Process modules for transport polymerization of low epsilon thin films
a technology of process modules and thin films, applied in the direction of machines/engines, flexible member pumps, positive displacement liquid engines, etc., can solve the problems of unacceptable cross talk and resistance-capacitance delay, rc delay has become a serious problem for ics, and current dielectric materials used in the manufacturing of ics have already proved inadequa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
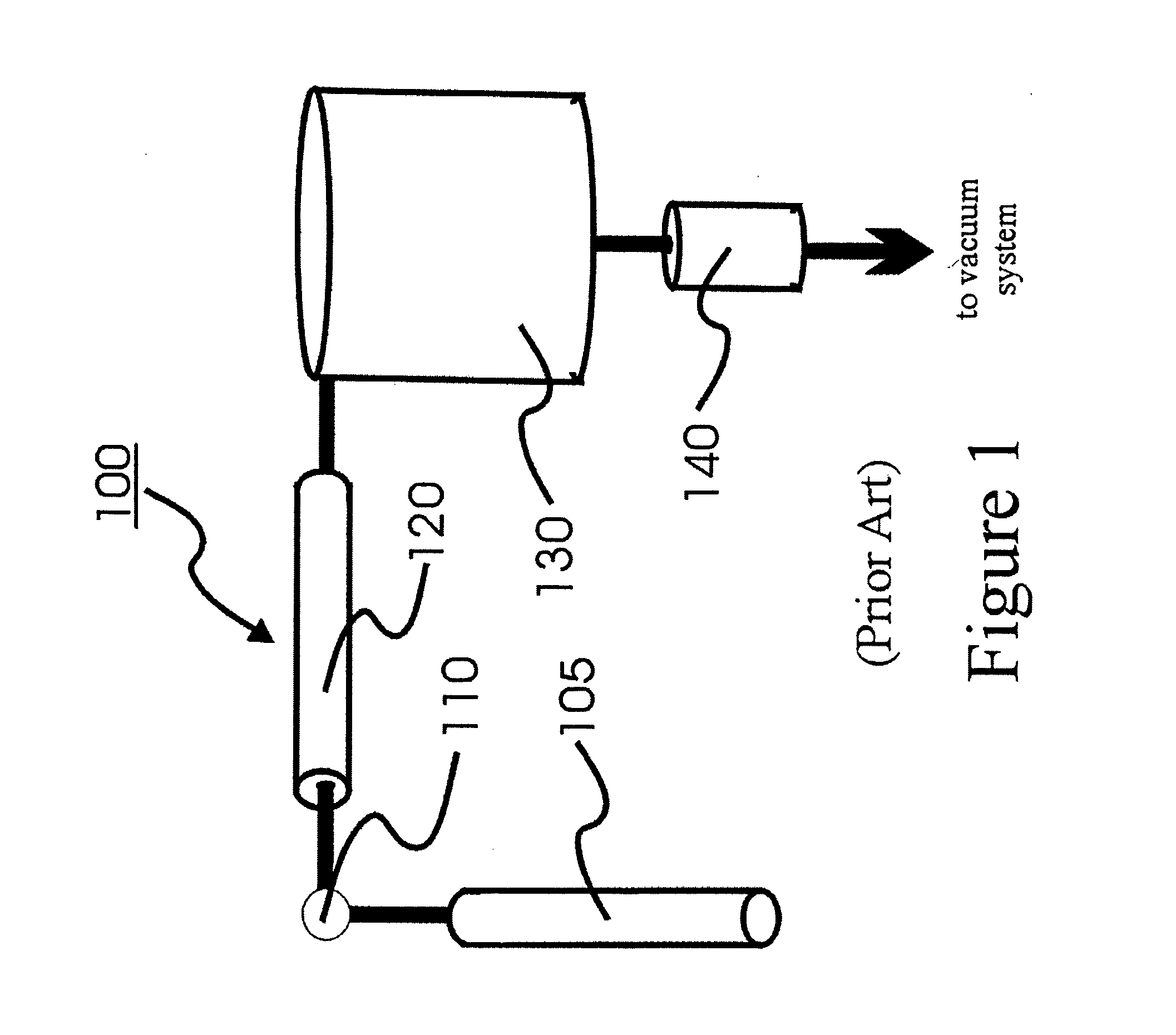
