Process for preparing big aperture active carbon fibers
A technology of activated carbon fiber and large pore size, applied in the chemical characteristics of fibers, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of no adsorption effect, poor adsorption effect, etc., and achieve the effect of appropriate strength and expansion of the application range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
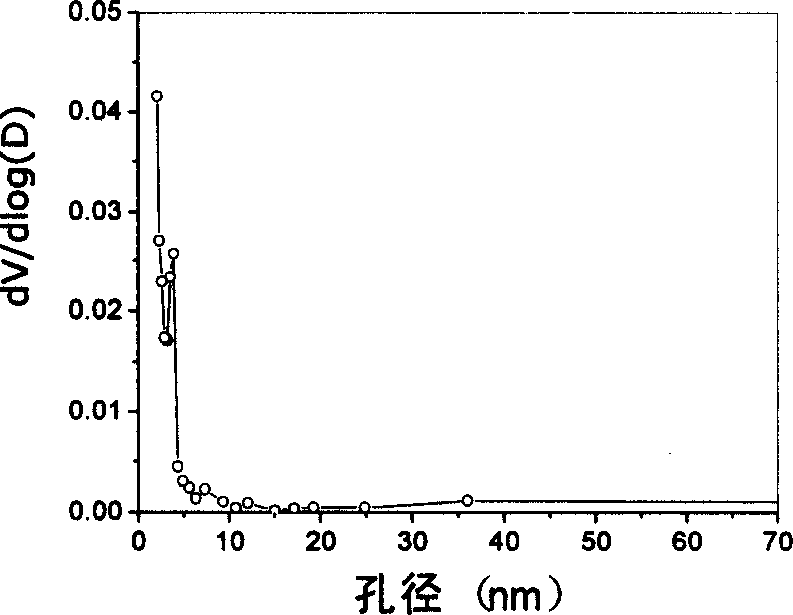
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Immerse the viscose fiber in an aqueous solution containing 1% sodium sulfate, 5% ammonium hydrogen phosphate, and 0.2% ferric chloride for 15 minutes, take it out, and squeeze dry to remove excess solution. After the fiber is dried at 90°C, it is placed in an electric furnace, heated and oxidized in the air below 250°C for 110 minutes, gradually heated and carbonized in nitrogen at 300°C-900°C for 150 minutes, and activated in water vapor at 1050°C for 35 minutes. Then, it was naturally cooled to room temperature in nitrogen, and fully washed with dilute hydrochloric acid and water to obtain the above-mentioned macroporous activated carbon fiber.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Immerse the viscose fiber in an aqueous solution containing 2% sodium sulfate, 3.5% ammonium hydrogen phosphate, and 1.5% ferric chloride for 35 minutes, take it out, and squeeze dry to remove excess solution. After the fiber is dried at 120°C, it is placed in an electric furnace, heated and oxidized in the air at 240°C for 80 minutes, gradually heated and carbonized in nitrogen at 280°C-850°C for 100 minutes, and activated step by step in water vapor at 850°C for 80 minutes. Then, it was naturally cooled to room temperature in nitrogen, and fully washed with dilute hydrochloric acid and water to obtain the above-mentioned macroporous activated carbon fiber.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Immerse the viscose fiber in an aqueous solution containing 3% sodium sulfate, 1.5% ammonium hydrogen phosphate, and 2.5% ferric chloride for 15 minutes, take it out, and squeeze dry to remove excess solution. After the fiber is dried at 150°C, it is placed in an electric furnace, heated and oxidized in air below 260°C for 50 minutes, gradually heated and carbonized in nitrogen below 1000°C for 70 minutes, and activated step by step in water vapor at 1000°C for 40 minutes. Then, it was naturally cooled to room temperature in nitrogen, and fully washed with dilute hydrochloric acid and water to obtain the above-mentioned macroporous activated carbon fiber.
[0025] In Examples 4 to 6, 3.5% ammonium hydrogen phosphate and 1%, 1.5%, and 2.5% potassium sulfate were respectively added to the catalyst aqueous solution of viscose fiber, and the rest of the process conditions were unchanged to obtain the above-mentioned activated carbon fiber with large aperture.
[0026] Appli...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com