Method and apparatus for enhanced purification of high-purity metals
a high-purity metal and purification method technology, applied in the direction of metallurgical equipment, process efficiency improvement, chemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of large equipment and prolonged time needed to separate and recover indium, reduce the yield of purification, and reduce the efficiency of purification process, so as to achieve marked improvement in the speed of purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
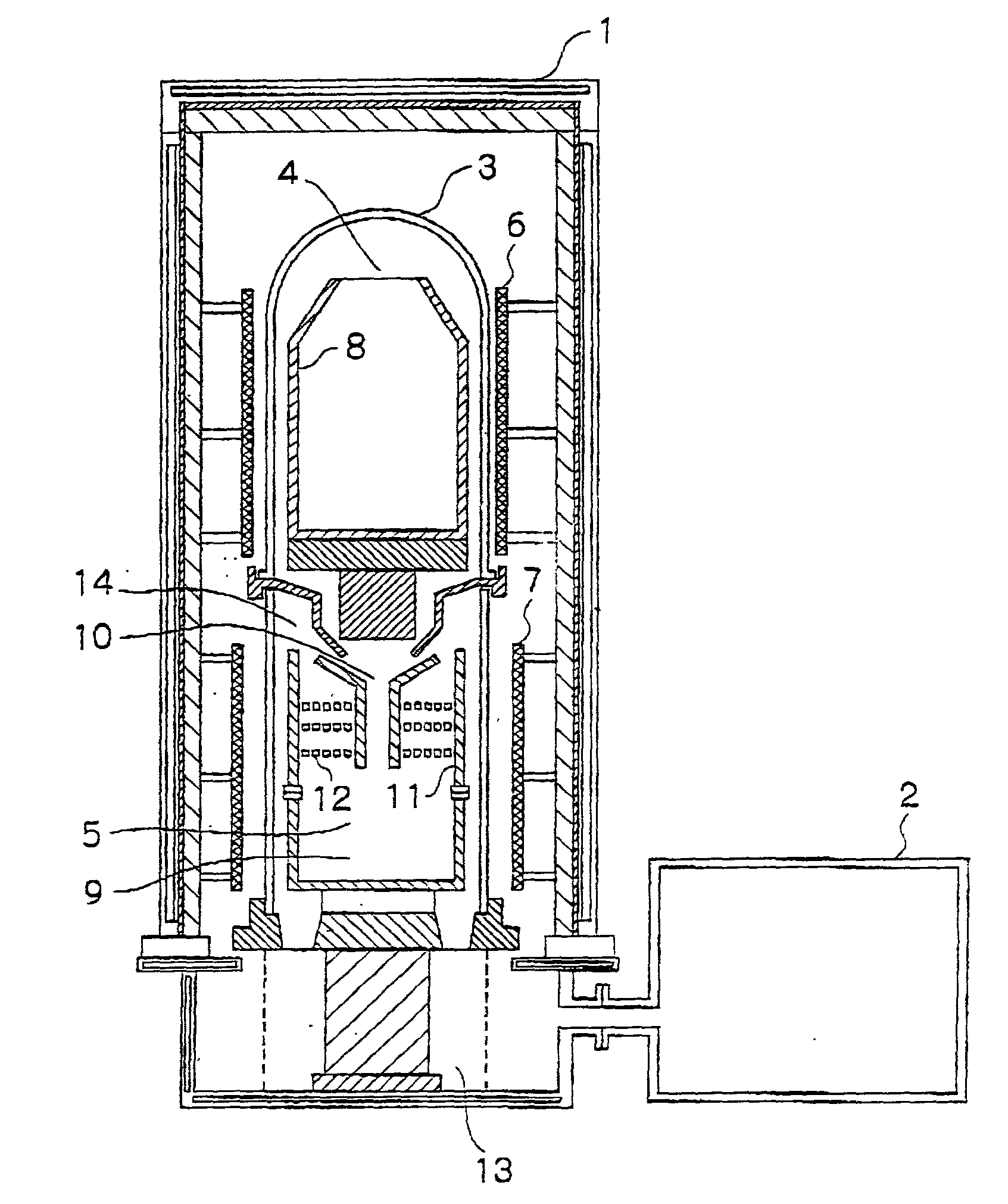
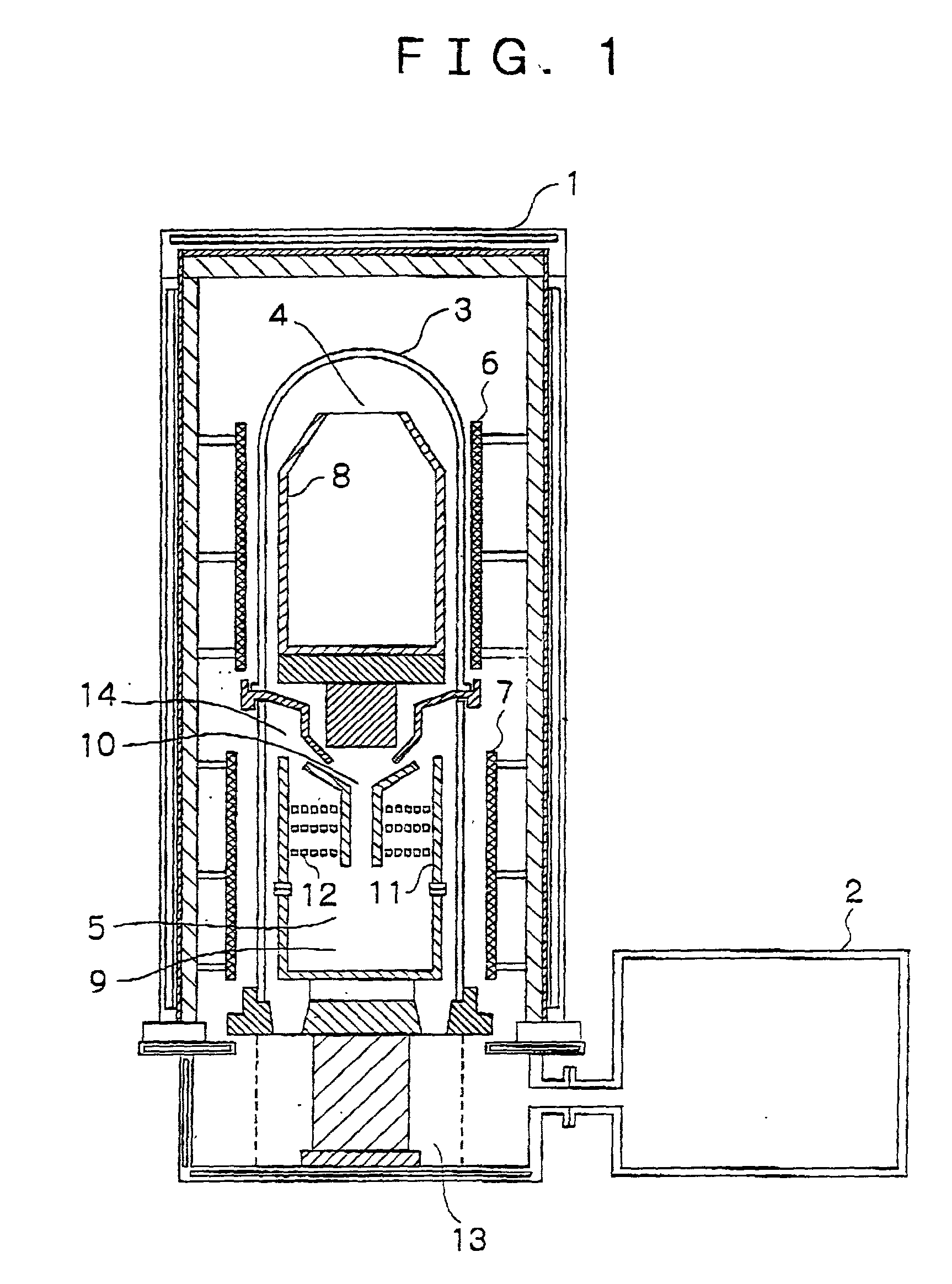
[0035] Twenty kilograms of 99.99% pure metallic indium feed was charged into the feed crucible 8 and subjected to the same purification procedure as in Example 1, except that the heating temperature in the first thermal purification step was varied at 1150.degree. C., 1250.degree. C. and 1300.degree. C. and that the duration of the second thermal purification step was 15 hours. In each of the three test runs, indium could be purified to a purity of at least 99.9999%. The respective rates of indium purification are shown in Table 2 below together with the result of Comparative Example 2.
2TABLE 2 Rates of indium purification Temperature Example 2 Comparative Example 2 1150.degree. C. 2.95 g / min 0.8 g / min 1250.degree. C. 10.4 g / min 8.7 g / min 1300.degree. C. 15.2 g / min 13.3 g / min
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com