Conventional Chemical Vapor Depostion (“CVD”)
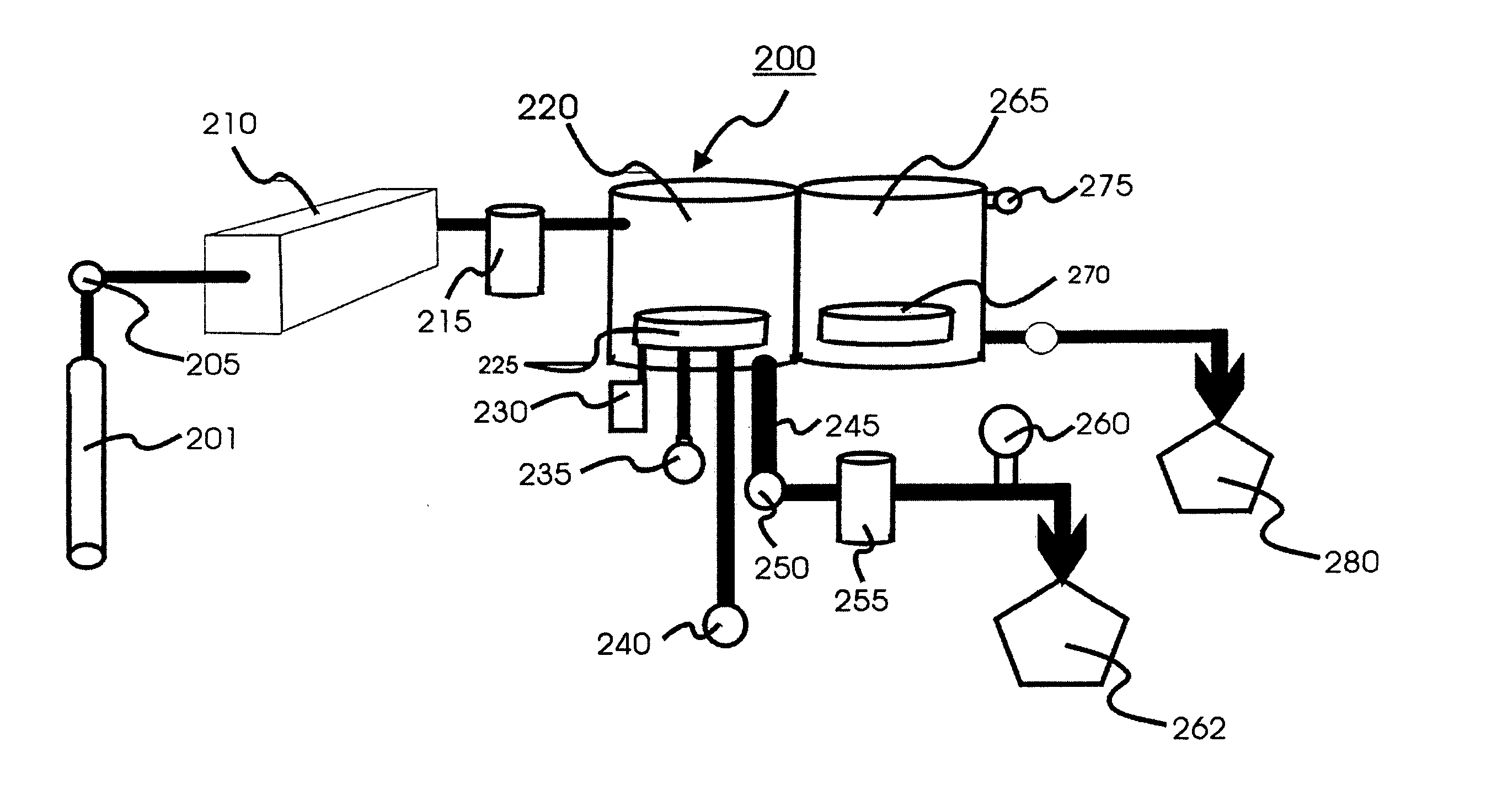
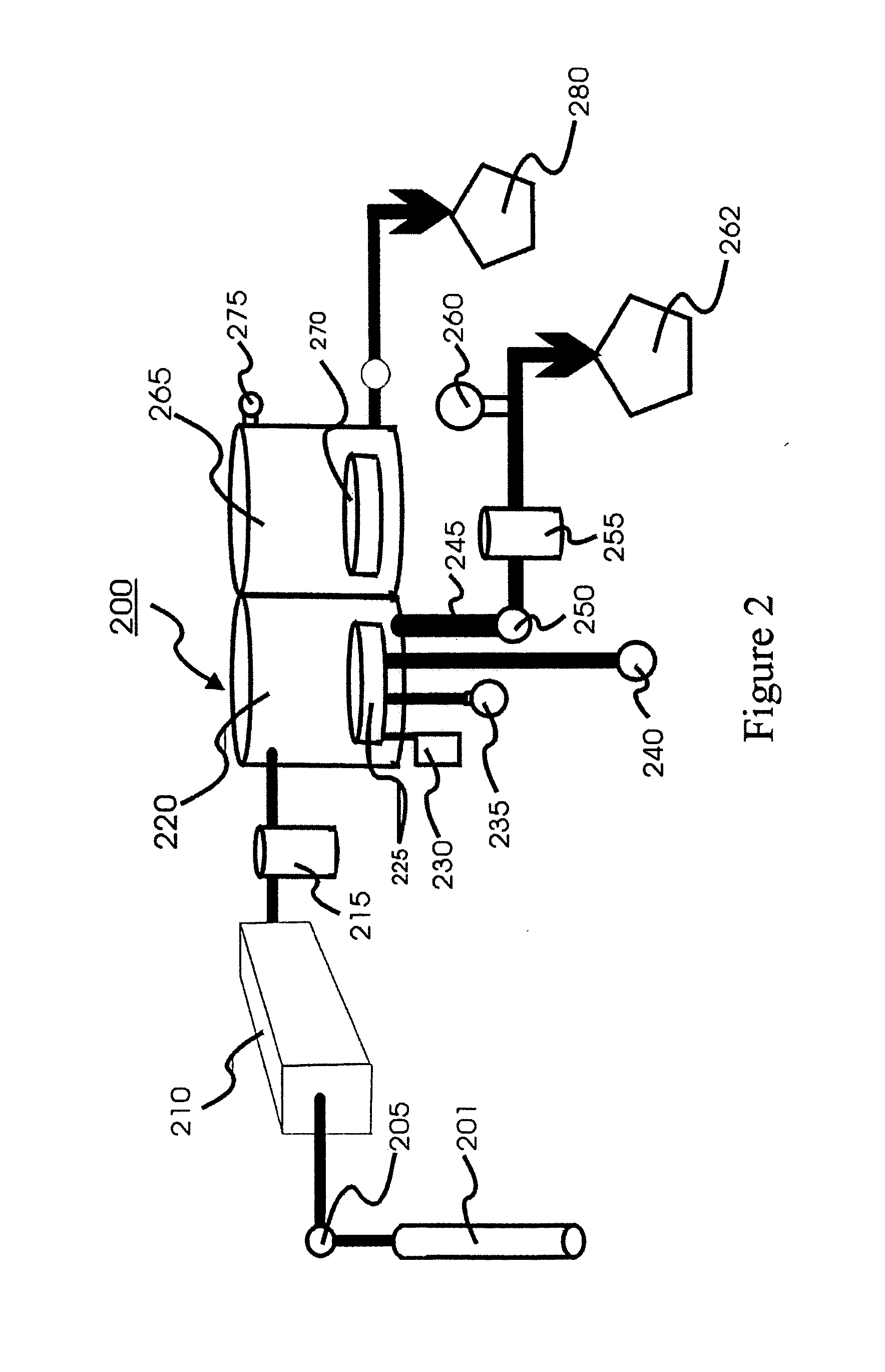
There are several fundamental differences between a transport polymerization (“TP”) process and a conventional Chemical Vapor Deposition (“CVD”) process. Additionally, there are distinctive differences in the Process Module (“PM”) described in the current invention when compared to the PM of a conventional CVD system.
A conventional CVD process begins when the starting chemicals are introduced into a traditional CVD chamber and are subjected to plasma or ozone to generate reacting intermediates. The CVD chamber is normally operated under sub-atmosphere pressure, or even moderate vacuum in the ranges of few mTorrs to few Torrs. A wafer is heated at high temperatures to remove any unstable products. A film grows not only the wafer surface but also on other surfaces inside a deposition chamber. Such non-selective deposition requires frequently cleaning for these surfaces inside the CVD chamber. Traditional CVD process that utilizes. ozon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com