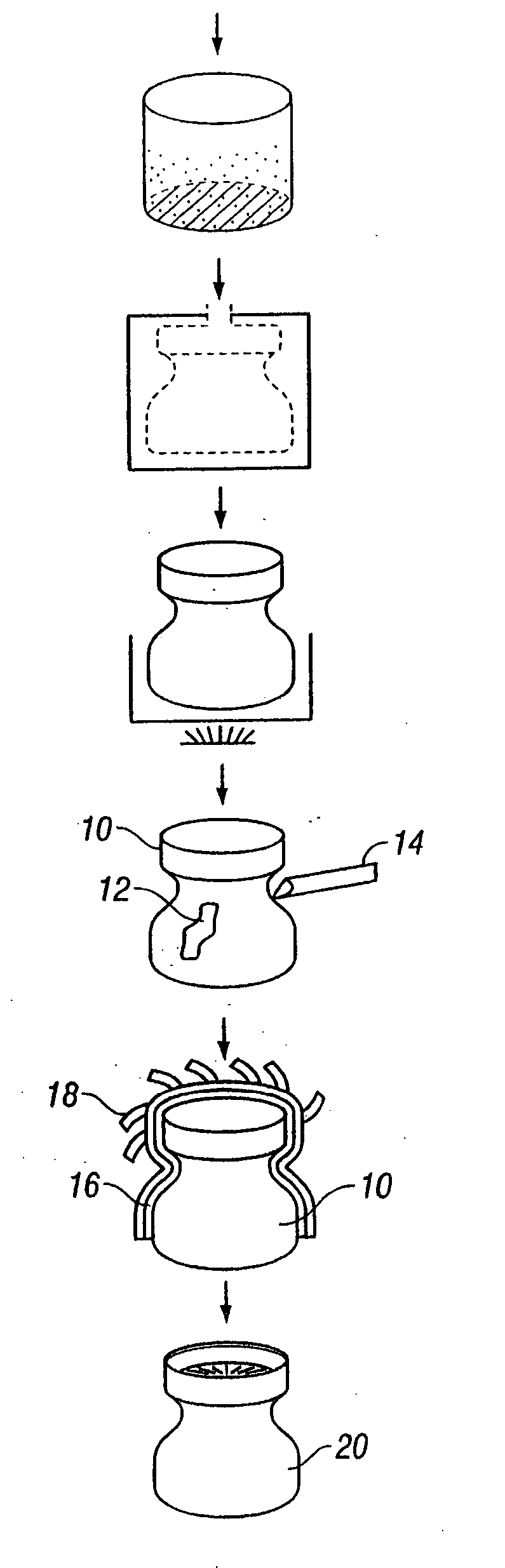
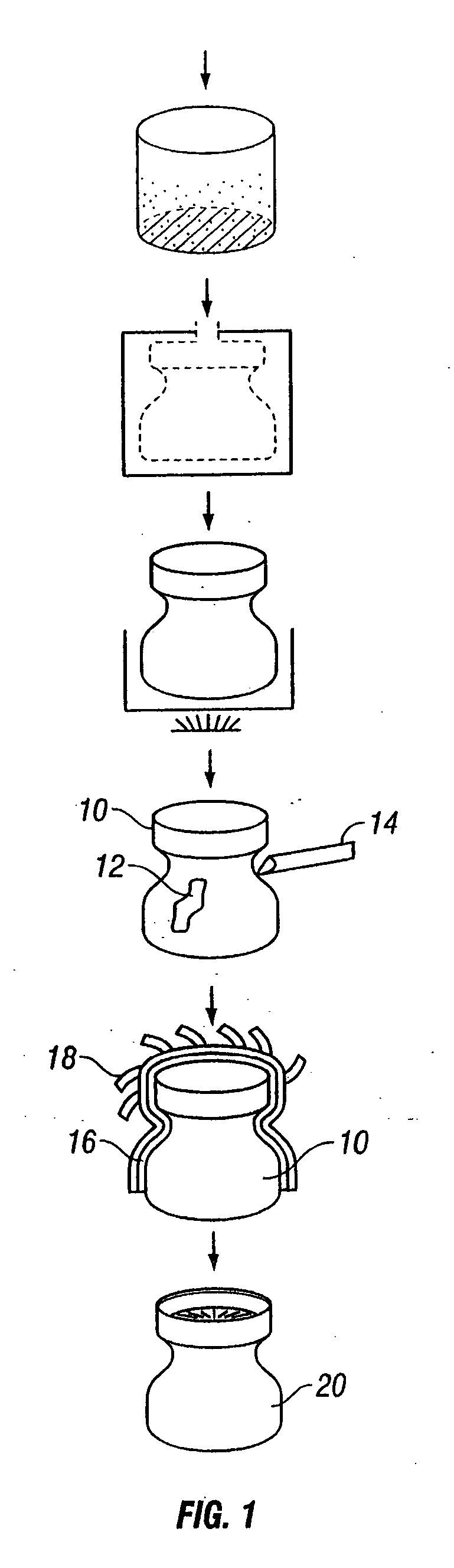
Water soluble tooling materials for composite structures
a tooling material and composite technology, applied in the field of new coring and tooling materials for polymer composites, can solve the problems of complex and expensive tooling that is required for their fabrication, limited performance requirements of composite components, and inability to meet the requirements of secondary structures, etc., and achieves the effects of easy washing away from the finished part, easy shaping, and easy water soluble solubl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0043] This example illustrates a composite blend for use as a core form for the fabrication of composite parts. The coring material includes a composite blend of hollow ceramic-microballons and a high thermal stability thermoplastic binder. In preparing the composite blend, the thermoplastic binder is mixed with water to form a first solution. The first solution is subsequently mixed with a ceramic micro-sphere filler to provide a composite blend in the form of a moist, formable paste. The paste can be shaped and dried in a drying oven at between about 100 to about 125° C. for about 1 hour per inch of thickness. The dried paste form can be subsequently machined as desired, thereby producing a mandrel or core having a desired configuration. Examples of composite blends containing PVP and ceramic microsphere filler are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
TABLE 1Wt.(lbs.)Wt. %SolutionPVP K900.2415%Water1.485%Total1.60100% PasteSolution1.6020%Extendospheres SLG6.4080%Total8.00100%
[0044]
TABLE 2W...
