Optically variable security devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
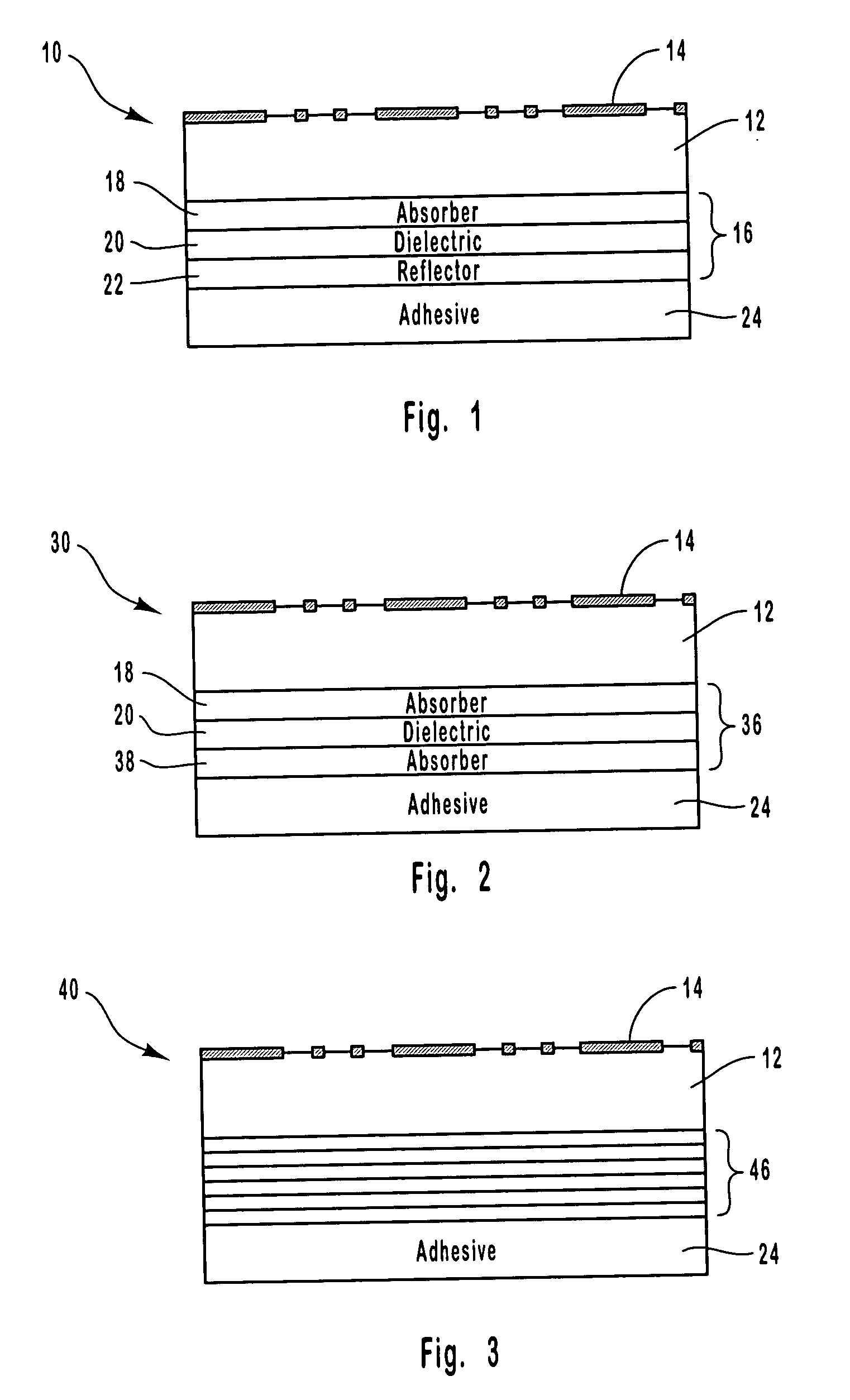
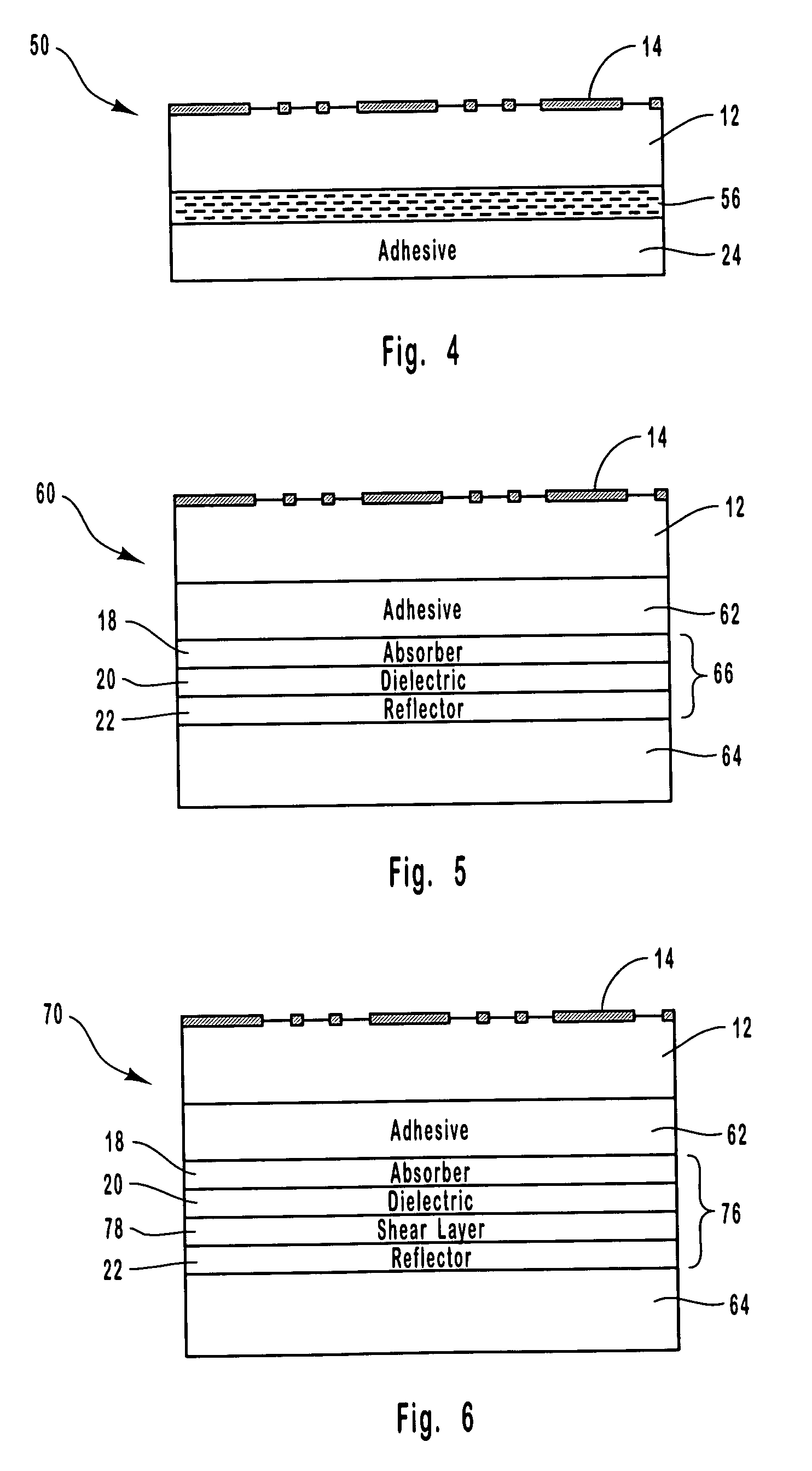
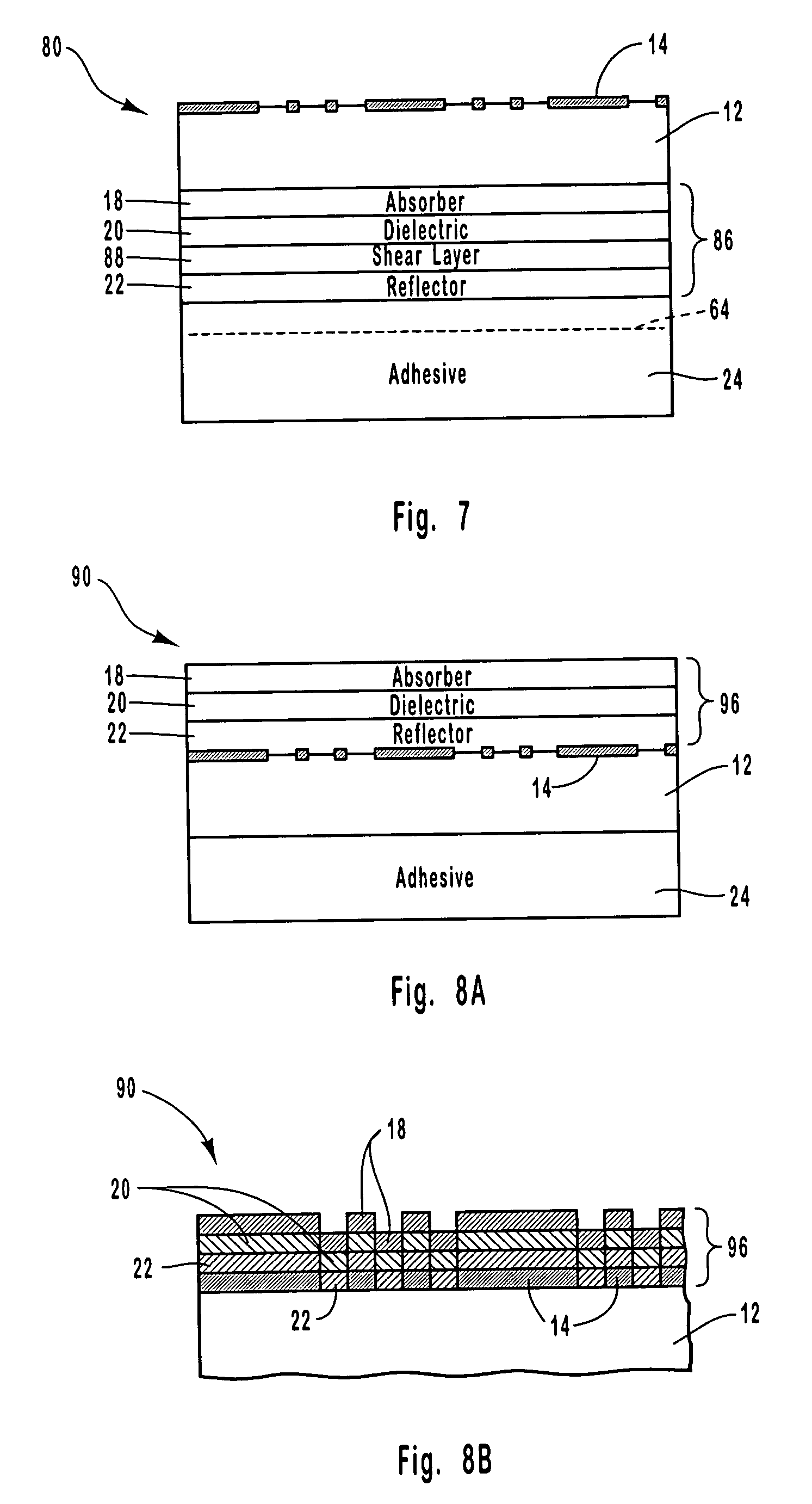
[0115] A color shifting optical coating having a three-layer design was formed on an embossed transparent film to produce a security article. The optical coating was formed on the flat surface of the transparent film on the side opposite from the embossed surface. The optical coating was formed by depositing an absorber layer composed of chromium on the flat surface of the transparent film, depositing a dielectric layer composed of magnesium fluoride on the absorber layer, and depositing a reflector layer of aluminum on the dielectric layer.
[0116] Alternatively, the aluminum layer can be deposited so that it is essentially transparent. This would allow printed information on an object to be read underneath the optical coating. Further, the reflector layer can alternatively be composed of a magnetic material. Such a magnetic feature in the color shifting component when added to the holographic component would give three independent security features to the security article.
