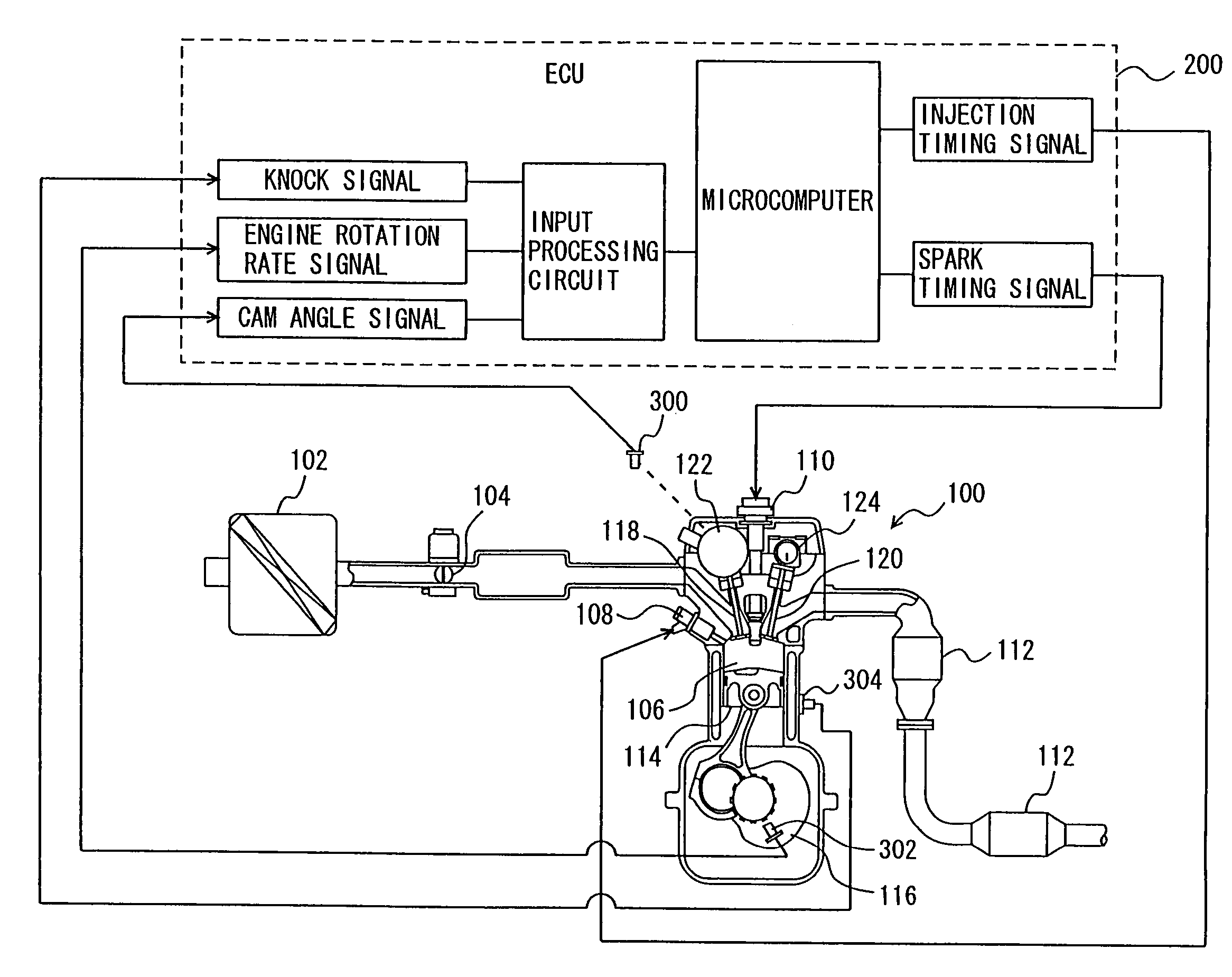
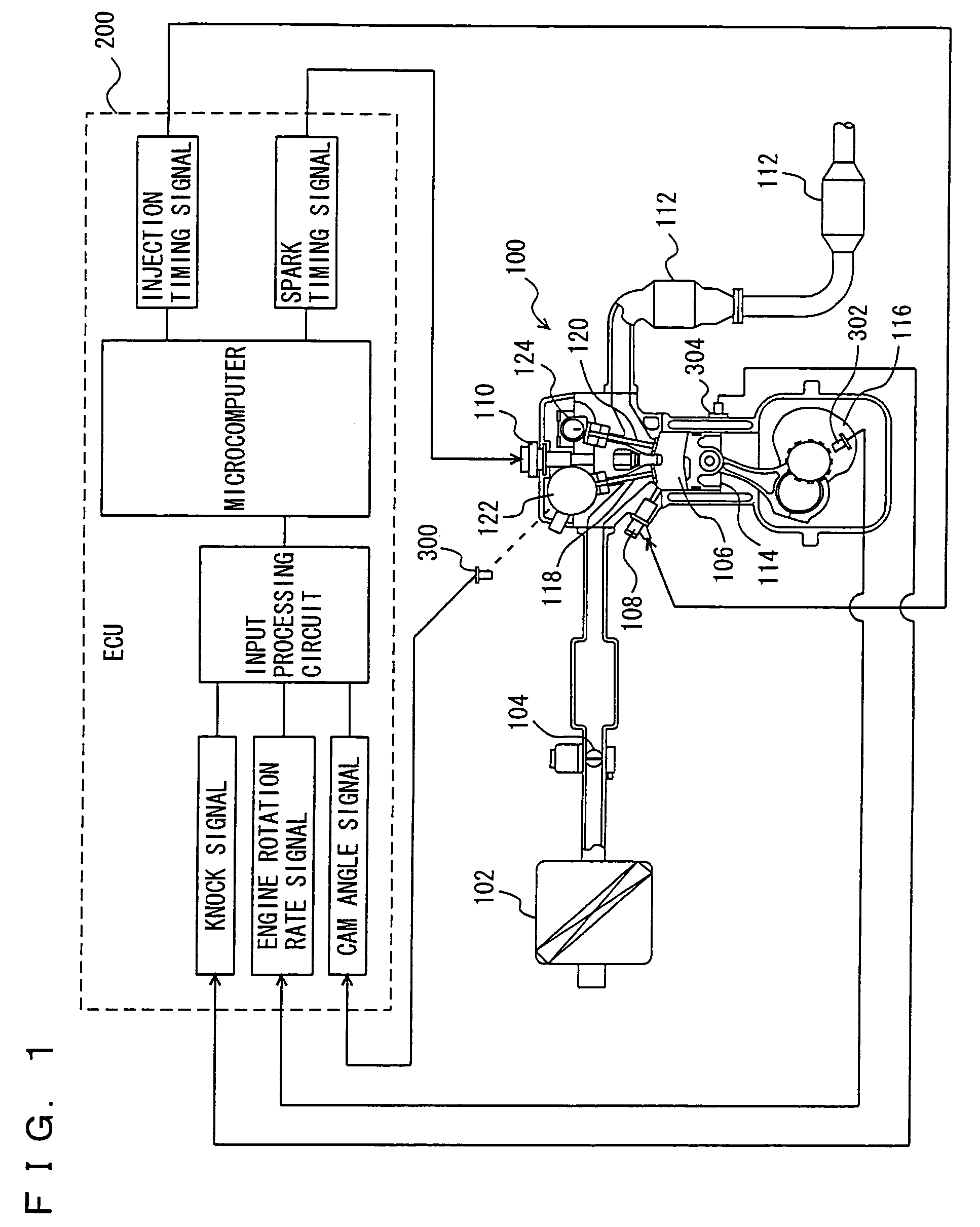
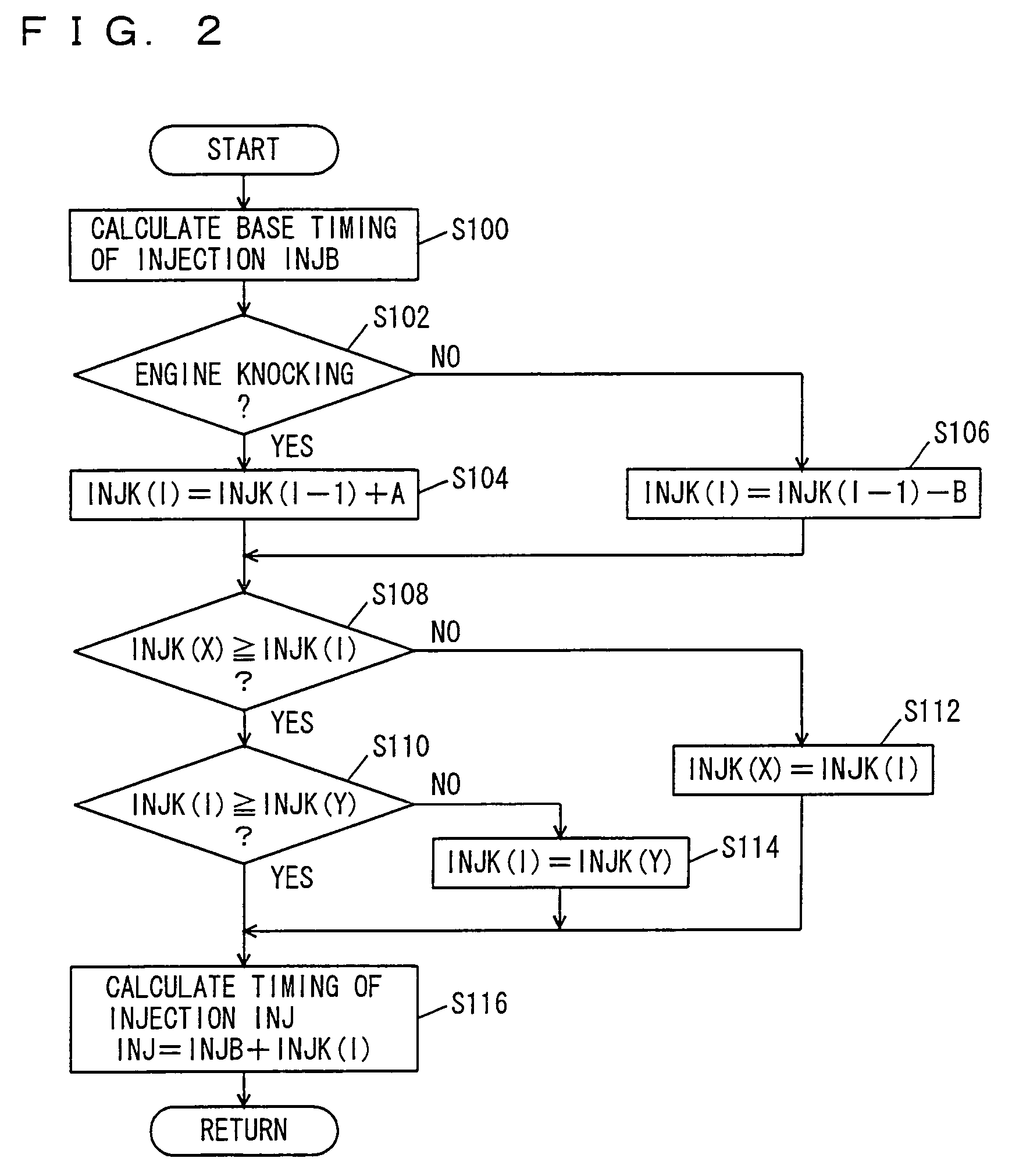
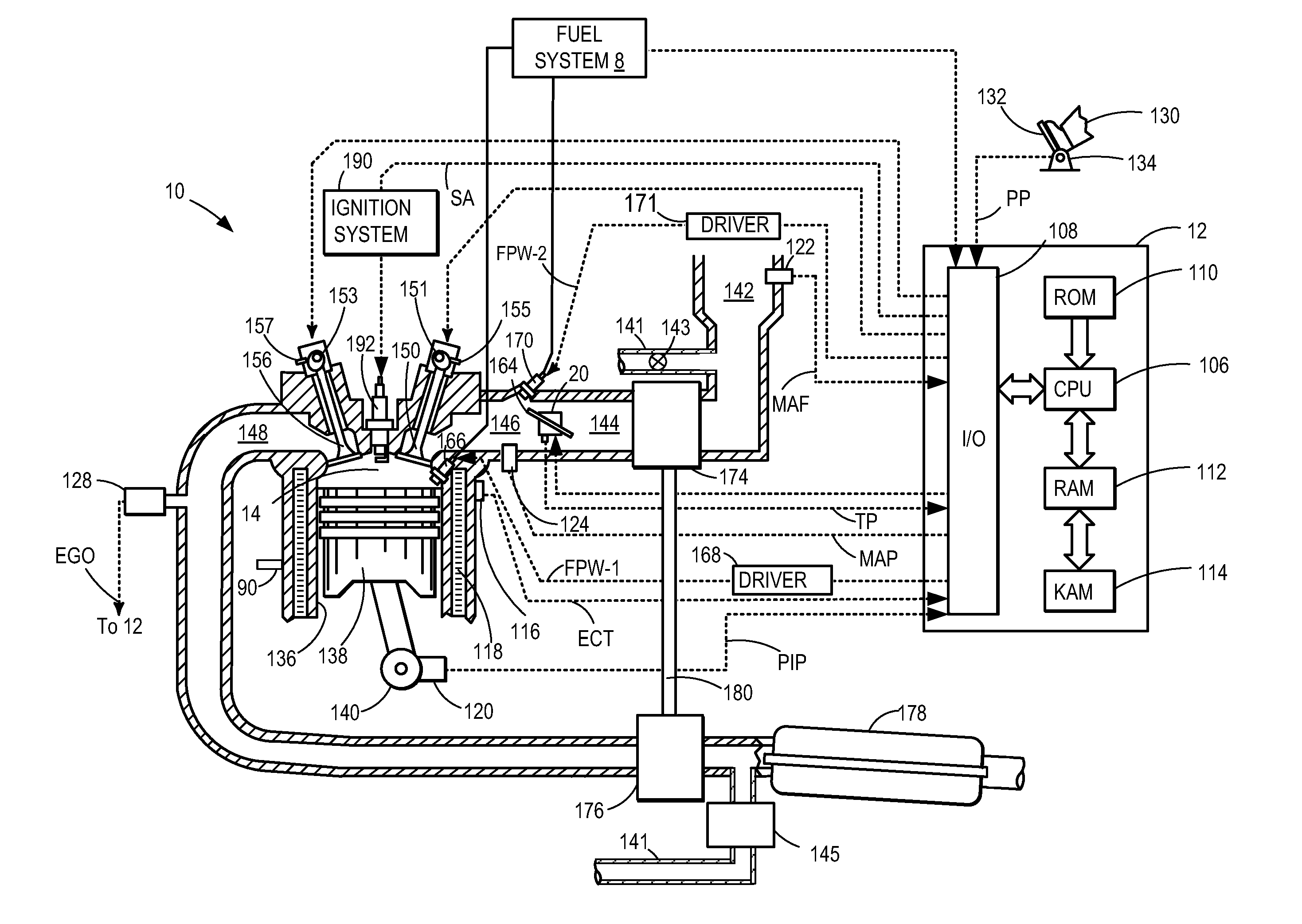
Patents
Literature
940 results about "Engine knocking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Knocking (also knock, detonation, spark knock, pinging or pinking) in spark ignition internal combustion engines occurs when combustion of some of the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder does not result from propagation of the flame front ignited by the spark plug, but one or more pockets of air/fuel mixture explode outside the envelope of the normal combustion front. The fuel-air charge is meant to be ignited by the spark plug only, and at a precise point in the piston's stroke. Knock occurs when the peak of the combustion process no longer occurs at the optimum moment for the four-stroke cycle. The shock wave creates the characteristic metallic "pinging" sound, and cylinder pressure increases dramatically. Effects of engine knocking range from inconsequential to completely destructive.
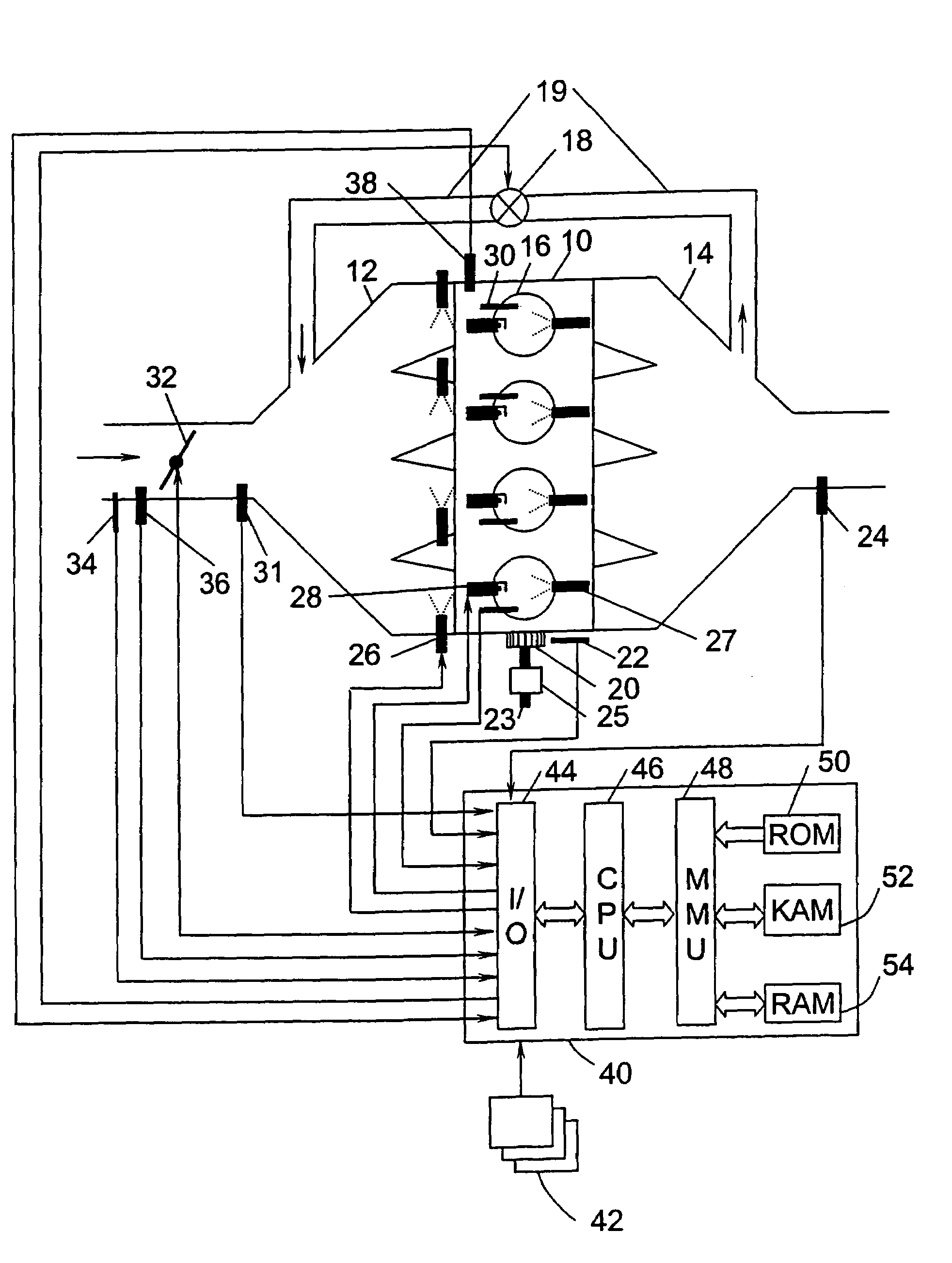
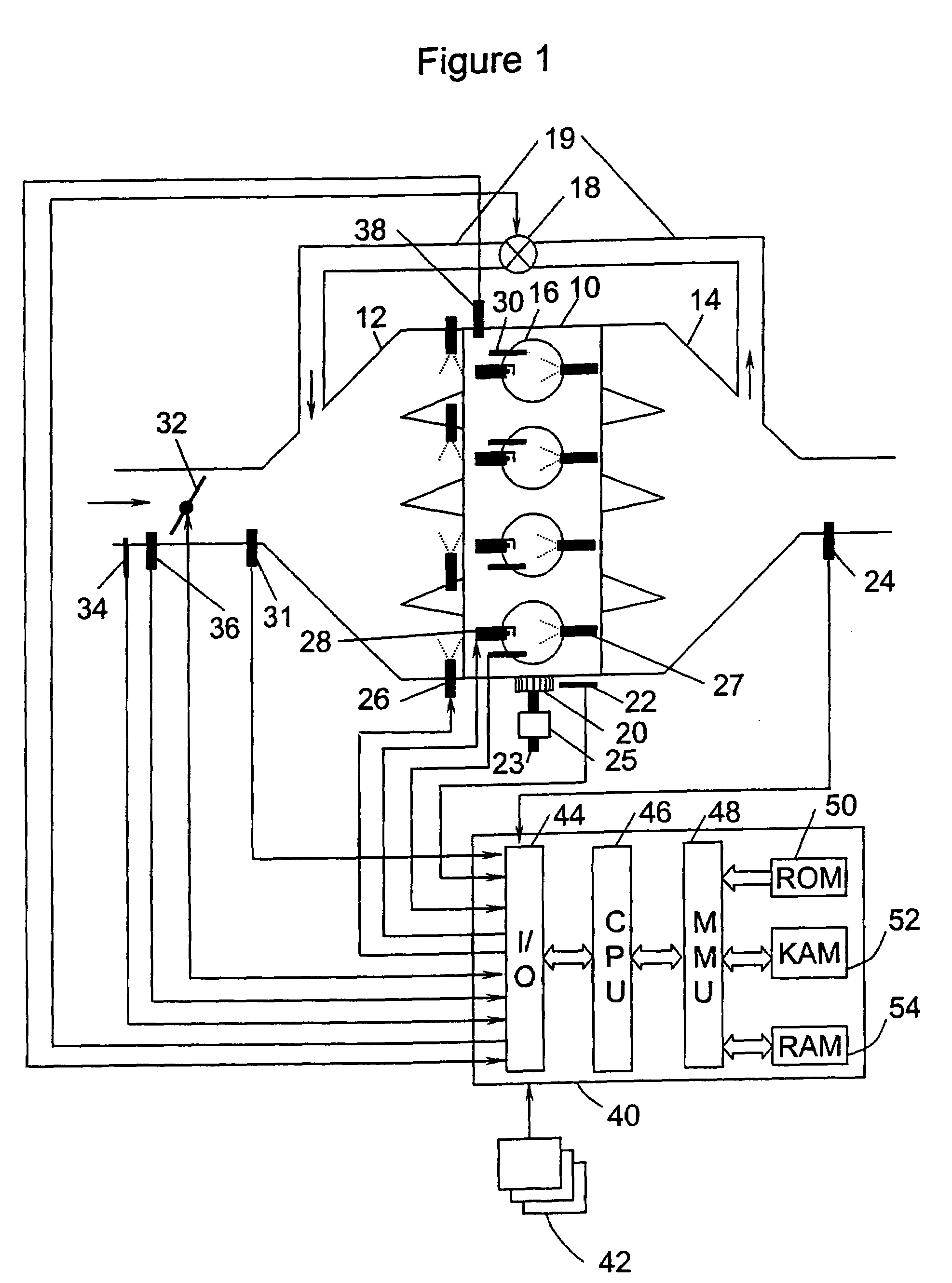
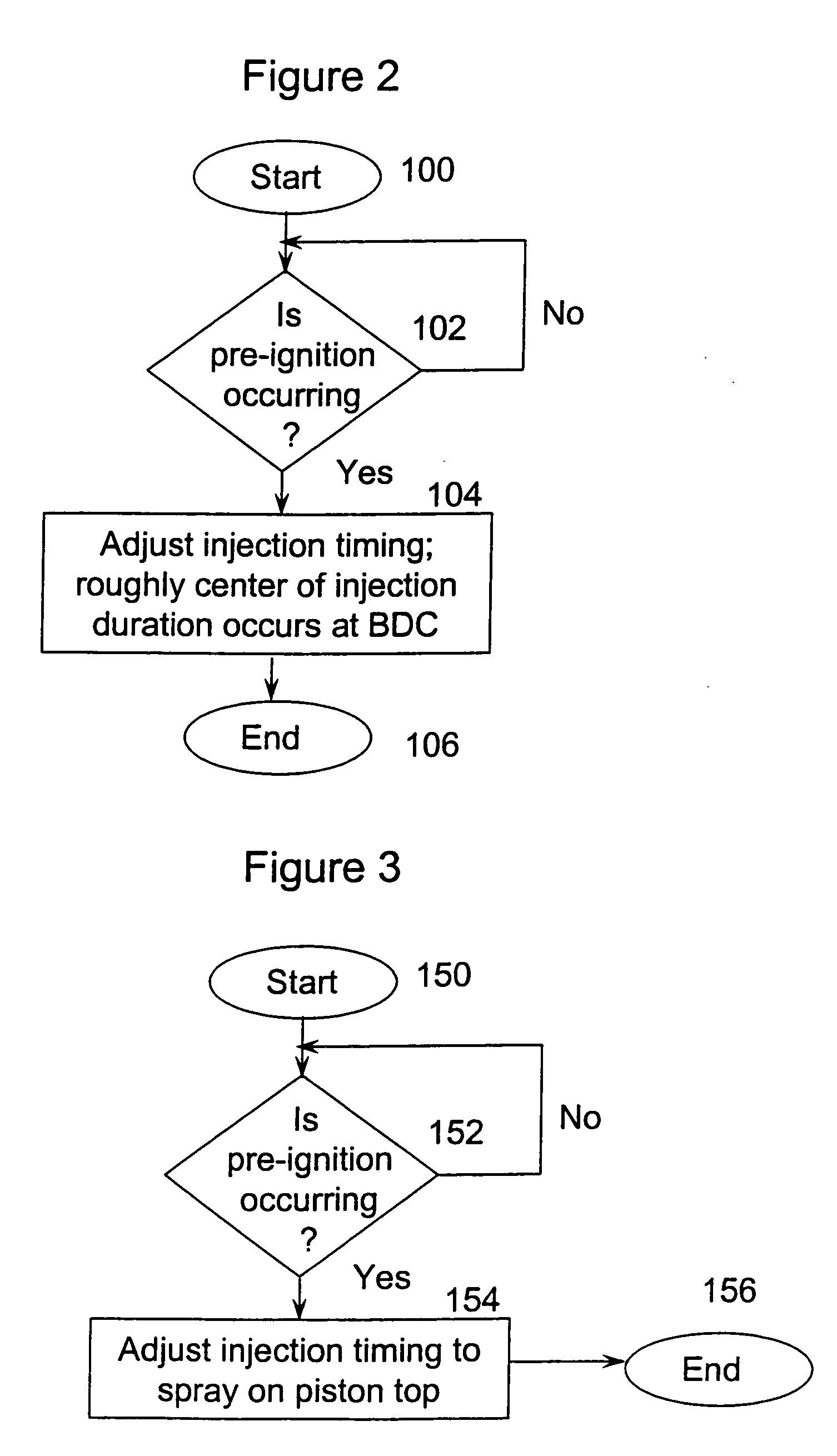
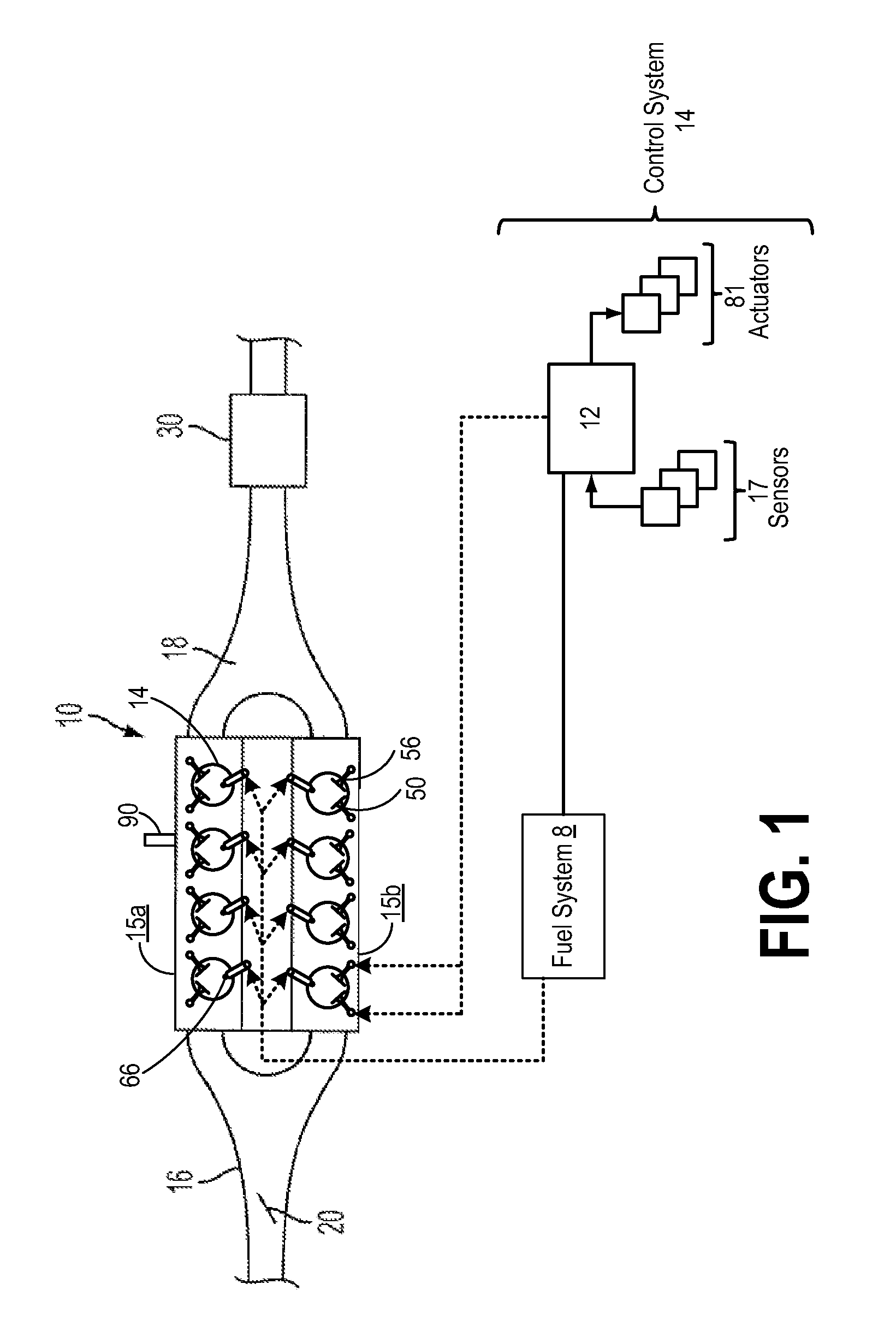
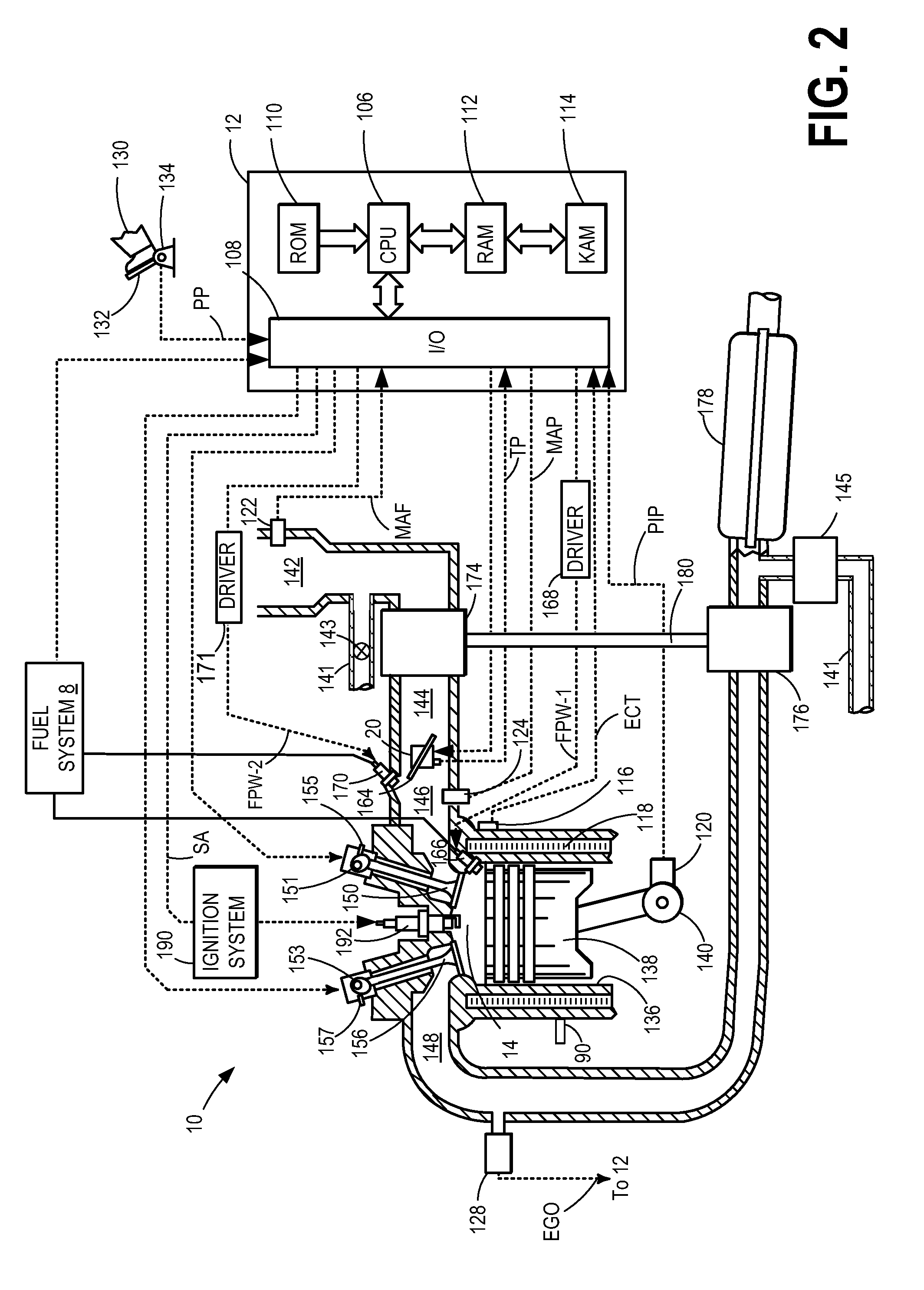
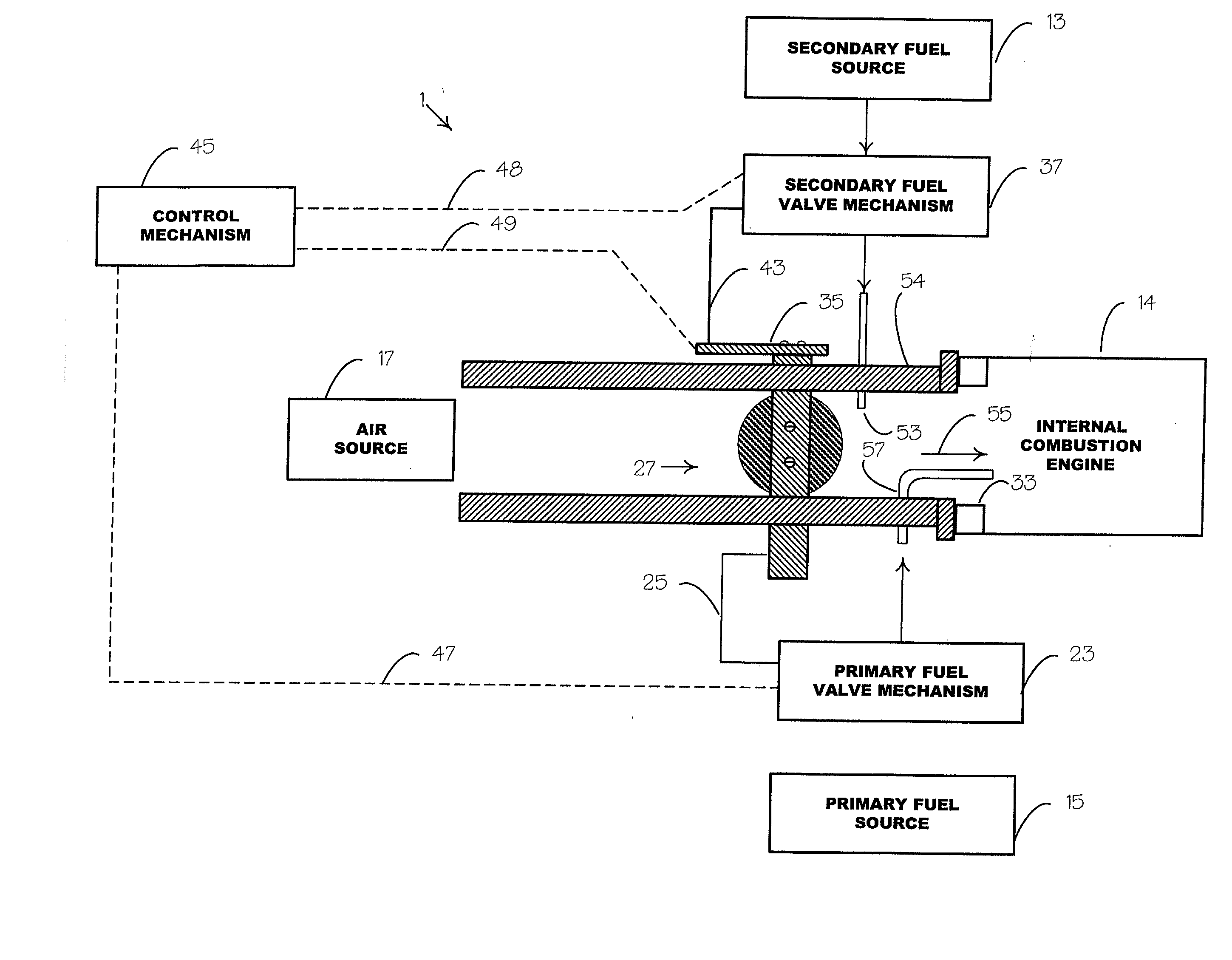
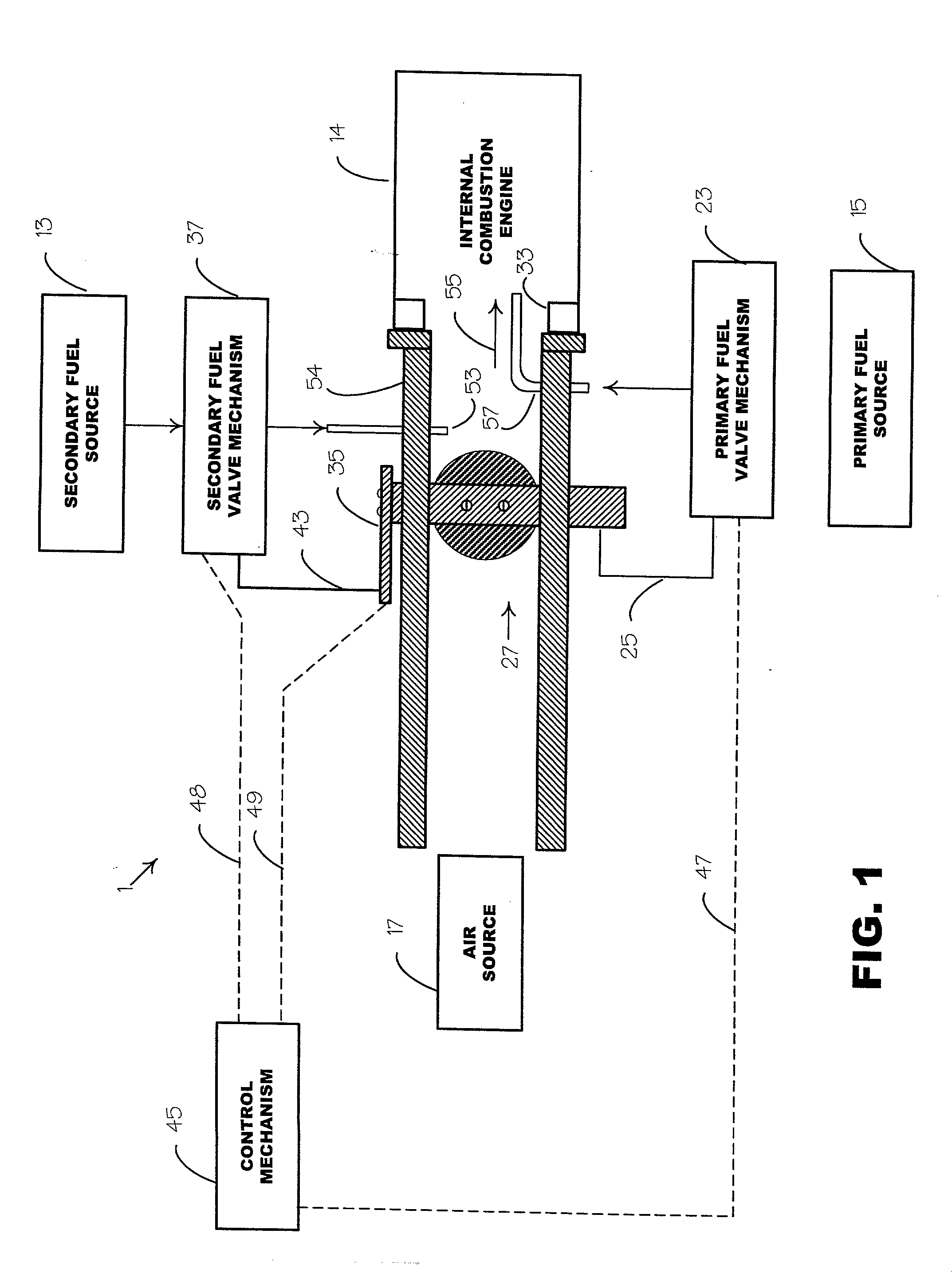
System and method to pre-ignition in an internal combustion engine
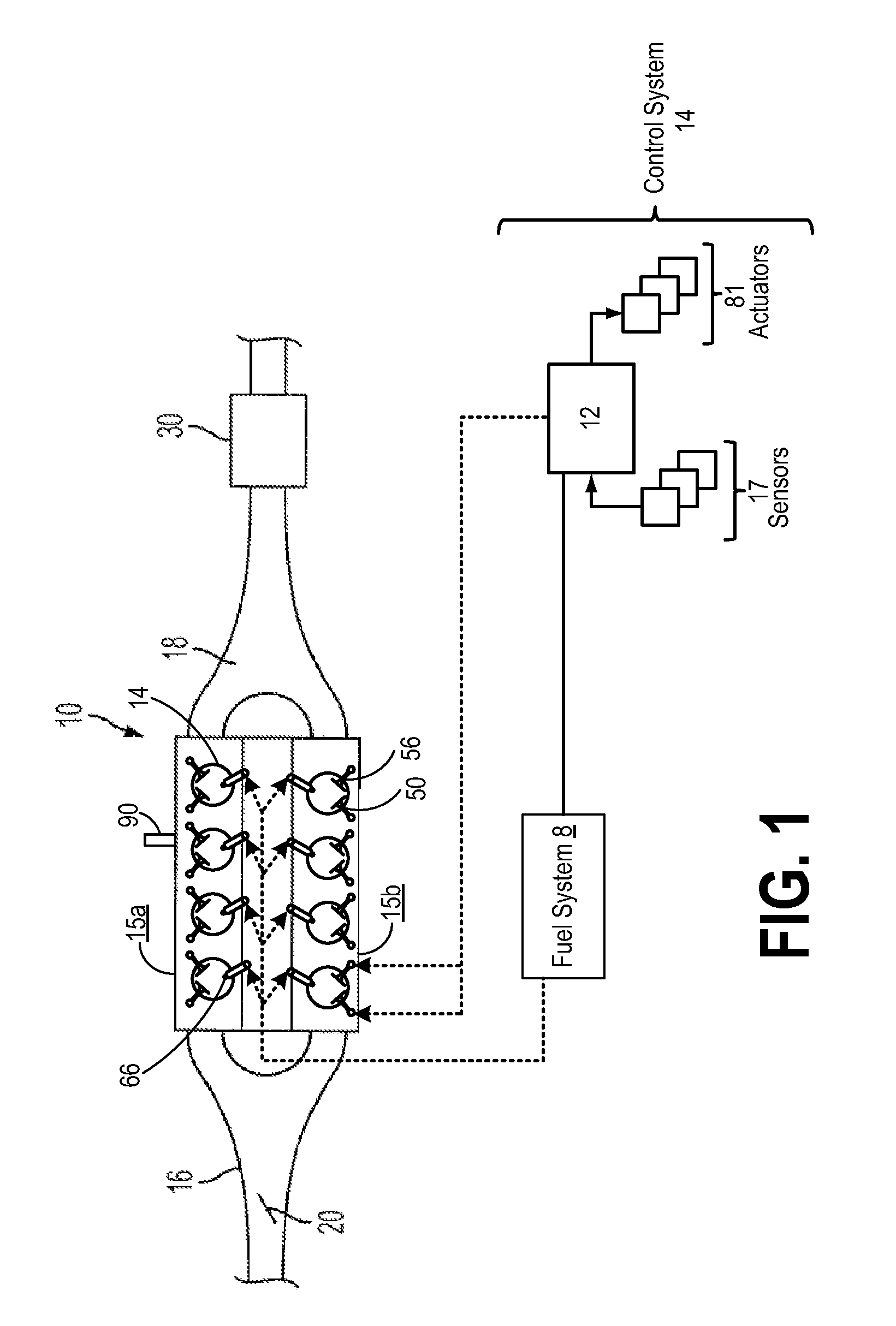
ActiveUS7178503B1Mitigate pre-ignitionReduce air densityAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustion chamberAlcohol fuel
An engine system and method are disclosed for controlling pre-ignition of an alcohol fuel. In one embodiment, the fuel injection timing is adjusted to cause the fuel to avoid combustion chamber surfaces. In another embodiment, the fuel injection timing is adjusted to spray the fuel directly onto the piston surface to cool the piston. Also disclosed is a cylinder cleaning cycle in which engine knock is purposely caused for one to hundreds of engine cycles by adjusting the fuel content away from alcohol toward gasoline. Further measures to cause knock which are disclosed: adjusting spark timing, intake boost, exhaust gas fraction in the cylinder, cam timing, and transmission gear ratio.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Internal combustion system using acetylene fuel
InactiveUS6076487AInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCarbon chainInternal combustion engine
