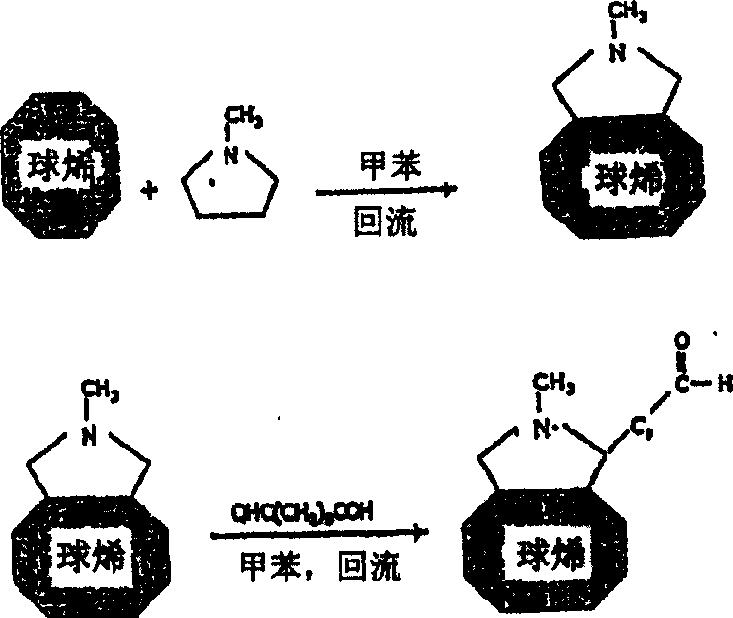
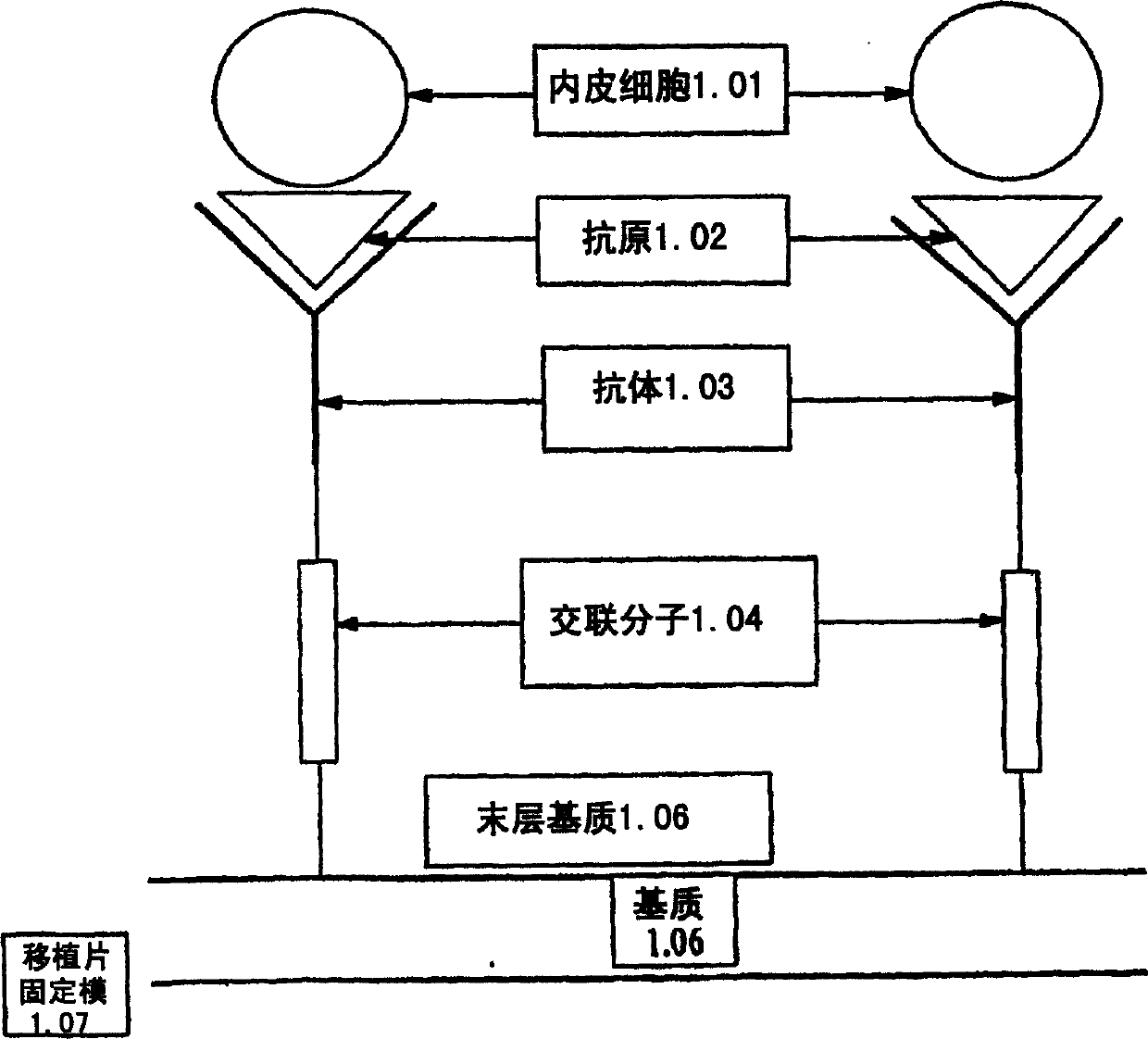
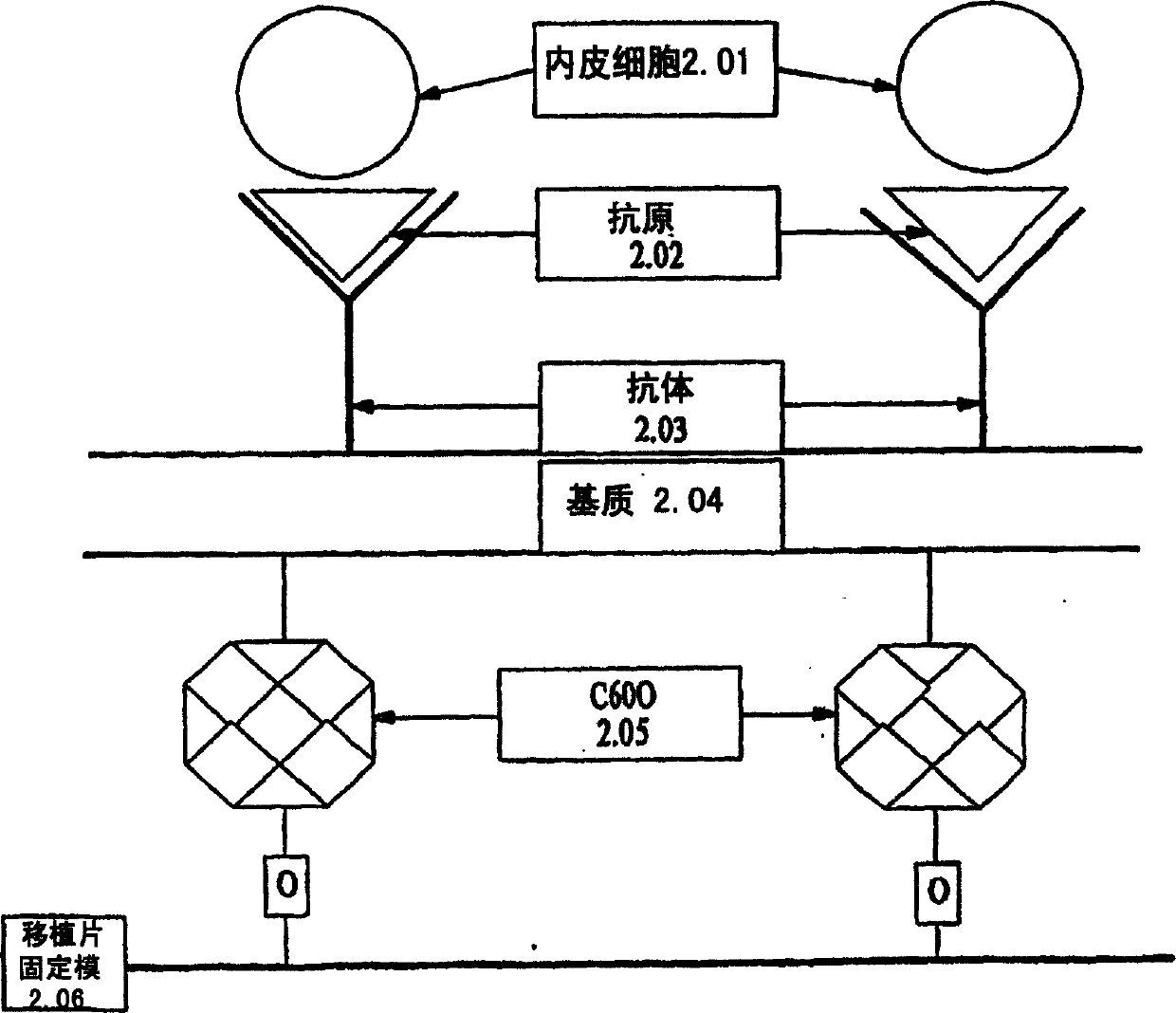
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence and differentiation
A medical device and endothelial cell technology, which can be applied to devices of human tubular structures, medical preparations containing active ingredients, organic active ingredients, etc., and can solve the problems of cells losing endothelial cell function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0161] Phenotypic characterization of endothelial progenitor cells
[0162] A method for the isolation of putative endothelial cells for angiogenesis was recently described (Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A et al. science , 1997; 275:964-967), endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) can be isolated by CD34+ magnetic bead separation method (Dynal Biotech) or enriched medium separation method. The method is generally as follows: obtain peripheral venous blood from healthy male volunteers, and separate the mononuclear cell composition by density gradient centrifugation. The cell material was plated in culture medium on culture slides (Bcton Dickinson) coated with human