Concentrated fluoroploymer dispersions
A dispersion, polymer technology, applied in polyether coatings, layered products, synthetic resin layered products, etc., can solve the problem of not realizing the important role of surfactant shear stability, and achieve high shear The effect of stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0087] Unless otherwise stated, solution concentrations are expressed in % by weight based on the total weight of solute and solvent water.
[0088] Preparation of polymer resin (core / shell)
[0089] A polymerization tank having a horizontal stirrer and a water capacity of 240 parts by weight was charged with 123.5 parts of demineralized water and 5.82 parts of paraffin wax supplied by Exxon. The contents of the polymerization kettle were heated to 65°C, and the polymerization kettle was evacuated and purged with tetrafluoroethylene (TFE). Into the evacuated polymerization kettle was charged 3.24 parts of a solution containing 0.0616 parts of ammonium perfluorooctanoate. The contents of the polymerization kettle were stirred at 50 rpm. The temperature was raised to 90°C. TFE was then added until the pressure was 2.72 MPa. Then 1.29 parts of fresh initiator solution of 0.01 parts of disuccinyl peroxide and 0.00005 parts of ammonium persulfate (APS) per part of water was add...
Embodiment 1
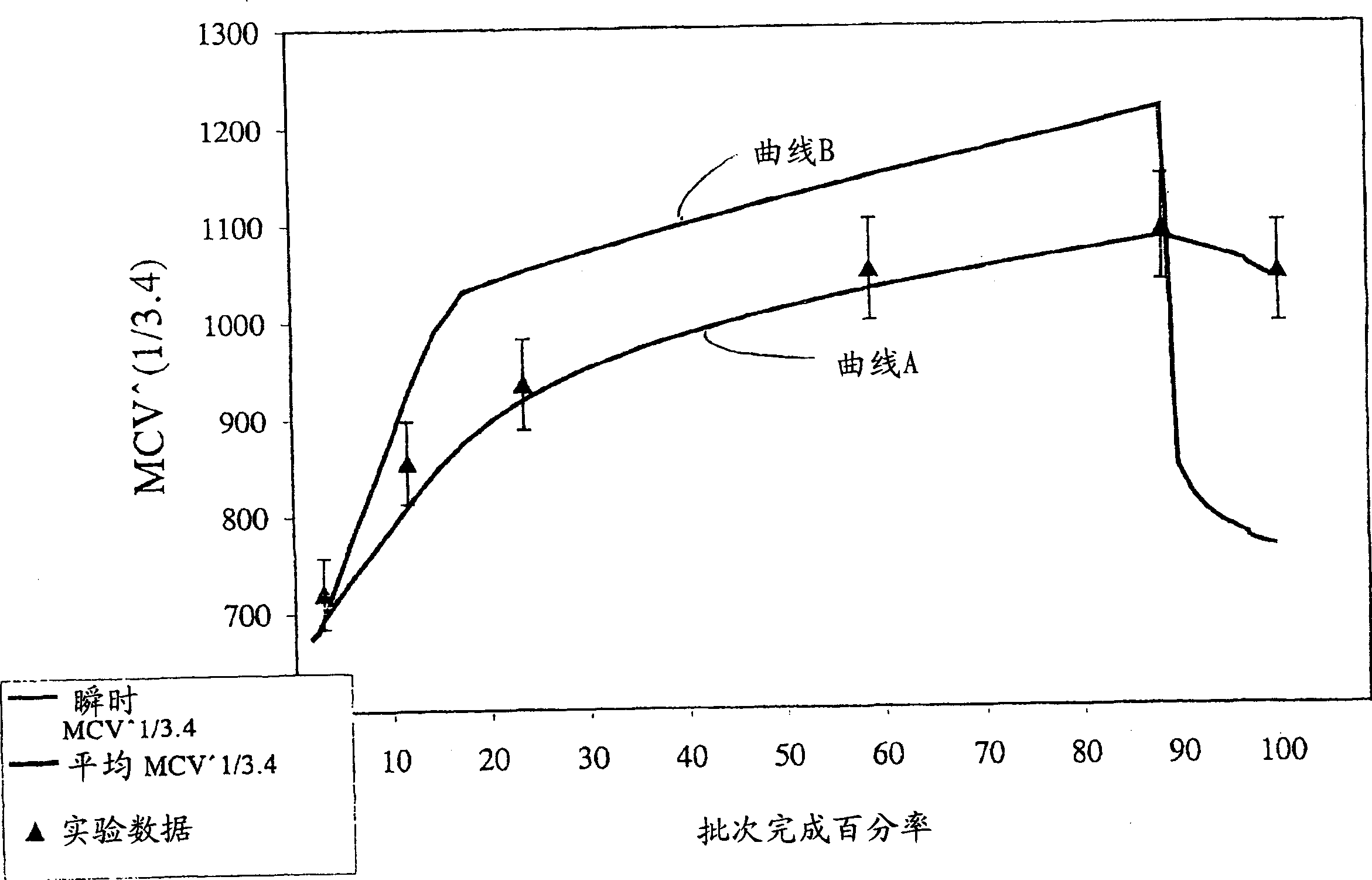
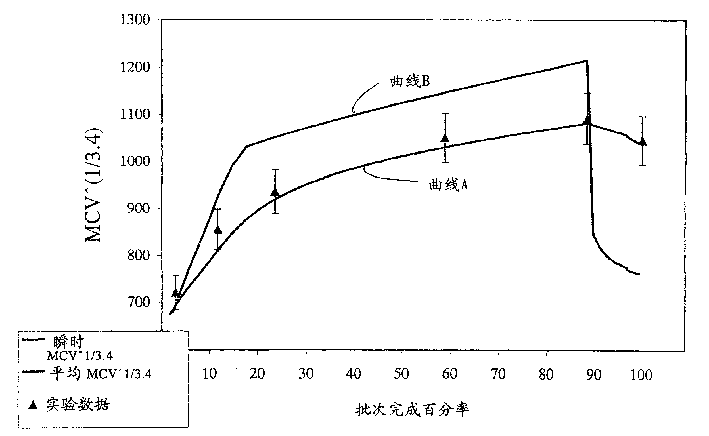
[0097] The base dispersion was concentrated hot using Leocol SC-90 available from Lion Corporation, Japan. The surfactant is a branched chain ethoxylate, represented by the general formula C 12 h 25 O(C 2 h 4 O) 9 H and C 14 h 29 O(C 2 h 4 O) 9 H indicates that it is formed from secondary alcohols. The surfactant is liquid at room temperature with a viscosity of 65 cps. After adjusting the solids to 60% and the surfactant to 6% on PTFE solids, the gel time was determined to be 850 seconds.
Embodiment 2
[0099] The base dispersion was thermally concentrated using Leocol TD-90 available from Lion Corporation, Japan. The surfactant is a branched chain ethoxylate, represented by the general formula C 13 h 27 O(C 2 h 4 O) 9 H indicates that it is formed from branched secondary alcohols. Pure surfactants are solids at room temperature. After adjusting the solids to 60% and the surfactant to 6% on PTFE solids, the gel time was determined to be 1241 seconds.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| cloud point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cloud point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| gel time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com