An environmentally clean dual fuel for an internal combustion engine, comprising acetylene as a primary fuel and a combustible fuel, such as one or more fluids selected from an alcohol such as ethanol, methanol or any other alcohol or alcohols from the group comprising C1-C20 carbon chains, ethers such as from the group comprising dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, methyl t-butyl ether, ethyl t-butyl ether, t-amyl methyl ether, di-isopropyl ether and the like, low-molecular-weight esters such as from the group comprising methyl formate, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, methyl propionate, ethyl propionate and the like, or other suitable combustible fluid such as mineral spirits and the like, as a secondary fuel for operatively preventing early ignition and knock arising from the primary fuel. The dual fuel, internal combustion system, which generally utilizes a two-stage process for start-up and operation and can be operated with air- or liquid-cooling, is environmentally clean with hydrocarbon, CO, NOx, and SOx emissions substantially eliminated.
Owner:GOTEC
Method and system of transient control for homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engines
InactiveUS20100031924A1Reduce computing loadRobust engine controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesApplying knowledgeHcci combustion
A HCCI engine with a model reference adaptive feedback control system maintains stable HCCI combustion during speed / load transitions by: (1) estimating the maximum rate of pressure rise (MRPR), for each cycle, from an extra-cylinder sensor metric, such as a crankshaft dynamics or knock sensor metric, via statistical vector-to-vector correlation; (2) periodically self-tuning the vector-to-vector correlation; (3) applying knowledge base models to guide cycle-to-cycle adjustments of fuel quantity and other engine parameters, to maintain a target MRPR value.
Owner:U S ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE
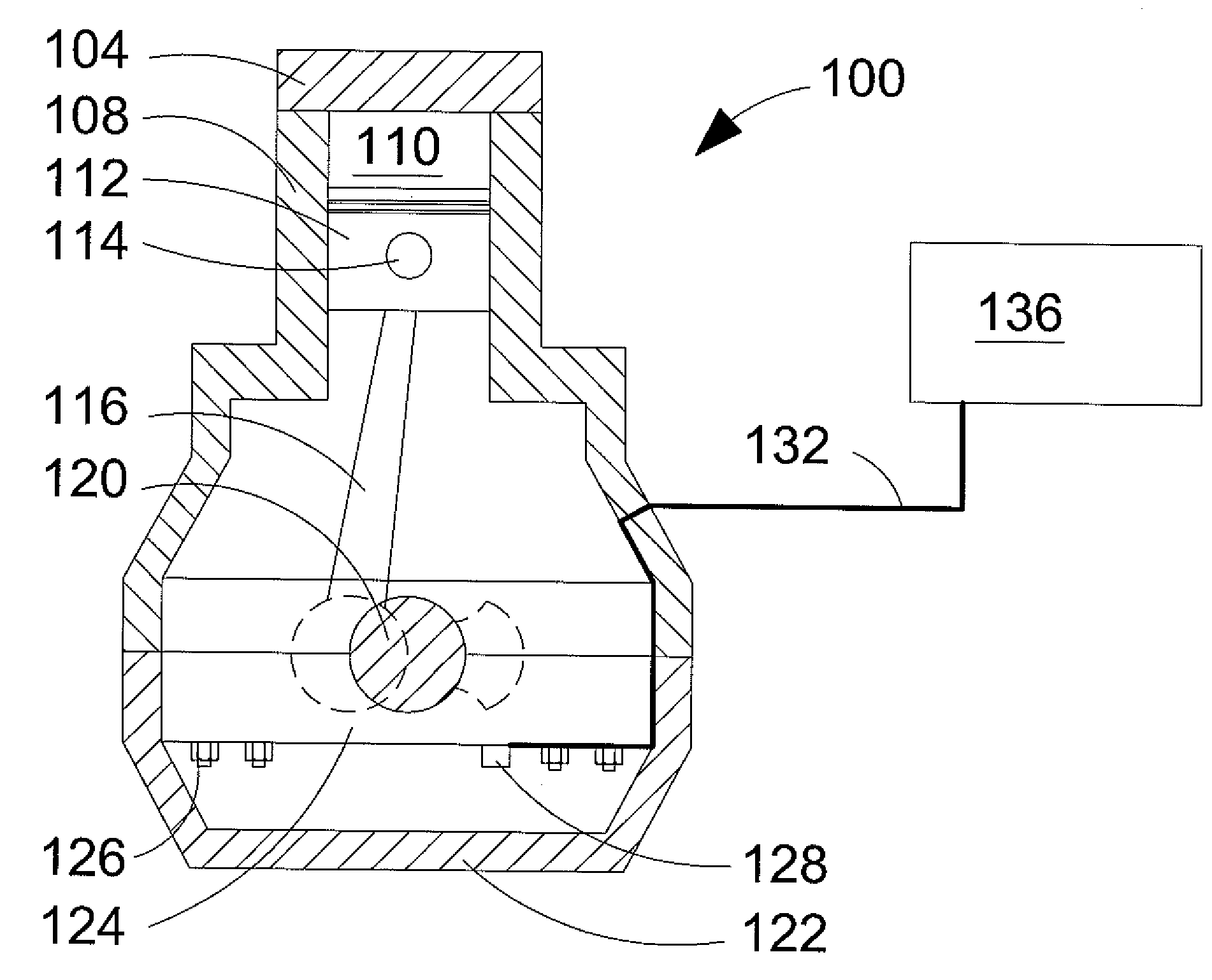
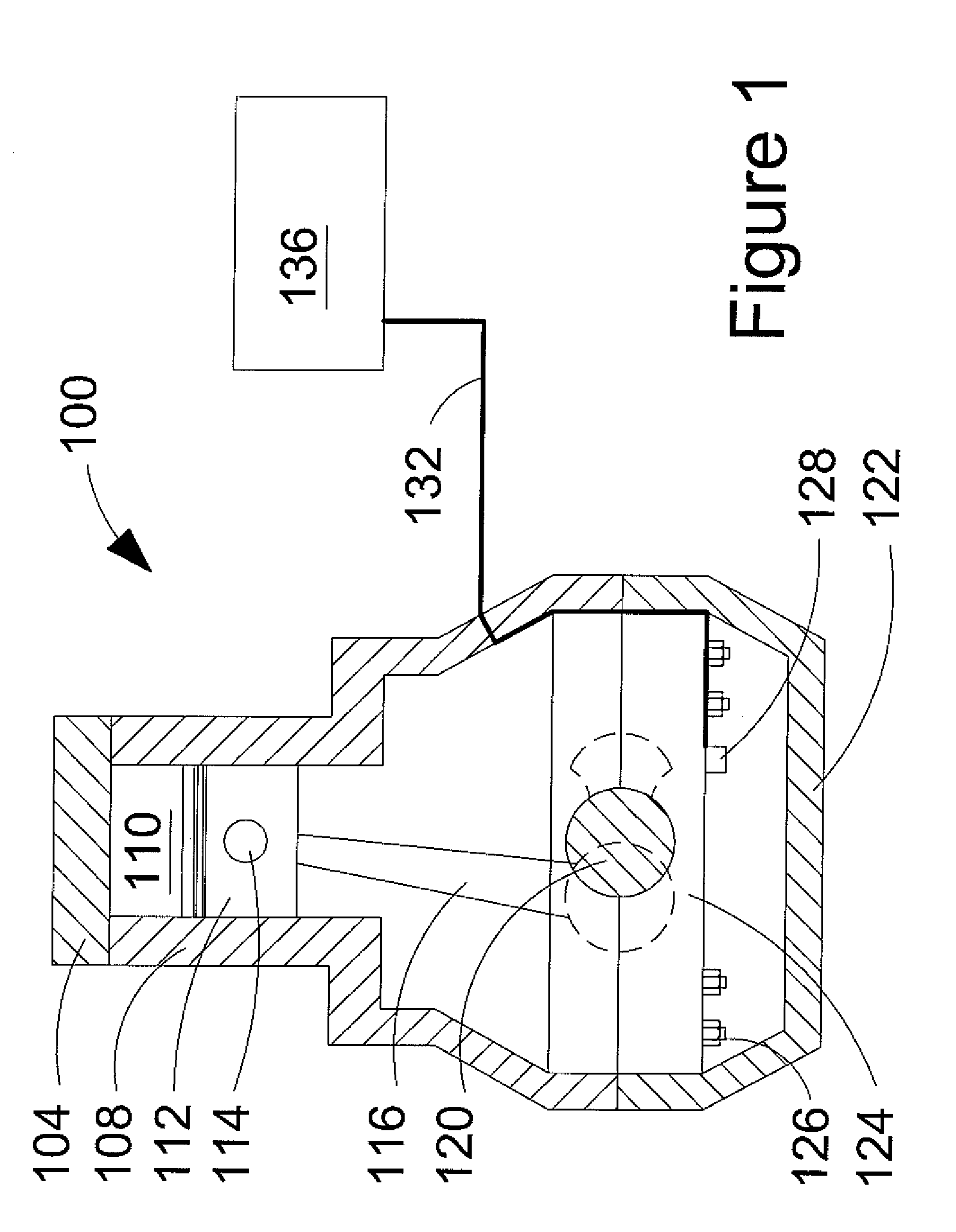
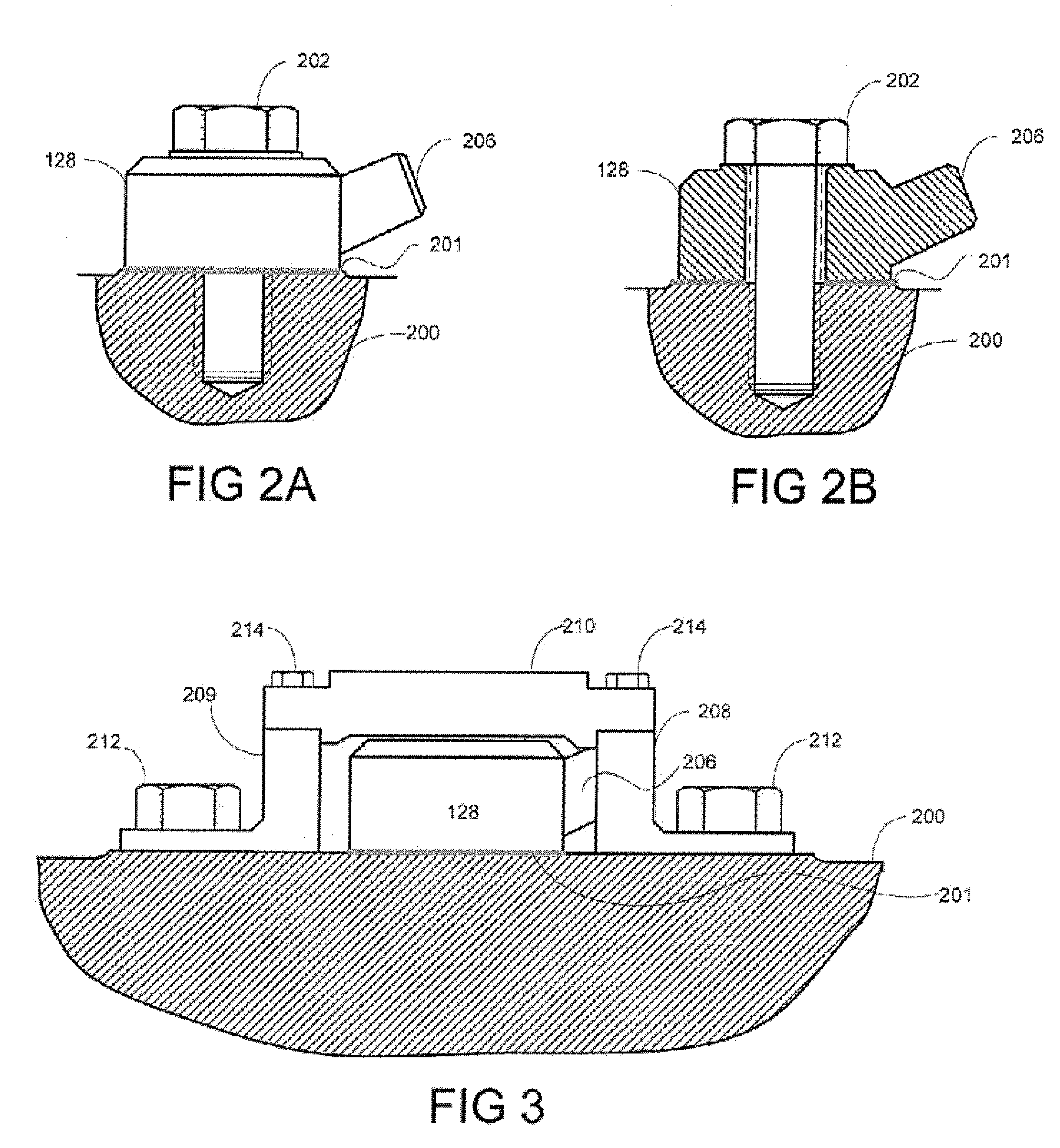
Method of mounting an accelerometer on an internal combustion engine and increasing signal-to-noise ratio
ActiveUS20080035108A1Increases signal output 's signal-to-noise ratioRaise the ratioAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal-combustion engine testingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Accelerometer
