Method, an arrangement, and a computer readable storage device for controlling homogeneous charge compression ignition combustion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
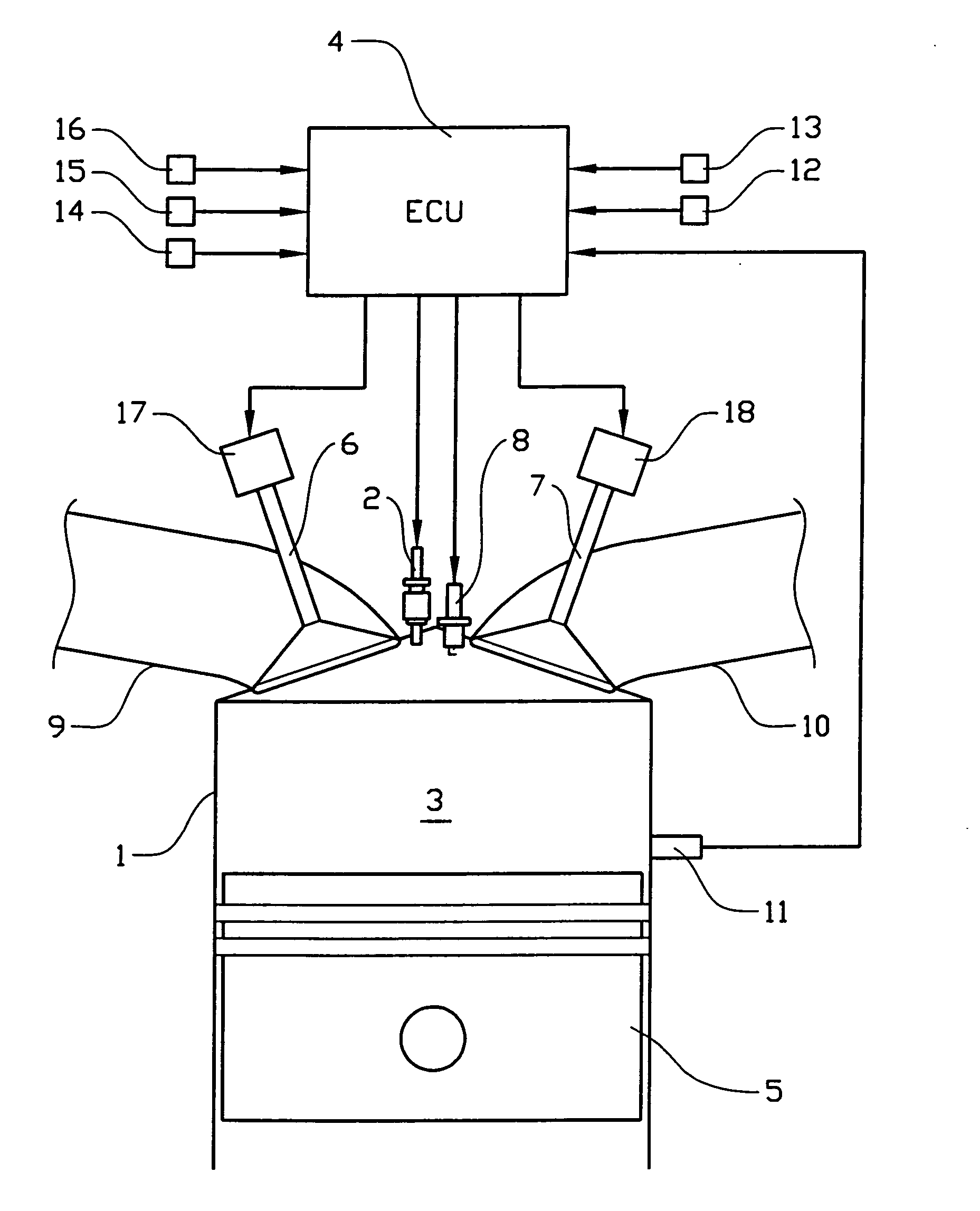
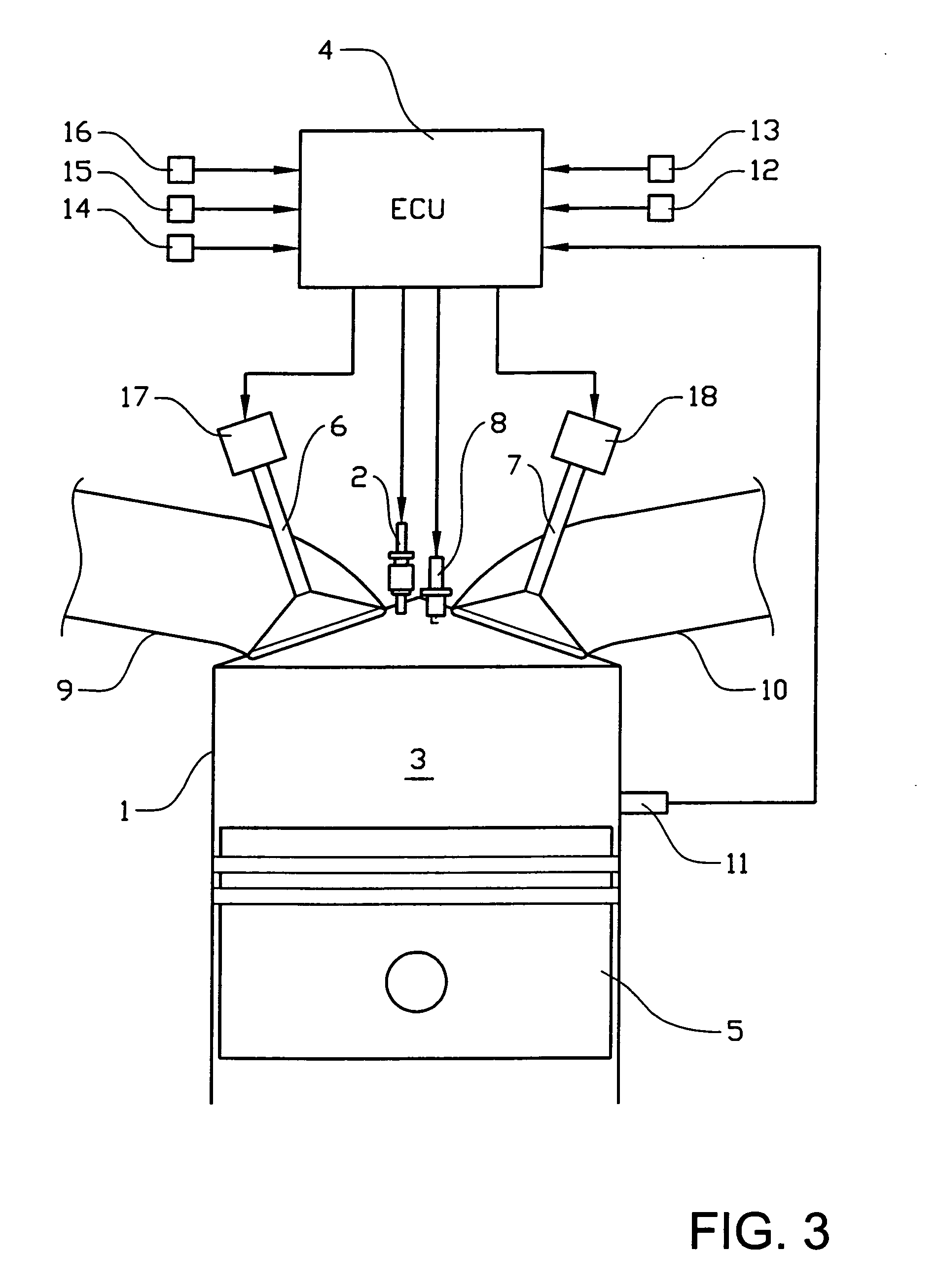
[0036]FIG. 3 shows a schematic illustration of an internal combustion engine according to the invention. The engine is provided with at least one cylinder 1 and comprises a fuel injector 2, through which fuel is injected into a combustion chamber 3, for each cylinder. A fuel injection control unit 4 controls fuel injection quantity per combustion cycle injected through each fuel injector. A piston 5 in the engine cylinder has a compression action that causes a mixture of air and fuel within the combustion chamber to be ignited during HCCI-mode. The cylinder is provided with at least one inlet valve 6 for admitting gas which includes fresh air into the cylinder and at least one exhaust valve 7 for exhausting combusted gases from the cylinder. Air is supplied through an intake conduit 9 connected to an intake manifold, while exhaust gas is exhausted through an exhaust conduit 10. During SI-mode, the ignition of the fuel / air mixture is ignited by a spark plug 8.
[0037] The control unit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com