Cytotoxicity mediation of cells evidencing surface expression of CD44
a cytotoxicity and surface expression technology, applied in the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment, can solve the problems of insufficient evidence, inconsistent findings, and increased likelihood of tumor invasiveness and induction of angiogenesis through the ecm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0076] The hybridoma cell line H460-16-2 was deposited, in accordance with the Budapest Treaty, with the American Type Culture Collection, 10801 University Blvd., Manassas, Va. 20110-2209 on Sep. 4, 2002, under Accession Number PTA-4621. In accordance with 37 CFR 1.808, the depositors assure that all restrictions imposed on the availability to the public of the deposited materials will be irrevocably removed upon the granting of a patent.
Antibody Production:
[0077] H460-16-2 monoclonal antibody was produced by culturing the hybridoma in CL-1000 flasks (BD Biosciences, Oakville, ON) with collections and reseeding occurring twice / week. The antibody was purified according to standard antibody purification procedures with Protein G Sepharose 4 Fast Flow (Amersham Biosciences, Baie d'Urfé, QC). It is within the scope of this invention to utilize monoclonal antibodies that are human, humanized, chimerized or murine antibodies.
example 2
Normal Human Tissue Staining
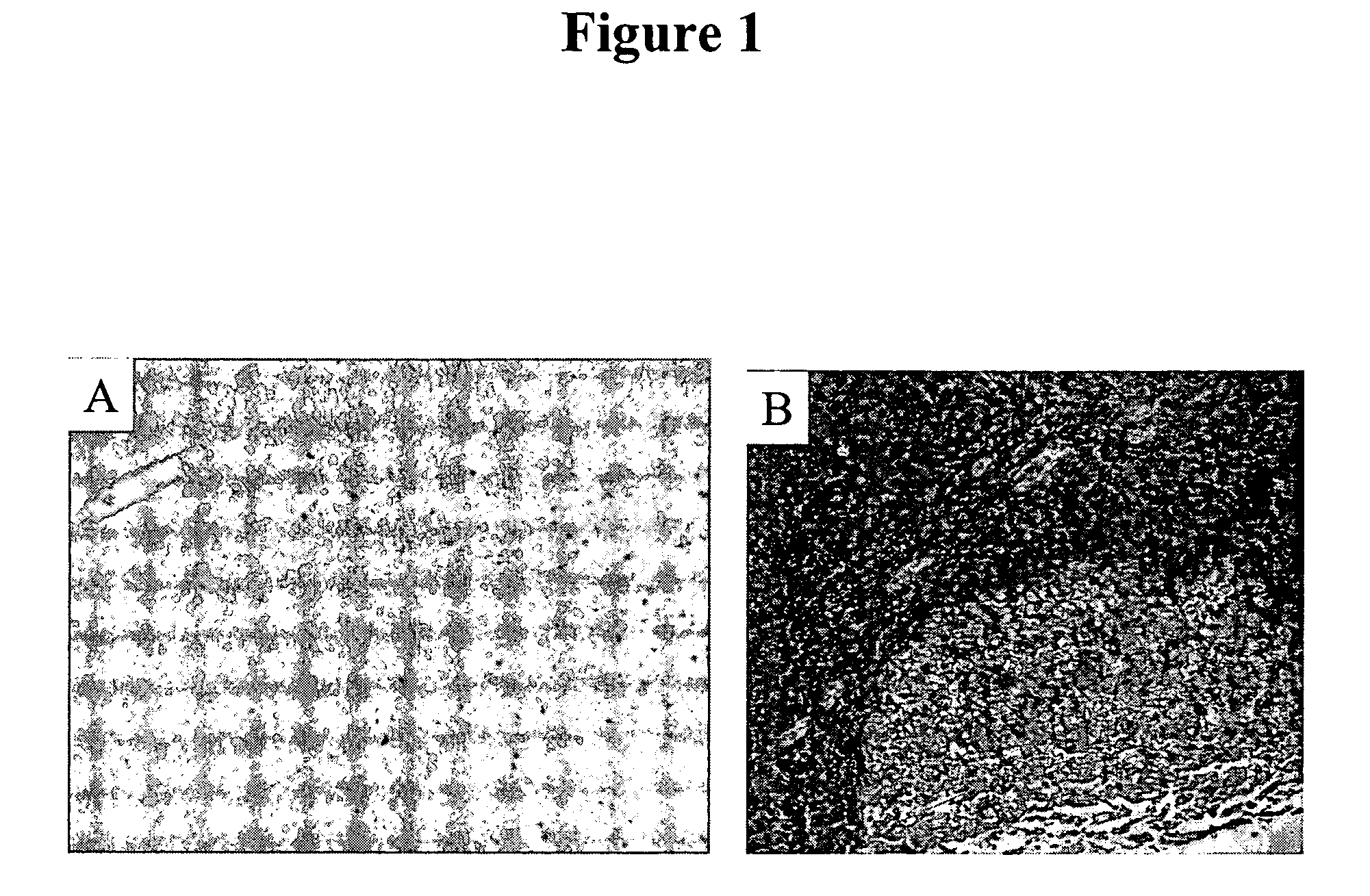
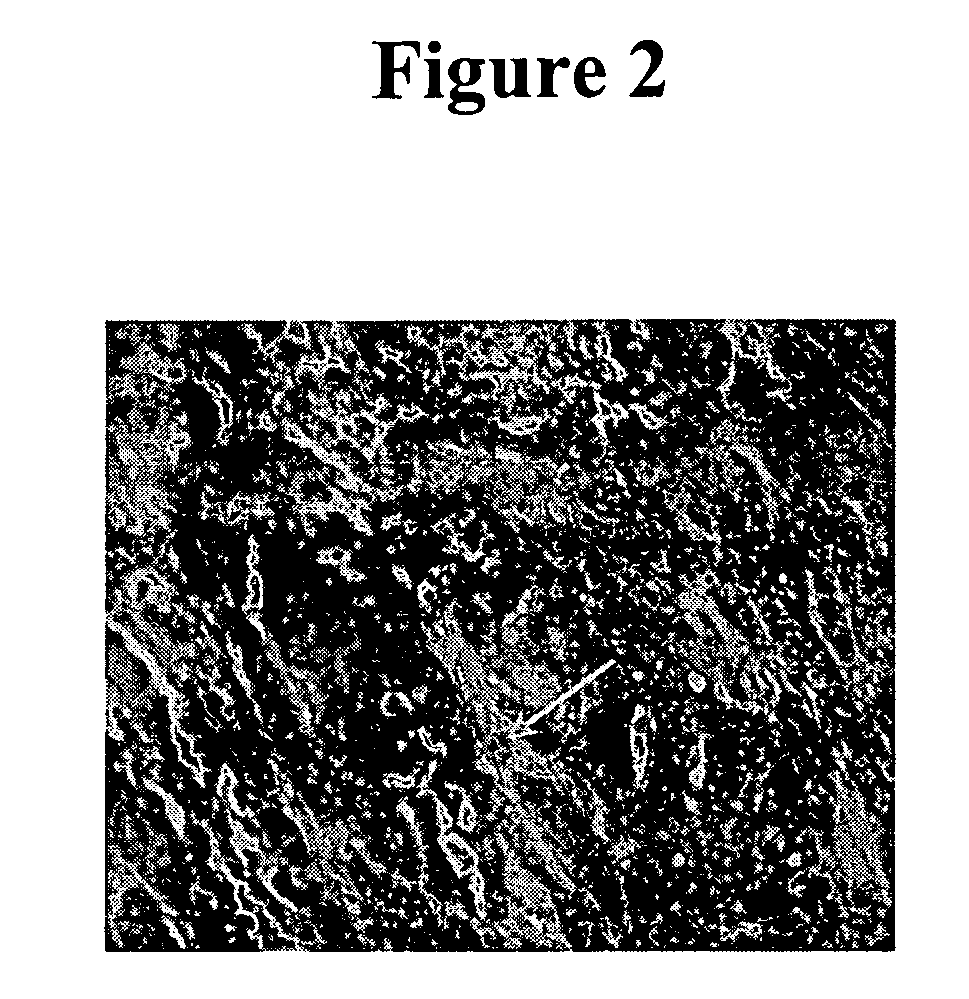
[0078] IHC studies were previously conducted to characterize H460-16-2 antigen distribution in humans (Ser. No. 10 / 603,000) and in comparison to L178 (Ser. No. 10 / 647,818). The current studies compare H460-16-2 to another antibody directed against CD44 (BU75) since the H460-16-2 antigen may be a cancer variant of CD44 as determined previously by biochemical methods. Binding of antibodies to 59 normal human tissues was performed using a human normal organ tissue array (Imgenex, San Diego, Calif.). All primary antibodies (H460-16-2; BU75 anti-CD44 (BIOCAN Scientific Inc., Mississauga, ON); and mouse IgG, negative control (Dako, Toronto, ON)) were diluted in antibody dilution buffer (Dako, Toronto, ON) to a concentration of 5 μg / ml (found to be the optimal concentration in previous optimization steps). The negative control antibody has been shown to be negative to all mammalian tissues by the manufacturer. The procedure for IHC is as follows.