A method of mounting an accelerometer to an internal combustion engine comprises securing the accelerometer to a mating surface on an engine component external to a combustion chamber where the accelerometer can generate a signal output that is characteristic of engine knock, when it occurs, and at least one other combustion behavior inside the combustion chamber during a combustion event. The method further comprises connecting a signal wire at one end to the accelerometer and at an opposite end to a signal processor, and increasing the signal output's signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
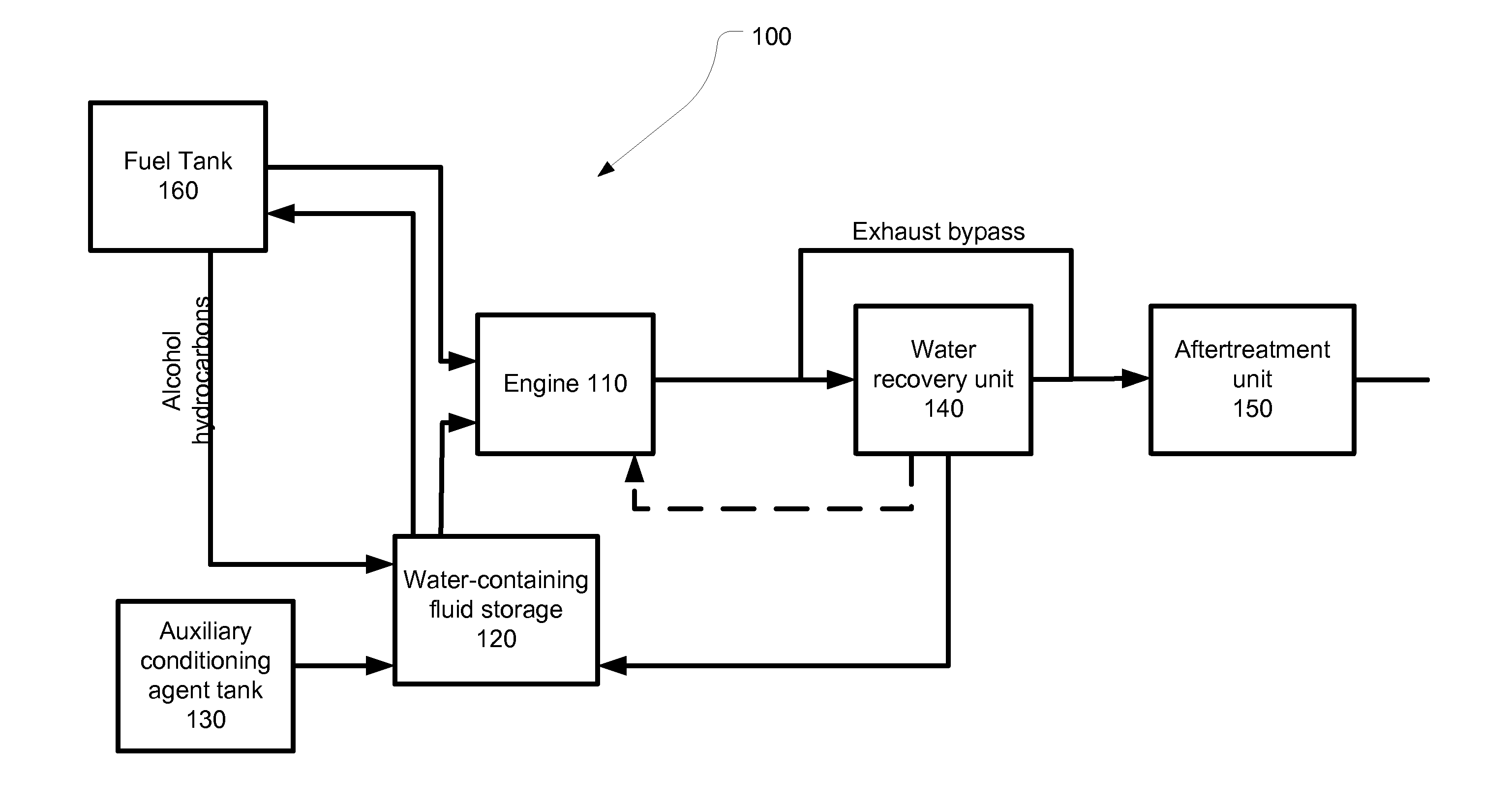
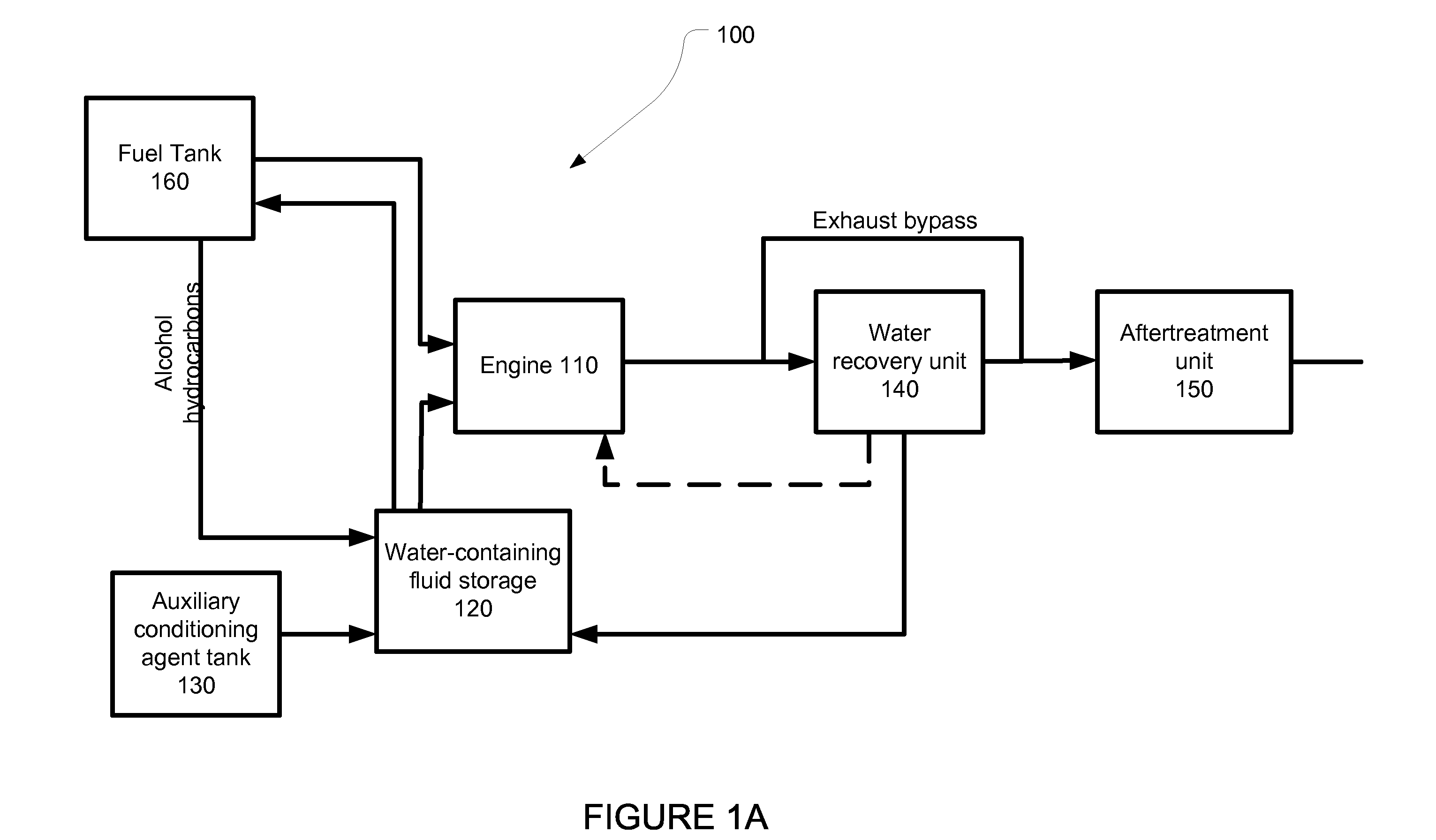
System for Variable Blending Of Ethanol And Exhaust Water For Use As An Anti-Knock Agent
InactiveUS20110168128A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHybrid systemWater source
The present application describes systems for water retrieval from the engine exhaust. This collected water can be used both for removing ethanol from ethanol-gasoline blends, and for use as a knock suppressant. The water that is removed from the exhaust can be used as the only source of water or in combination with water that is externally supplied. The present application also describes new means for removal of water from the exhaust that can be employed for applications. In some embodiments, an auto-heat exchanger is employed to recover water from the engine exhaust.
Owner:ETHANOL BOOSTING SYST LLC
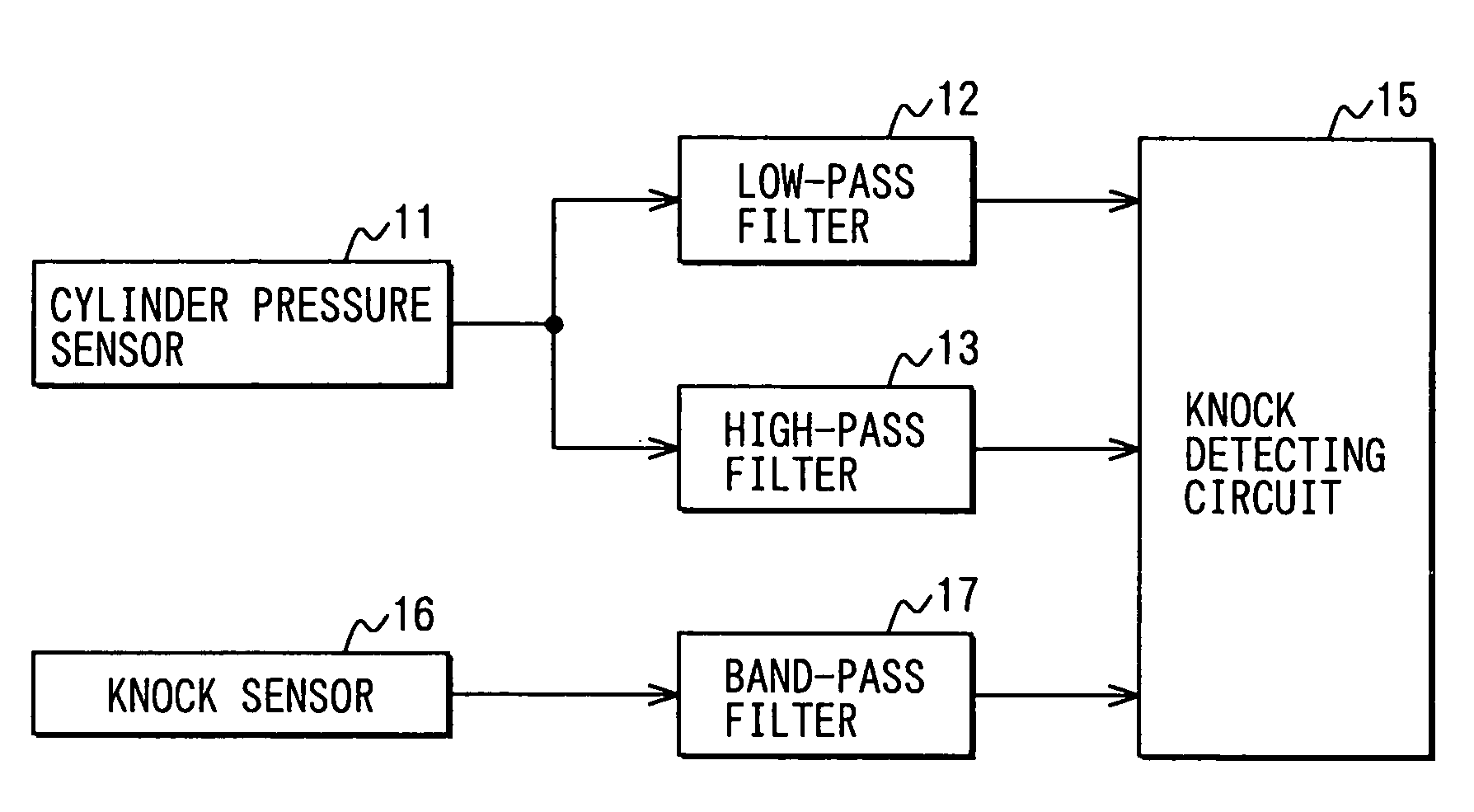
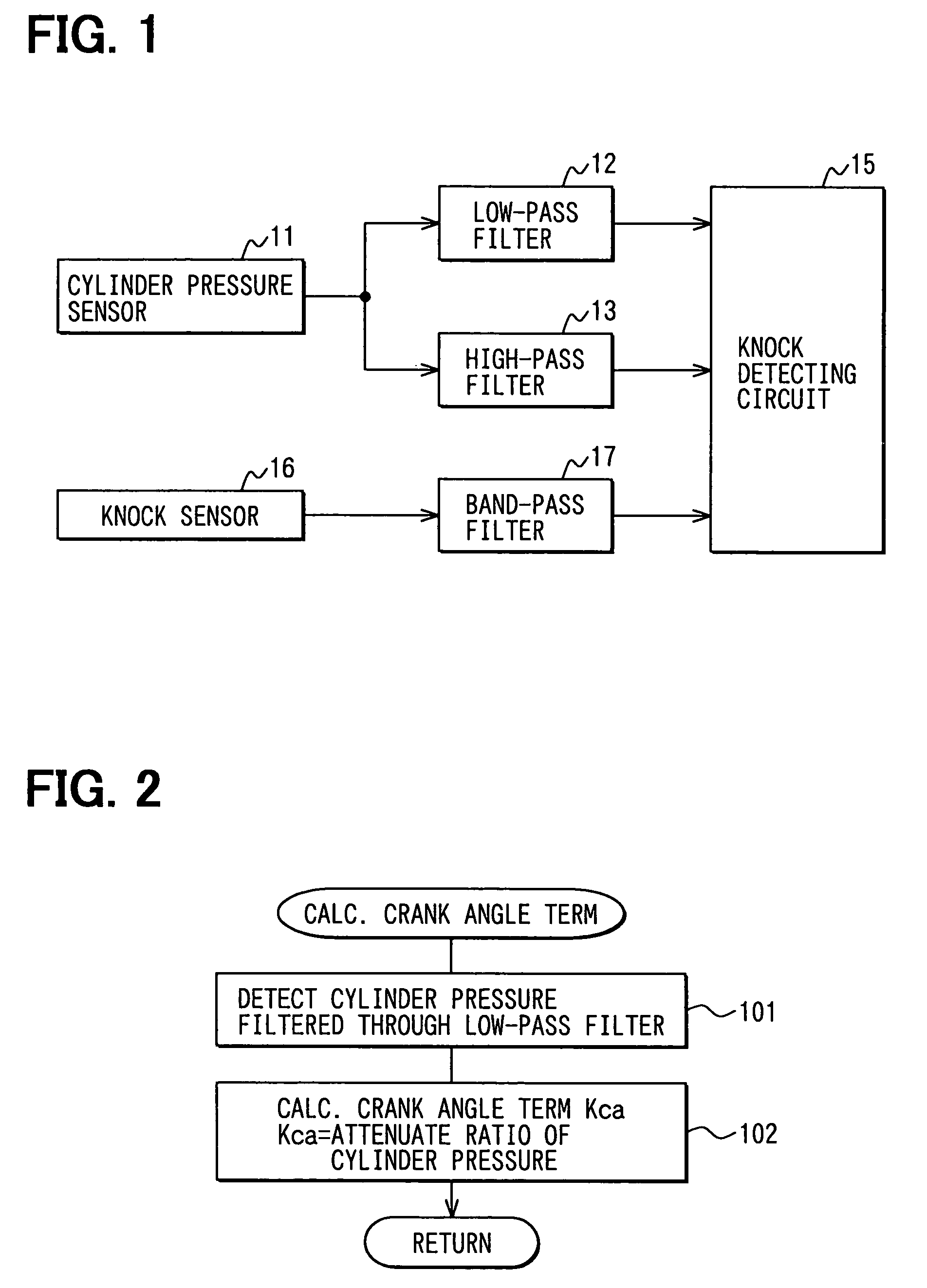
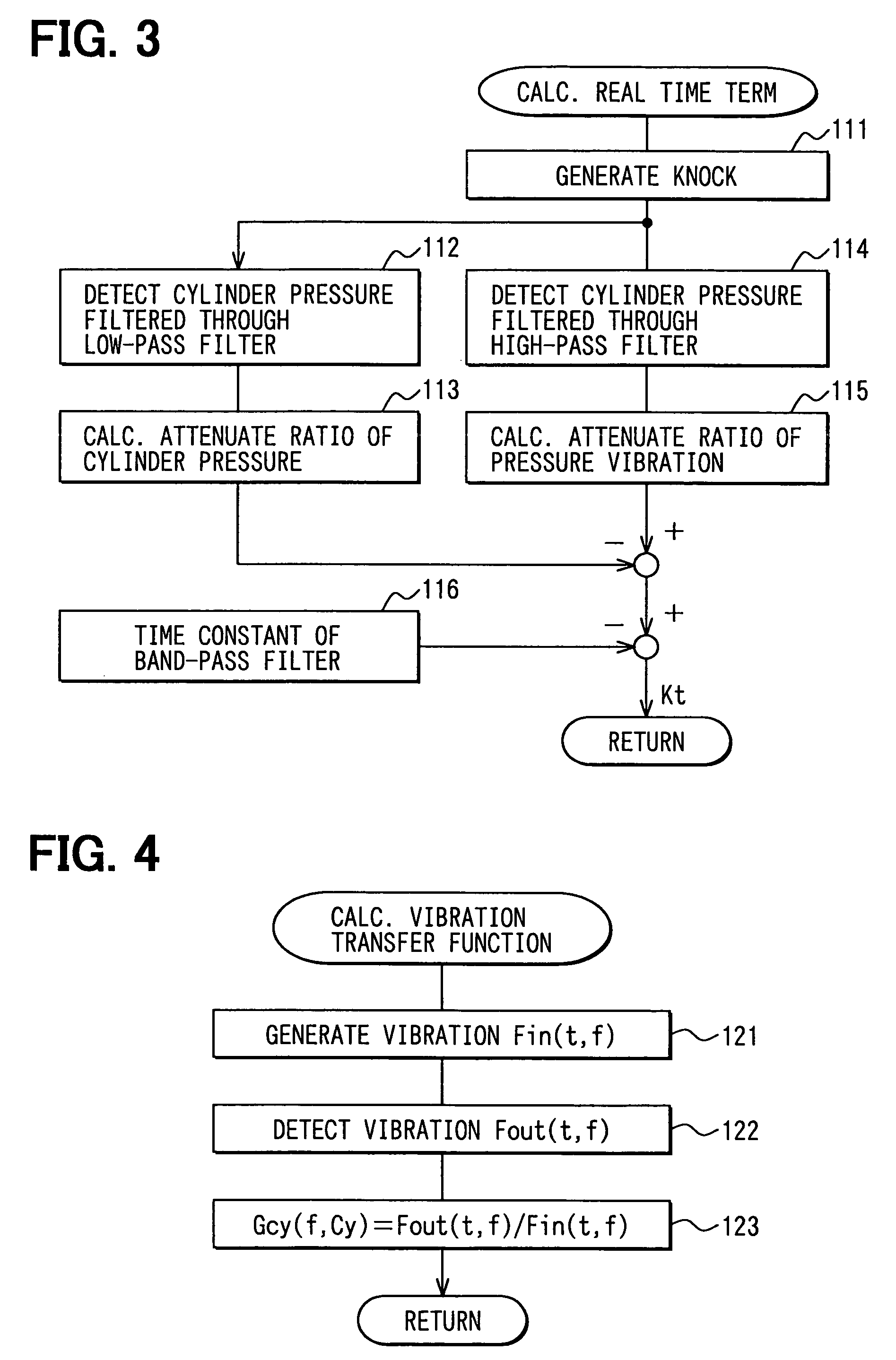
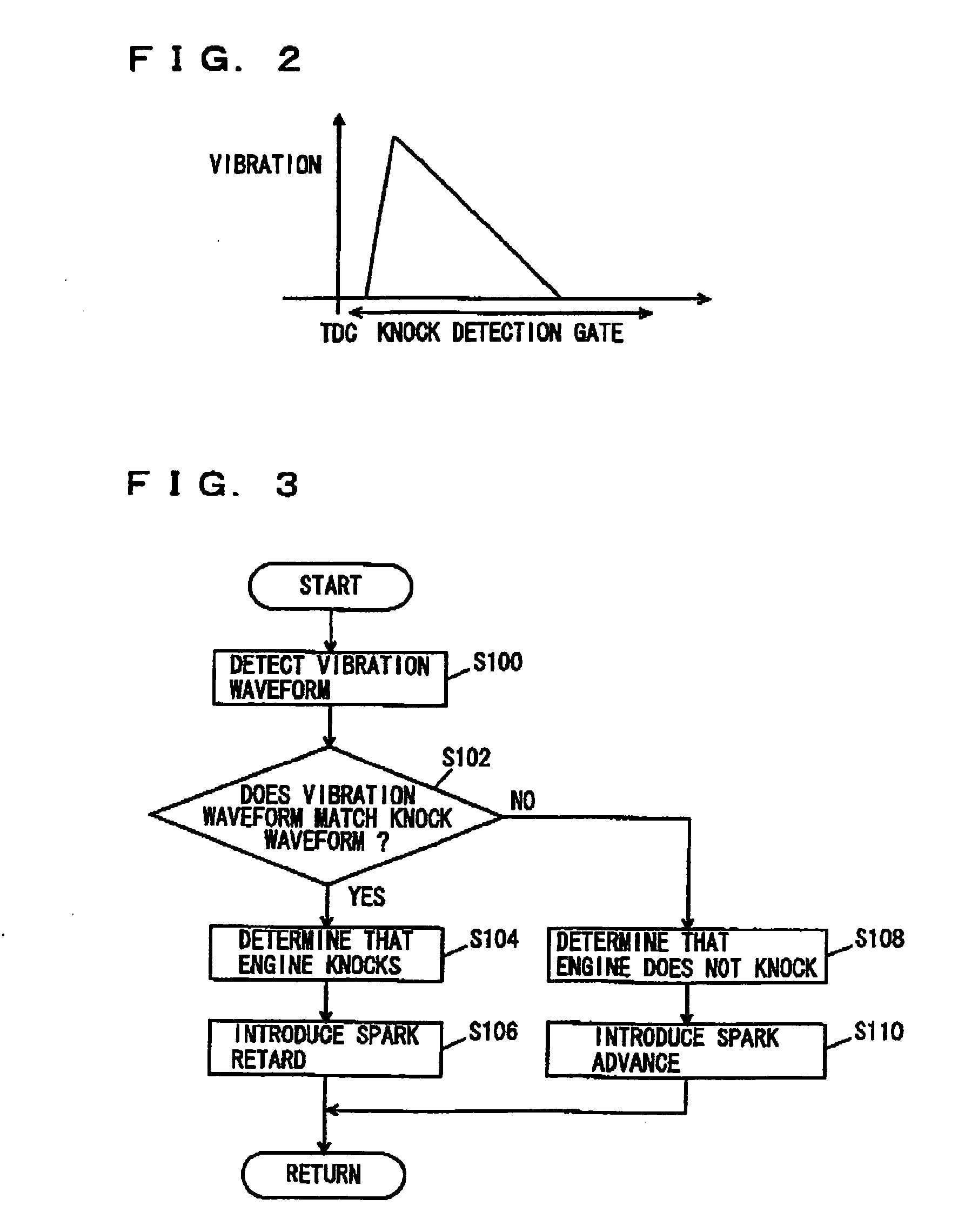
Knock detecting apparatus for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7243529B2Accurate detectionElectrical controlSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCombustion chamberWave form
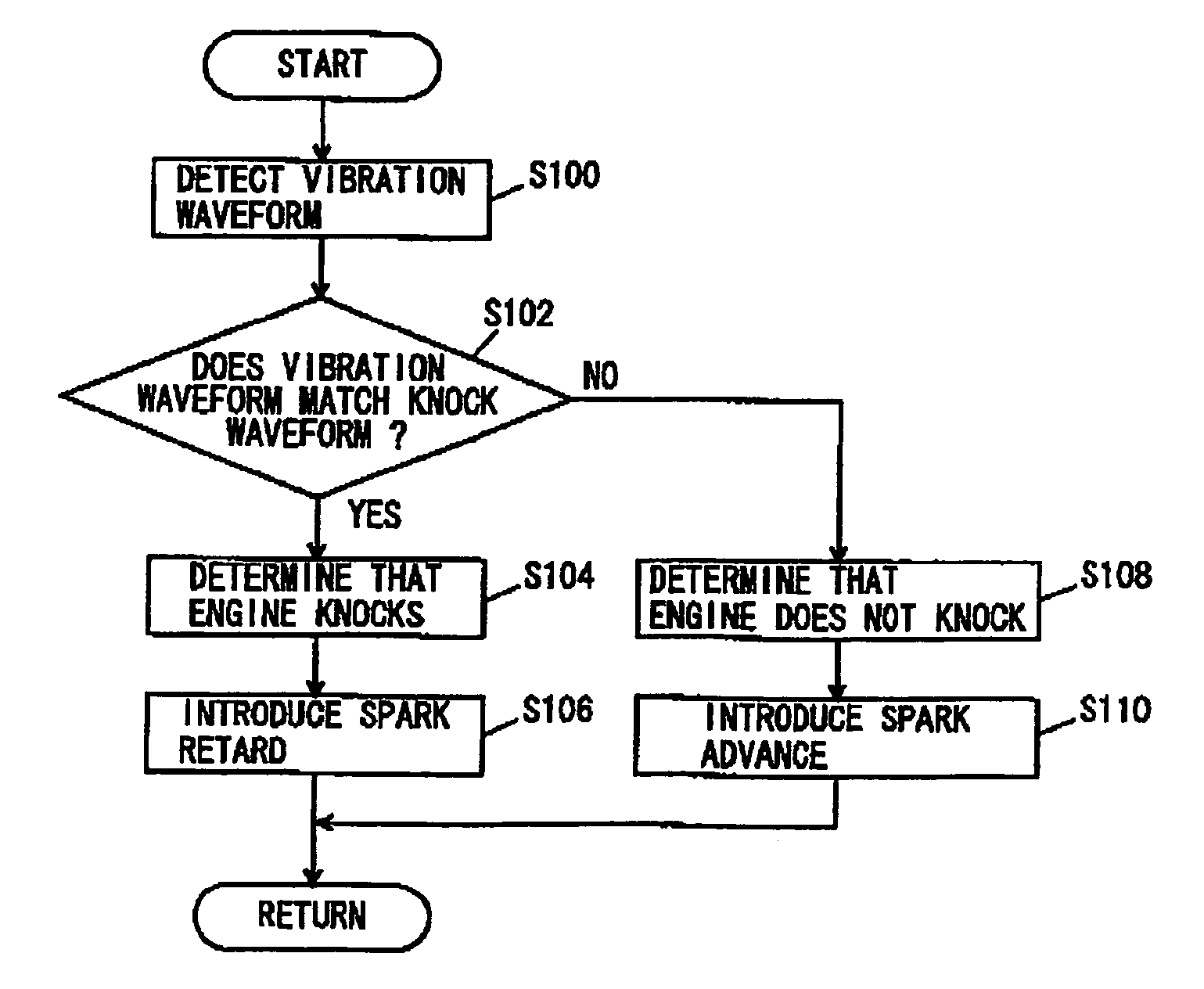
A waveform knock signal detected by a knock sensor is filtered through a band-pass filter. The detected wave form signal is compared with an ideal reference knock waveform to determine an engine knock. The ideal reference knock waveform is derived on the basis of a factor depending on a crank angle, a factor depending on a real time and a factor depending on an engine construction. The factor depending on the real time is calculated based on an energy loss in a combustion chamber and a time constant of the band-pass filter. The factor depending on the engine construction is calculated based on a knock vibration which is generated in a cylinder, transferred to a cylinder block and detected by the knock sensor.