fibronectin. The medium was EC basal medium-2 (EBM-2) (Clonetics) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum, human vascular endothelial growth factor-A, human fibroblast growth factor-2, human epidermal growth factor , insulin-like growth factor-1 and ascorbic acid, the medium was changed every 48 hours, and the endot...
Embodiment 2
[0166] Capture of Inner Cells by Stainless Steel Disc Coated with Anti-CD34 Antibody
[0167] Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) (American Culture Collection) were grown in endothelial cell growth medium throughout the experiments. Cells were grown on samples coated with CMDX and gelatin with or without bound antibody on the surface, or on bare stainless steel (SST) samples. After incubation, the medium was removed and the samples were washed twice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Cells were fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 minutes, and washed three times with phosphate buffered saline for 10 minutes each to ensure that the fixative was completely removed. Each sample must be incubated with blocking solution for 30 minutes at room temperature to block any non-specific blocking phenomena. After the samples were washed once with phosphate-buffered saline, they were exposed to VEGF receptor-2 antibody diluted 1:100 and incubated overnight. The samples...
Embodiment 3
[0172] Staining Effects of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2 and Tie-2 on Progenitor Endothelial Cells
[0173] Progenitor cells were isolated from human blood as described in Example 1 and cultured in growth medium in vitro for 24 hours, 7 days, and 3 weeks. After incubation, the medium was removed and samples were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline. The cells were then fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 minutes, and then washed with phosphate buffered saline three times, 10 minutes each time. To ensure removal of all fixative components. Each sample was incubated with 440 microliters of goat (for VEGF receptor-2) or equine (for Tie-2) blocking solution for 30 minutes at room temperature. to block all non-specific binding. The samples were washed once with phosphate-buffered saline, then vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor-2 or Tie-2 antibody diluted 1:100 with blocking solution was added, and the samples were incubated overnight....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com