Substrate for labo-on-a-chip
A lab-on-a-chip and substrate technology, which can be used in material inspection products, measuring devices, and material analysis through electromagnetic means, and can solve problems such as weak binding between polyalkylene glycol and substrates, and inability to separate and swim proteins.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
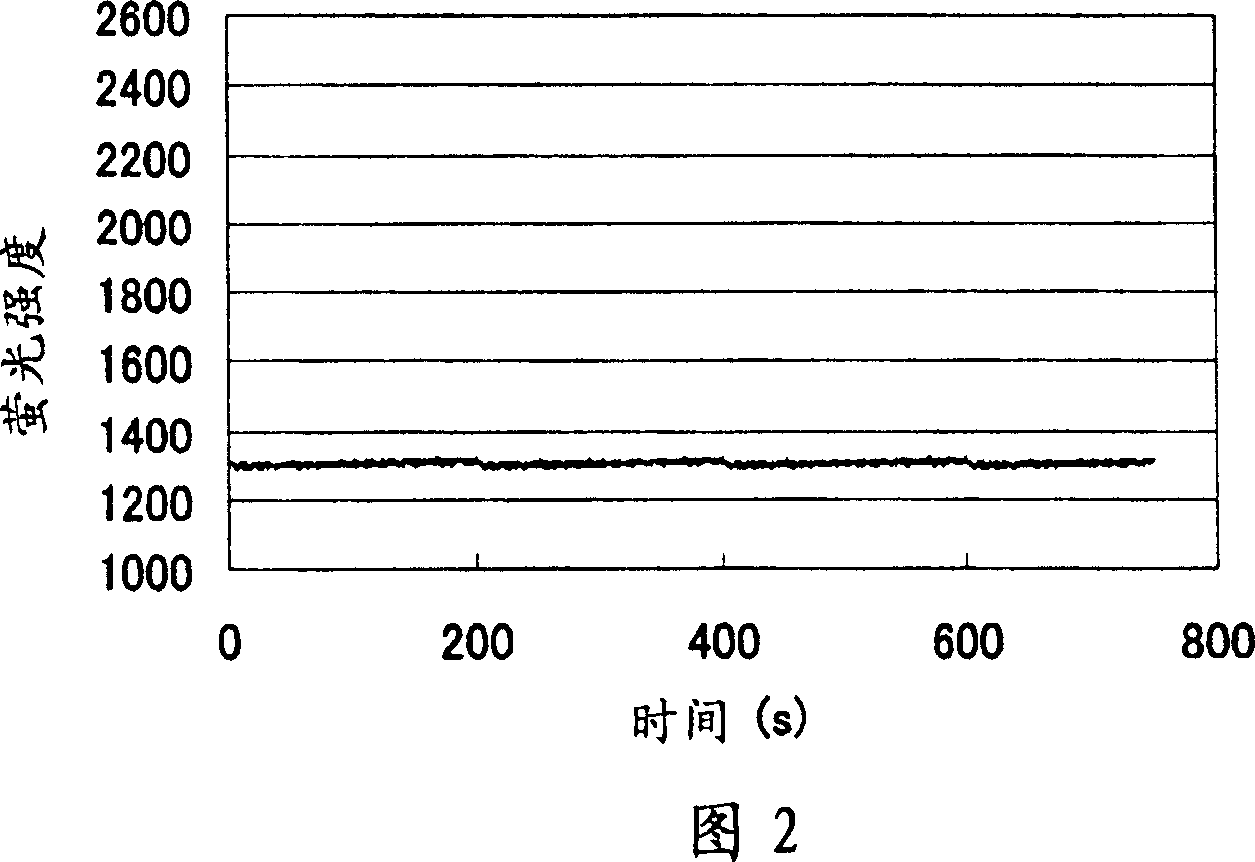
[0088] A polymethyl methacrylate substrate having a size of 20×60 mm and a thickness of 0.2 mm was immersed in an aqueous polyethylene glycol solution having a molecular weight of 500,000 and 2,000 ppm. The dipped polymethyl methacrylate plate was sealed and irradiated with 2.5 kGy of gamma rays to perform grafting. The substrate irradiated with γ-rays was dried, and attached to a fluorescent plate having holes in the light-transmitting portion. On the attached fluorescent plate, an aqueous solution of FITC-labeled BSA protein and IgG protein diluted to 10 μg / ml was solidified at room temperature for 10 minutes, and after removing the solution, it was washed with phosphate buffer (PBS) to measure fluorescence. strength.
