Method for evaluating polymer for liquid crystal directional agent and the directional agent thereof
A liquid crystal orientation and evaluation method technology, which is applied to liquid crystal materials, chemical instruments and methods, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of poor coating, narrowing the range of material selection, and increasing the manufacturing cost of liquid crystal panels, so as to increase production and improve pinpoints. Pore defects, easy screening effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0100] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically by way of examples, but the present invention is not limited to these examples. The method of each measurement and evaluation of an Example and a comparative example was performed as follows.
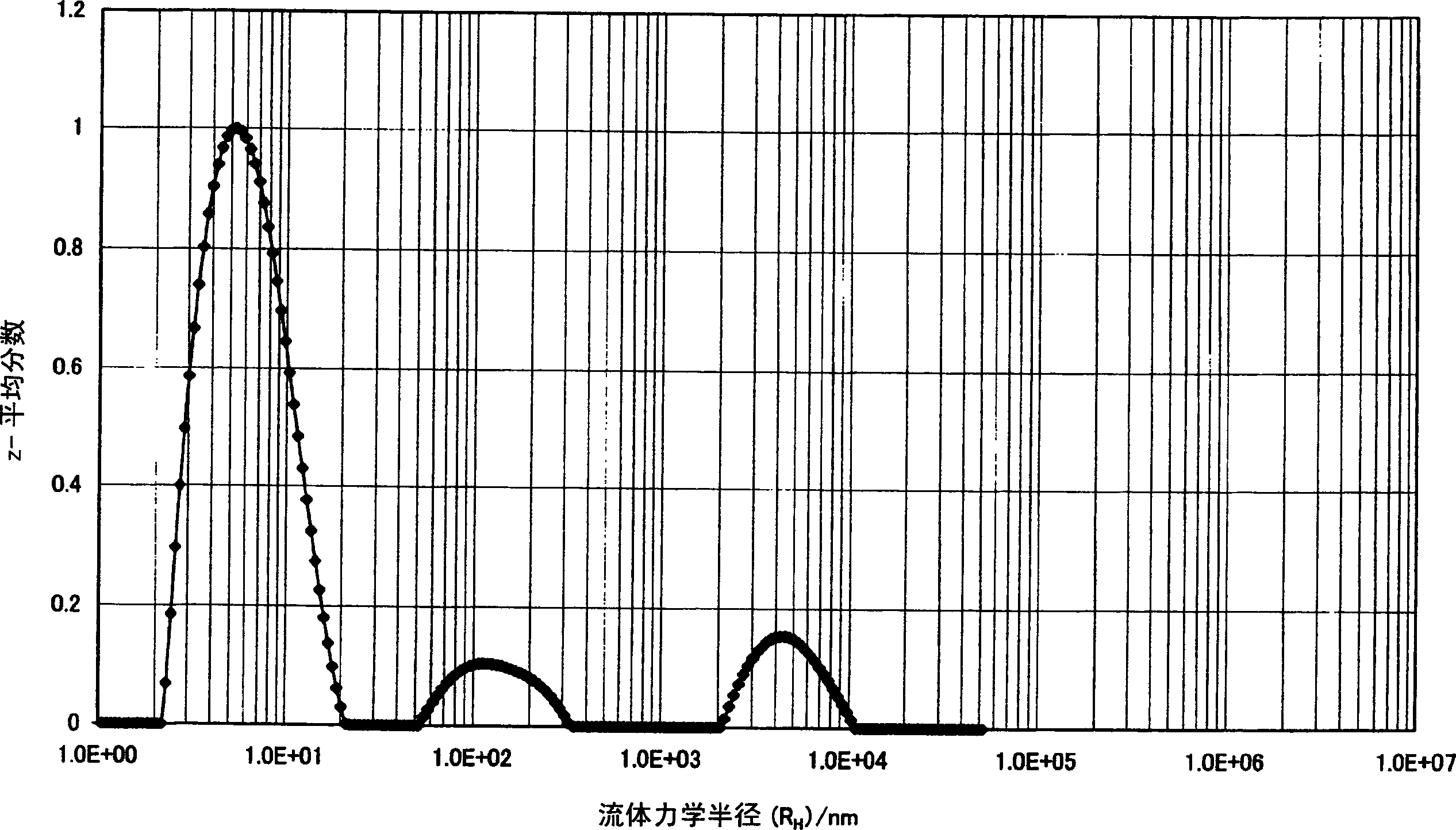
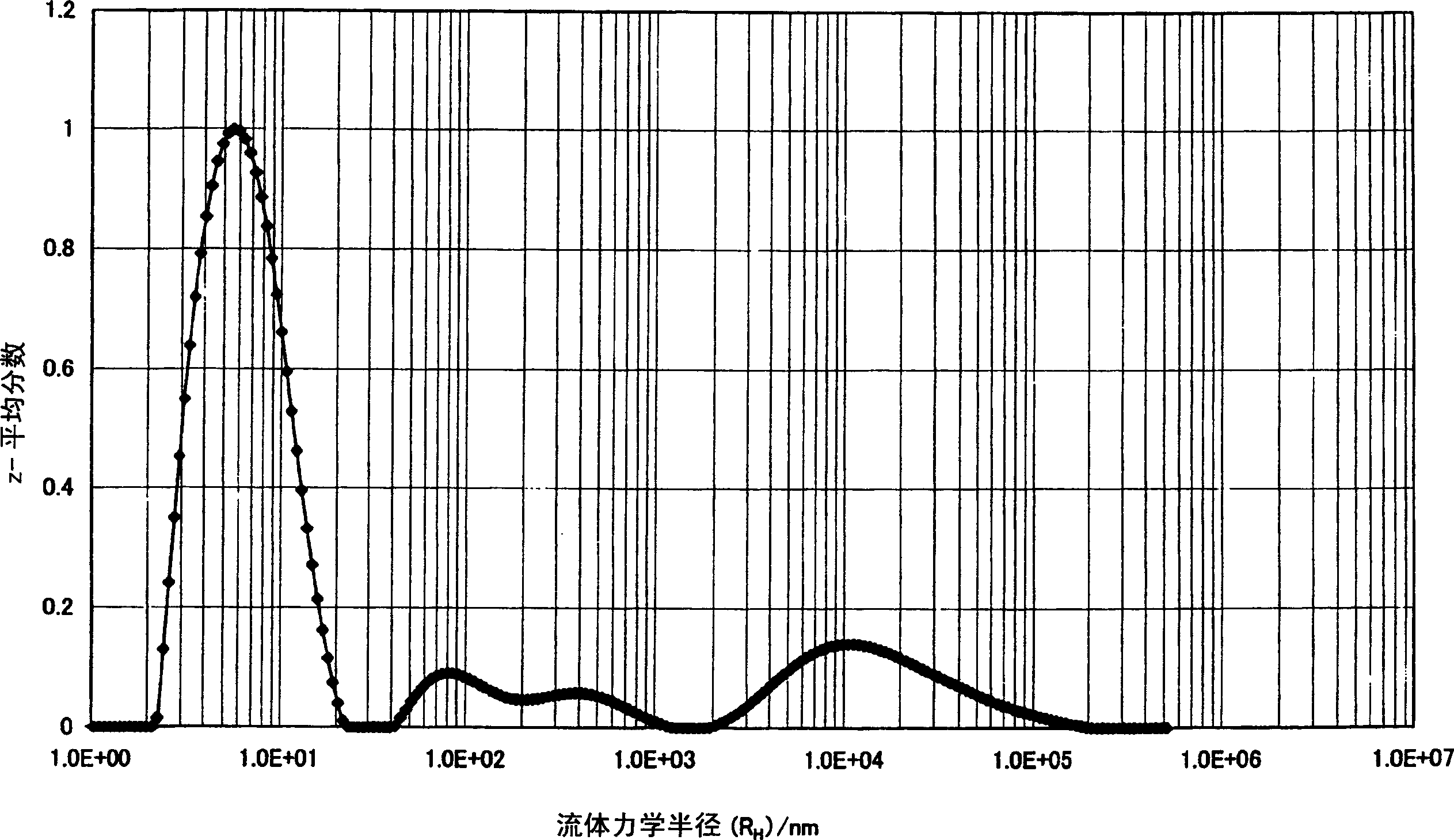
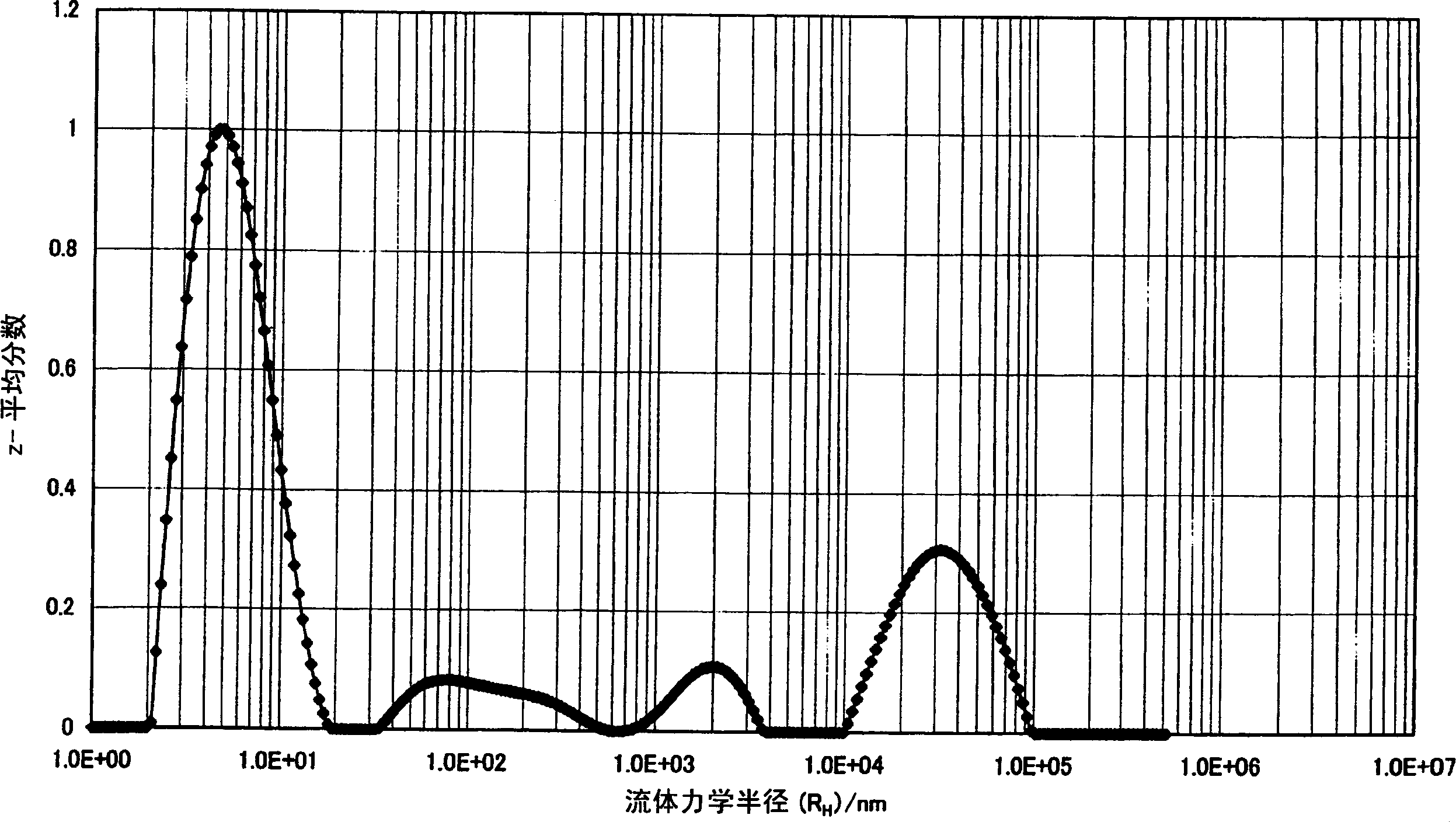
[0101] [The hydrodynamic radius of the condensate (R H )]
[0102] The polymers obtained in the following Synthesis Examples 1 to 2 and Comparative Synthesis Example 1 were formulated into a solution at a predetermined concentration of 7.3% by weight, and then sufficiently stirred to obtain a uniform solution. The mixing ratio of the solvent used here was γ-butyrolactone / N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone=81.3 / 11.4 (% by weight). This resin solution was filtered through a filter (for polar solvents) with a pore diameter of 0.45 μm, washed in a methanol reflux cleaner for 2 hours or more, and placed in a quartz glass cell with a diameter of 20 mm. Since solution viscosity is temperature dependent, dynamic light scatteri...
Synthetic example 1
[0108] 219.69 g (0.98 mol) of 2,3,5-tricarboxycyclopentyl acetic acid dianhydride as tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 106.52 g (0.985 mol) of p-phenylene diamine as diamine compound, and the above formula 7.81 g (0.015 mol) of the diamine represented by (9) was dissolved in 4500 g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, and it was made to react at 60 degreeC for 6 hours. Next, the reaction solution was added to a large excess of methanol to precipitate the reaction product. Then, it wash|cleaned with methanol, and dried under reduced pressure at 40 degreeC for 15 hours, and obtained 280 g of polyamic acids with the shear viscosity of 13 mPa*s of 4 weight% of solid content. 30 g of the obtained polyamic acid was dissolved in 570 g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, 23.4 g of pyridine and 18.1 g of acetic anhydride were added, dehydration and ring closure were carried out at 110° C. for 4 hours, and precipitation, cleaning, and reduction were carried out in the same manner as above. 17.8 g of polyimide...
Synthetic example 2
[0110] 221.93 g (0.99 mol) of 2,3,5-tricarboxycyclopentyl acetic acid dianhydride as tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 106.52 g (0.985 mol) of p-phenylenediamine as diamine compound, and the above formula 7.81 g (0.015 mol) of the diamine represented by (9) was dissolved in 4500 g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, and it was made to react at 60 degreeC for 6 hours. Next, the reaction solution was added to a large excess of methanol to precipitate the reaction product. Then, it wash|cleaned with methanol, and dried under reduced pressure at 40 degreeC for 15 hours, and obtained 290 g of the polyamic acids of 4 weight% of solid content and the shear viscosity of 34 mPa*s. 30 g of the obtained polyamic acid was dissolved in 570 g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, 23.4 g of pyridine and 18.1 g of acetic anhydride were added, dehydration and ring closure were carried out at 110° C. for 4 hours, and precipitation, cleaning, and reduction were carried out in the same manner as above. 18.3 g of polyimi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com