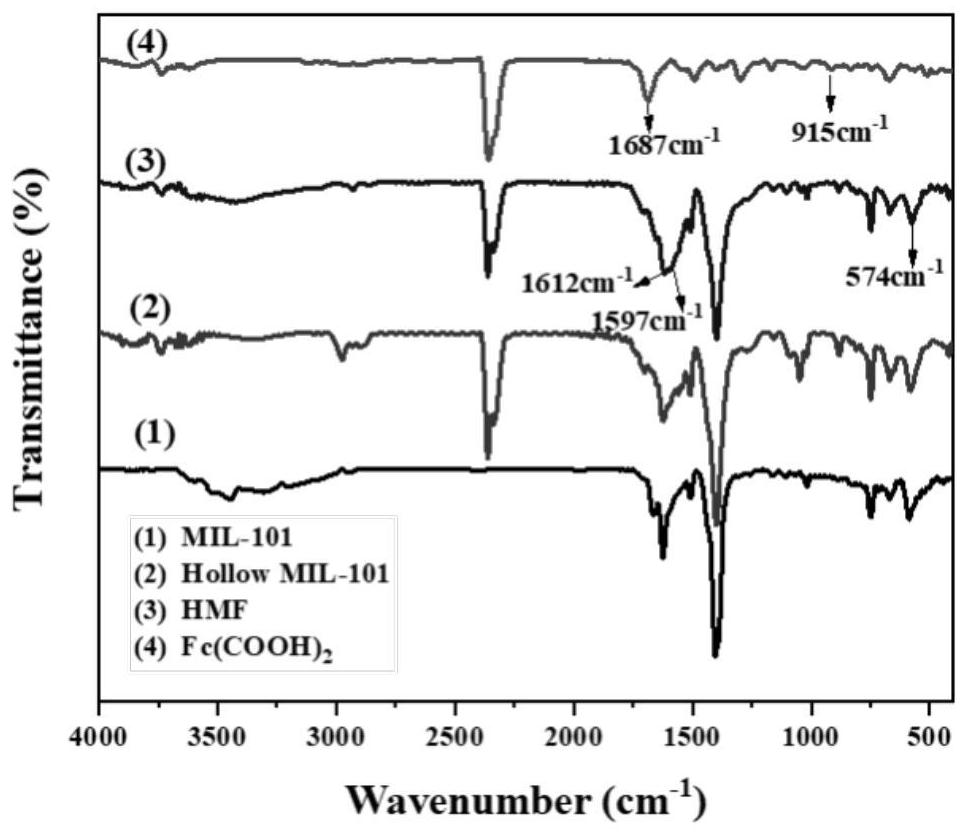
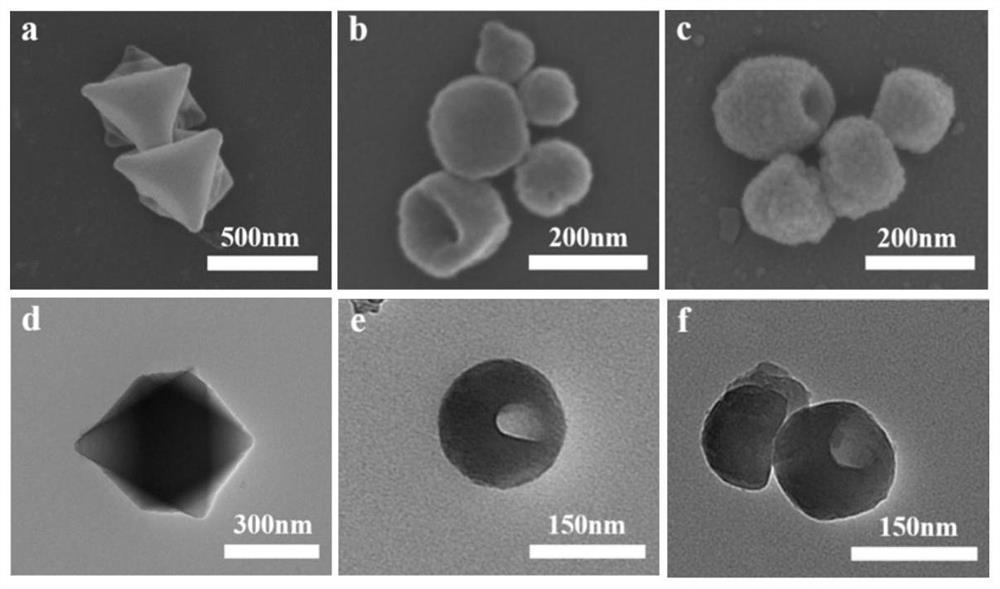
Ligand-exchanged hollow MIL-101 metal organic framework material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114573825AImprove adsorption capacityMultifunctionalOther chemical processesWater conservationAcid etchingMetal-organic framework
The invention discloses a 1, 1 '-ferrocene dicarboxylic acid ligand exchanged hollow MIL-101 metal organic framework material as well as a preparation method and application thereof, the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an MIL-101 metal organic framework material, and performing acid etching on the MIL-101 metal organic framework material to obtain the hollow MIL-101 metal organic framework material; and (2) dispersing the hollow MIL-101 metal organic framework material and 1, 1 '-ferrocenedicarboxylic acid into a solvent, adding acetic acid, uniformly mixing to form a suspension, reacting at 80-160 DEG C for 6-24 hours, cooling, centrifuging, washing and drying to obtain the