Owner:50 TO TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Method of mounting an accelerometer on an internal combustion engine and increasing signal-to-noise ratio
ActiveUS7444231B2Raise the ratioReduce signal noiseInternal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesAccelerometerSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method of mounting an accelerometer to an internal combustion engine comprises securing the accelerometer to a mating surface on an engine component external to a combustion chamber where the accelerometer can generate a signal output that is characteristic of engine knock, when it occurs, and at least one other combustion behavior inside the combustion chamber during a combustion event. The method further comprises connecting a signal wire at one end to the accelerometer and at an opposite end to a signal processor, and increasing the signal output's signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
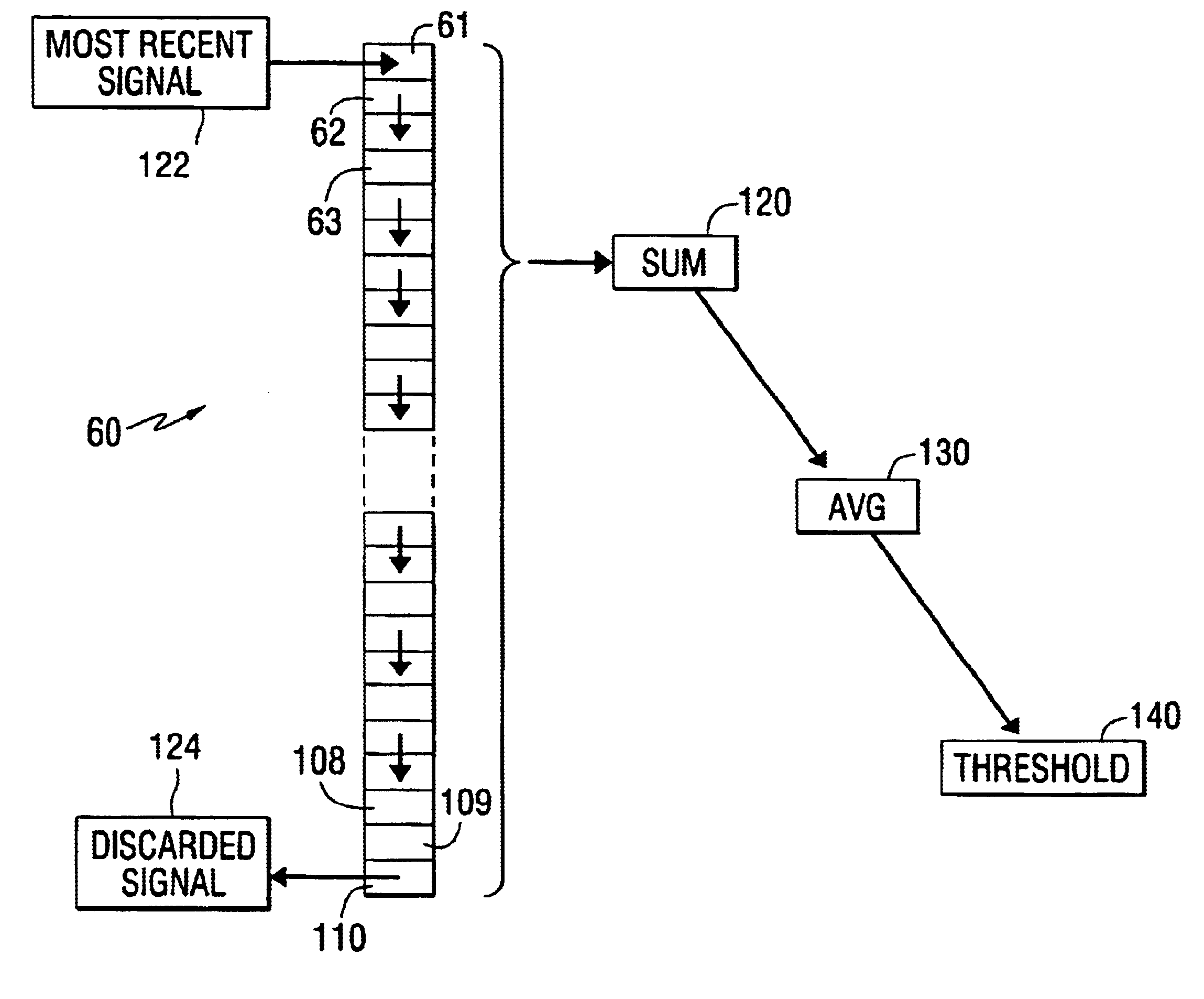
Method for detecting engine knock
InactiveUS6845312B1Simple stepsAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlAccelerometerComputer science
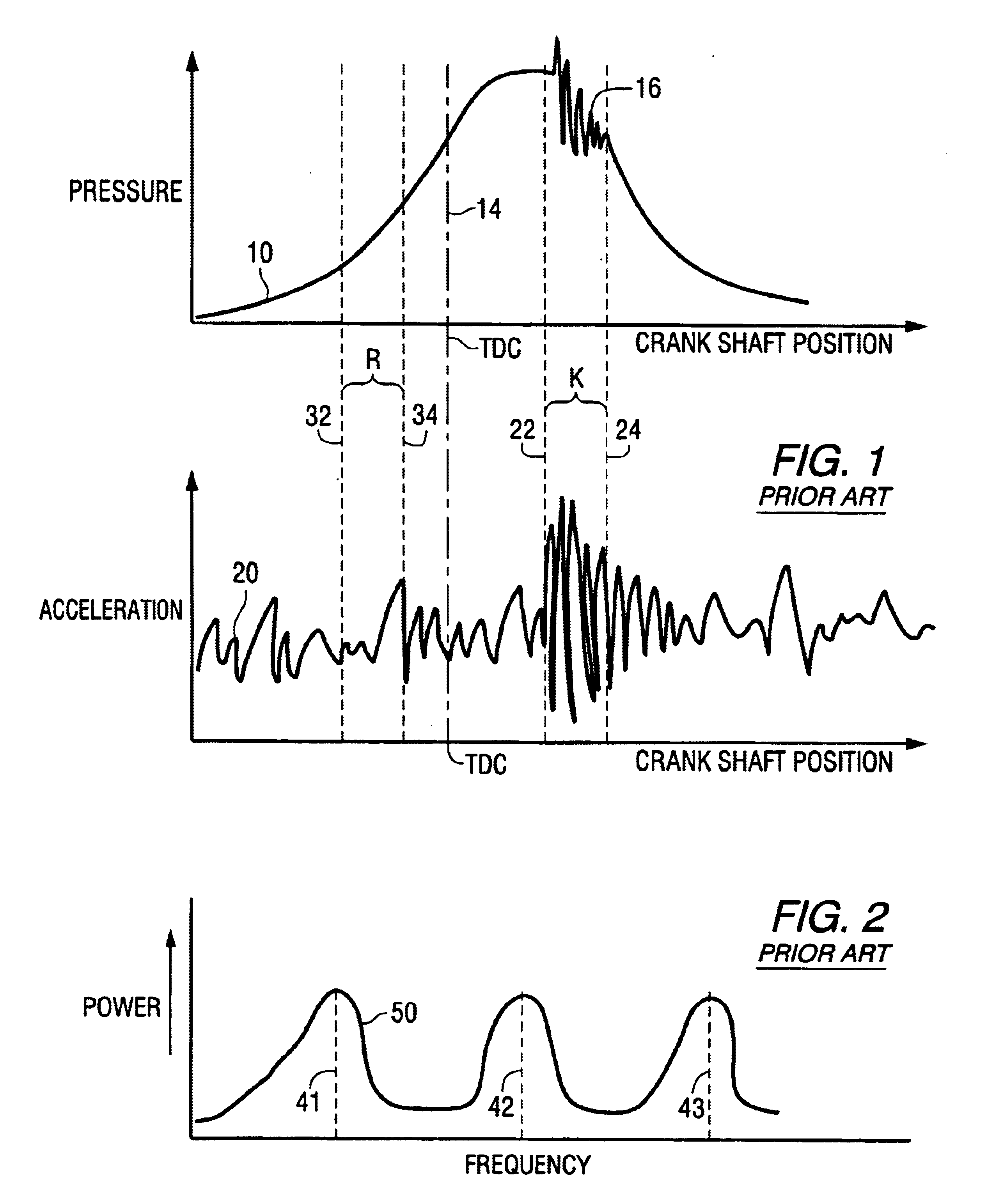
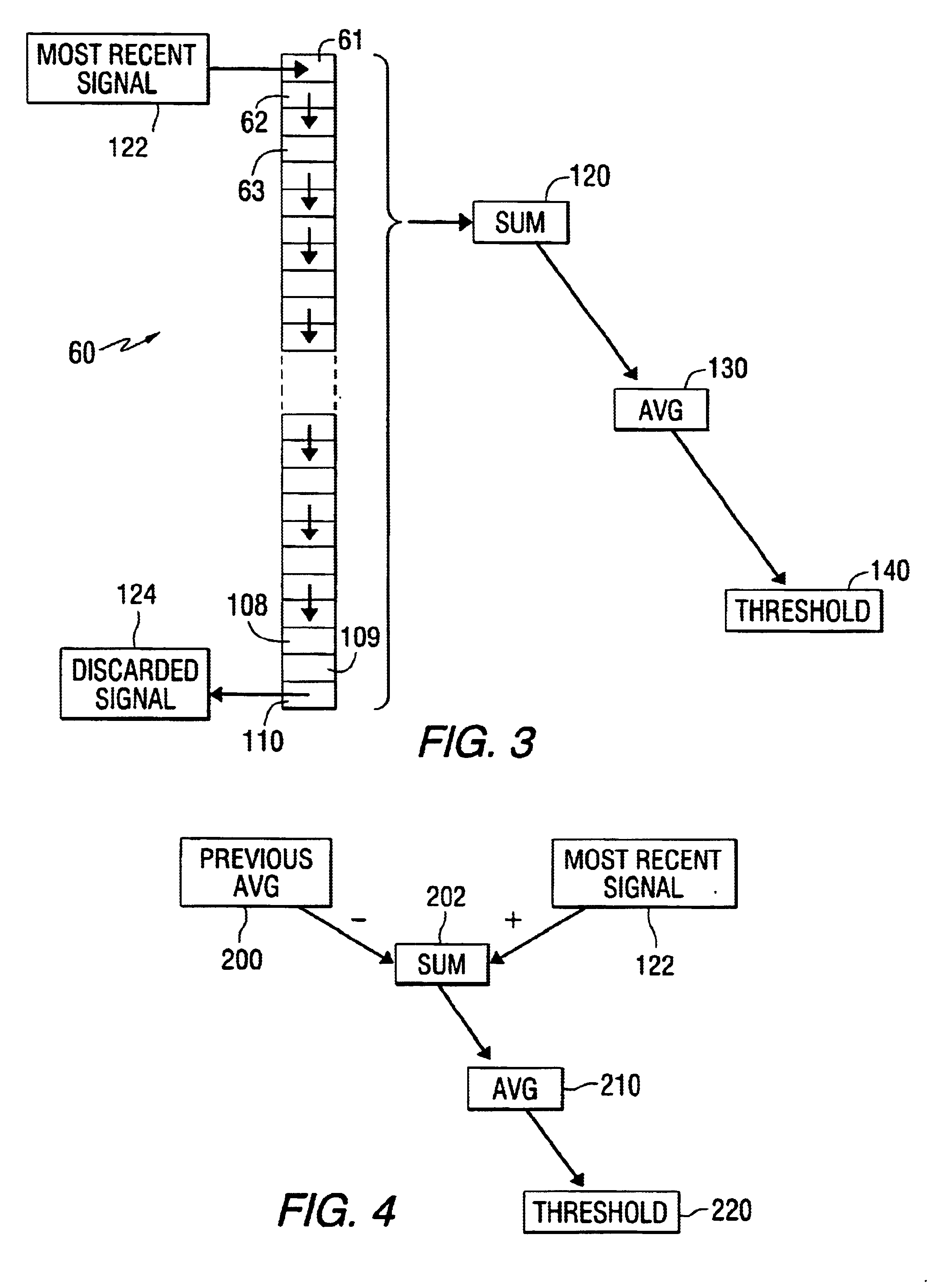
A method for processing knock-related data reduces the memory locations required for the method and also simplify the processing steps needed to determine a sum, average, and threshold value relating to magnitudes of knock ratios. Inputs from either pressure sensor or accelerometers are filtered and then used to form a ratio between a knock portion of a curve and a reference portion. Sequential magnitudes of the knock ratio are received and analyzed in a manner that reduces required memory locations and improves processing speed.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
If method and system for engine knock control
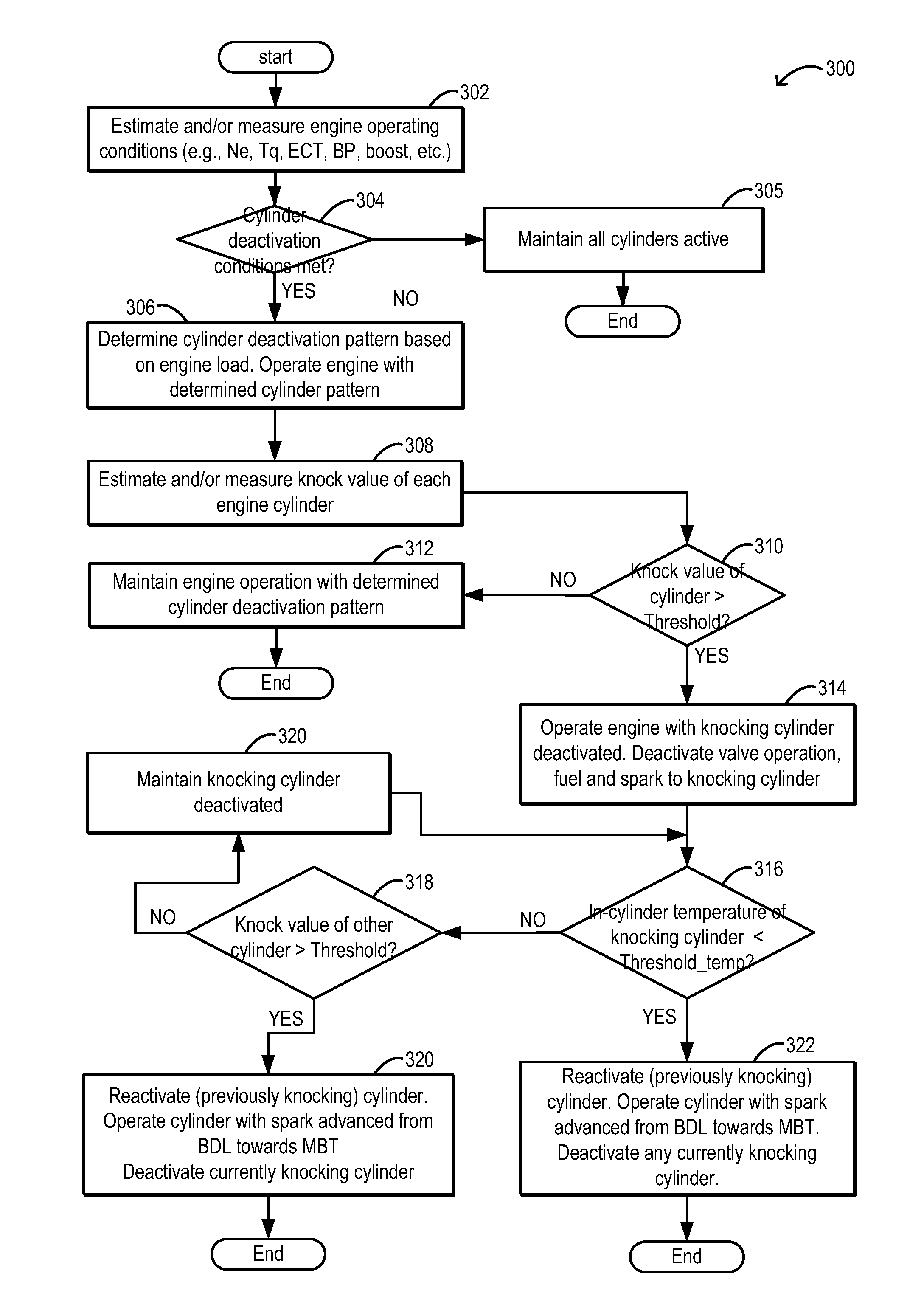
ActiveUS9506411B2Large tendency to knockImprove knockingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fuel on-site mixing and compressed ignition internal combustion engine and control method
InactiveCN101215996AWide adaptabilityExpand the range of working conditionsElectrical controlMachines/enginesMixed fuelPower performance
The invention provides a fuel field mixing compression ignition internal combustion engine and a control method thereof, in particular relates to fuel preparation, supply and combustion control of a combustion engine. The invention adopts a high-octane and high-cetane fuel field mixing and auxiliary ignition technology, and can meet the requirement that the internal combustion engine makes use of the fuel of different octane numbers under different loads, namely, more high-cetane fuel is mixed in the high-octane fuel under low load or ignition is assisted in, to improve the ignition property of the mixed fuel so that the mixed fuel can be fired reliably under low load and temperature with the firing time controllable. The quantity of high-cetane fuel to be mixed in is reduced under medium load; a signal high-octane fuel is adopted under large load to avoid engine detonation. By adopting the fuel field mixing compression ignition combustion mode, not only an even premixing compression ignition engine is prevented from being on fire under low load, but also the working condition range under large load can be widened. In addition, the power performance of the engine is improved. In this way, the even premixing compression ignition engine is practical.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Control device for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7246600B2Avoid knockingReduce smokeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
Owner:NIPPON SOKEN +1
If method and system for engine knock control
ActiveUS20160108828A1Large tendency to knockImprove knockingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMechanical engineeringEngine knocking
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
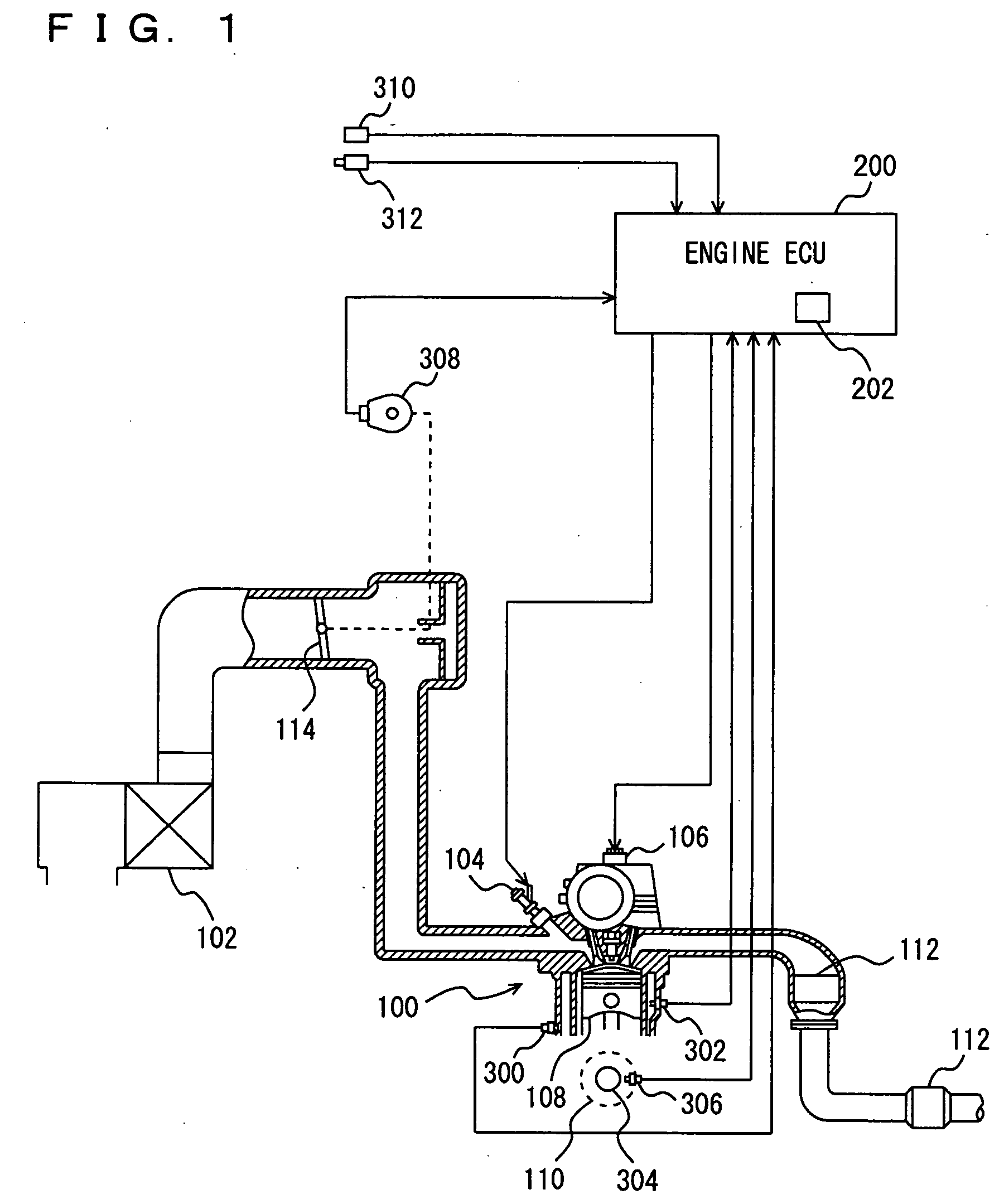
Knock determination device for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20060136117A1Improve accuracyAnalogue computers for vehiclesMachines/enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
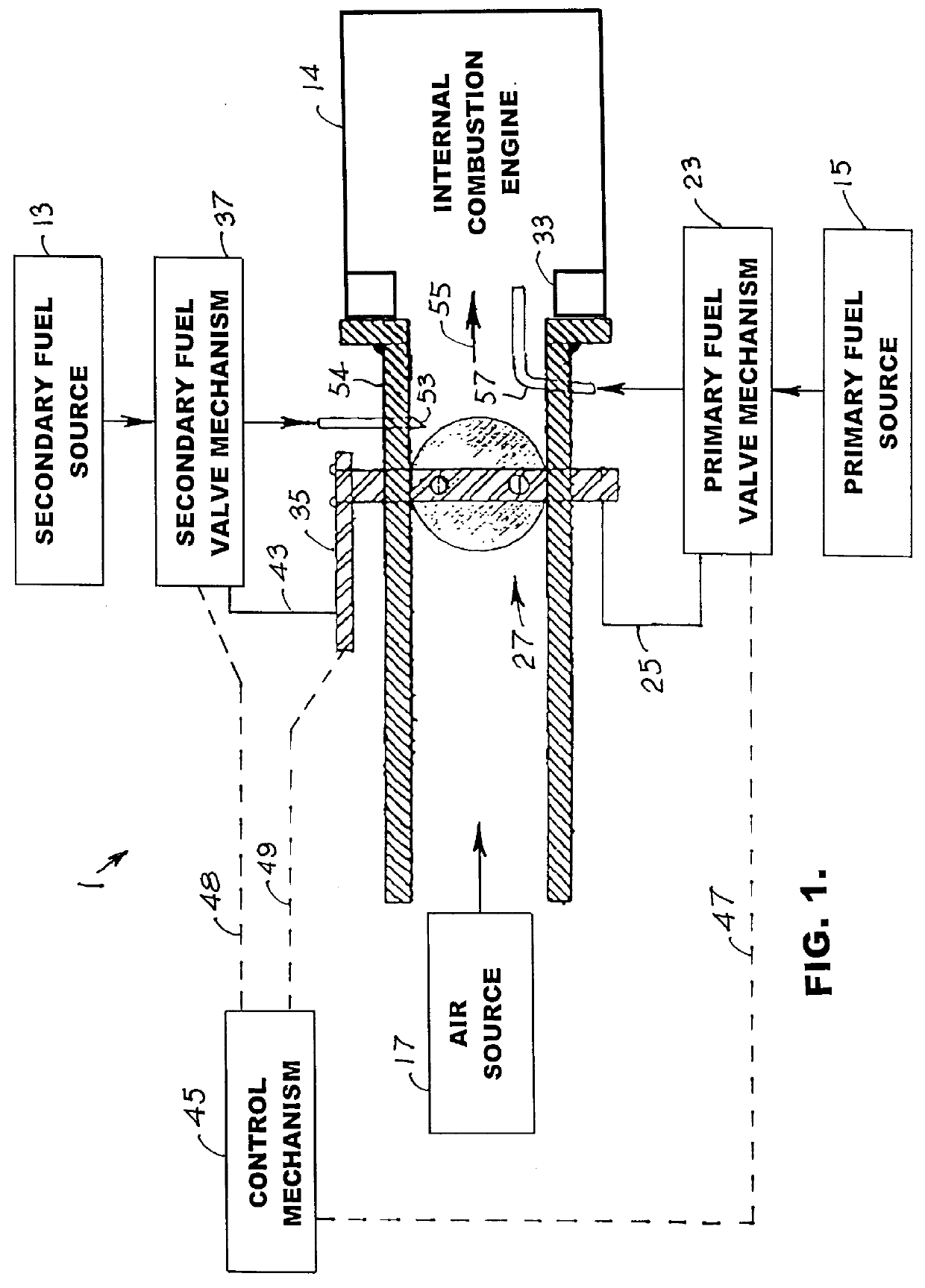
Process for use with dual-fuel systems
InactiveUS7387091B2Rapidly readjustReducing occurrence and duration and intensityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionDiesel engine
A system and method is provided to reduce the occurrence of engine knock for engines that utilize a dual-fuel fumigation system. Typically, dual fuel systems inject a gaseous-fuel flow into the air intake stream of a diesel engine. This results in more complete combustion within the engine as well as reduced diesel fuel usage. Such dual fuel systems are susceptible to engine knocking due to premature detonation of the gaseous fuel air intake mixture that is often caused by sudden changes to the operating conditions of the engine. The present system utilizes a knock sensor to identify early stages of such engine knocking. To eliminate such engine knocking conditions, the system temporarily interrupts the gaseous fuel flow to resume operation in full diesel mode. The gaseous fuel flow is then reestablished based on the present operating conditions of the engine.
