Pesticide composition containing pseudolaric acid and application of pesticide composition to prevention and treatment of plant diseases
A hibiscus bark acetic acid and composition technology, applied in the field of pesticide composition containing hibiscus bark acetic acid and its application in preventing and controlling plant diseases, to achieve the effects of improving the control effect, prolonging the service life, and delaying the generation of drug resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
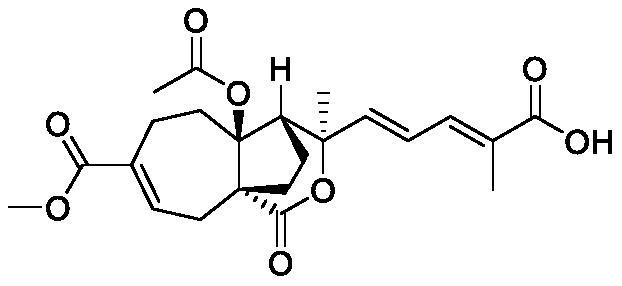
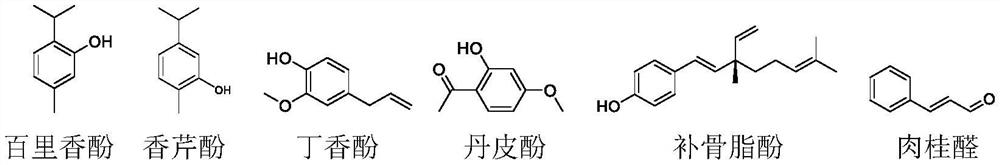
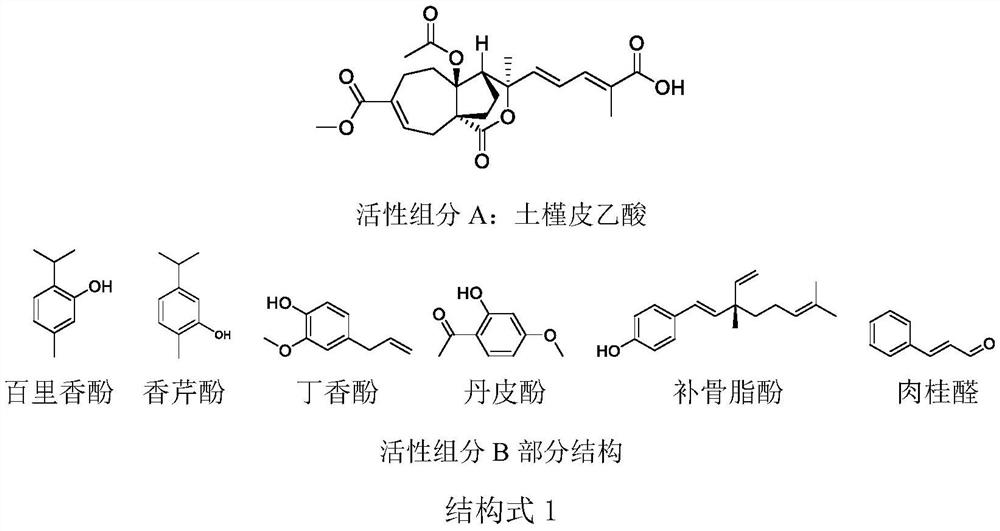
[0016] Embodiment 1: a fungicide composition containing hibiscus acetic acid, small molecular phenolic compounds, and plant essential oils, comprising active component A and active component B (as shown in structural formula 1), the active component A It is hibiscus bark acetic acid, and the active component B is a small molecule phenolic compound and a plant essential oil.
[0017]
[0018] Active ingredient B: thymol, carvacrol, eugenol, paeonol, bakuchiol, thyme essential oil, patchouli essential oil, clove essential oil, oregano essential oil, cinnamon essential oil, cinnamaldehyde.
[0019] Table 1 Antibacterial activity of hibiscus acetic acid and active component B against 7 agricultural pathogens
[0020]
[0021]
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Indoor activity determination of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by mixing hibiscus bark acetic acid and active component B
[0023] The phytopathogenic bacteria used in this experiment were strains stored at 4°C in the laboratory, and the medium used was potato agar-dextrose medium (PDA for short). PDA medium formula: potato (peeled) 200g, glucose 20g, agar 15g, distilled water 1000mL, natural pH.
[0024] PDA medium configuration method: Wash and peel the potatoes, weigh 200g and cut them into small pieces, boil in distilled water for about 20min (the potato pieces are soft but not rotten), filter with eight layers of gauze, make up the filtrate to 1000mL with distilled water, add 15g of agar , 20g glucose, stir to make it fully dissolved, pack it in a conical flask, sterilize at 121 ℃ for 20 minutes, and cool it for later use.
[0025] The indoor activity was measured by the mycelial growth rate method.
[0026] (1) Activation of strains: Plant pathogenic bacte...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Determination of indoor activity of hibiscus bark acetic acid and active component B on tomato Botrytis cinerea
[0040] Table 3 shows the indoor virulence synergistic effect of the mixture of hibiscus bark acetic acid and active component B on tomato Botrytis cinerea.
[0041] Table 3. Indoor virulence synergistic effect of hibiscus bark acetic acid and active component B on tomato Botrytis cinerea
[0042]
[0043]
[0044]
[0045]It can be seen from Table 3 that the mixing mass ratio of hibiscus acetic acid and active component B is 1:1, 1:10, 1:30, 1:50, 1:100, which has obvious synergistic effect on tomato Botrytis cinerea , among them, the SR values were as high as 13.02, 14.44, and 11.00 respectively at the mass ratio of ginseng bark acetic acid and cinnamaldehyde, paeonol, and bakuchiol; , Bakuchiol at a mass ratio of 1:10, the SR values are as high as 11.13, 10.82, 11.58, 10.80, respectively; at the mass ratio of 1:30, the SR values ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com