hollow MIL-101 metal organic framework material exchanged by the 1, 1'-ferrocenedicarboxylic acid ligand. The ligand-exchanged hollow MIL-101 metal organic framework material has the characteristics of large specific surface area, high water adsorption capacity, rapid adsorption and desorption kinetics, excellent light absorption and photothermal conversion capability, outstanding antibacterial performance and the like, and can be used in the fields of solar-driven atmospheric water collection, fruit and vegetable preservation, intelligent sterilization and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
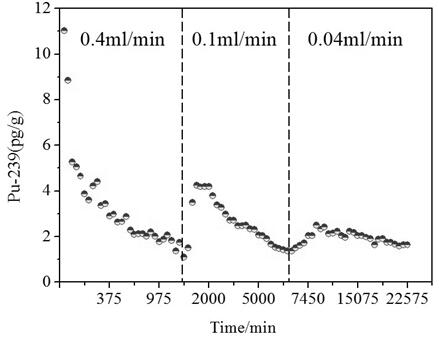
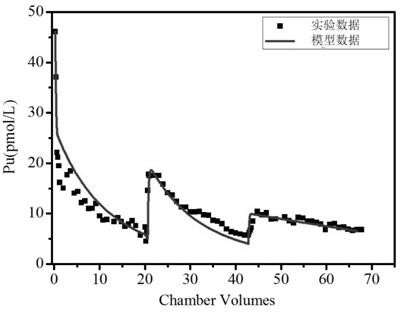
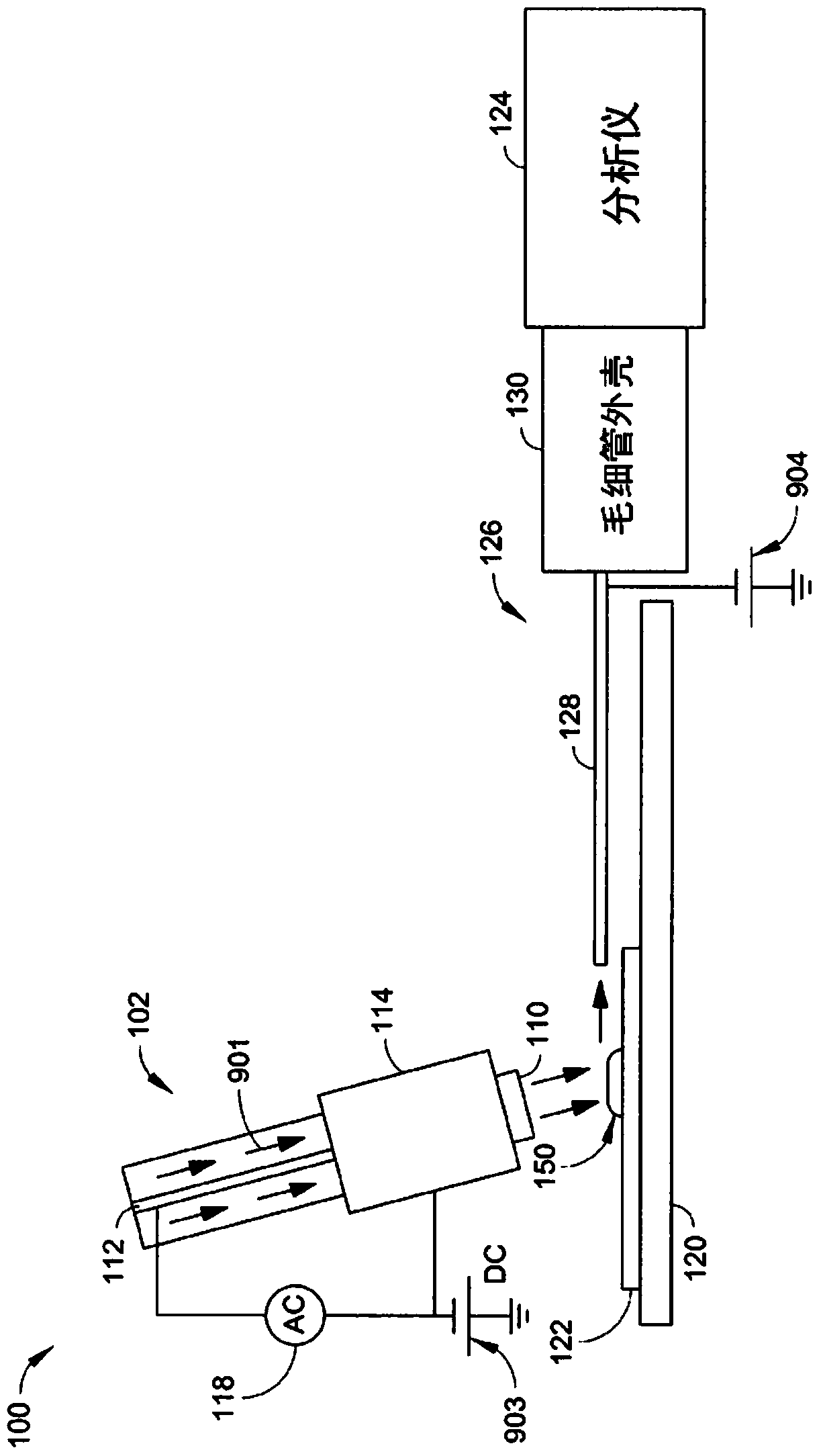
Method for establishing dynamic desorption model of plutonium on mineral surface
PendingCN114792048AThe principle of the method is simpleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMaceralAtomic physics
Owner:63653 FORCES PLA
In Situ Chemical Transformation and Ionization of Inorganic Perchlorate Surfaces
ActiveCN105531577BWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationChemical reactionAnalyte
The present invention discloses a method for providing in situ chemical conversion and ionization of a portion of a sample (eg, an inorganic oxidizing agent) by an analyte detection system. The method includes introducing a gas into an ionization source of the analyte detection system via an inlet. The method further includes generating ions within the ionization source and directing the gas and generated ions through and out of the ionization source and toward the sample. The sample is located proximal to the ionization source in the ambient environment. The ions chemically react with the sample and desorb and ionize an analyte from the sample, the analyte being generated by the inorganic oxidizing agent, the desorbed analyte having a lower melting point and / or higher desorption kinetics. The method further includes receiving the desorbed analyte by an analyzer of the analyte detection system.