Owner:TGI
Internal combustion system adapted for use of a dual fuel composition including acetylene
InactiveUS20020014226A1Early ignition be preventEfficient in operationInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelChemistryFormate Esters
An internal combustion engine adapted to use an environmentally clean multi-fuel composition, comprising acetylene as a primary fuel and a combustible fuel, such as one or more fluids selected from an alcohol such as ethanol, methanol or any other alcohol or alcohols from the group comprising C1-C12 carbon chains, ethers such as from the group comprising dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, methyl t-butyl ether, ethyl t-butyl ether, t-amyl methyl ether, di-isopropyl ether and the like, low-molecular-weight esters such as from the group comprising methyl formate, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, methyl propionate, ethyl propionate, ethyl malate, butyl malate, and the like, or other suitable combustible fluid such as mineral spirits and the like, as a secondary fuel for operatively preventing early ignition and knock arising from the primary fuel.
Owner:GOTEC
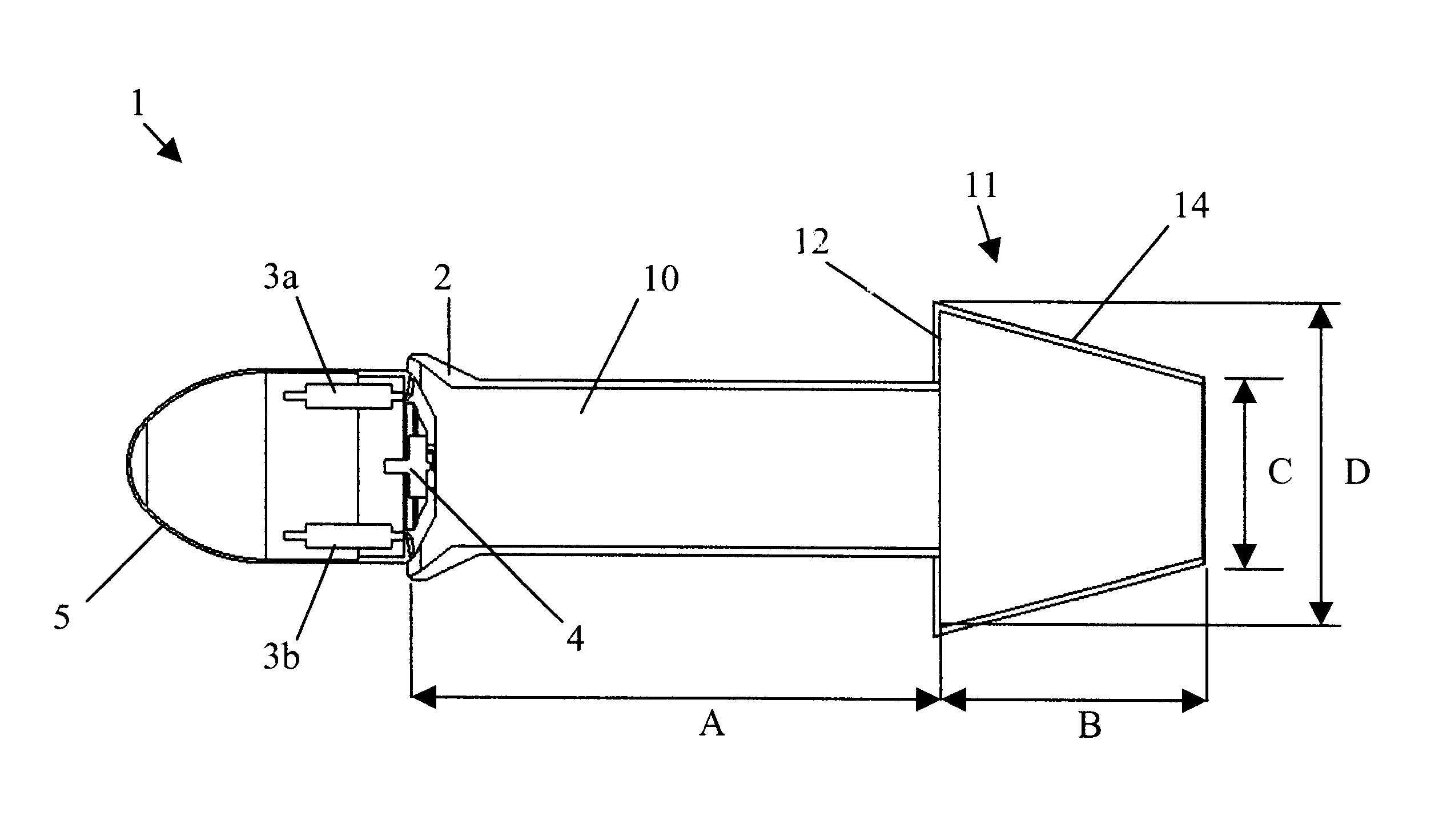
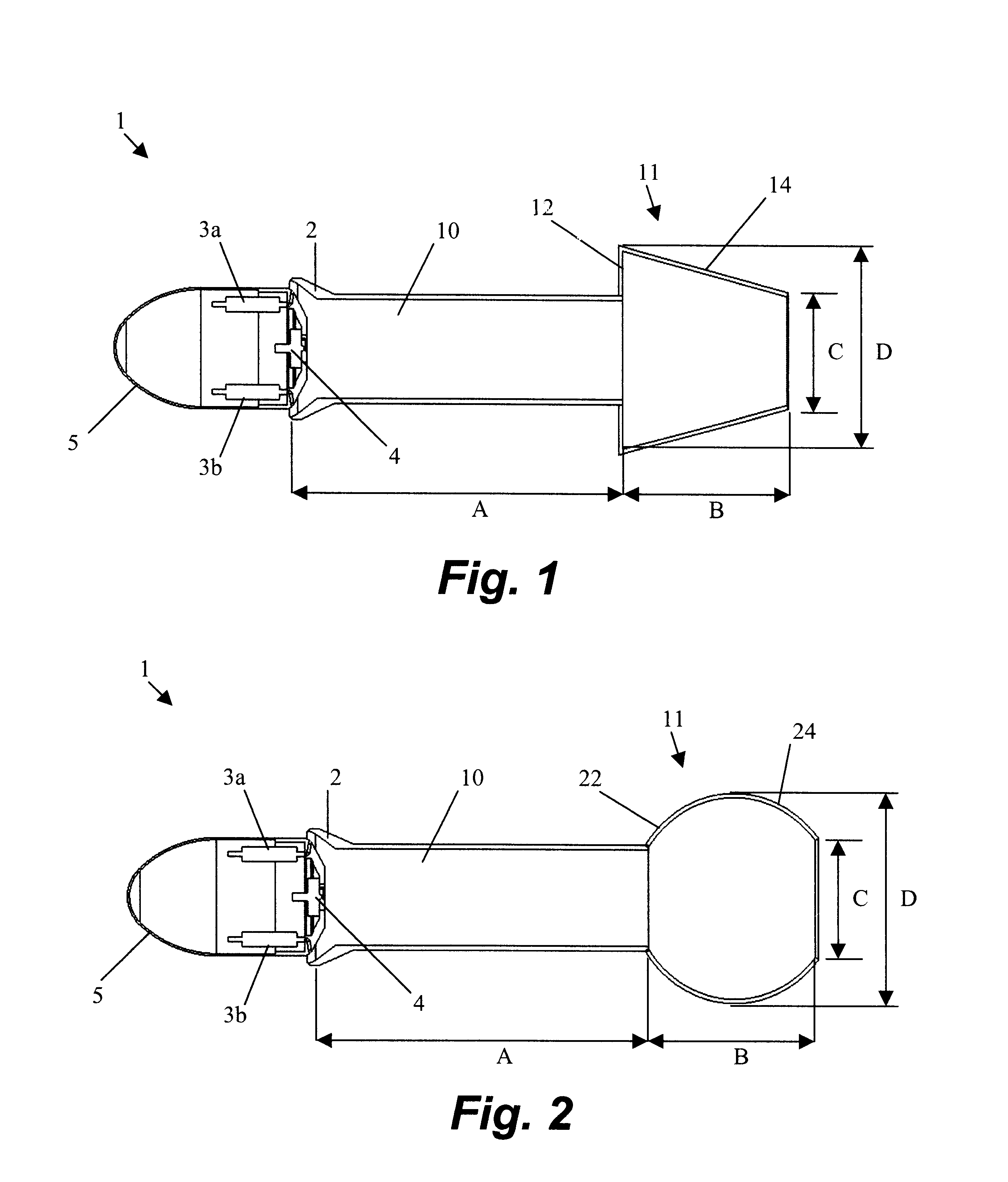
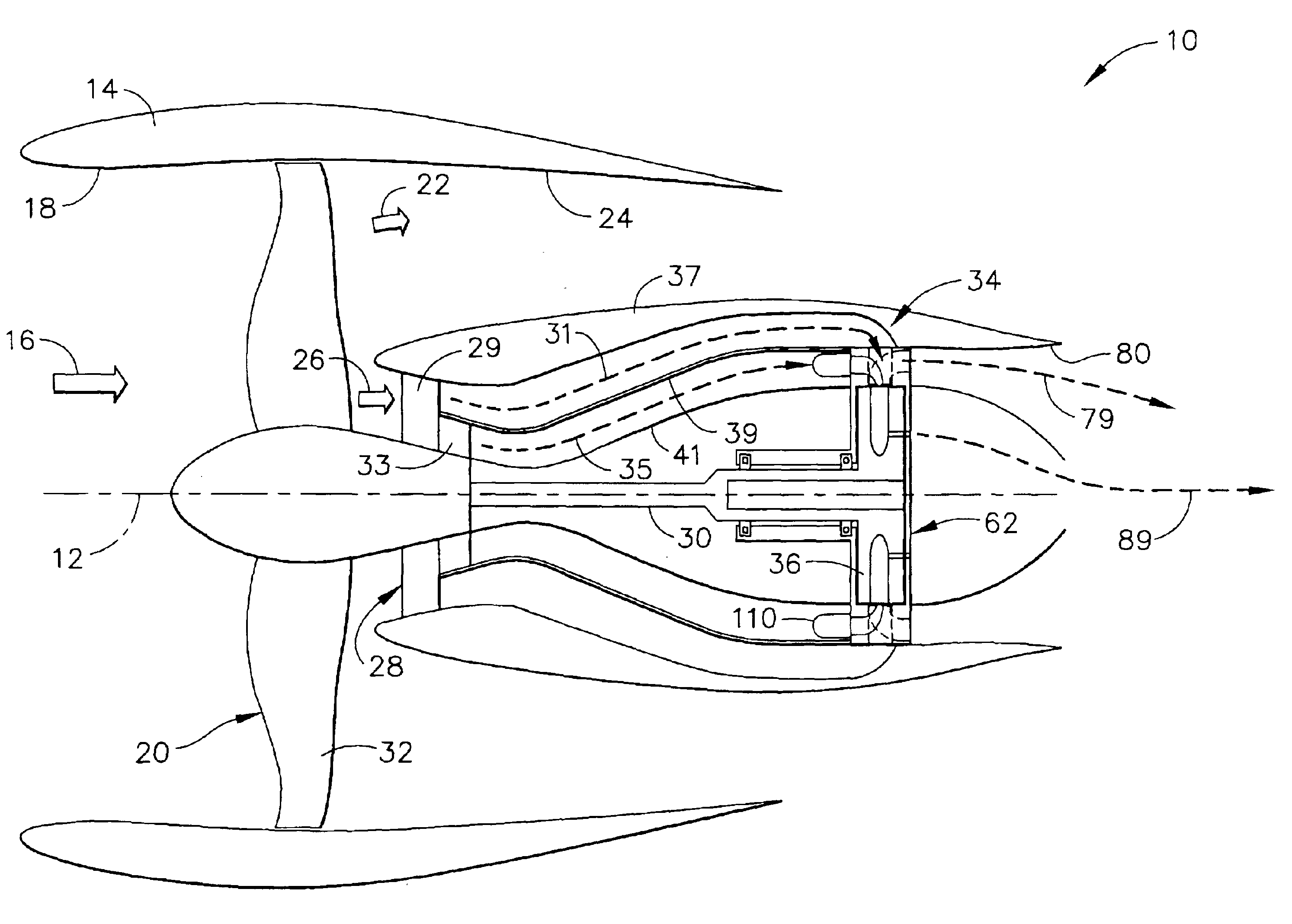
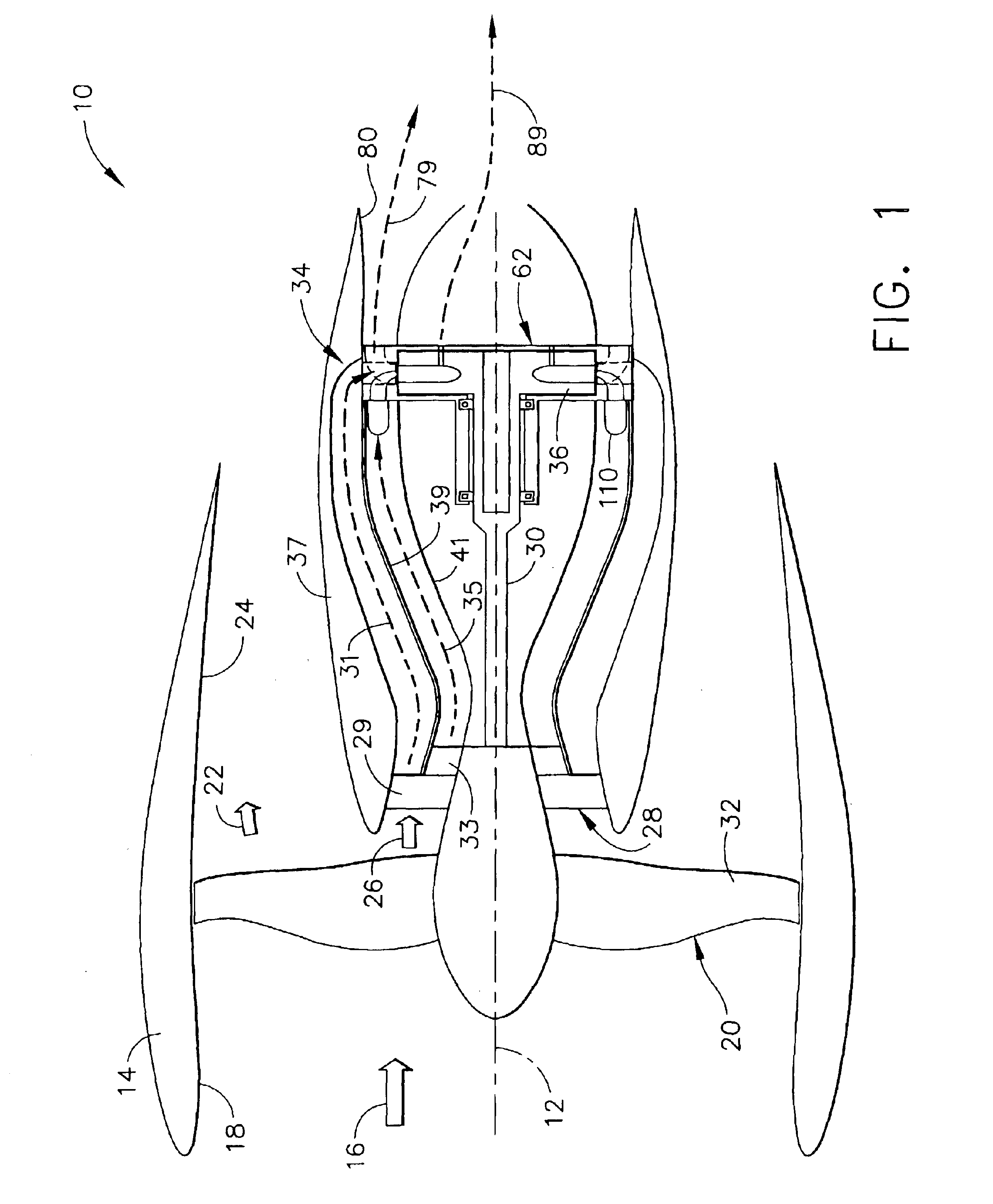
Method and apparatus for improving the efficiency of pulsed detonation engines
InactiveUS6662550B2Improve efficiencyShort and more compactTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionPulse detonation engineNozzle
A pulsed detonation engine having improved efficiency has a detonation chamber for receiving a detonable mixture, an igniter for igniting the detonable mixture, and an outlet for discharging detonation products. A diverging-converging nozzle is provided at the outlet of the detonation chamber. The geometry of the diverging-converging nozzle is selected to enable a relatively short nozzle to significantly improve efficiency of the pulsed detonation engine.
Owner:LEIDOS
High efficiency, reduced emissions internal combustion engine system, especially suitable for gaseous fuels
InactiveUS20040083715A1Internal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelChemical reactionMass ratio
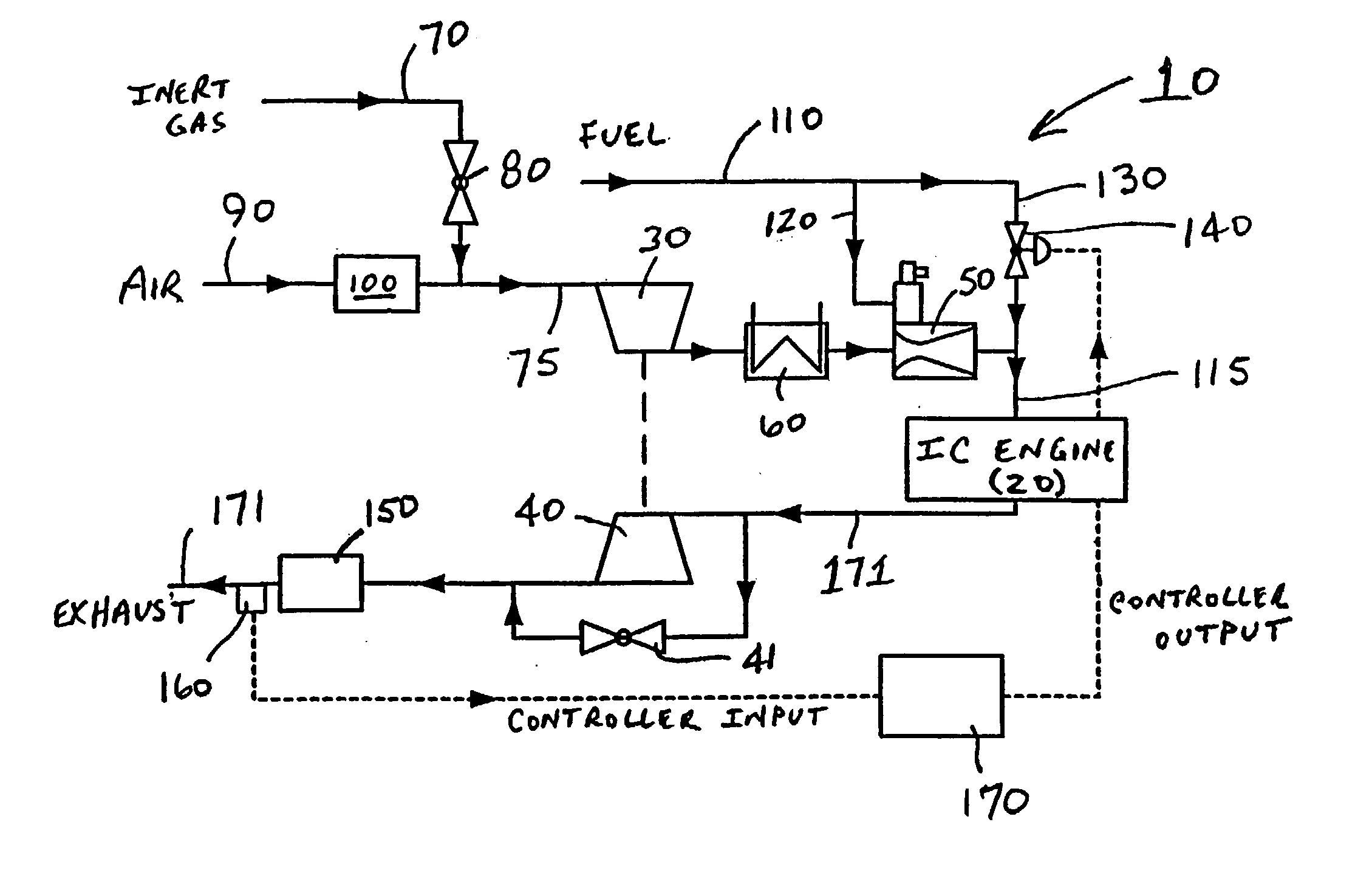
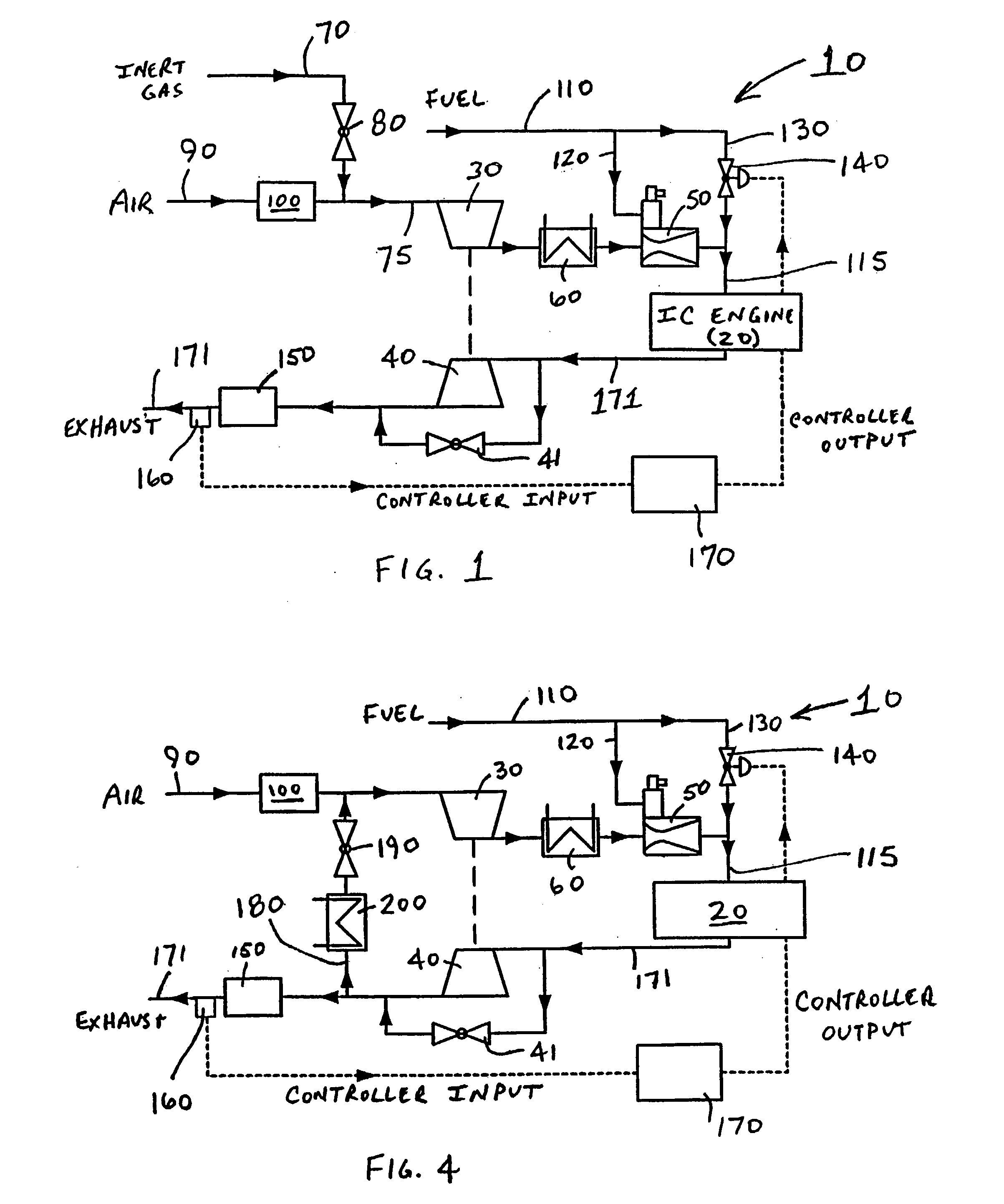
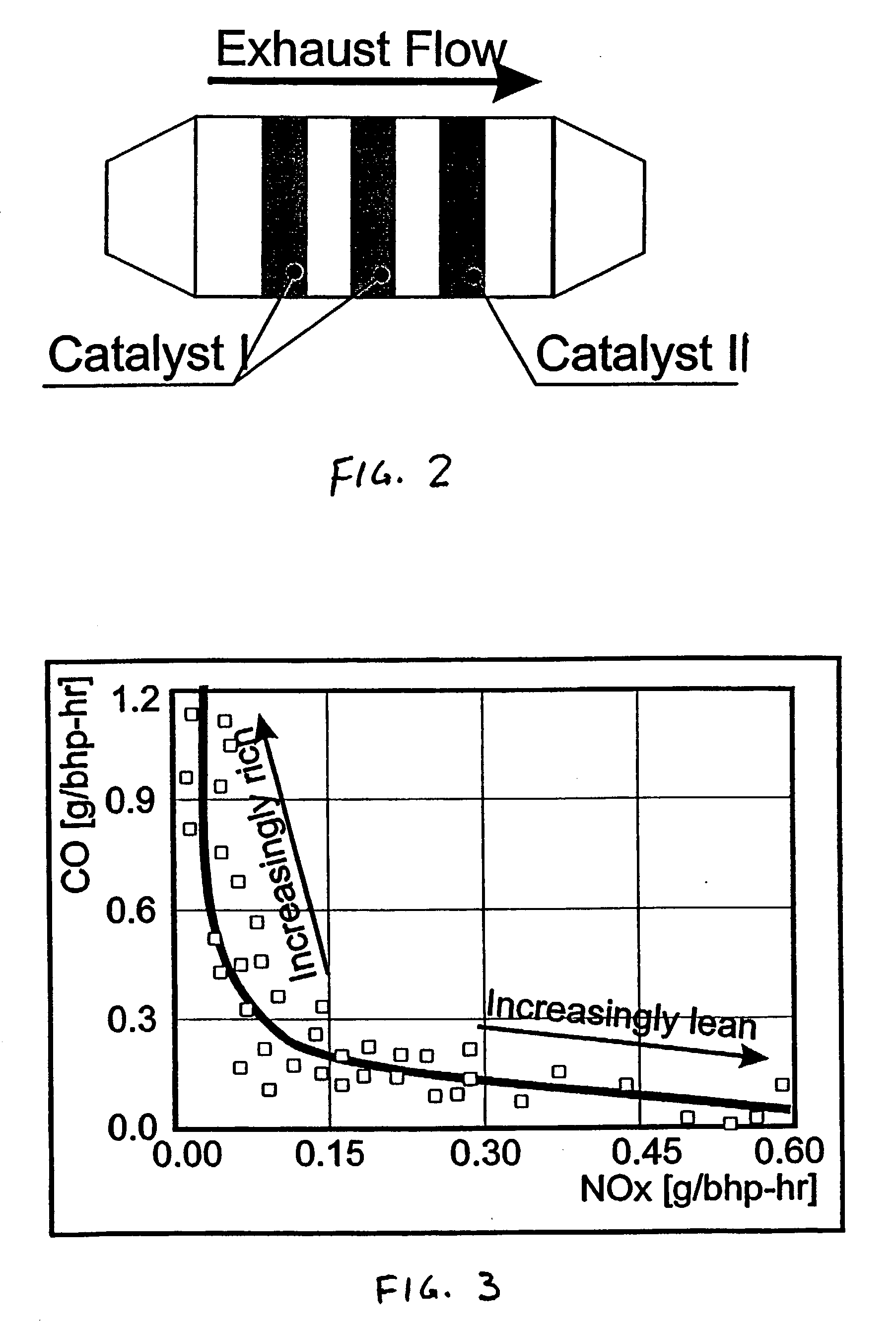
Internal combustion ("IC") engine system for high fuel conversion efficiency and low exhaust emissions, particularly although not exclusively with gaseous fuels. An IC engine operates at approximately stoichiometric (lambda=1) air / fuel mass ratios. A higher-than-normal compression ratio for typical stoichiometric operation is possible for the engine, due to the introduction of an inert (i.e., not chemically reactive in the combustion process) gas into the air / fuel mixture. The inert gas slows the combustion rate to avoid uncontrolled combustion rates and engine "knock." The elevated compression ratio yields higher fuel conversion efficiency. Stoichiometric air / fuel ratio permits catalytic processing of the exhaust gas stream to reduce CO, NOx, and HC emissions via a combination of non-selective catalytic reduction process.
