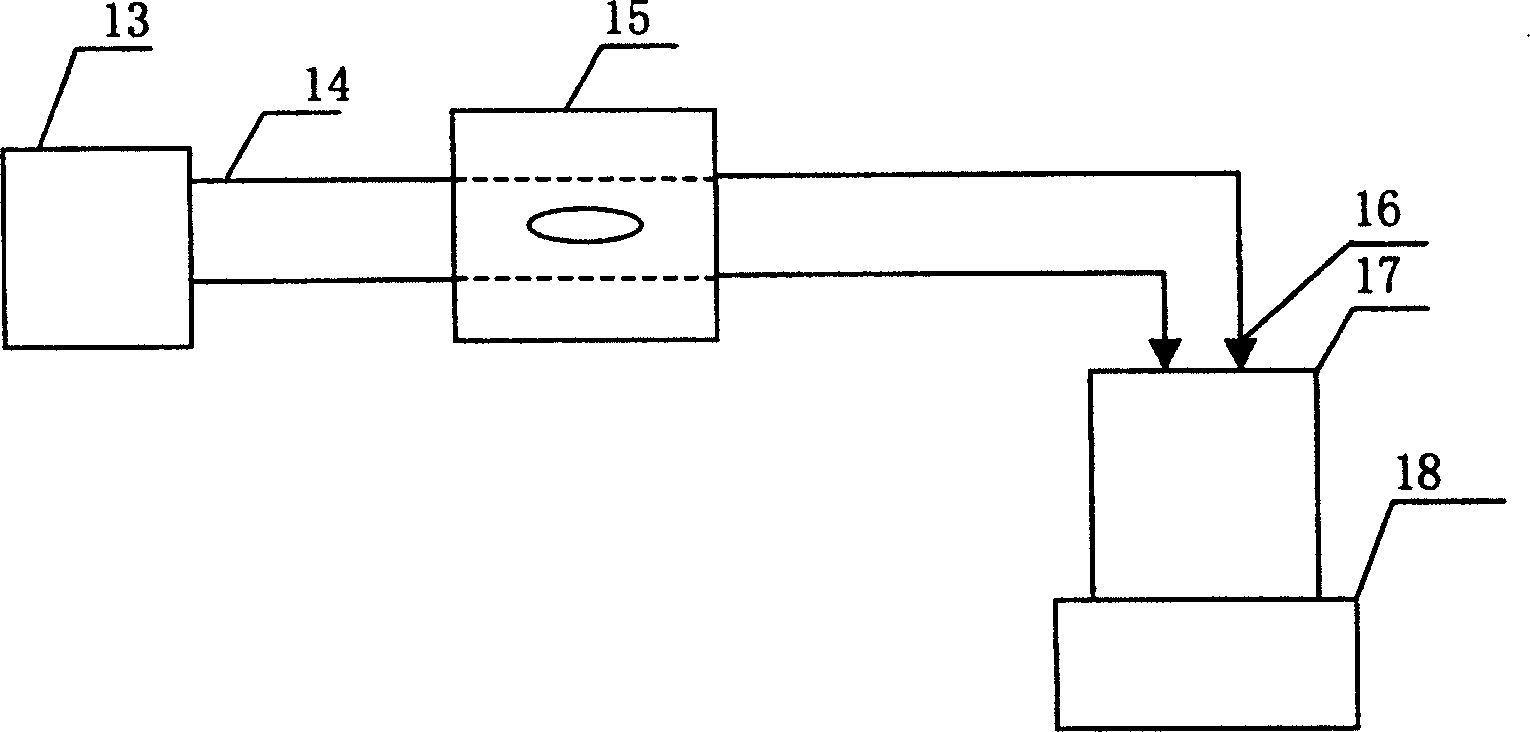
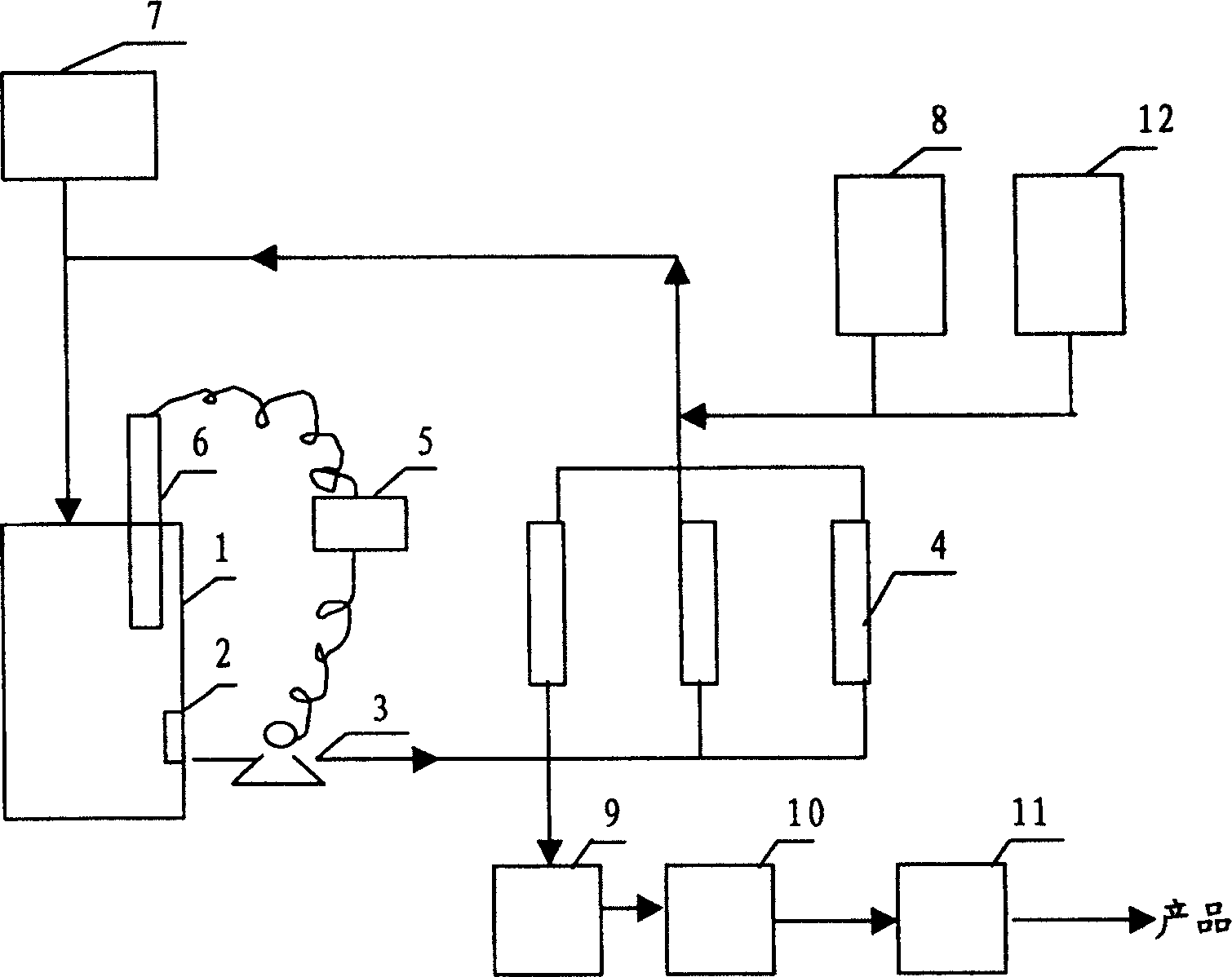
Lactobacillus fixed cell in-situ separating-fermenting lactic-acid production process
A technology of immobilized cells and in-situ separation, applied in the field of lactic acid preparation, can solve the problems that fermentation broth cannot pass continuously and evenly, block the entrance of resin column, and reduce active cells, and achieve long service life, low consumption and fast proliferation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A. Cell immobilization
[0026] (a) Preparation of bacterial suspension: Cultivate lactic acid bacteria to the end of exponential growth, centrifuge for 10 minutes with a centrifugal force of 9000g, discard the supernatant, and disperse the bacteria suspension with an equal weight of sterilized normal saline. Take 22~38.7 grams of the bacterial suspension;
[0027] (b) Preparation of a mixture of embedding agent and bacterial suspension: Dissolve 8-12 grams of polyvinyl alcohol and 2-4 grams of sodium alginate in 100 milliliters of distilled water, heat in a water bath to dissolve them, and sterilize after mixing. After cooling to 40°C, add 22~38.7 grams of sterilized 2% carrageenan distilled water solution to the bacterial suspension of (a). The weight ratio is bacterial suspension: 2% carrageenan solution: 8-12 % Polyvinyl alcohol and 2~4% sodium alginate mixture = 1:1:3~5 mix well;
[0028] (c) Preparation of cross-linking agent: Weigh 2-8 grams of calcium chloride and 1...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Choose polyvinyl alcohol, sodium alginate, and carrageenan to formulate four embedding agents in different proportions according to the percentage concentration in Table 1, which are used to make bead-type immobilized cell granule beads. Use the following method to test the embedded bacteria Bead strength: Place embedded particles of equal size between two glass slides, put weights on the glass slides until the particles are crushed, and use the weight of the weights to characterize the strength of the particles and measure its various indicators. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0040] Preface
[0041] Experiments have proved that using a single calcium alginate or alginic acid as an embedding agent can hardly form beads. When polyvinyl alcohol or sodium alginate is used as an embedding agent to prepare beads, the embedding agent tends to stick together when cross-linked to form a large aggregate. When carrageenan and sodium alginate are used as embedding agen...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Lactic acid was produced according to the process of Example 1, and the immobilized lactic acid bacteria beads of the present invention were repeatedly used three times. Under exactly the same conditions, unimmobilized lactic acid bacteria beads are used for production. The product concentration results are shown in Table 2.
[0044] reaction system
[0045] It can be seen from the test results that, although the product concentration of the immobilized lactic acid bacteria beads of the present invention is slightly lower than that of the unimmobilized bacteria liquid when used for the first time, it can be reused and can maintain reactivity.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bronsted acidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com