System and method for cryogenic optoelectronic data link
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
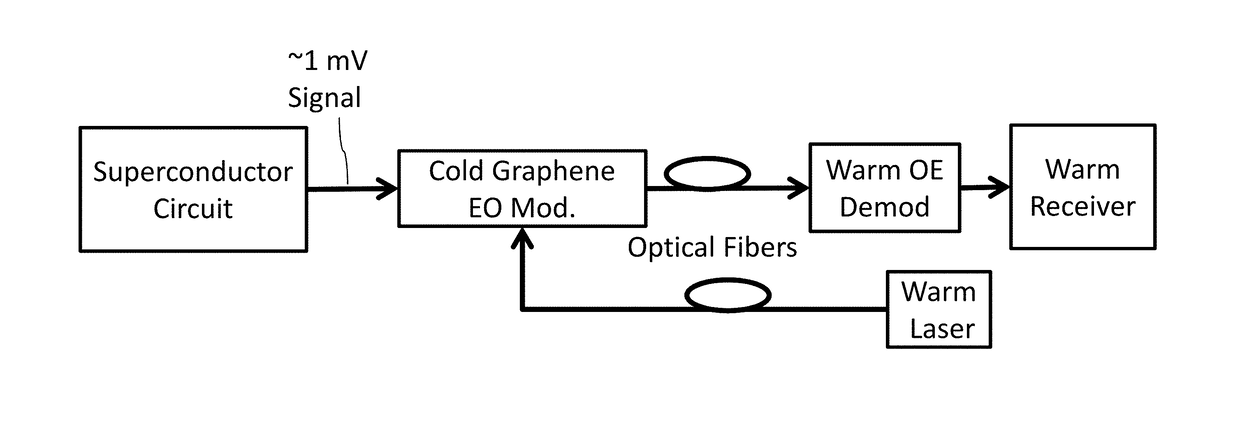
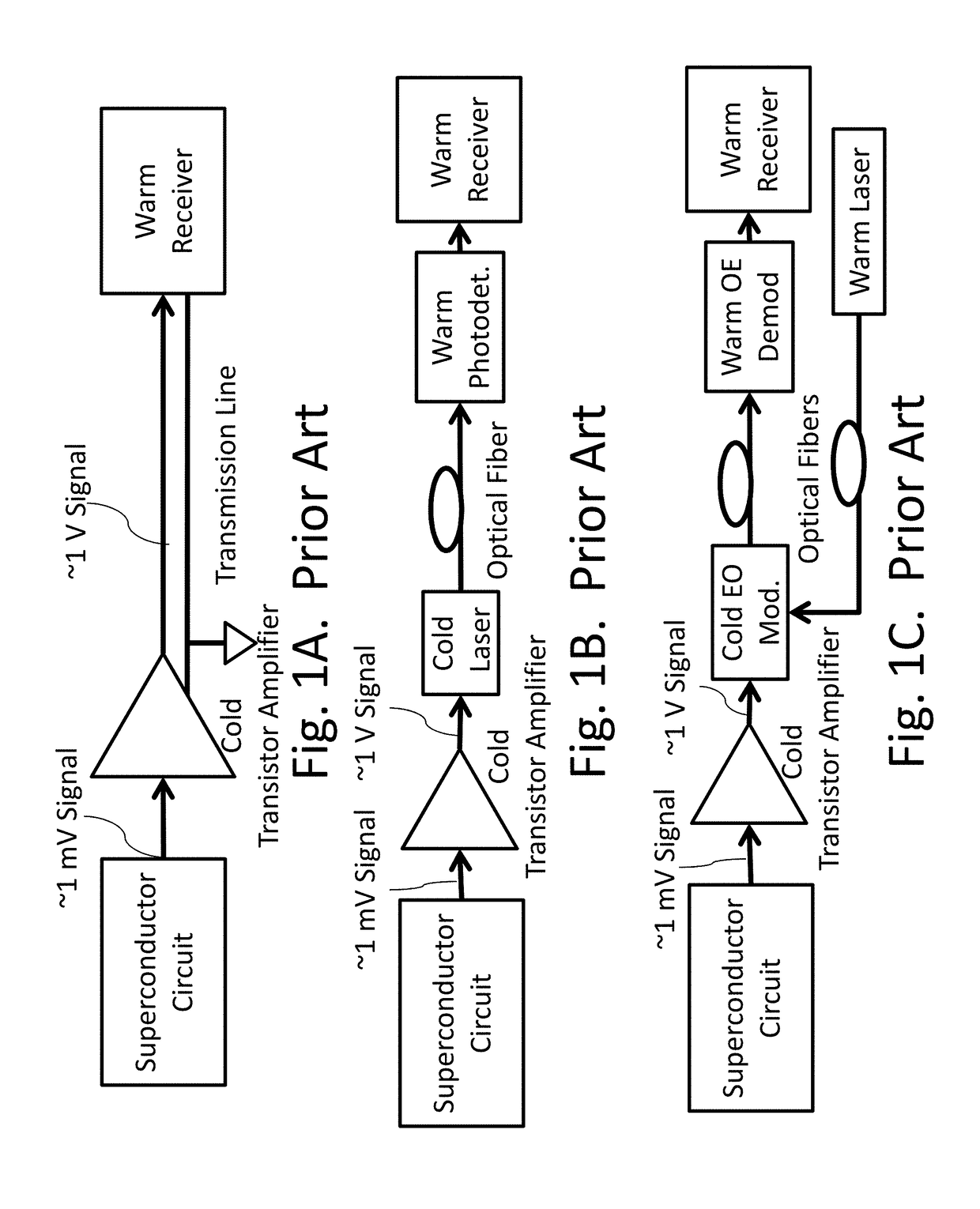
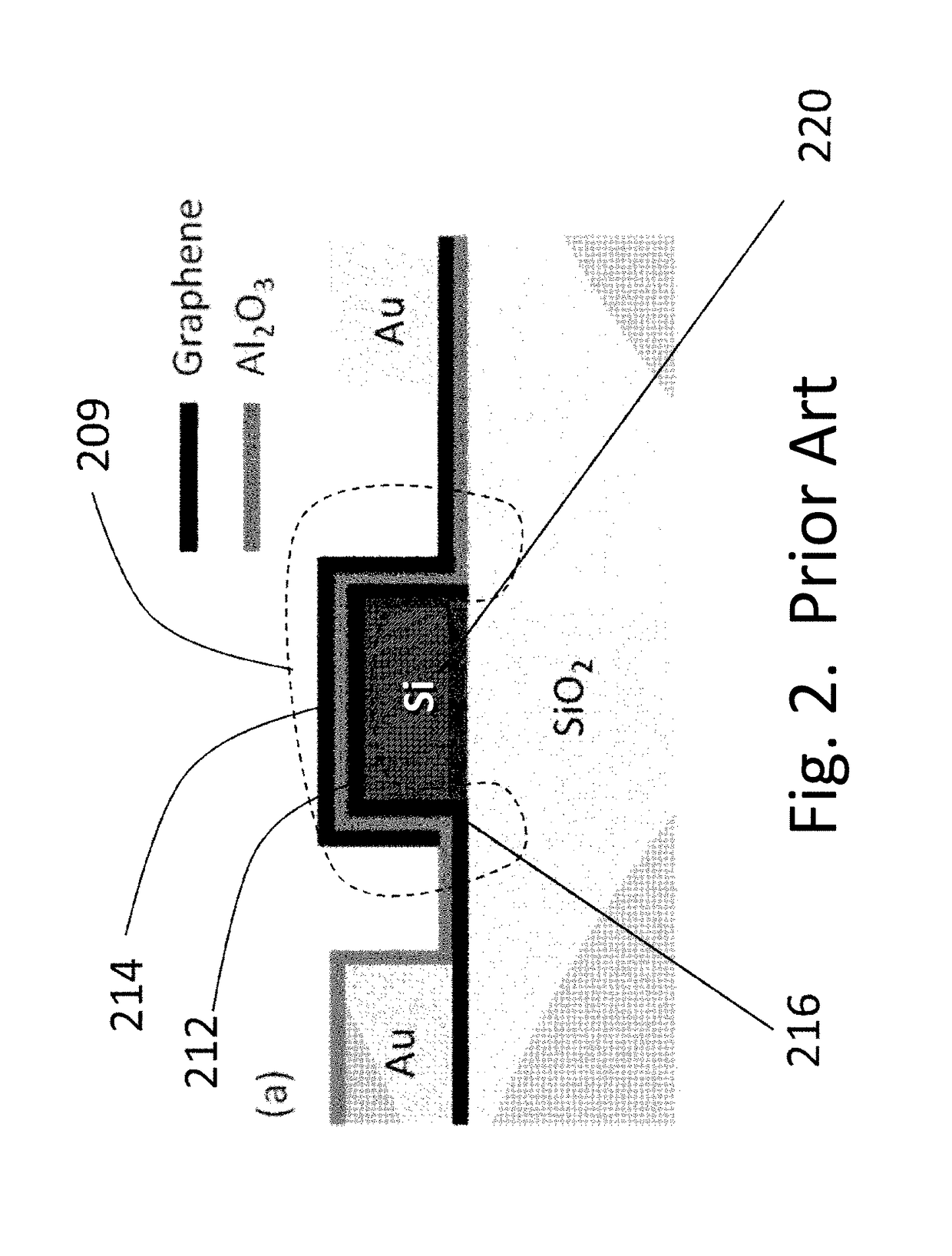
[0092]The present technology may be used to provide an external interface for a superconducting circuit comprising an ultrafast microprocessor that generates 64-bit digital words at a clock rate of 25 GHz, at a temperature of 4 K. Such a circuit could be designed using Rapid-Single-Flux-Quantum (RSFQ) logic, or one of its low-power alternatives known as Reciprocal Quantum Logic (RQL), Energy-Efficient RSFQ, or Quantum Flux Parametron. See, for example, U.S. Pat. No. 8,571,614; U.S. Pat. No. 7,843,209; U.S. Pat. No. 7,786,748.
[0093]Logic gates in these technologies exhibit switching energies of order 10−18 J / gate, corresponding to signal levels of order 1 mV and 0.5 mA for 2 ps. For a chip with one million gates at a clock rate of 25 GHz, this corresponds to a total power dissipation of 25 mW. The power associated with input / output lines and drivers at 4 K should be comparable to this. Taking a 64-bit data bus from 4 K to room temperature, 25 mW corresponds to 0.015 pJ / bit, an extrem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com