Owner:ATTAINMENT TECH
Abnormal combustion detection method for internal-combustion engines
InactiveUS20090308146A1Internal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlCombustionCombustion chamber
The present invention relates to a method for detecting abnormal combustion in the combustion chamber of at least one cylinder of a spark-ignition supercharged internal-combustion engine, characterized in that it comprises:measuring a quantity linked with the combustion of the fuel mixture in the chamber,producing a signal whose amplitude depends on the amplitude of the measured quantity,comparing the amplitude of the signal produced with the amplitude of a threshold signal corresponding to the amplitude of a signal during combustion with engine knock,determining the presence of a rumble type abnormal combustion in the combustion chamber when the amplitude of the signal produced exceeds the amplitude of said threshold signal by a significant value.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Apparatus for processing sensor signal from knock sensor of internal combustion engine
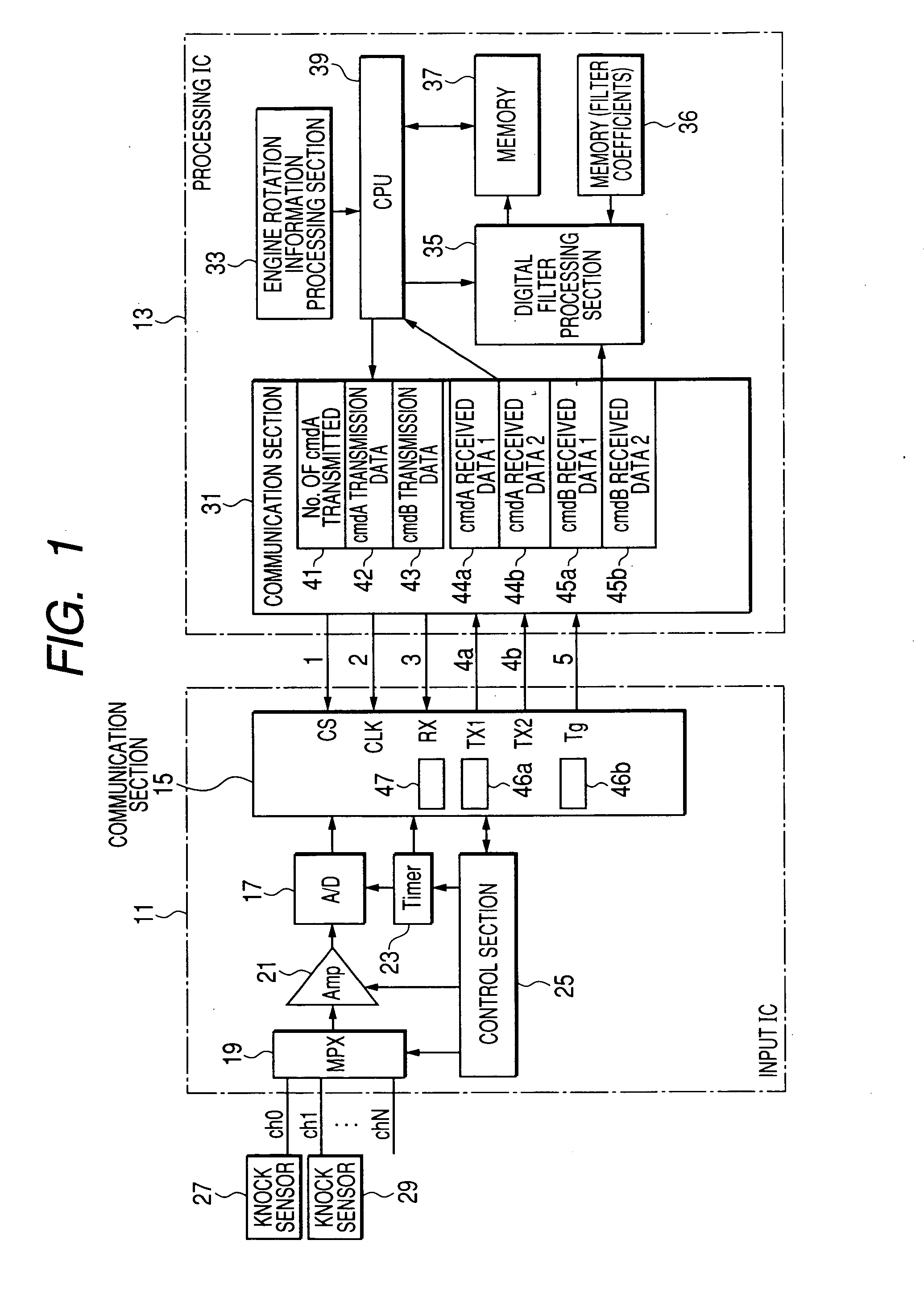
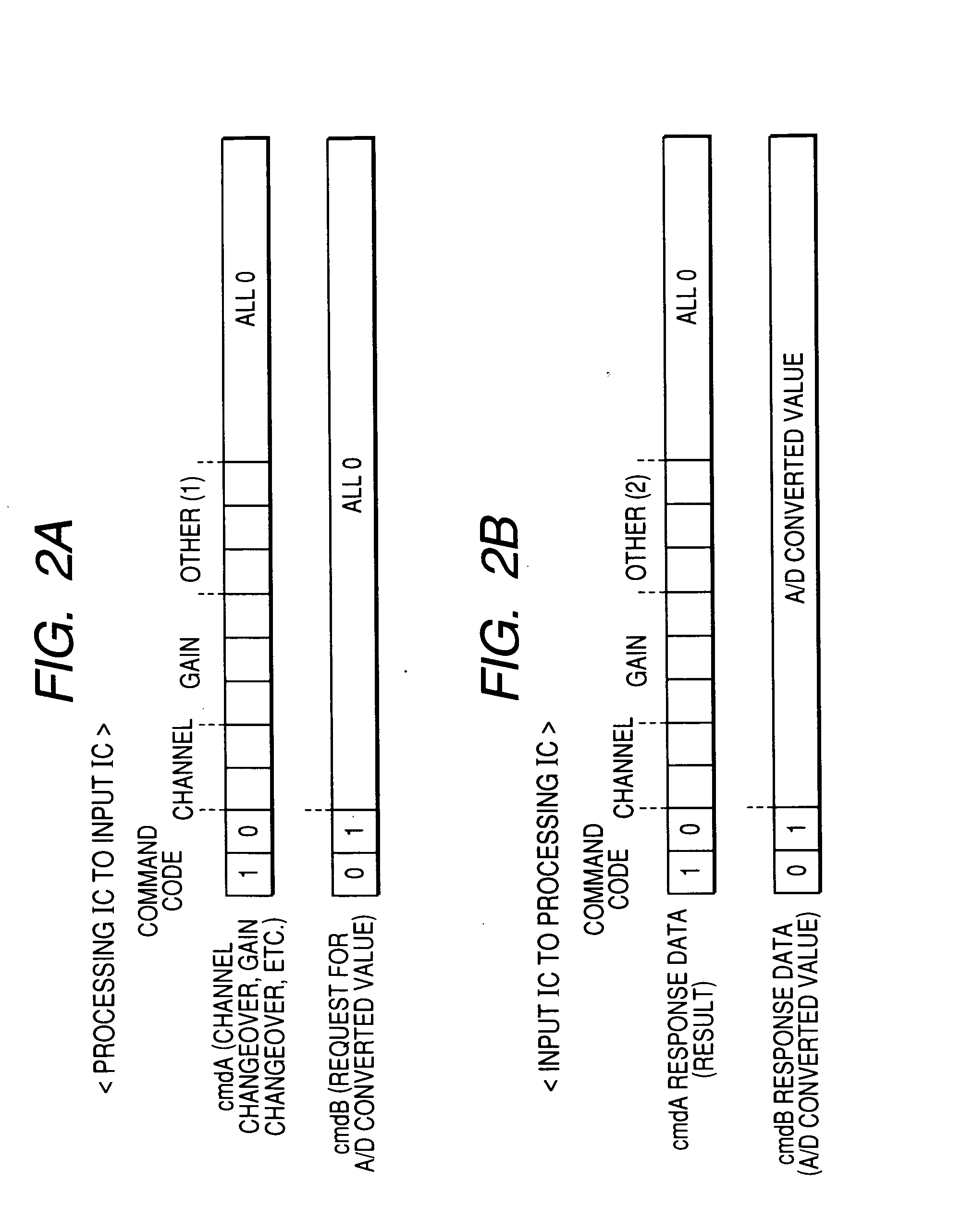
InactiveUS20070175268A1Increase in levelShorten the overall cycleEngine testingElectrical testingLow data rateData rate
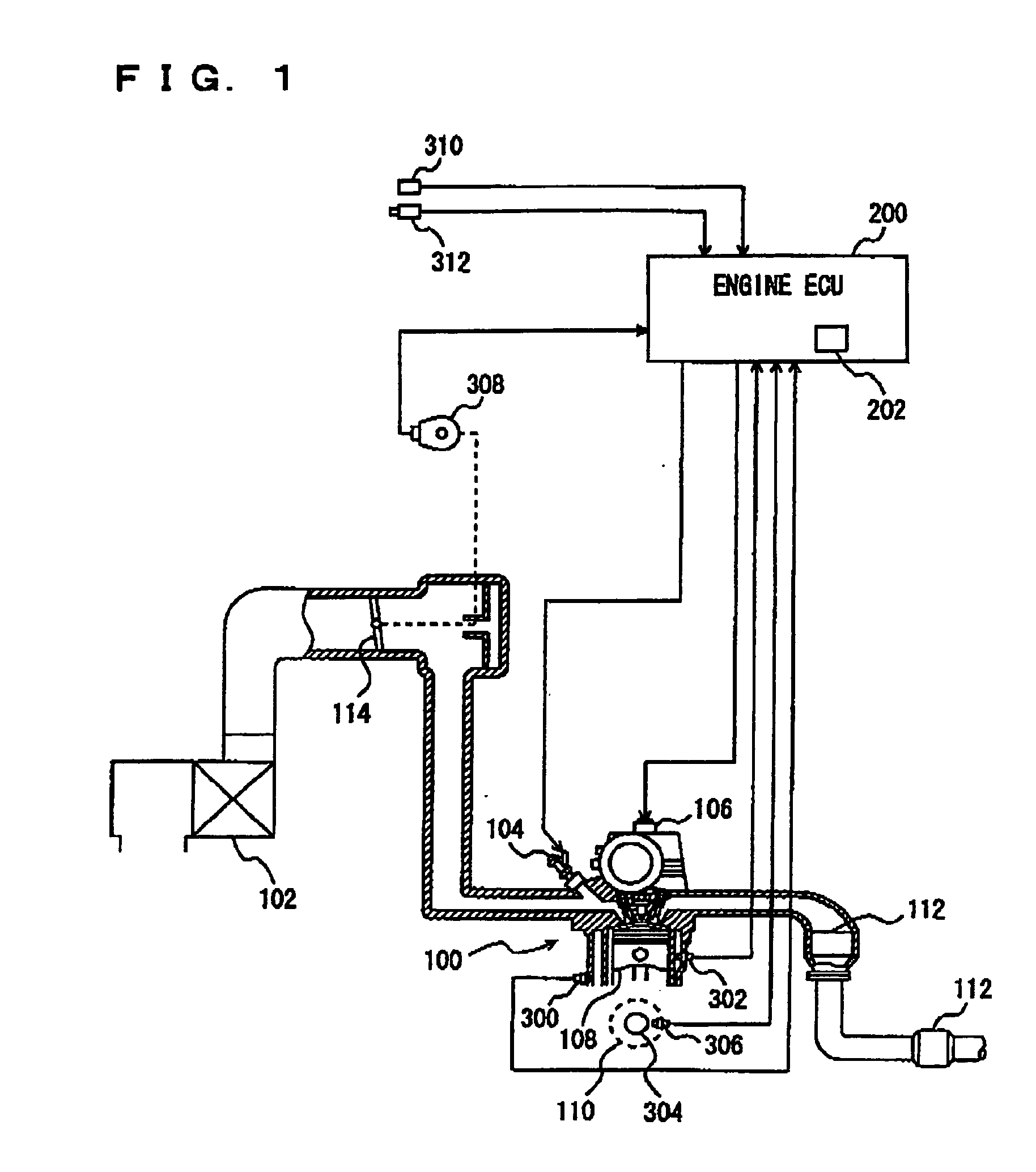
In a knock sensor signal processing apparatus, a first apparatus which receives an engine knock sensor signal performs A / D conversions of the signal with a predetermined period and transmits successive pluralities of A / D values in parallel, by serial data communication, to a second apparatus in response to respective commands received from the second apparatus. The number of communication lines provided for transmitting the A / D values is made greater than those for transmitting commands from the second apparatus to the first apparatus, so that a high A / D conversion frequency together with low data rate of transmitting the A / D values can be achieved, thereby reducing communication-generated noise.
Owner:DENSO CORP
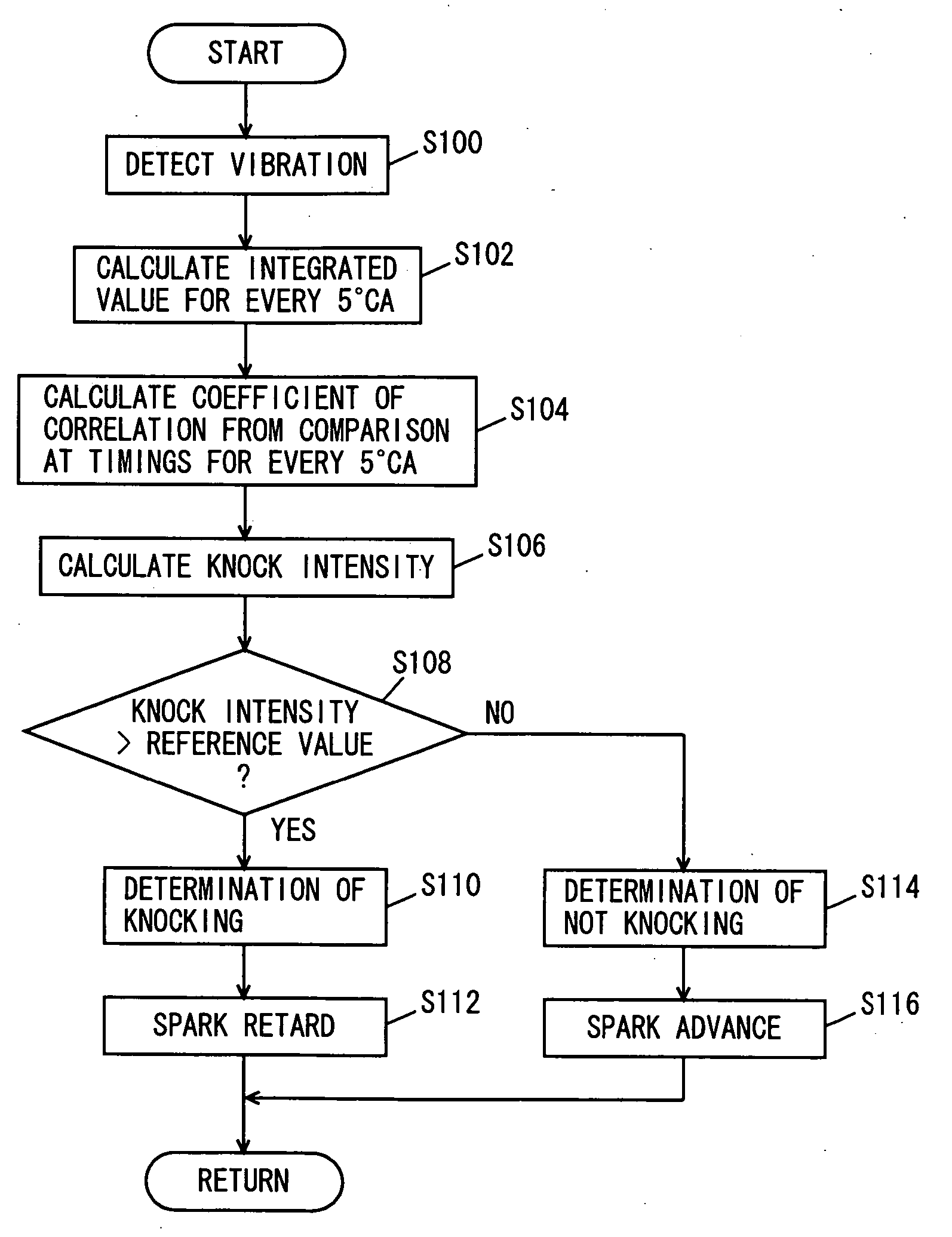
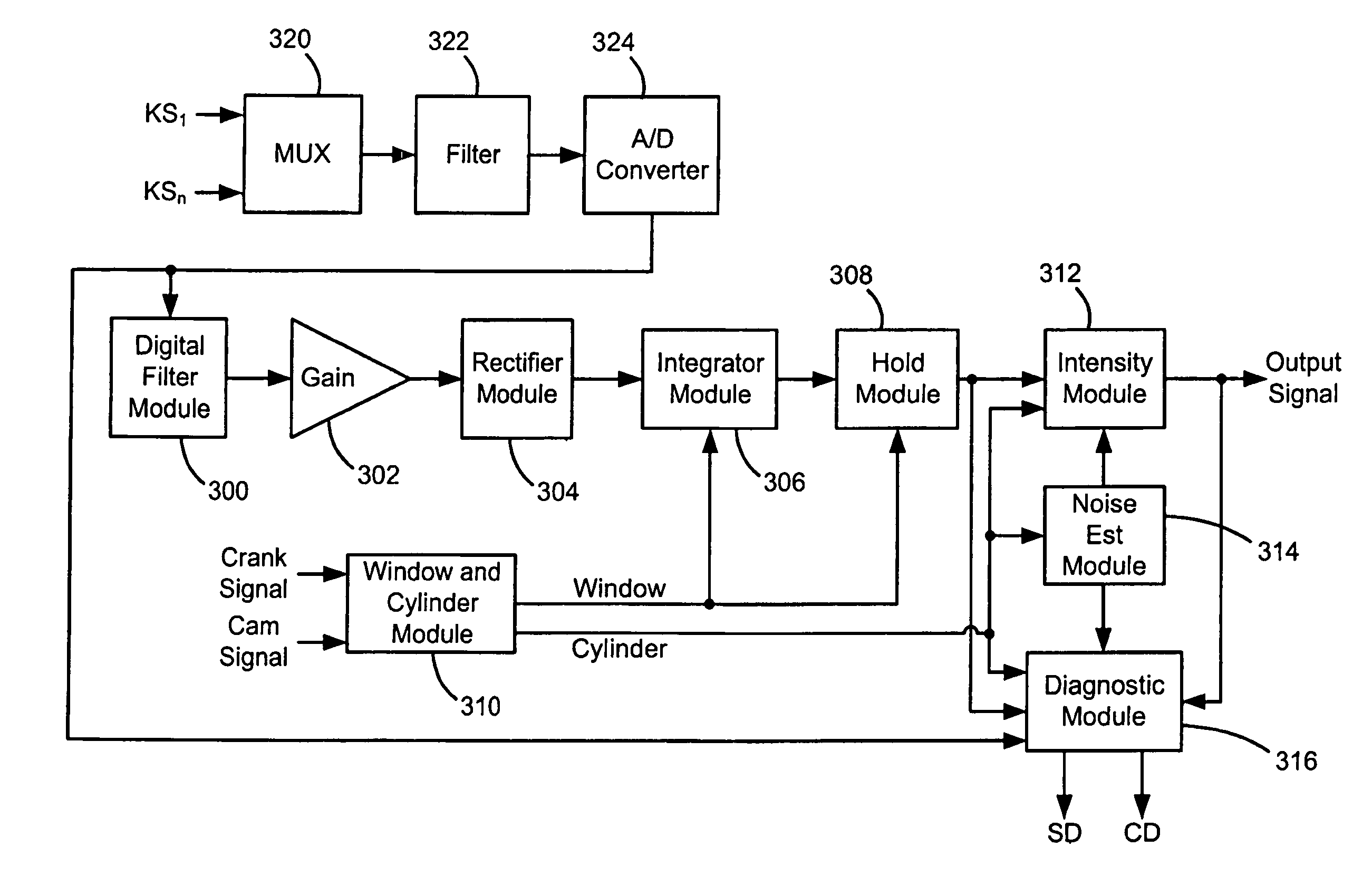
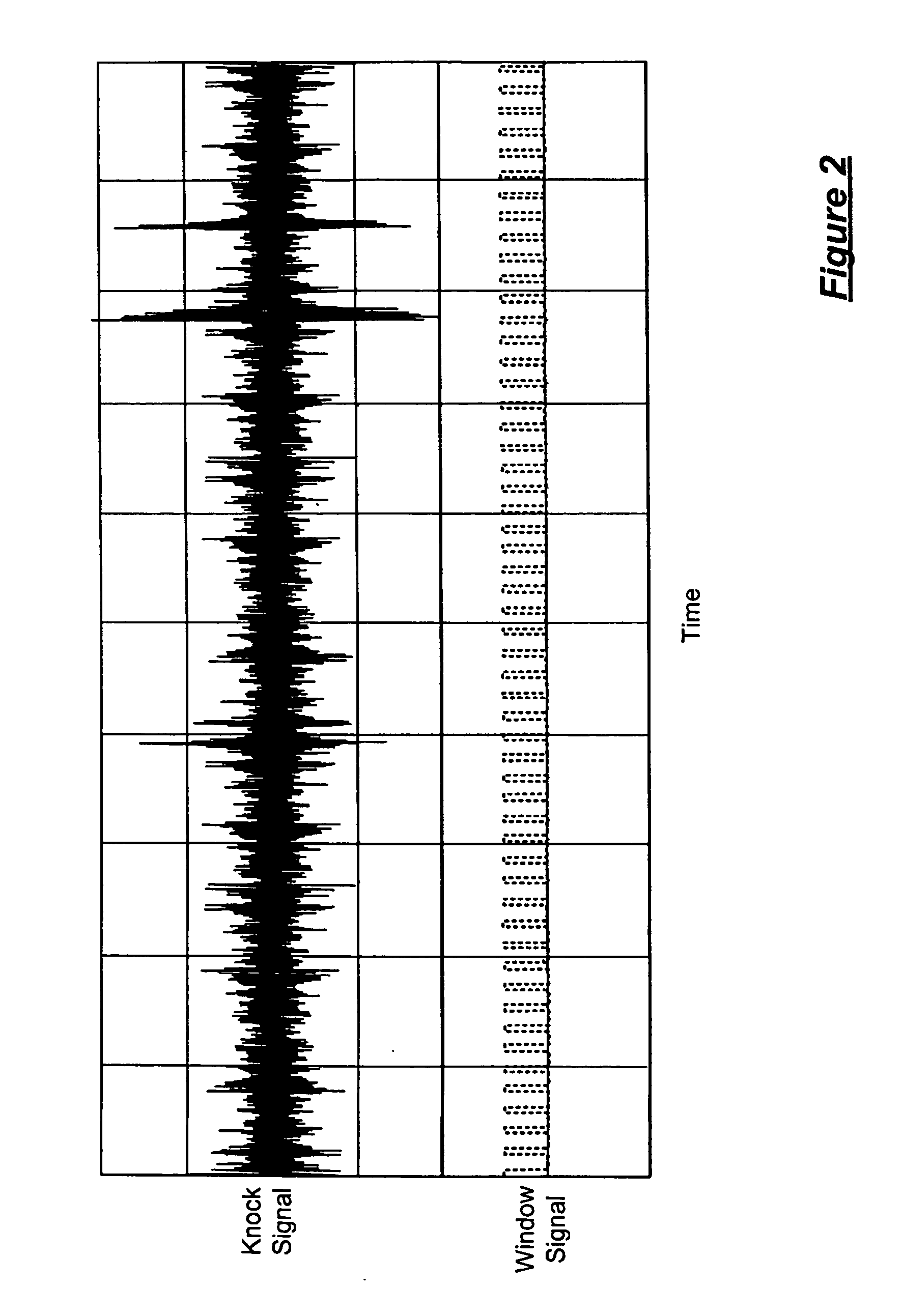
DSP-based engine knock detection including knock sensor and circuit diagnostics
ActiveUS20070028893A1Internal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersEnergy basedIgnition timing
A knock detection system for a spark-ignition engine includes a knock sensor that is responsive to vibration of the engine and that generates a knock signal. A first module calculates a knock energy based on the knock signal and a second module calculates a knock intensity based on the knock energy. A third module regulates a spark timing of the engine based on the knock intensity.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for detecting abnormal combustion conditions in reciprocating engines having high exhaust gas recirculation
InactiveUS6935310B2Reliable detectionInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlExhaust fumesEngineering
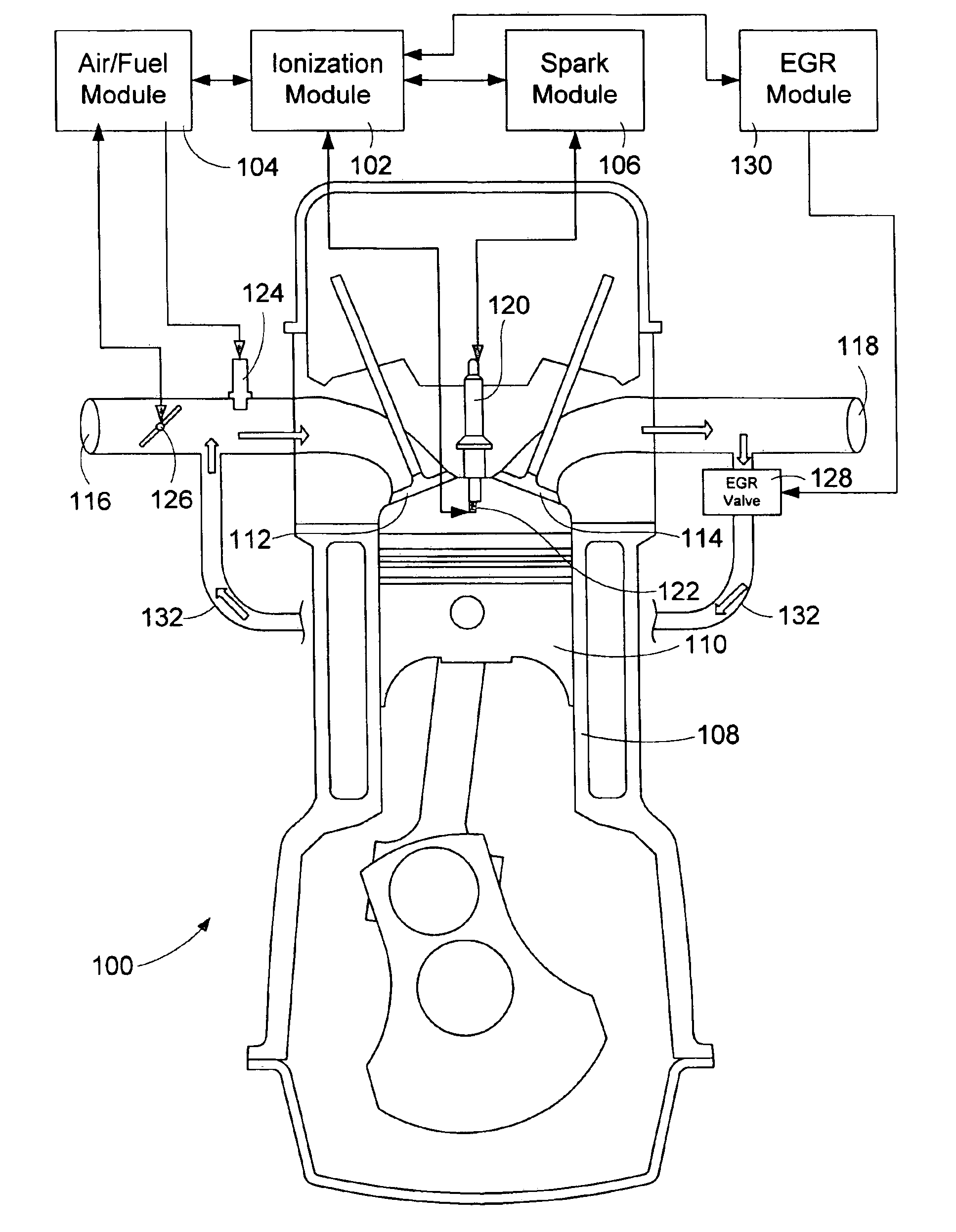
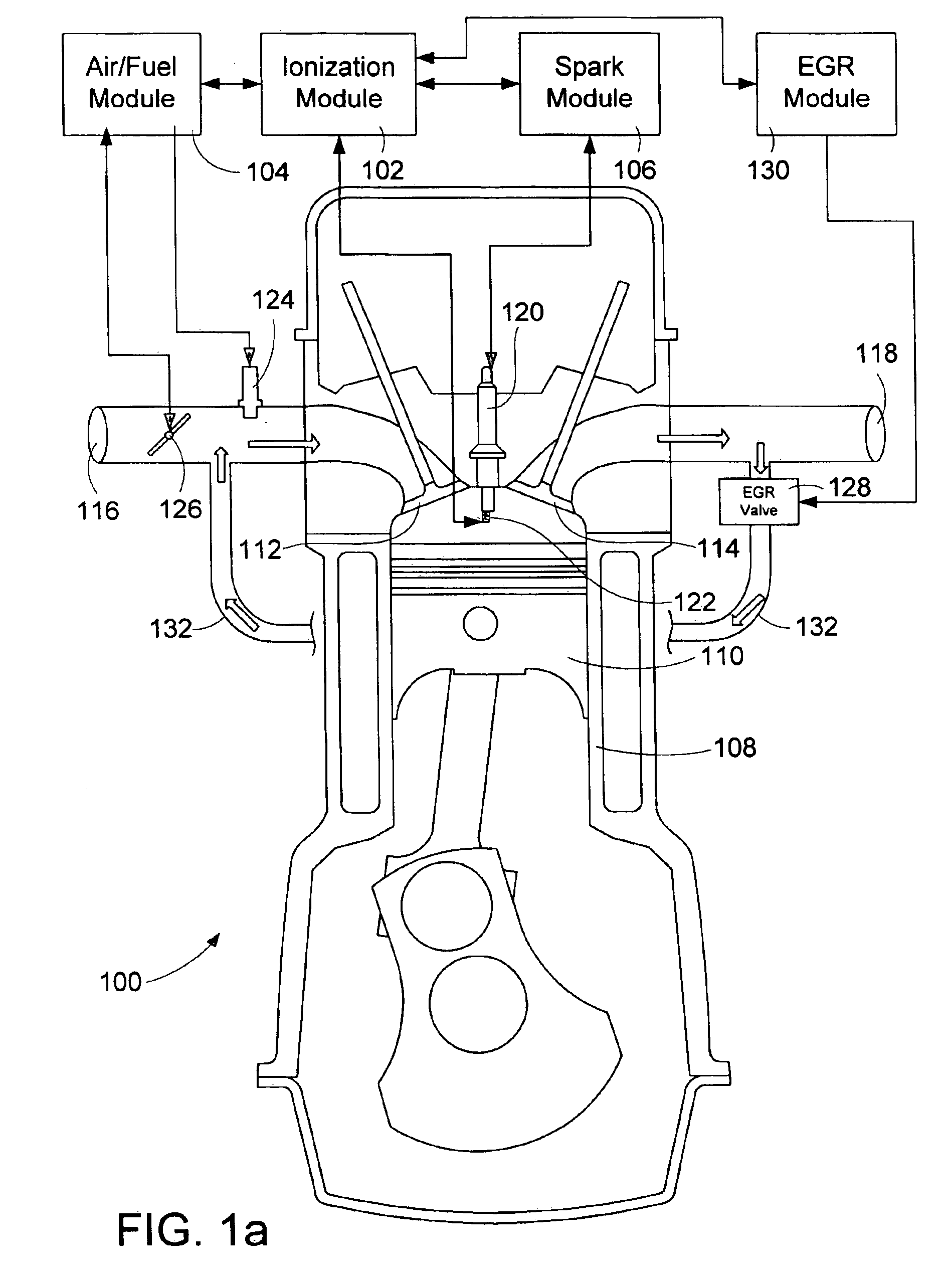
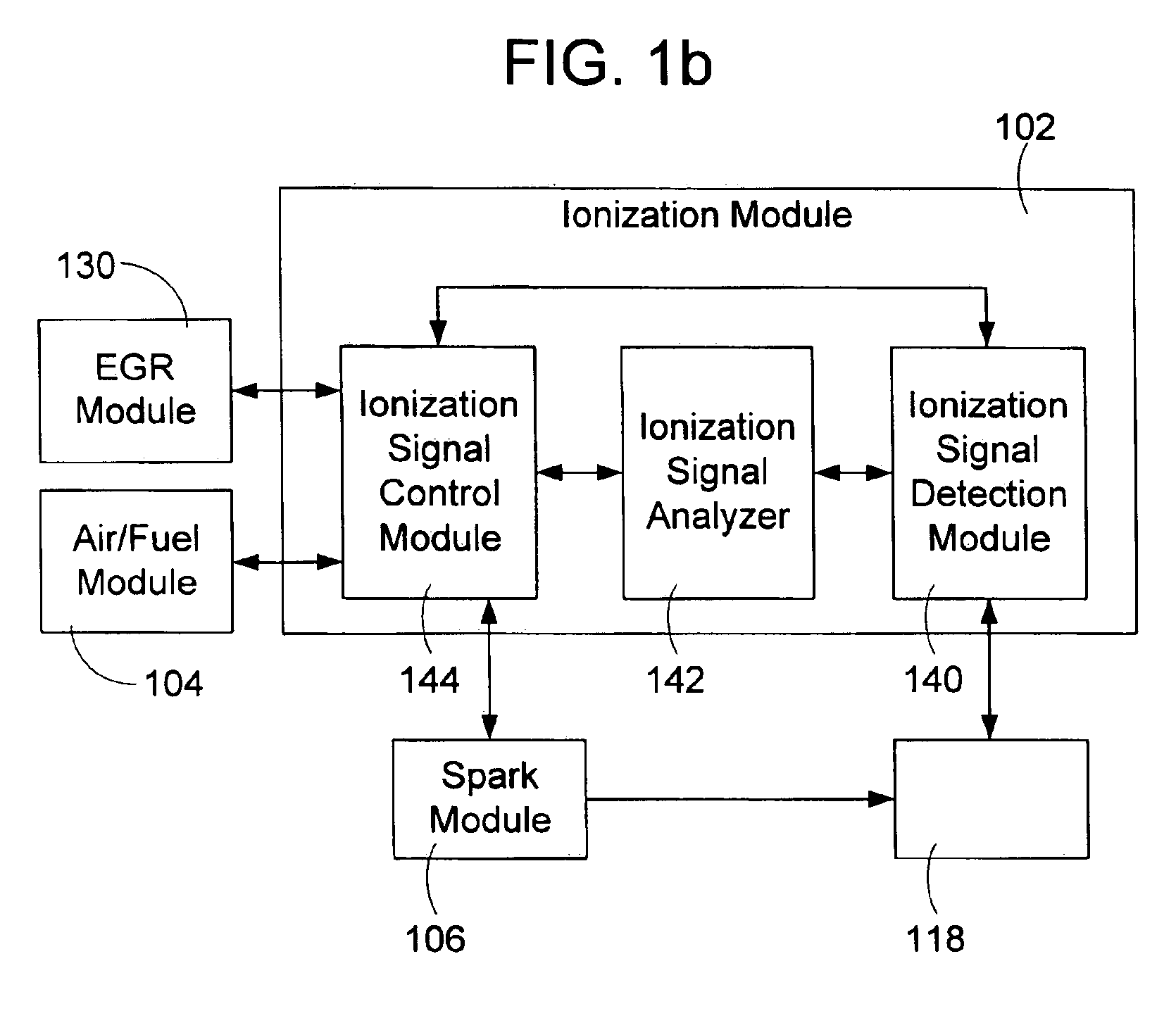
