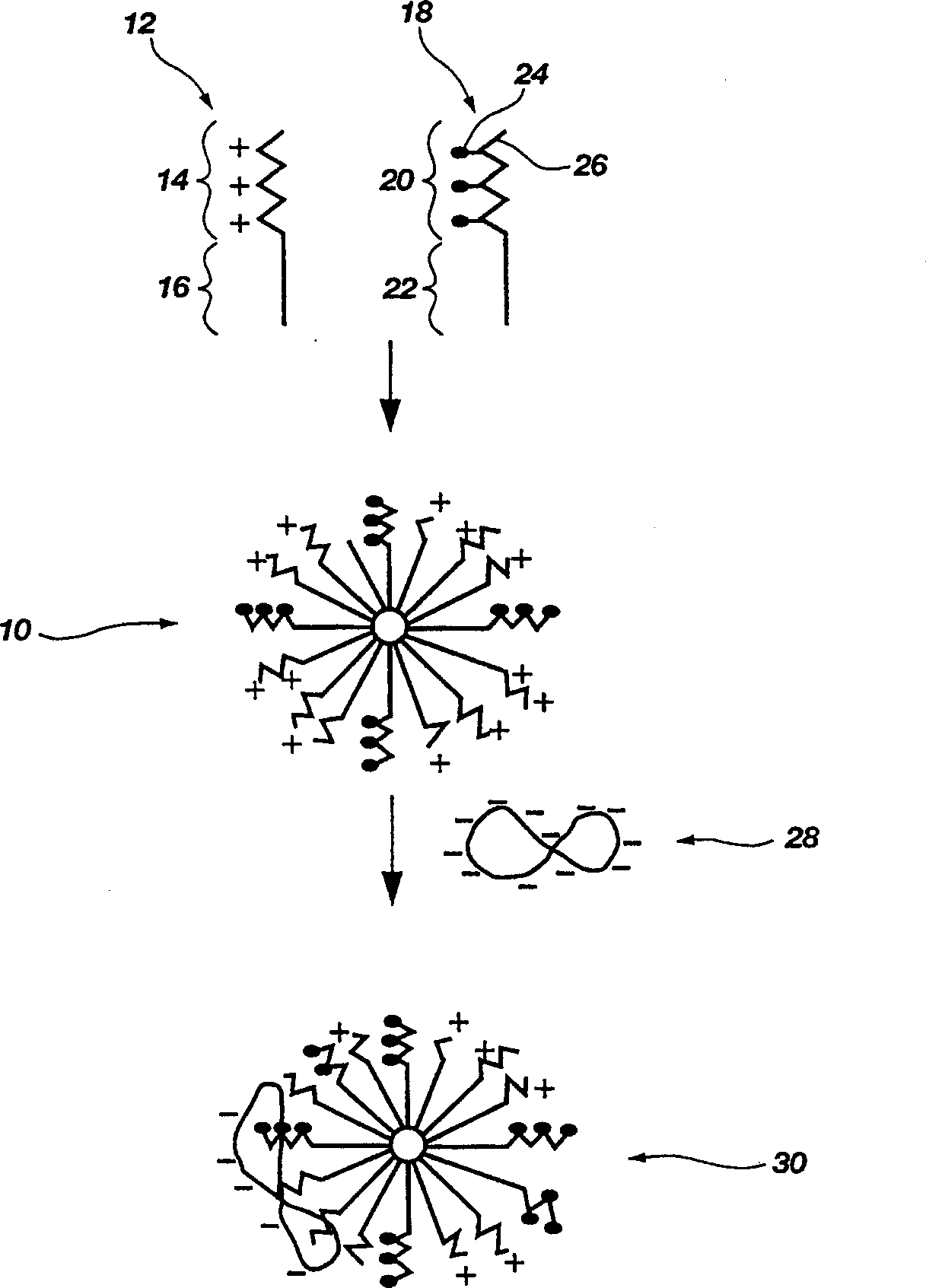
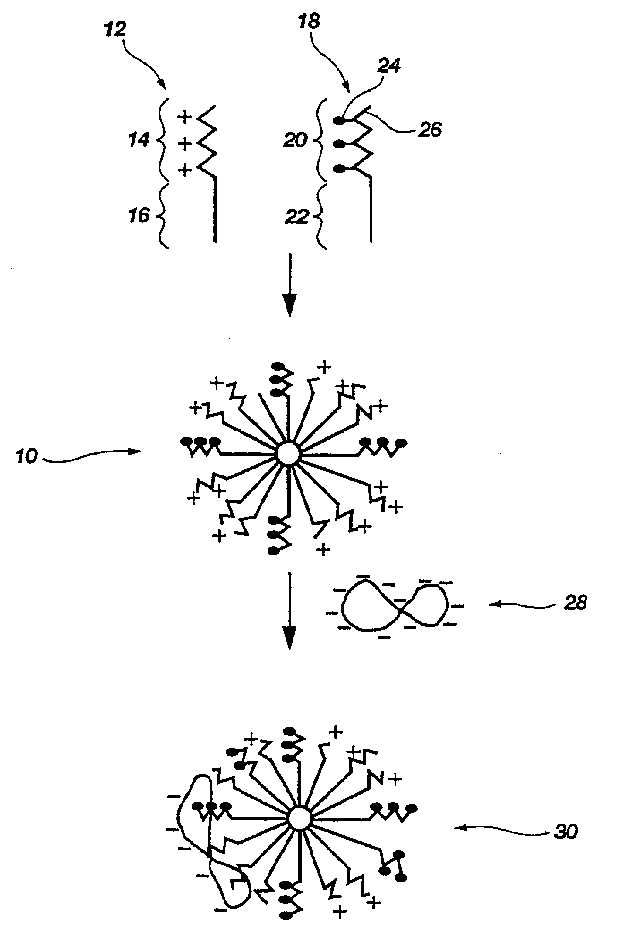
Biodegradable mixed polymeric micelles for gene delivery
A polymer and polyester technology, applied in gene therapy, use of microcapsules, applications, etc., can solve the problems of replicating host immune responses, cytotoxic complaints, and only orientation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This example describes poly(L-lactic acid)-poly(L-serine ester) diblock copolymers and poly(L-lactic acid)-poly(N-lactosyl-L-serine ester) diblock copolymers Process for preparing mixed polymeric micelles.
[0037] Poly(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-serine ester) diblock copolymer. First, according to the steps described in Macromolecules, No. 23, 1990, pages 65-70 (incorporated herein for reference), equimolar amounts of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine and p-toluenesulfonic acid were added in the absence of React in water and benzene to obtain 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate. Put 2.392 grams of N-benzyloxycarbonyl (N-CBZ) serine into a double-necked round-bottomed flask equipped with a stirring bar, a nitrogen pipeline and a rubber septum, under nitrogen protection, add 30 milliliters of tetrahydrofuran with a syringe, and dissolve it dissolve. A solution of 2.94 g of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium 4-toluenesulfonate and diisopropylcarbodiimide in 80 ml of dichl...
Embodiment 2
[0043] This example describes poly(L-lactic acid)-poly(L-serine ester) diblock copolymers and poly(L-lactic acid)-poly(N-lactosyl-L-serine ester) diblock copolymers Process for preparing mixed polymeric micelles.
[0044] The procedure is the same as in Example 1, except that the amine-terminated poly(L-lactic acid) is prepared by ring-opening polymerization of L-lactide initiated by N-trityl ethanolamine. At room temperature, 3 g of trityl chloride was stirred in 20 ml of ethanolamine to obtain N-trityl ethanolamine. After filtration, the product was separated out, and the product was recrystallized in methanol-water (9:1) for purification. The polymerization of L-lactide was initiated with N-trityl ethanolamine in refluxing toluene in the presence of a catalytic amount of stannous octoate. Poly(L-lactic acid) was precipitated with a large excess of diethyl ether. Trityl groups were removed with 0.1 M trifluoroacetic acid in dioxane.
Embodiment 3
[0046] This example describes poly(L-lactic acid)-poly(L-lysine) graft copolymers and poly(L-lactic acid)-poly(N-lactosyl-L-lysine) graft copolymers Process for preparing mixed polymeric micelles.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com