[0079] Tissue...
example 3
Human Breast Tumor Tissue Staining
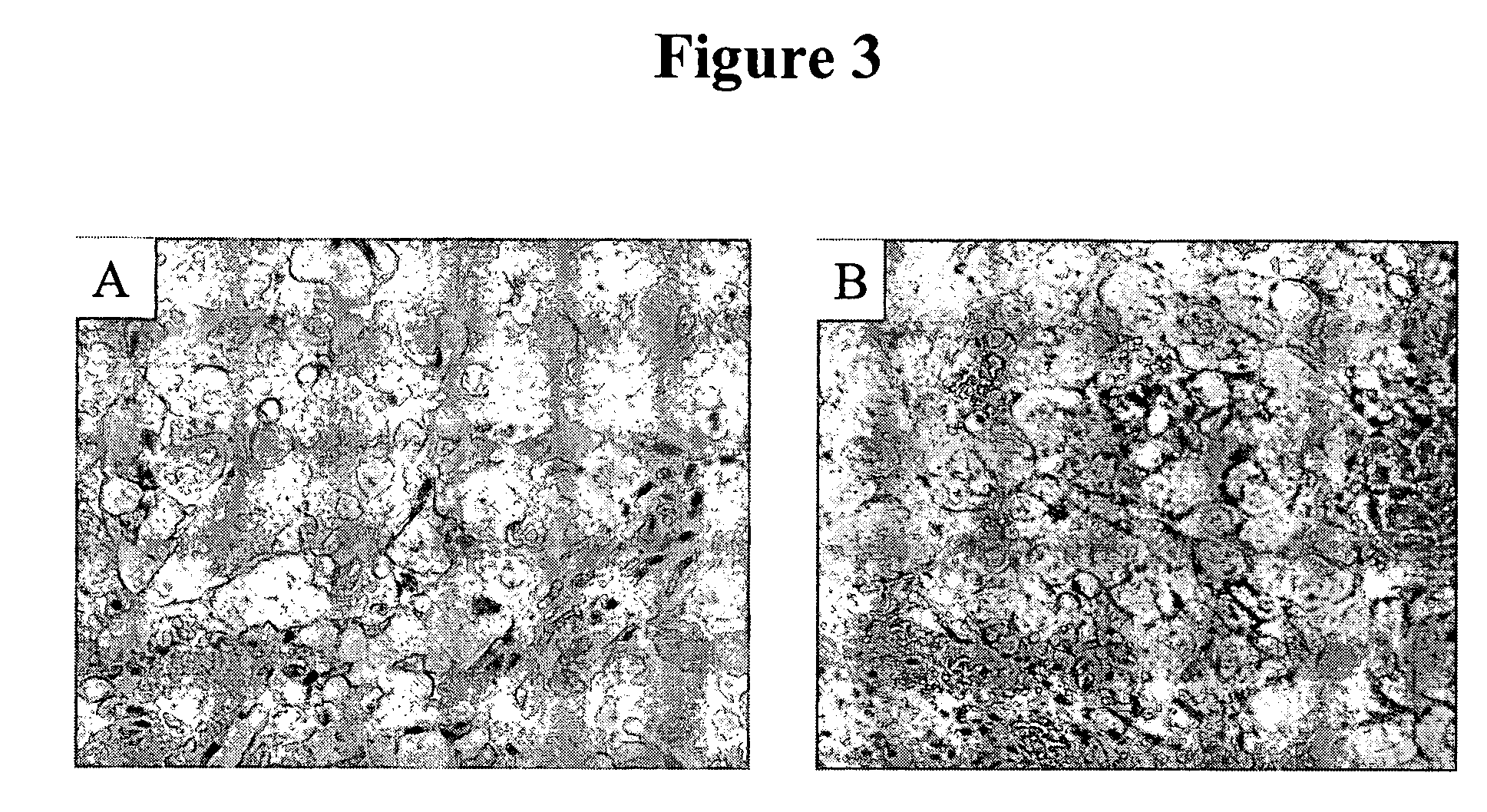
[0082] Previous IHC studies were undertaken to determine the cancer association of the H460-16-2 antigen with human breast cancers and whether the H460-16-2 antibody was likely to recognize human cancers (Ser. No. 10 / 603,000) and how it compared to anti-CD44 staining with L178 (Ser. No. 10 / 647,818). Currently, a comparison was made for BU75 anti-CD44 staining, c-erbB-2 anti-Her2 and an antibody directed towards Aspergillus niger glucose oxidase, an enzyme which is neither present nor inducible in mammalian tissues (negative control). A breast cancer tissue array derived from 50 breast cancer patients and 10 samples derived from non-neoplastic breast tissue in breast cancer patients was used (Imgenex Corporation, San Diego, Calif.). The following information was provided for each patient: age, sex, American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) tumor stage, lymph node, estrogen receptor (ER) and projesterone receptor (PR) status. The procedure for IHC f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com