An apparatus and method to detect abnormal combustion conditions for use as a feedback control of an EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) controlled reciprocating engine using ionization signals is presented. The system receives a succession of ionization signals for successive cycles of a running engine and processes a plurality of related ionization signals for signal stability. The ionization signals are checked to determine if an abnormal combustion condition such as knock or misfire has occurred. The variation of an ionization signal that changes with respect to an engine parameter over a combustion event of the reciprocating engine is measured and a floating bounded space is associated with the ionization signal. An indication that the abnormal combustion condition has been detected is provided if a portion of the ionization signal is within the floating bounded space.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
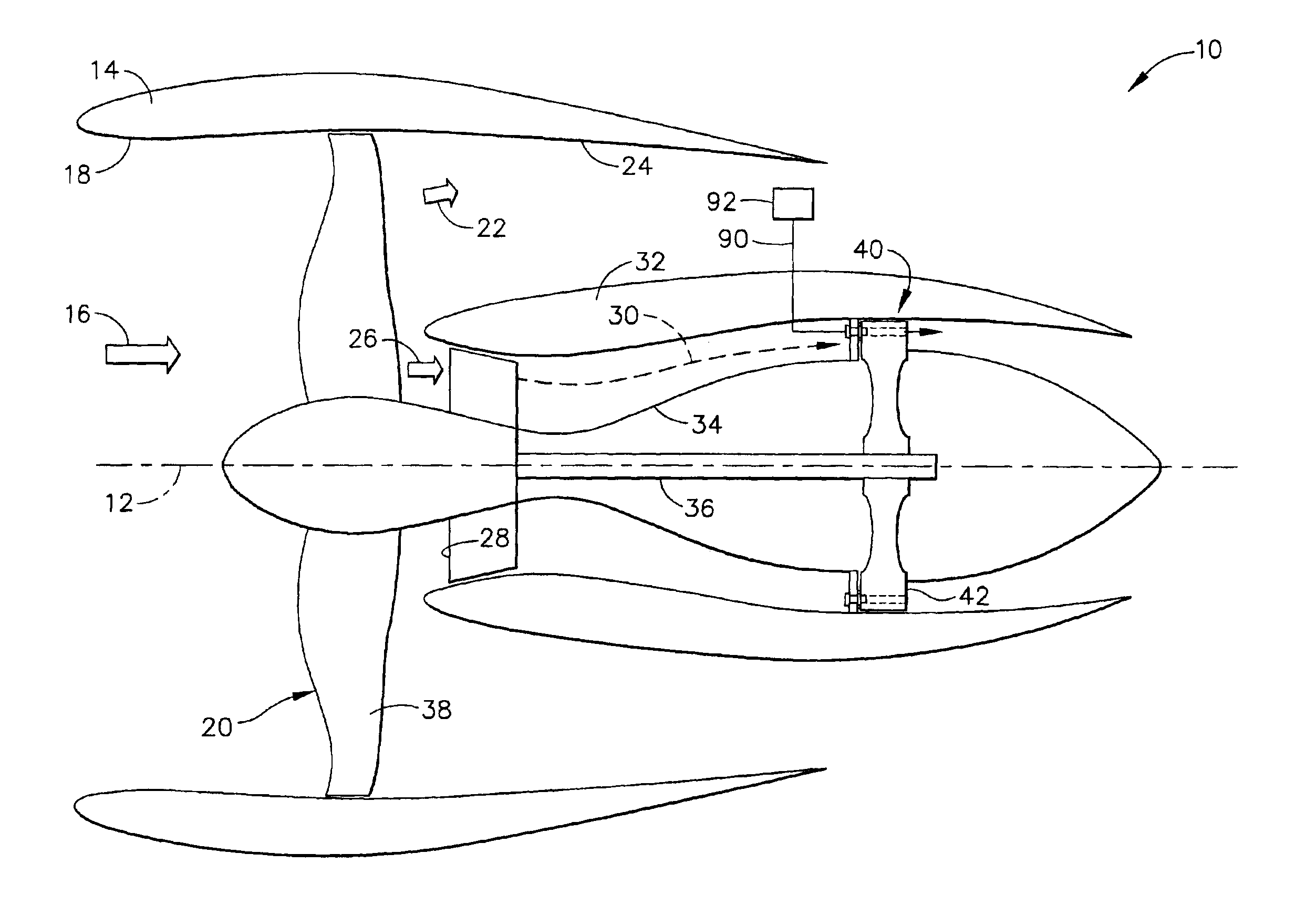
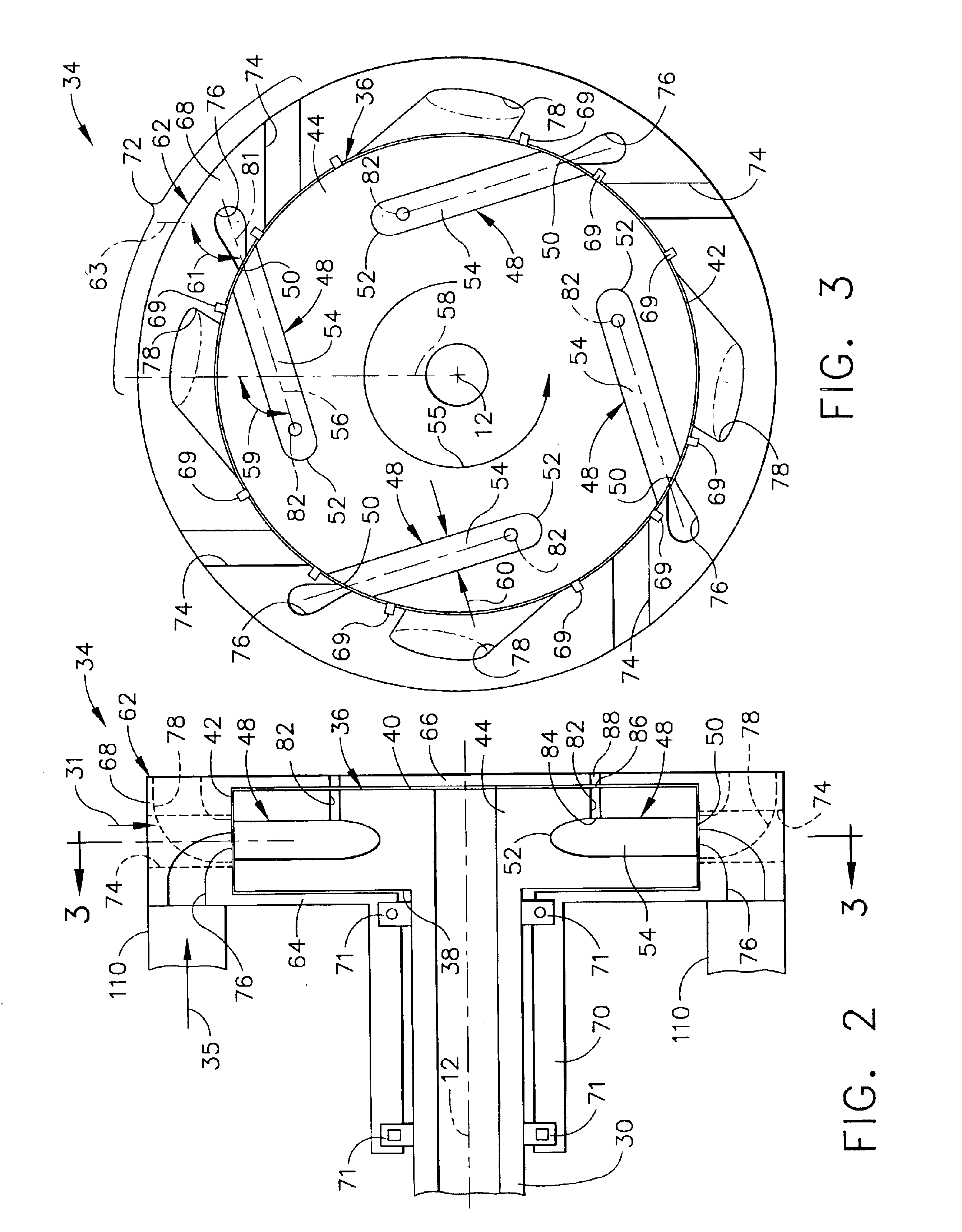
Pulse detonation system for a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS6928804B2Turbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionCombustionDetonation
A pulse detonation system for a gas turbine engine having a longitudinal centerline axis extending therethrough, the pulse detonation system includes an air inlet duct in flow communication with a source of compressed air, the air inlet duct including at least one port formed therein for permitting compressed air to flow therethrough, a fuel injector mounted to the air inlet duct in circumferentially spaced relation to each port, and a device mounted to the air inlet duct in circumferentially spaced relation to each fuel injector for initiating a detonation wave. A rotatable ring member is also positioned in coaxial relation around a portion of the air inlet duct, with the ring member including at least one stage of detonation disposed therein. Accordingly, a detonation wave is produced in each detonation stage and combustion gases following each detonation wave create a torque which causes the ring member to rotate. Each detonation stage in the ring member further includes a plurality of circumferentially spaced detonation ducts extending tangentially from an inner surface of the ring member, wherein the detonation ducts are aligned with each port, the fuel injector and the initiation device in a predetermined timing and sequence so that detonation waves are produced therein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
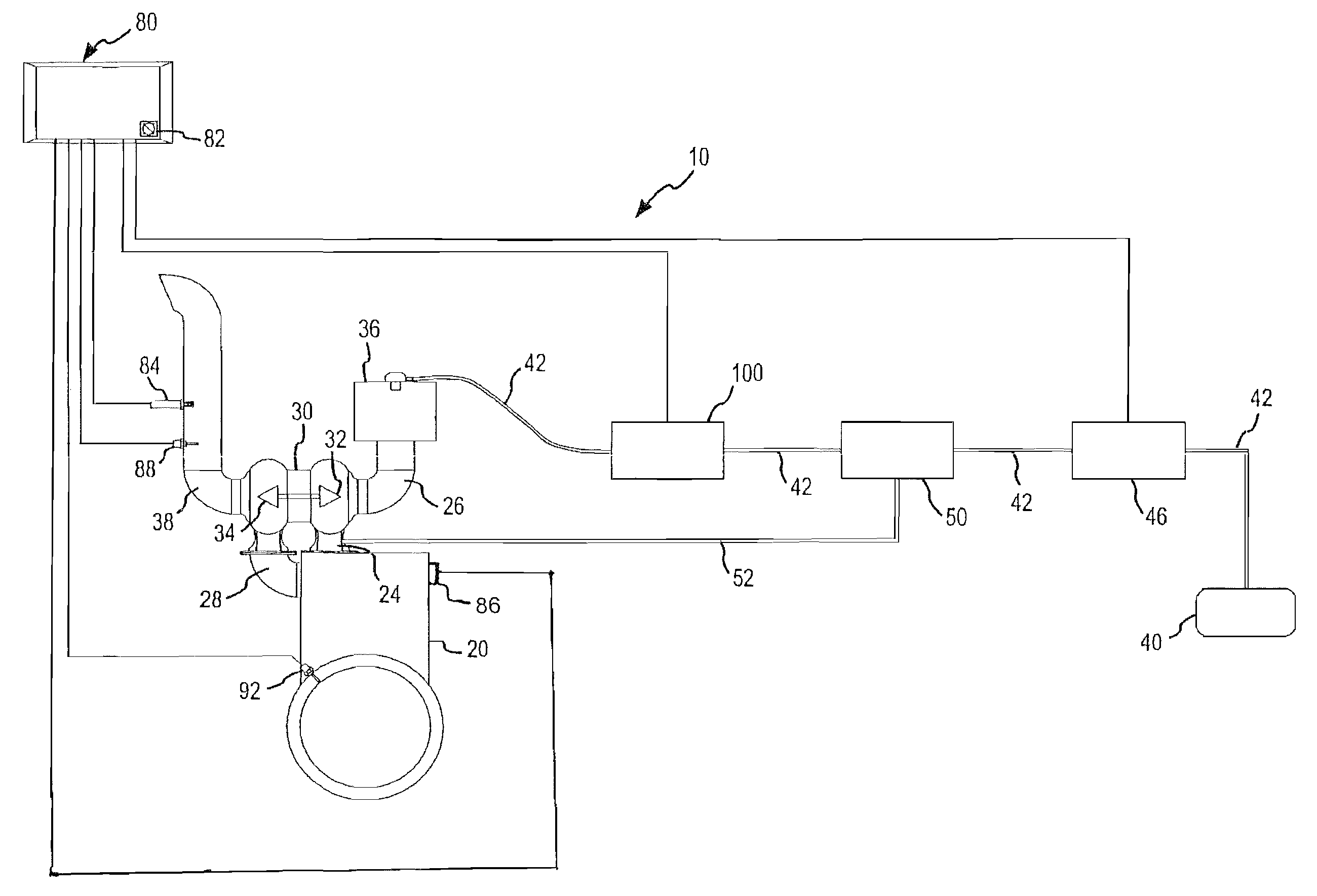
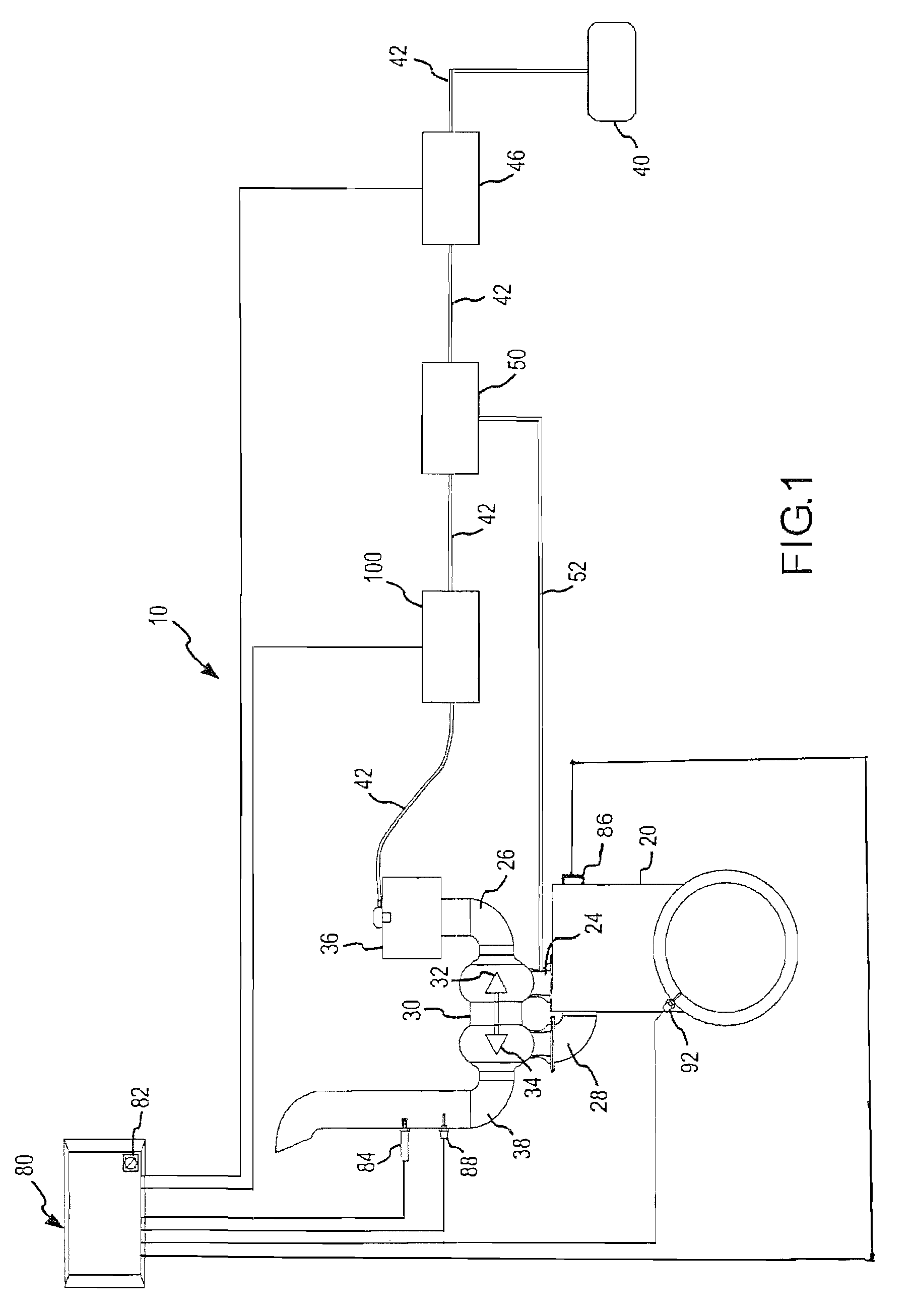
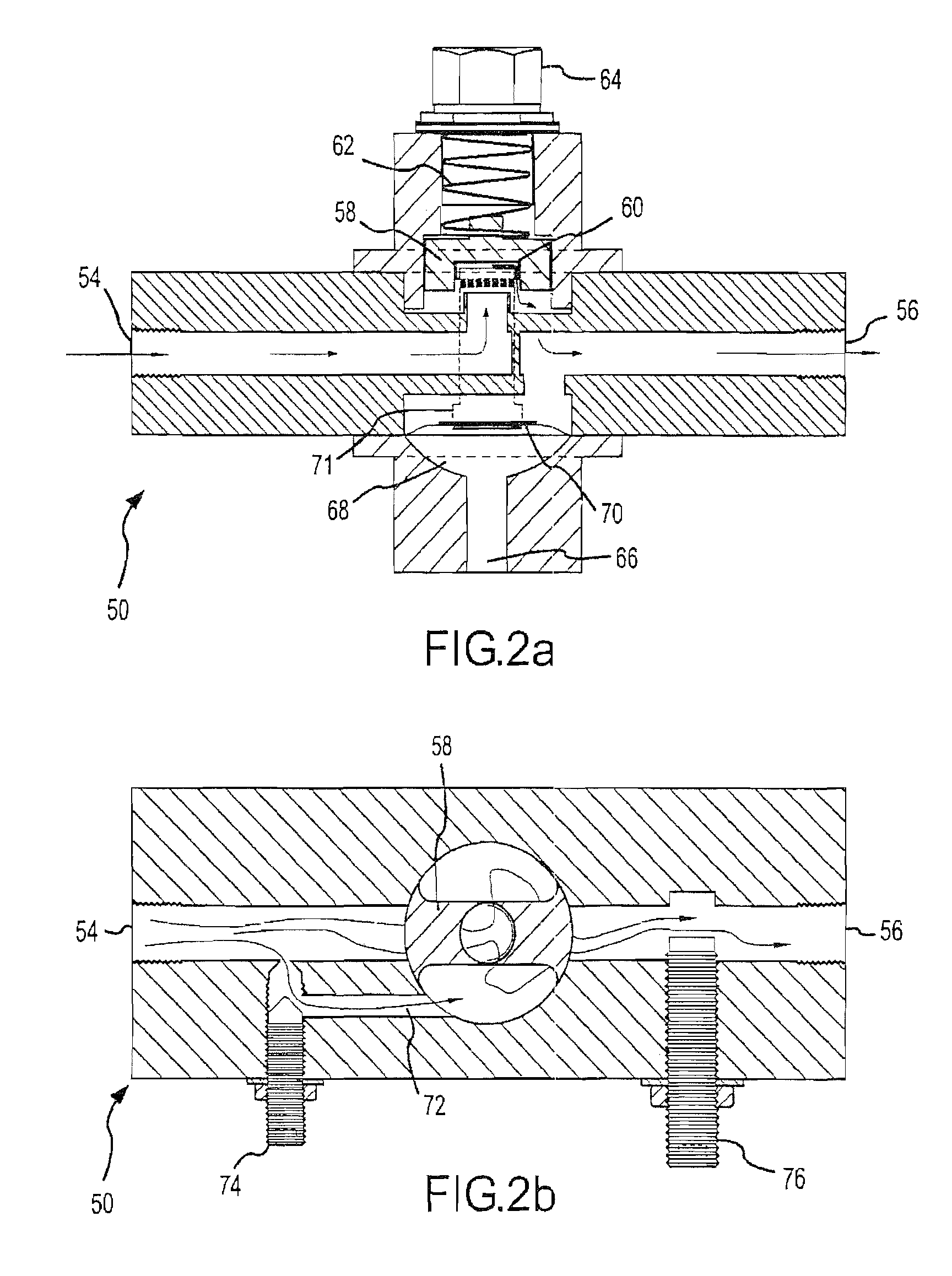
Method and related system of dithering spark timing to prevent pre-ignition in internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20110265761A1Pre-ignition can be preventedElectrical controlAutomatic controlCombustion chamberLow speed
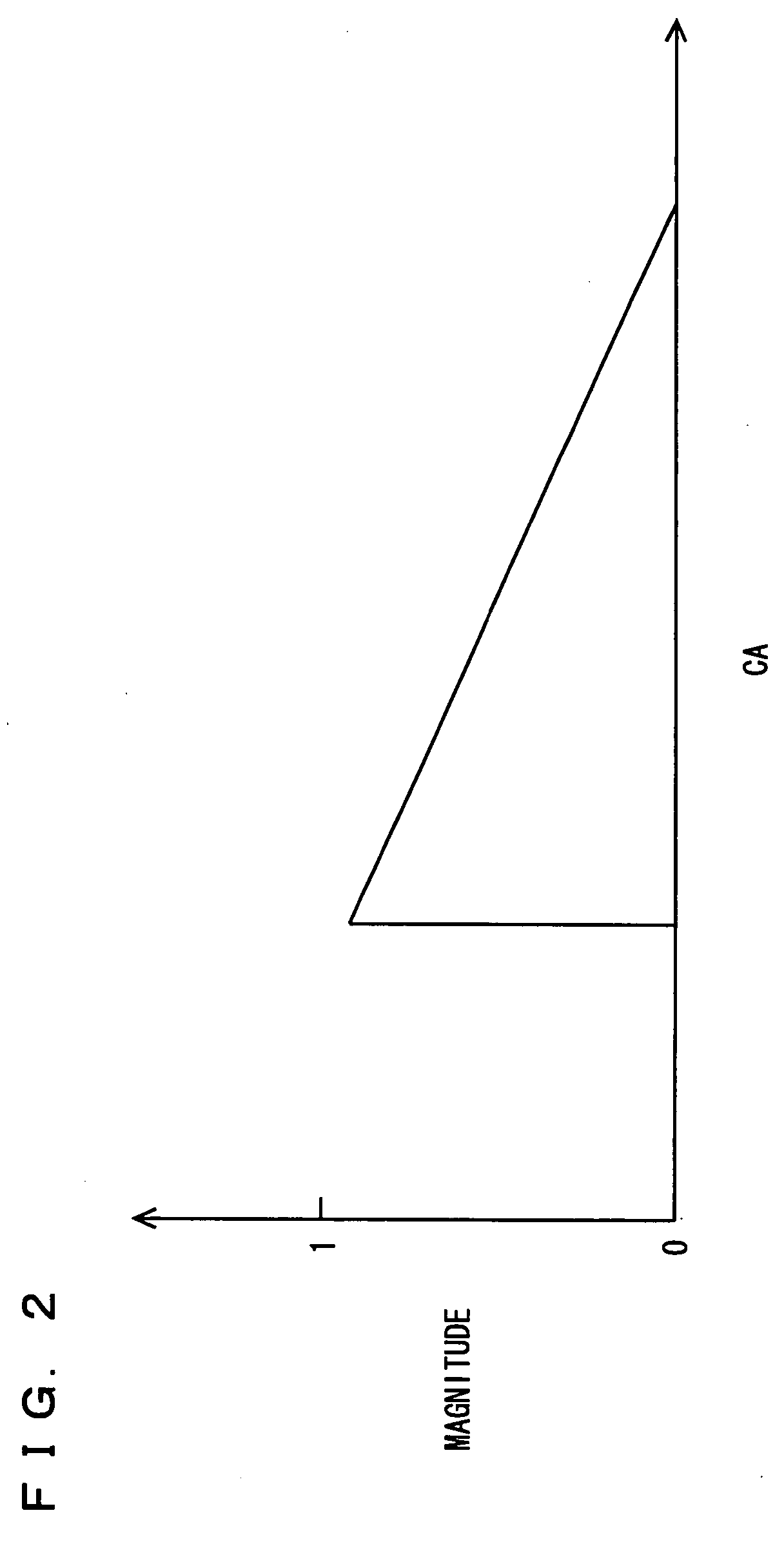
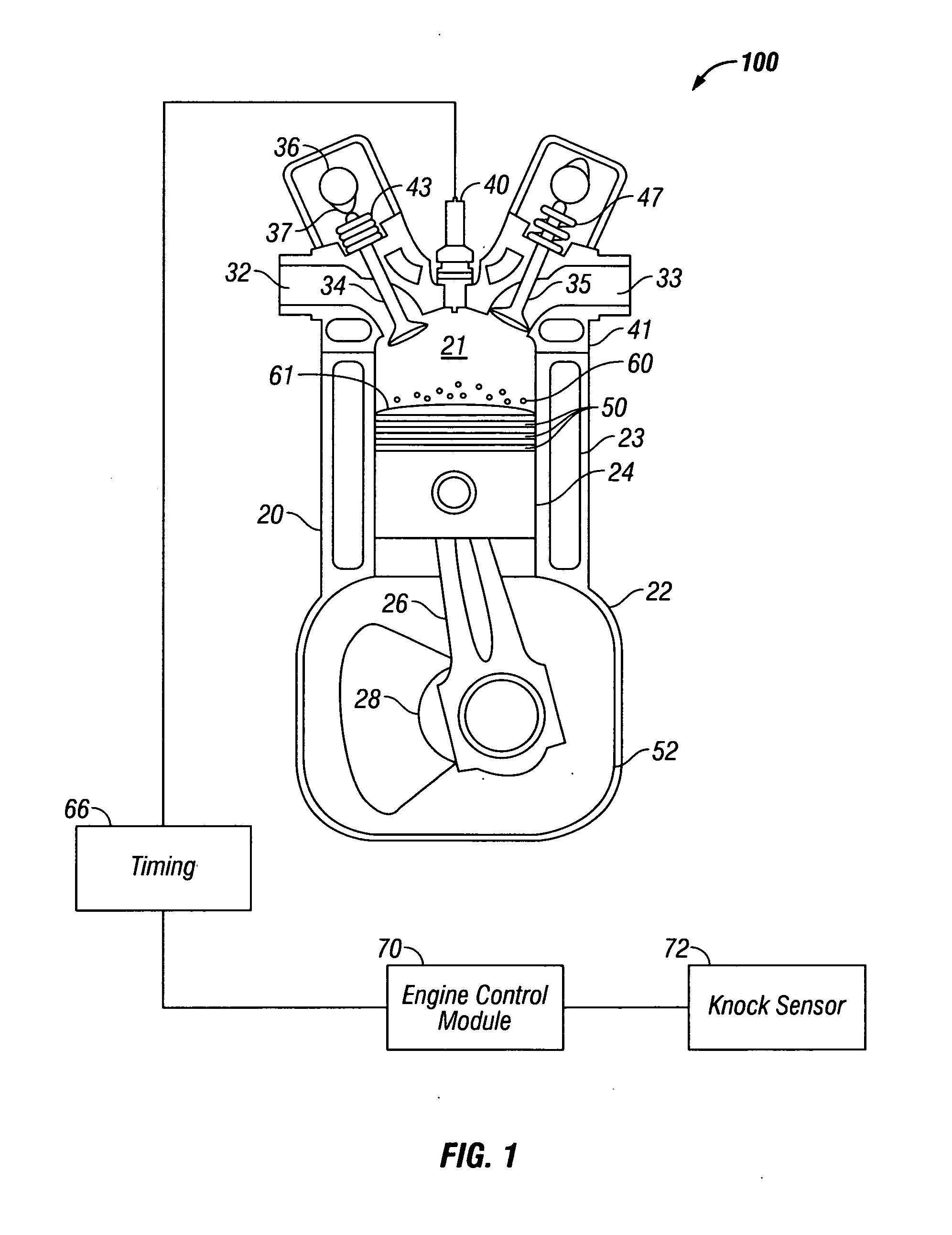
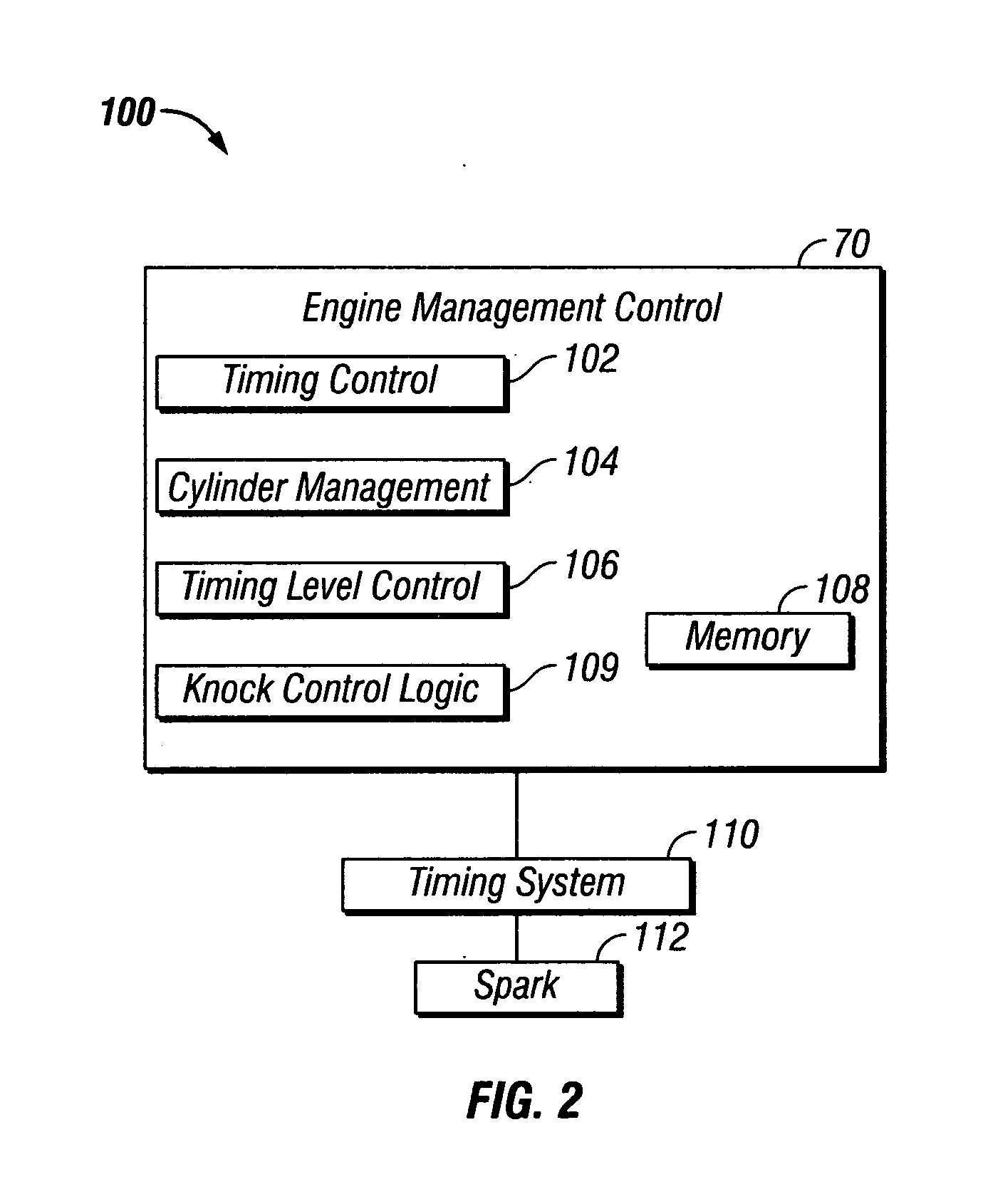