example 2
[0047] This example illustrates a composite blend for use as a tooling material for fabrication of composite parts. The tooling material comprises a composite blend having a high thermal stability thermoplastic binder and either metal filler or high conductivity ceramic filler. The metallic or ceramic fillers used in the composite blend increase the overall thermal conductivity of the blend, and thus, provide a tooling material that can be tailored to provide specific values of thermal expansion and heat transfer. Conventional tooling materials, although inexpensive, are inferior due to their inability to have tailored coefficient of thermal expansion and thermal conductivity.
[0048] High conductivity ceramic fillers, such as graphite, alumina, and silicon carbide, can be used in the present invention. Tables 3 and 4 illustrate composite blends containing PVP and graphite powder. Note, composite blends having graphite powder as the ceramic filler require dispersants for the graphite...
example 3
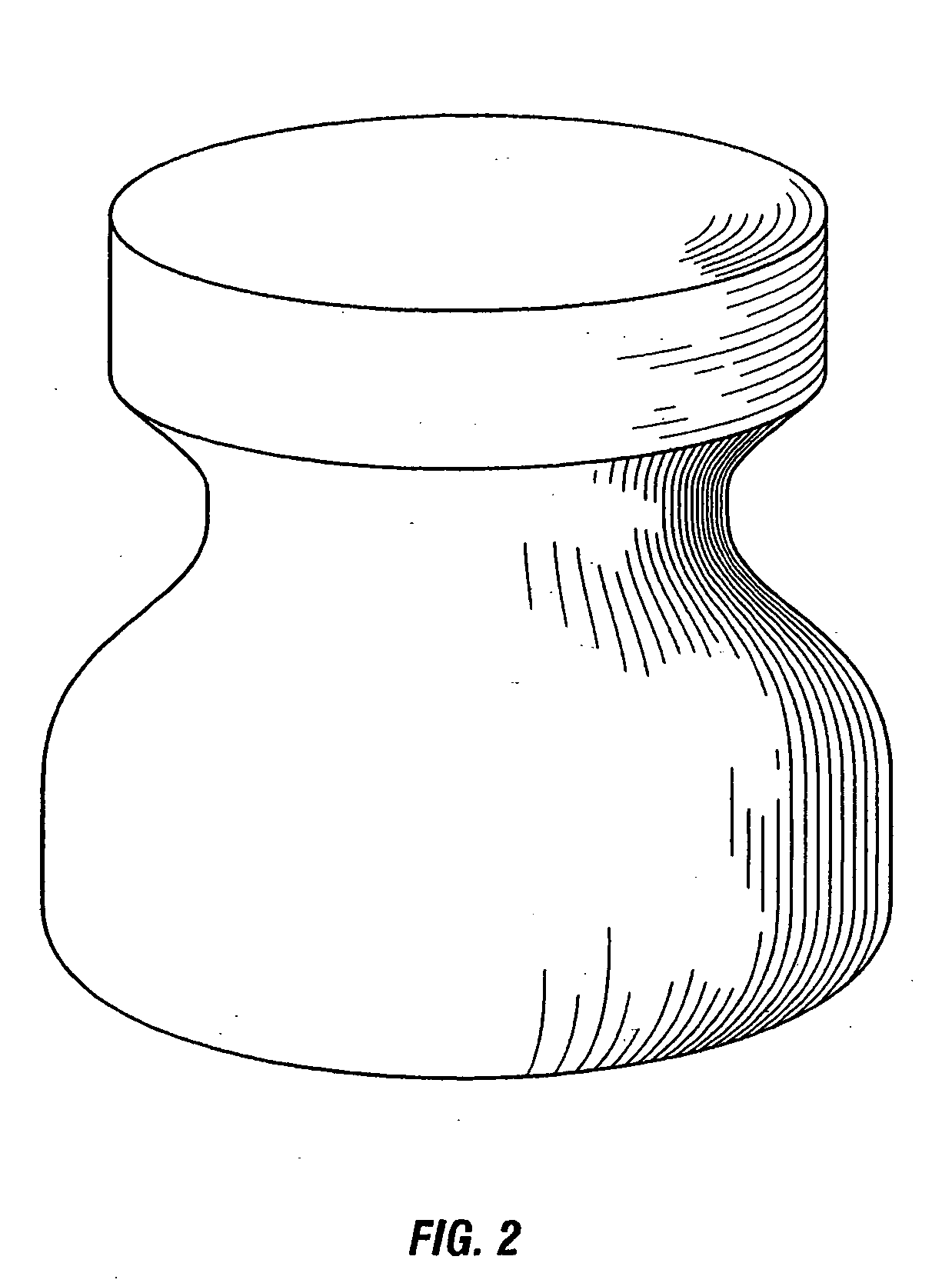
[0052] This example illustrates formation of a mandrel and its ability to be machined. A mandrel, as shown in FIG. 2, has a specific gravity of 0.3 (dry) and 0.8 (wet). The important properties are shown in Table 5.
TABLE 5PropertyValueCompressive Strengthapproximately 700-1000psiDensity28.1lbs / ft3 (wet)23.1lbs / ft3 (dry)Coefficient of Thermal6 × 10−6in / in ° C.Expansion
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com