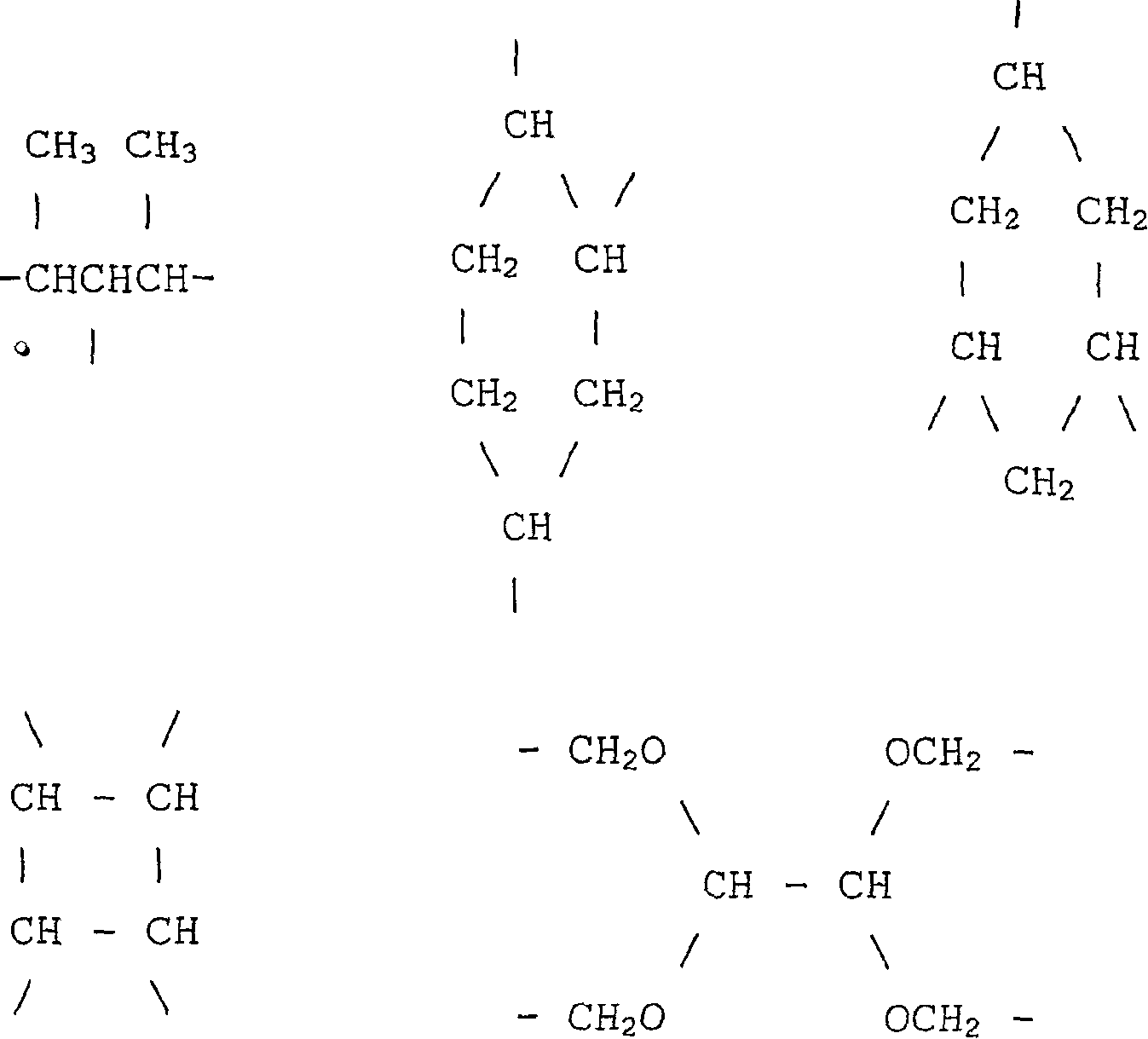
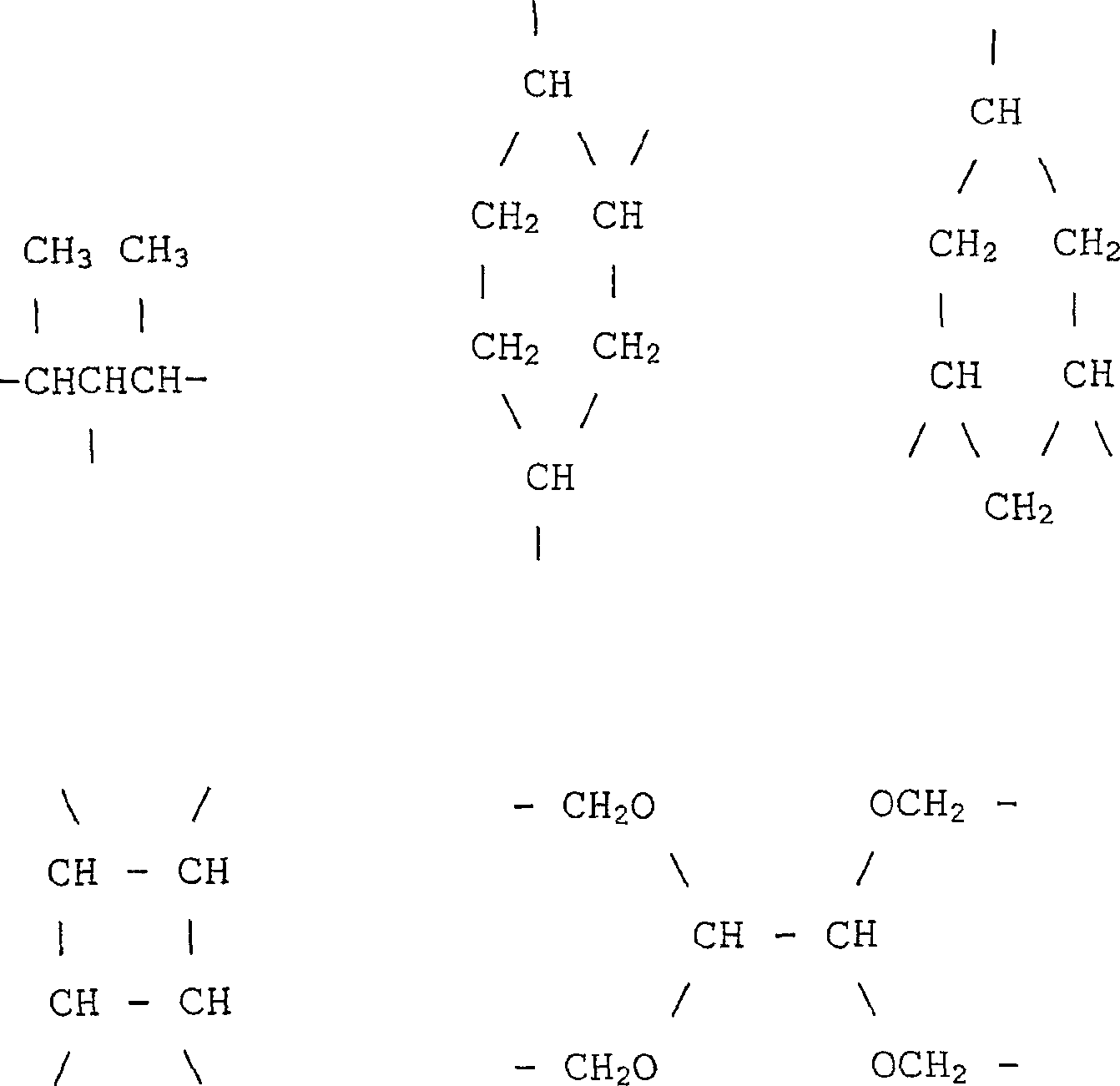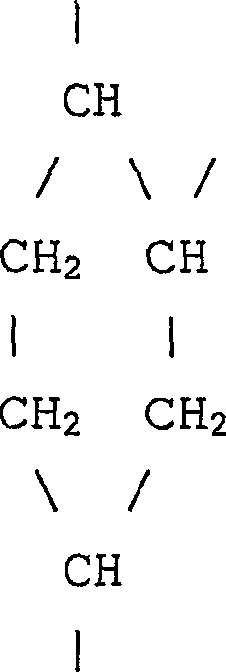Silicone polymerisates
A polymer, silicone technology, applied in the direction of graft polymer adhesives, adhesive types, hair care, etc., can solve the problems of large polymers, insoluble components of undesired gel particles, non-uniformity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 4
[0118] (Copolymer like Comparative Example 25, with component b))
[0119] 2.60 kg of water, 298.04 g of W 25 / 140 (polyvinyl alcohol; 10% strength solution), 212.88 kg of Genapol X 150 (40% strength in water), 157.9 g of Mersolat (30% strength in water), 68.12 g of vinylsulfonic acid Sodium (25% concentration), 851.53 grams of vinyl acetate, 170.31 grams of PDMS mixture and 851.53 grams of VeoVa 10 were placed in a 19 liter autoclave. The acidity value was adjusted to 5 with the aid of 10% strength formic acid. In addition, 9.7 ml of Trilon B (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; 2% strength in water) and 30.6 ml of ferric ammonium sulfate (1% strength in water) were added. The autoclave was heated to 70°C and pressurized with 14 bar of ethylene. When the reactor reached thermal equilibrium, 68 g / h of a 5.41% strength ammonium peroxosulfate solution (APS solution) and 85 g / h of a 4.16% strength sodium sulfite solution were immediately fed. After 25 minutes, a feed consi...
Embodiment 5
[0125] (similar to Example 4, without Mersolat)
[0126] 2.16 kg of water, 955.94 g of W 25 / 140 (polyvinyl alcohol; 10% strength solution), 84.60 g of component b), 156.87 g of Mersolat (30% strength in water), 67.68 g of sodium vinylsulfonate (25% strength) , 845.96 grams of vinyl acetate, 169.19 grams of PDMS mixture and 845.96 grams of VeoVa 10 were placed in a 19 liter autoclave. The acidity value was adjusted to 5 with the aid of 10% strength formic acid. In addition, 9.7 ml of Trilon B (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; 2% strength in water) and 30.6 ml of ferric ammonium sulfate (1% strength in water) were added. The autoclave was heated to 70°C and pressurized with 14 bar of ethylene. When the reactor reached thermal equilibrium, 68 g / h of a 5.41% strength ammonium peroxosulfate solution (APS solution) and 85 g / h of a 4.16% strength sodium sulfite solution were immediately fed. After 25 minutes, a feed consisting of 5.75 kg of vinyl acetate, 820.58 g of V...
Embodiment 6
[0132] The steps of Example 5 were repeated without adding polyvinyl alcohol.
[0133] Dispersion Analysis Results: See Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com