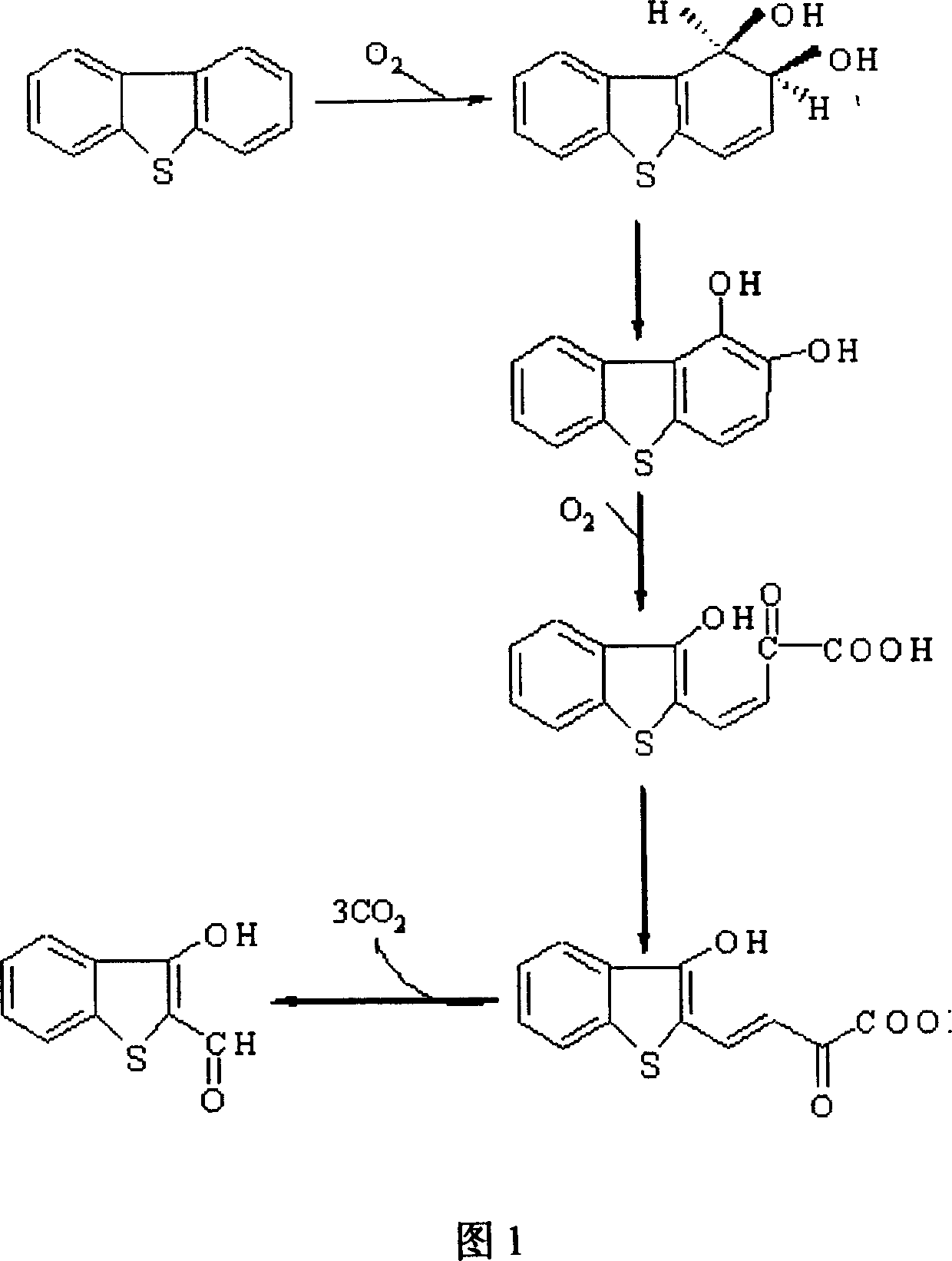
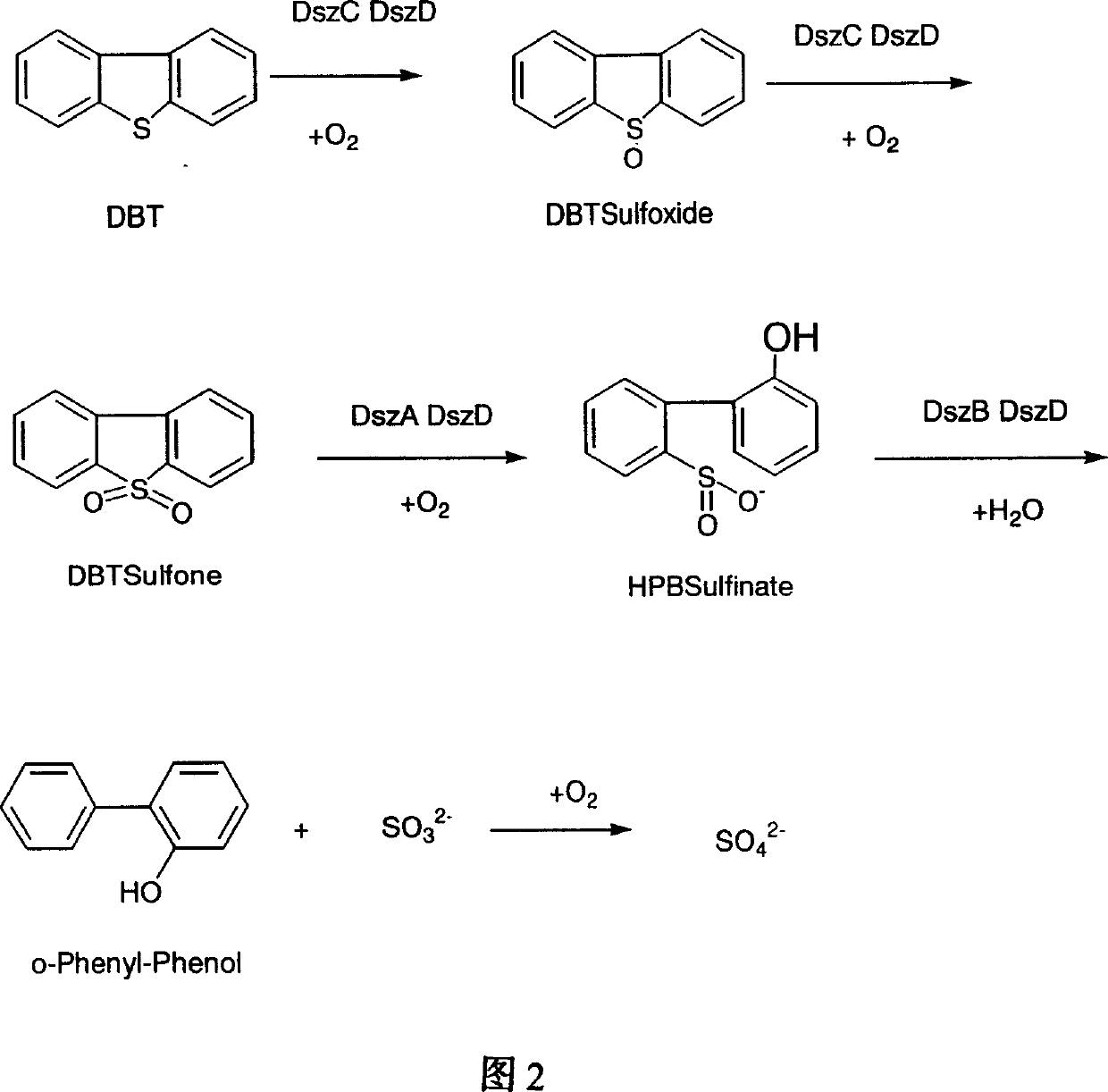
Rhodococcus erythropolis and application in removing sulfur element in surfide thereof
A technology of Rhodococcus erythropolis and compound, applied in application, bacteria, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problems of no ownership of fungi and impossible industrial production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0042] Pick the LSSE8-1 strain cultured on the nutrient slant and add it to 25 ml of basal medium. The composition of the medium: deionized water 1000 ml, KH 2 PO 4 2.44 g; Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 14.03 g; NH 4 Cl2.00g; MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.36 g; CaCl 2 2H 2 O 0.001 g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O 0.001 g MnCl 2 4H 2 O 0.004 g; Glucose 10 g, Na 2 SO 4 1mmol / L. After culturing at 30°C and 150 rpm for 24-48 hours, it was added to 500 ml of basal medium, and after 48-72 hours, it was centrifuged to obtain bacterial cells. Place the bacterial cells in 50 ml of physiological saline containing 1 mmol / L DBT, mix on a shaker for 2-4 hours, and centrifuge to obtain the bacterial cells again. Example 3: Obtaining LSSE8-1 Active Stem Cells
Embodiment 3
[0043] Pick the LSSE8-1 strain cultured on the nutrient slant and add it to 25 ml of basal medium. The composition of the medium: deionized water 1000 ml, KH 2 PO 4 2.44 g; Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 14.03 g; NH 4 Cl2.00g; MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.36 