Photocuring intelligent energetic material and preparation method thereof
A light-curing, intelligent technology, applied in offensive equipment, additive processing, explosives processing equipment, etc., can solve problems such as lack of environmental awareness and response characteristics, and difficulty in adapting to combat environments.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
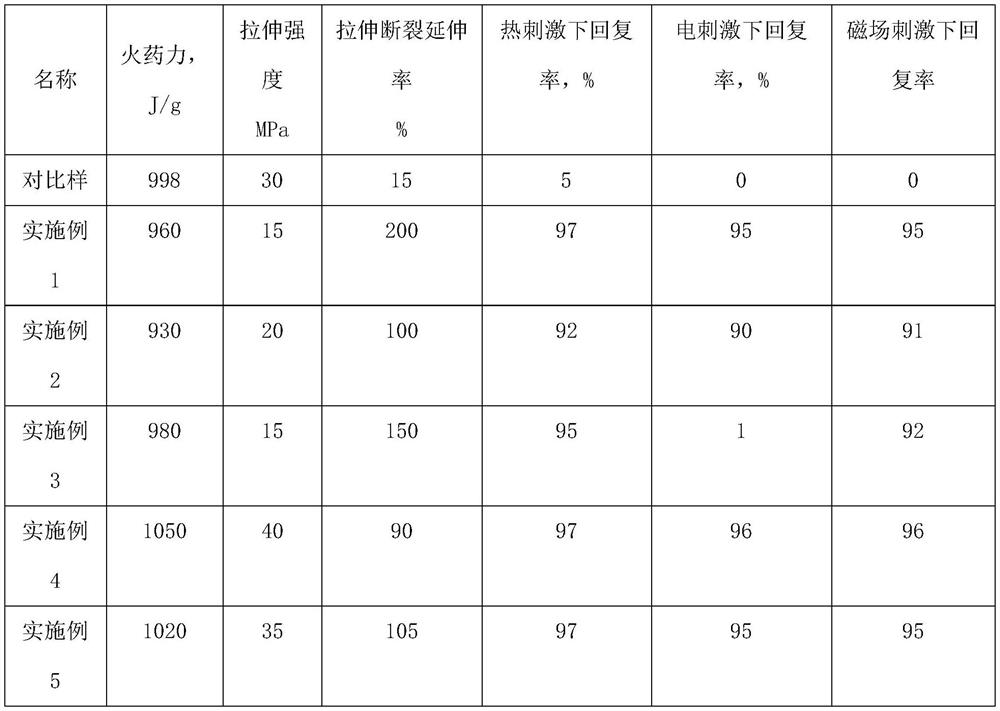
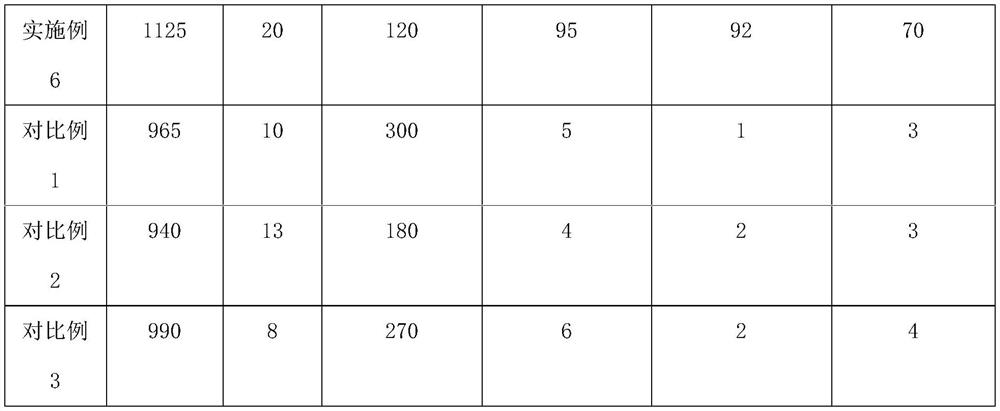
[0034] The formula of this example is as follows: 70 parts of polyurethane acrylic resin; 30 parts of epoxy acrylic resin; 34 parts of 1,6-hexanediol diacrylate; 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl-ethoxy- 6 parts of phenyl phosphorus oxide; 45 parts of polycaprolactone (molecular weight 65000-80000); 550 parts of RDX (particle size 0.2-40 μm); 50 parts of nitroglycerin; 6 parts of graphene.
[0035] The preparation step is to set the temperature above the melting point of the crystalline polymer, which is 70° C. in this example, and mix all the components with a stirrer in the dark for 3 hours at a rotational speed of 200 rpm.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Different from Example 1, the formula of this example is as follows: 100 parts of epoxy acrylic resin; 50 parts of ethoxylated oxyphenyl acrylate; 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphenylphosphonic acid ethyl 10 parts of ester; 40 parts of polydecyl adipate (molecular weight: 30,000-40,000); 650 parts of HMX crystals (particle size: 0.2-40 μm); and 6 parts of carbon nanotubes.
[0040] The difference between the preparation process and Example 1 is that the mixing temperature is set to 85°C.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Different from Example 1, the formula of this example is as follows: 100 parts of polyether acrylate; 20 parts of trimethylolpropane triacrylate; 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-phenylacetone-1,1- 6 parts of hydroxy-cyclohexyl benzophenone; 20 parts of polyhexamethylene sebacate (molecular weight 30,000-40,000); 500 parts of CL-20 crystals (particle size 0.2-40 μm); 2 parts of iron tetroxide.
[0045] The difference between the preparation process and Example 1 is that the mixing temperature is set to 85°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com