Embodiment 2
[0100] Microvias of a polymethacrylate substrate having microvias of width 100 μm x depth 60 μm x length 50 cm were filled with aqueous polyethylene glycol solutions with molecular weights of 500,000 and 2,000 ppm, and 2.5 kGy of γ-rays were irradiated to perform grafting. After irradiation, the polyethylene glycol aqueous solution in the microchannel was taken out and washed with purified water. After injecting the cell-free protein synthesis reaction solution from Escherichia coli into the microchannel, place it at 30°C for 1 hour to synthesize chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT), which converts acetyl from Acetyl CoA transfers to the 3'-hydroxyl of chloramphenicol, 26,000 molecular weight enzyme. The CAT protein synthesized in the microchannel was recovered and quantified by ELISA as Example 2.
Embodiment 3
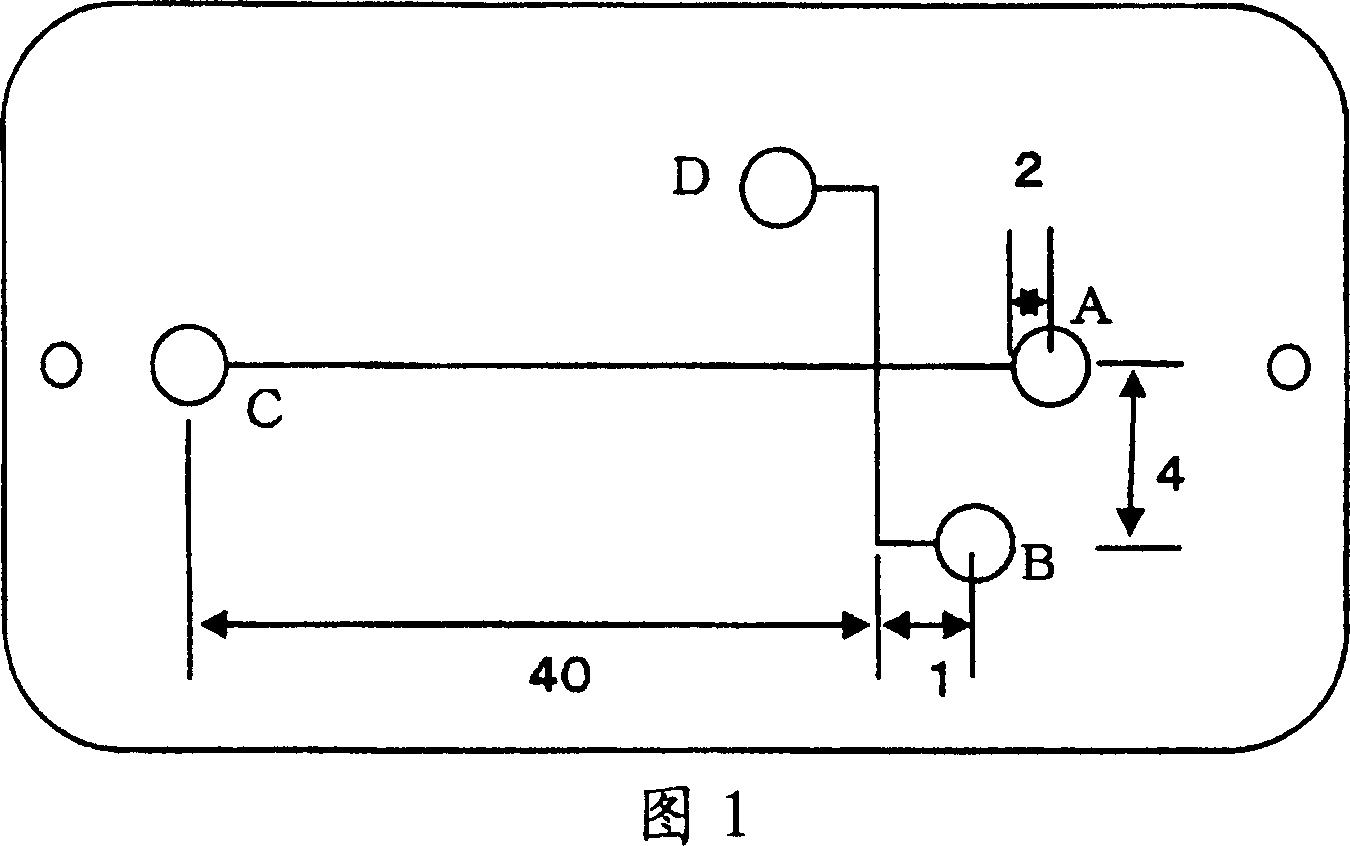
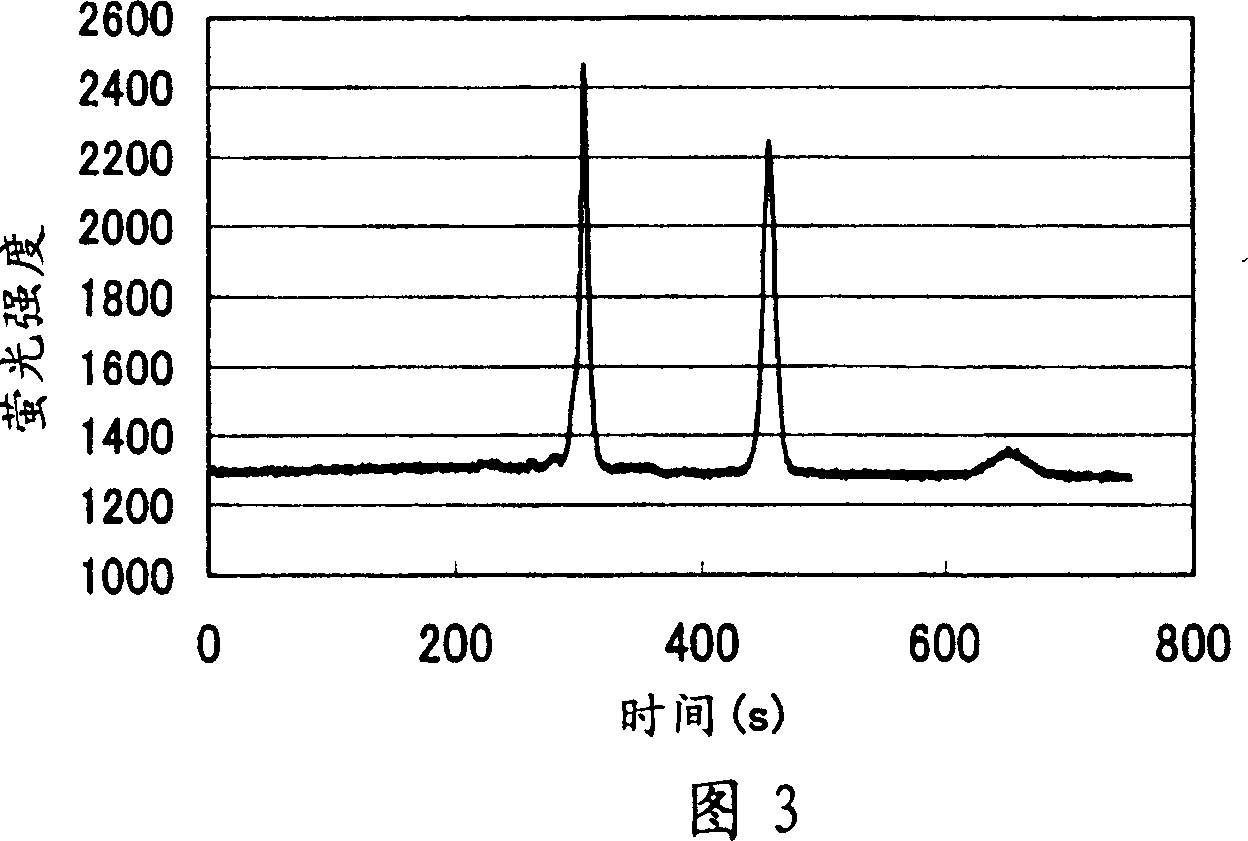
[0108] A chip for electrophoresis made of polymethyl methacrylate and having channels with a diameter of 100 μm was immersed in an aqueous polyethylene glycol solution having a molecular weight of 500,000 and 2,000 ppm. The dipped chip for electrophoresis was sealed and irradiated with 2.5 kGy of γ-rays to perform grafting. Remove the polyethylene glycol in the channel, fill with 5% polyacrylamide (molecular weight 600,000-1,000,000) 0.1M Tris-aspartic acid (pH8) solution, add 5% to parts A, B, and C of Figure 3 Polyacrylamide (molecular weight: 600,000-1,000,000) 0.1M Tris-aspartic acid (pH8) solution, add fluorescently labeled trypsin inhibitor and fluorescently labeled BSA to 0.05MTris-HCl containing 1% SDS in part D ( pH8) solution. Electrodes were inserted into parts A, B, C and D of the electrophoresis chip filled with polyacrylamide and protein solution, and a voltage of 350 V was applied to part B for 1 minute. Afterwards, 500V was applied to C, and 150V was applied ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com