Surface mount package
a surface mount and package technology, applied in the field of electronic devices, can solve the problems of low pin count and large die size, low integration device pin count, and often very small package size, and achieve the effect of maximizing the number of bond wires, high electrical and thermal conductivity, and maximum possible die siz
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
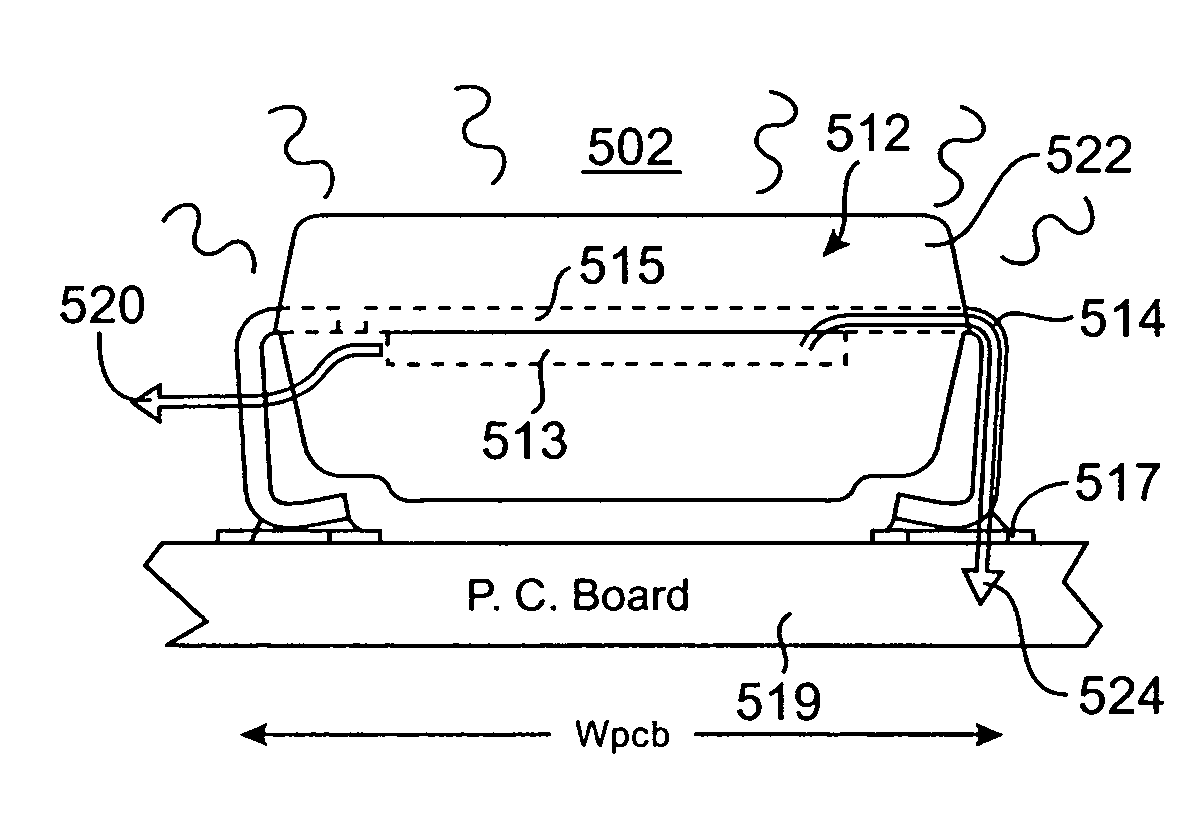
[0150] According to embodiments of the present invention, apparatuses and techniques for design of space-efficient packaging for microelectronic devices are provided. Packages in accordance with embodiments of the present invention allocate increased space in the package footprint to the packaged die, and in some embodiments offer improved the thermal resistance of the package, provide for a greater number of bond wires, offer improved bond wire angles and positioning, and accommodate both single and multiple die while maintaining a compact vertical profile for the package. A more comprehensive discussion of various aspects of the present invention is provided in detail below.
[0151] Embodiments of the present invention provide space-efficient package designs for low pin count, small footprint electronic devices as are typically utilized in portable applications. In one embodiment in accordance with the present invention, the present invention provides for space-efficient packaging ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com