g; CaCl 2 2H 2 O 0.001 g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O 0.001 g MnCl 24H 2 O 0.004 g; Glucose 10 g, Na 2 SO 4 1mmol / L. After culturing at 30°C and 150 rpm for 24-48 hours, it was added to 500 ml of basal medium, and after 48-72 hours, it was centrifuged to obtain bacterial cells. Place the bacteria in 50 ml of physiological saline containing 0.1 mmol / L DBT, mix on a shaker for 2-4 hours, and centrifuge to obtain the bacteria again. Freeze and vacuum dry to obtain active stem cells. Example 4: Strain LSSE8-1 removes sulfur in the simulated system DBT.
Embodiment 4
[0044] Add DBT to dodecane to make the concentration reach 0.2mmol / L. Pick the LSSE8-1 strain cultured on the nutrient slant and add it to 25 ml of basal medium. The composition of the medium: deionized water 1000 ml, KH 2 PO 4 2.44 g; Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 14.03 g; NH 4 Cl 2.00 g; MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.36 g; CaCl 2 2H 2 O 0.001 g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O 0.001 g MnCl 2 4H 2 O 0.004 g; glucose 10 g, DBT concentration 1 mmol / L. After culturing at 30° C. and 150 rpm for 24-48 hours, the simulated oil phase and bacterial culture were mixed at an oil-to-water ratio of 1:3. After culturing at 30° C. and 150 rpm for 24-48 hours, the sulfur is completely removed, and the product is HBP (as shown in FIG. 5 ). Example 5: Bacterial strain LSSE8-1 is used for deep desulfurization of diesel oil after hydrodesulfurization
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com