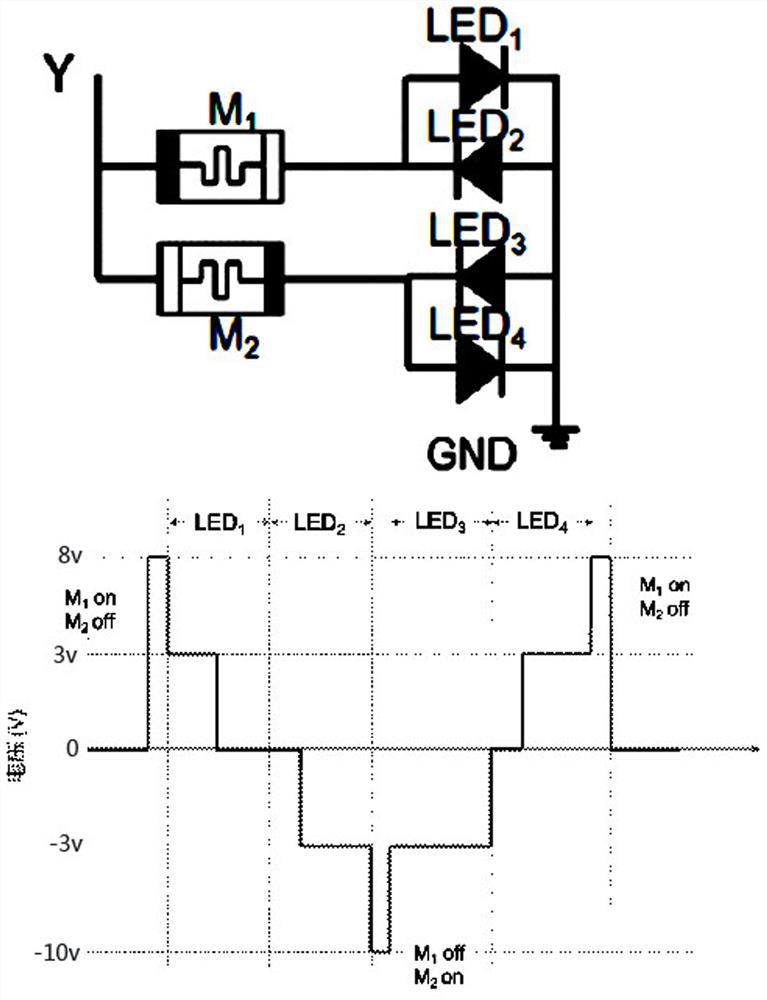
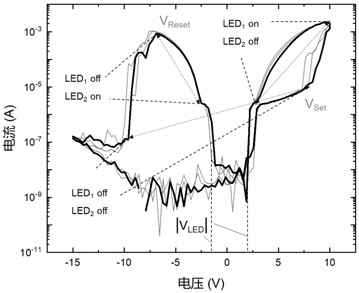
Basic display driving circuit driven by conductive wire type artificial neurons
An artificial nerve and display-driven technology, applied to electrical components, biological neural network models, static indicators, etc., to achieve the effect of high effective area and less wire
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040] The preparation method of the basic display driving circuit driven by the conductive filament type artificial neuron specifically includes the following steps:
[0041] (1) Based on a highly doped silicon wafer or copper and platinum inert metal materials with a thickness of 100-600nm;
[0042] (2) preparing a solid dielectric layer by sputtering insulating material on the bottom metal electrode layer obtained in step (1);
[0043] (3) A top metal electrode is prepared on the obtained solid dielectric layer by a thermal evaporation process.
specific Embodiment 1
[0044] 1) A heavily doped P-type silicon wafer with a size of 1.5cm×1.5cm and a length of 100nm silicon dioxide was cut, washed with acetone, isopropanol, chloroform and distilled water (three times), and then dried with nitrogen. Afterwards, a clean silicon wafer is obtained as a substrate.
[0045] 2) Sputtering a tantalum oxide insulating layer with a thickness of 50-70 nm on the silicon wafer obtained in step 1) by sputtering under the condition that the ratio of argon gas to oxygen gas is 20:5 and the sputtering pressure is 0.5pa.
[0046] 3) A 50nm-thick top silver electrode layer with a channel length of 30 μm and a width of 1000 μm is evaporated on the silicon wafer obtained in step 2) by thermal evaporation using a special mask.
[0047] 4) One end of the first conductive wire-type artificial neural component M1 is connected to the first light-emitting device LED1 and the second light-emitting device LED2, the other end of the first conductive wire-type artificial neu...
specific Embodiment 2
[0054] (1) The cut 1.5cm×1.5cm size, heavily doped P-type silicon wafer, washed with acetone, isopropanol, chloroform and distilled water (three times), and then dried with nitrogen to obtain clean CO2 Silicon wafer as substrate.
[0055] (2) 50nm thick copper with a length of 500 μm and a width of 500 μm is sputtered as a bottom metal electrode layer on the silicon wafer obtained in step 1) by means of magnetron sputtering using a special mask.
[0056] (3) Sputtering a tantalum oxide insulating layer with a thickness of 50-70 nm on the silicon wafer obtained in step 1) by sputtering under the conditions that the ratio of argon to oxygen is 20:5 and the sputtering pressure is 0.5pa.
[0057] (4) A 50-nm-thick top silver electrode layer with a channel length of 30 μm and a width of 1000 μm is vapor-deposited on the silicon wafer obtained in step 2) by thermal evaporation using a special mask.
[0058] (5) One end of the first conductive wire-type artificial neural component M...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com