Owner:SMITHS DETECTION MONTREAL
A kind of v-ti-ni based porous hydrogen evolution cathode material, preparation method and application
ActiveCN110373684BIncrease surface areaHigh hydrogen storage capacityElectrodesPorous substrateElectrolysis
The invention discloses a V-Ti-Ni-based porous hydrogen evolution cathode material, a preparation method and its application. The V-Ti-Ni-based hydrogen storage alloy powder is used as a raw material to prepare a hydrogen evolution cathode matrix by a solid-phase sintering method, and then the It is modified by coating to obtain the final hydrogen evolution cathode material, which is used as the cathode material in water electrolysis hydrogen production. On the one hand, the substrate itself is porous and has a large surface area, which can provide more reaction interfaces for the hydrogen evolution process of the electrode, making the reaction easier to proceed. The Ni-based alloy coating with high catalytic activity can be modified on the porous substrate to further reduce the activation energy of the reaction. Reduce the hydrogen evolution point and energy consumption; on the other hand, the matrix has a large hydrogen storage capacity and good hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics at room temperature. During normal electrolytic hydrogen production, it can absorb part of the hydrogen into the alloy. When the power is turned off, the absorbed hydrogen It can migrate to the surface of the electrode through diffusion, and replace the electrode components for oxidation reaction, thereby protecting the electrode material.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Ti-Fe based porous hydrogen evolution cathode material and preparation method and application
ActiveCN110373683AIncrease surface areaHigh hydrogen storage capacityElectrode shape/formsElectrolysisAlloy coating
The invention discloses a Ti-Fe based porous hydrogen evolution cathode material and a preparation method and application. Ti Fe based hydrogen storage alloy powder is taken as a raw material, a hydrogen evolution cathode matrix is prepared by adopting a solid-phase sintering method, and then is subjected to coating modification to obtain the final hydrogen evolution cathode material, and is usedas a cathode material in the hydrogen production by water electrolysis. On the one hand, the matrix has porous properties and large surface area, so that more reaction interfaces can be provided for the hydrogen evolution process of an electrode, and the reaction is easier; the porous matrix is modified with a Ni based alloy coating with high catalytic activity, the activation energy of the reaction can be further reduced, and the hydrogen evolution point location and energy consumption are reduced; on the other hand, the matrix has large hydrogen storage capacity and good room temperature hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics performance, in normal electrolytic hydrogen production, part of hydrogen can be absorbed into an alloy, and in case of power failure, the absorbed hydrogen can be transferred to the electrode surface through diffusion, the electrode components are replaced to generate oxidation reaction, so that the electrode material can be protected.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
A kind of ti-mn based porous hydrogen evolution cathode material, preparation method and application
ActiveCN110373682BIncrease surface areaHigh hydrogen storage capacityElectrodesPorous substrateElectrolysis
The invention discloses a Ti-Mn-based porous hydrogen-evolving cathode material, a preparation method and an application thereof. The Ti-Mn-based hydrogen-storage alloy powder is used as a raw material, and a hydrogen-evolving cathode substrate is prepared by a solid-phase sintering method, and then coated and modified. , to obtain the final hydrogen evolution cathode material, as the cathode material in water electrolysis hydrogen production. On the one hand, the substrate itself is porous and has a large surface area, which can provide more reaction interfaces for the hydrogen evolution process of the electrode, making the reaction easier to proceed. The Ni-based alloy coating with high catalytic activity can be modified on the porous substrate to further reduce the activation energy of the reaction. Reduce the hydrogen evolution point and energy consumption; on the other hand, the matrix has a large hydrogen storage capacity and good hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics at room temperature. During normal electrolytic hydrogen production, it can absorb part of the hydrogen into the alloy. When the power is turned off, the absorbed hydrogen It can migrate to the surface of the electrode through diffusion, and replace the electrode components for oxidation reaction, thereby protecting the electrode material.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
A high-performance double rare earth solid solution-based hydrogen storage material and its preparation method
ActiveCN109175349BSimple structureLower the hydrogen decomposition temperatureTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusHydrogen atmosphereHydrogen desorption
The invention relates to a high-performance double rare earth solid solution-based hydrogen storage alloy and a preparation method thereof. The hydrogen storage alloy includes a fair component of Mg 90‑a‑b RE1 a RE2 b alloy, and RE1 and RE2 are respectively a kind of lanthanide rare earth elements. The preparation method is to use medium frequency induction smelting technology to heat and smelt under the protection of inert gas, inject the molten alloy into a copper mold, and obtain a cylindrical alloy ingot after cooling, then mechanically crush and grind the ingot into a powder with a particle size of 200 meshes, and Add stearic acid as an additive in a mass ratio of cwt.%, then carry out high-energy ball milling, and then fully hydrogenate under a high-purity hydrogen atmosphere, MgH 2 / Mg-(EE1,RE2)H 2+x Composite material, the present invention is nano crystal grain, and is dispersed in Mg / MgH 2 In the matrix, it not only plays the catalytic role of the dihydrogen pump, but also provides a large number of nucleation active sites, grain boundaries and diffusion channels, which improves the hydrogen storage performance. The high hydrogen storage capacity and fast hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics are maintained; the hydrogen desorption temperature of the hydride is significantly reduced, and the stability of the hydrogen absorption and desorption cycle is significantly improved.
Owner:中稀(微山)稀土新材料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com