[0117] The...
example 3
[0118] A security article was formed by laminating a laser imaged optical coating structure to an embossed substrate according to the present invention. The security article included four main parts: 1) A laser ablated image, 2) a laser ablated bar code or serial number, 3) a multilayer color shifting thin film, and 4) a holographic image.
[0119] The color shifting thin film was deposited in a vacuum roll coater onto a clear polyester (PET) substrate that was 1 mil thick. The thin film was formed by depositing a metal layer of aluminum on the substrate, followed by a dielectric layer composed of magnesium fluoride being deposited on the metal layer, and an absorber layer composed of chromium being deposited on the dielectric layer. Thereafter, the thin film was subjected to laser ablation using a laser diode imaging system based on the Heidelberg Quickmaster printing system to provide digital encoding. The imaging system used a high-resolution diode laser array with a spot size of ap...
example 4
[0121] The security article of Example 3 was subjected to various tests to measure its optical performance, which are described as follows.
[0122] A. Instrumentation and Sample Orientation
[0123] A Zeiss GK / 311M goniospectrophotometer using a xenon flash lamp with angle adjustable fiber optics for both illumination and reflectance was used to characterize the security article. Three types of viewing conditions were examined, with the geometries utilized shown in FIGS. 17A and 17B. These viewing conditions included: a) set angle of illumination at 45 degrees, with the angles of measurement being 5 degree increments from 65 through 155 degrees (FIG. 17A); b) off-gloss, with the angles of illumination being 5 degree increments from 25 through 75 degrees and the angles of measurement being 5 degree increments from 100 through 150 degrees (FIG. 17B); and c) on-gloss (specular), with the angles of illumination being 5 degree increments from 25 through 80 degrees and the angles of measuremen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com