Methods of mitigating the occurrence of a low-speed pre-ignition event in a multi-cylinder internal combustion engine (10), the engine (10) having a computerized engine management control module (70) and an ignition timing module (66) controllable by the engine management control module (70). The computerized engine management module (70) monitors the operating conditions of the internal combustion engine (10) and at certain operating conditions dithers the ignition timing of at least one cylinder (20) of the engine (10) to induce light to medium SI engine knock temporarily. Due to the high temperature, high frequency pressure waves caused by SI engine knock, fuel and / or lubricant related deposits accumulated on combustion chamber components, i.e. top piston land crevices or piston crown, are consumed so that said deposits (60) cannot become a source of pre-ignition
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Internal combustion engine knock determination device and ignition control system including the same
ActiveUS20050251320A1Improve accuracyReduce knockingAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlInternal combustion engineIgnition control
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
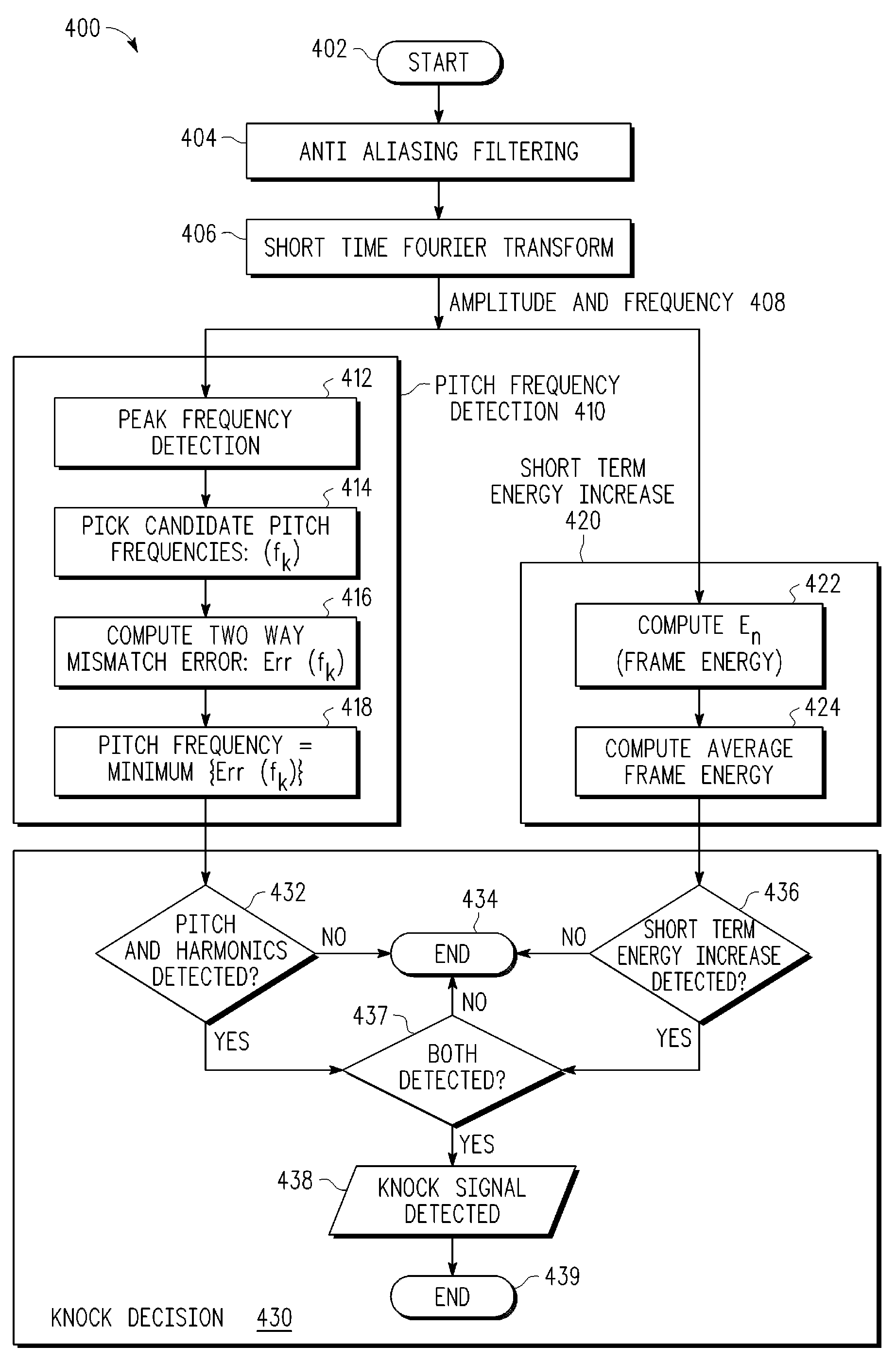
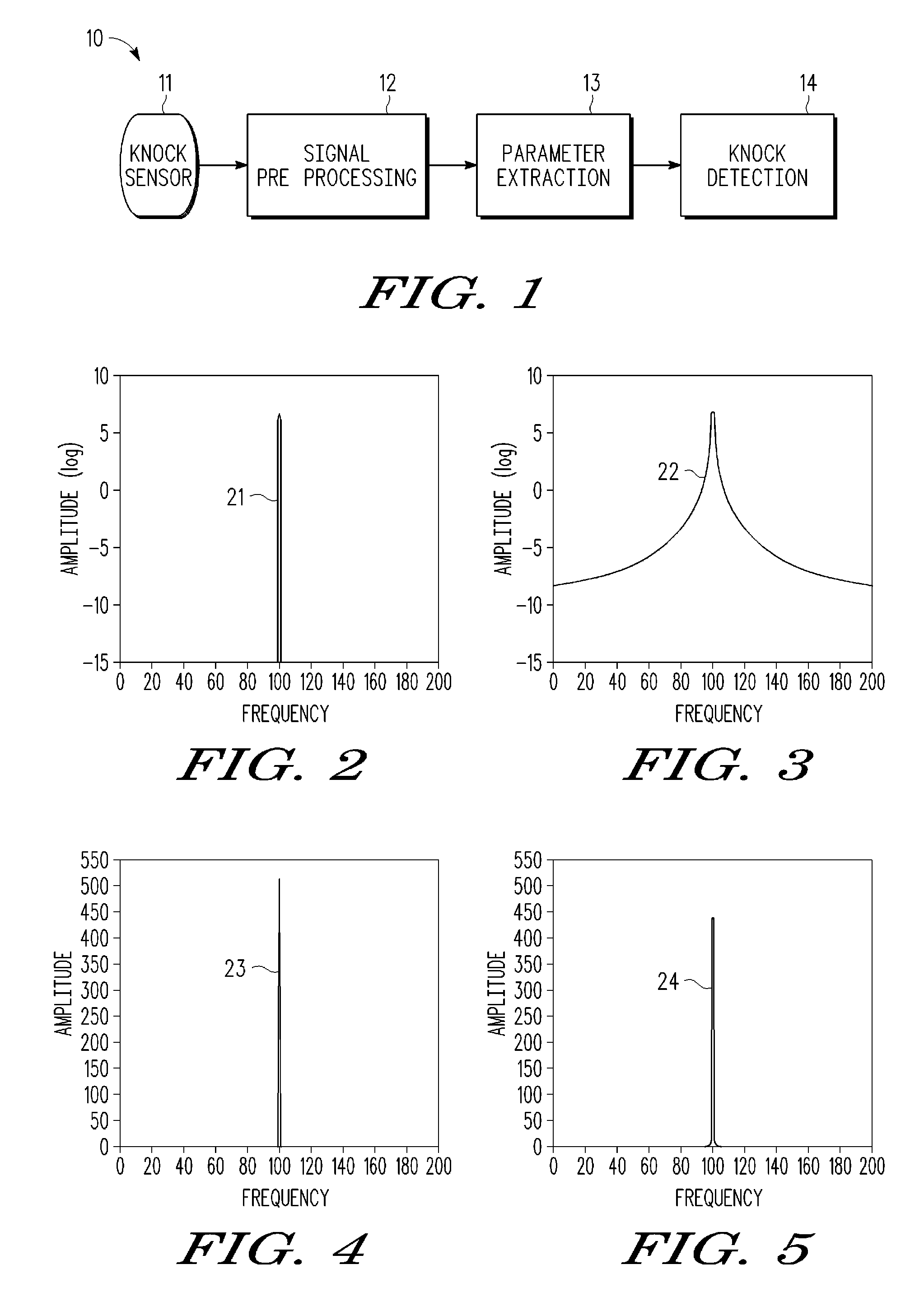
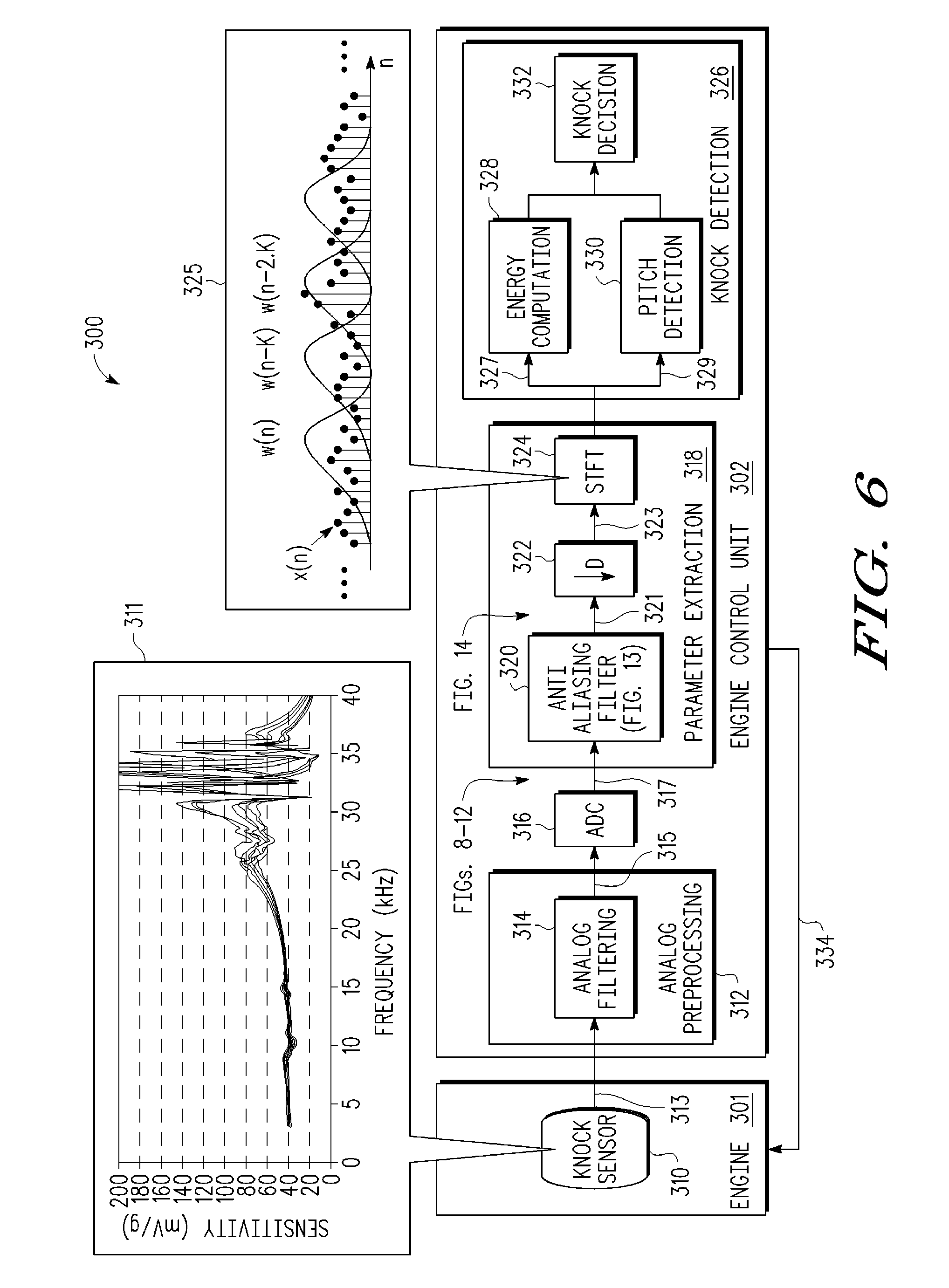
Knock signal detection in automotive systems
InactiveUS20090118989A1Analogue computers for vehiclesRapid change measurementAutomotive systemsAccelerometer
In an automotive system (300), a knock detection scheme is provided for detecting knock events in an internal combustion engine that are sensed by a transducer structure, such as a non-intrusive acoustic accelerometer sensor (310) to generate sensor signal information which is processed by a signal processing structure (312, 316, 318, 326) which extracts digital signal parameters from the sensor signal information to identify a predetermined pitch frequency (330) and any short-term energy increase (328) in the digital signal information which in combination are used to provide a positive indication of engine knock behavior. When a short term Fourier transform (324) is used to extract the digital signal parameters, time frequency resolution may be improved by appropriately windowing the digital signal being transformed.
Owner:NXP USA INC
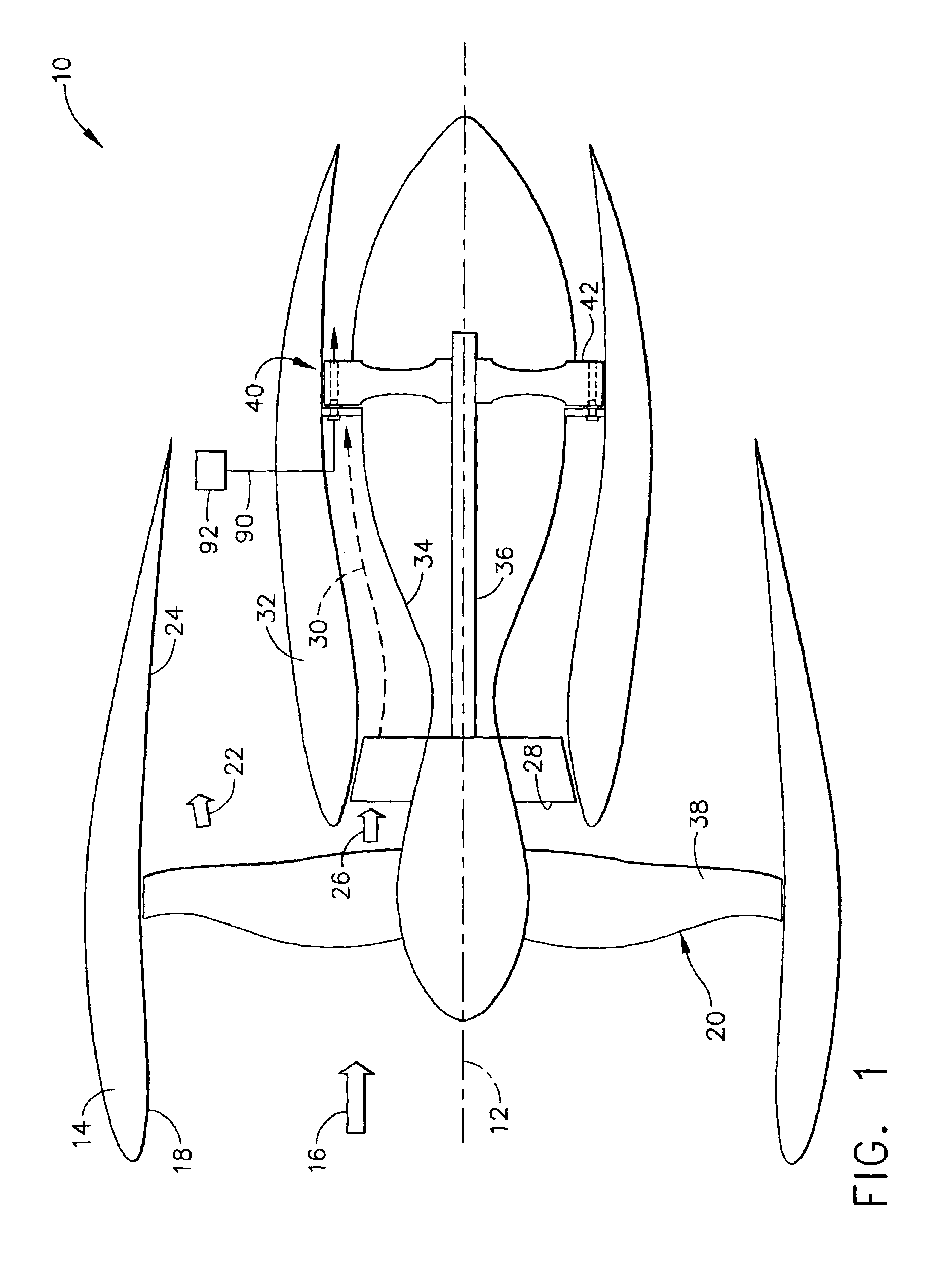
Rotating pulse detonation system for a gas turbine engine
A pulse detonation system for a gas turbine engine having a longitudinal centerline axis extending therethrough includes a rotatable cylindrical member having a forward surface, an aft surface, and an outer circumferential surface, where a plurality of spaced detonation passages are disposed therethrough. Each detonation passage includes at least a portion having a longitudinal axis extending therethrough oriented at a circumferential angle to the longitudinal centerline axis. The pulse detonation system further includes a shaft rotatably connected to the cylindrical member and a stator configured in spaced arrangement with the forward surface of the cylindrical member and a portion of the shaft. The stator has at least one group of ports formed therein alignable with the detonation passages as the cylindrical member rotates. In this way, detonation cycles are performed in the detonation passages so that combustion gases exit the aft surface of the cylindrical member to create a torque which causes the cylindrical member to rotate. Each detonation passage further includes a first end located adjacent the forward surface of the cylindrical member and a second end located adjacent the aft surface of the cylindrical member.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
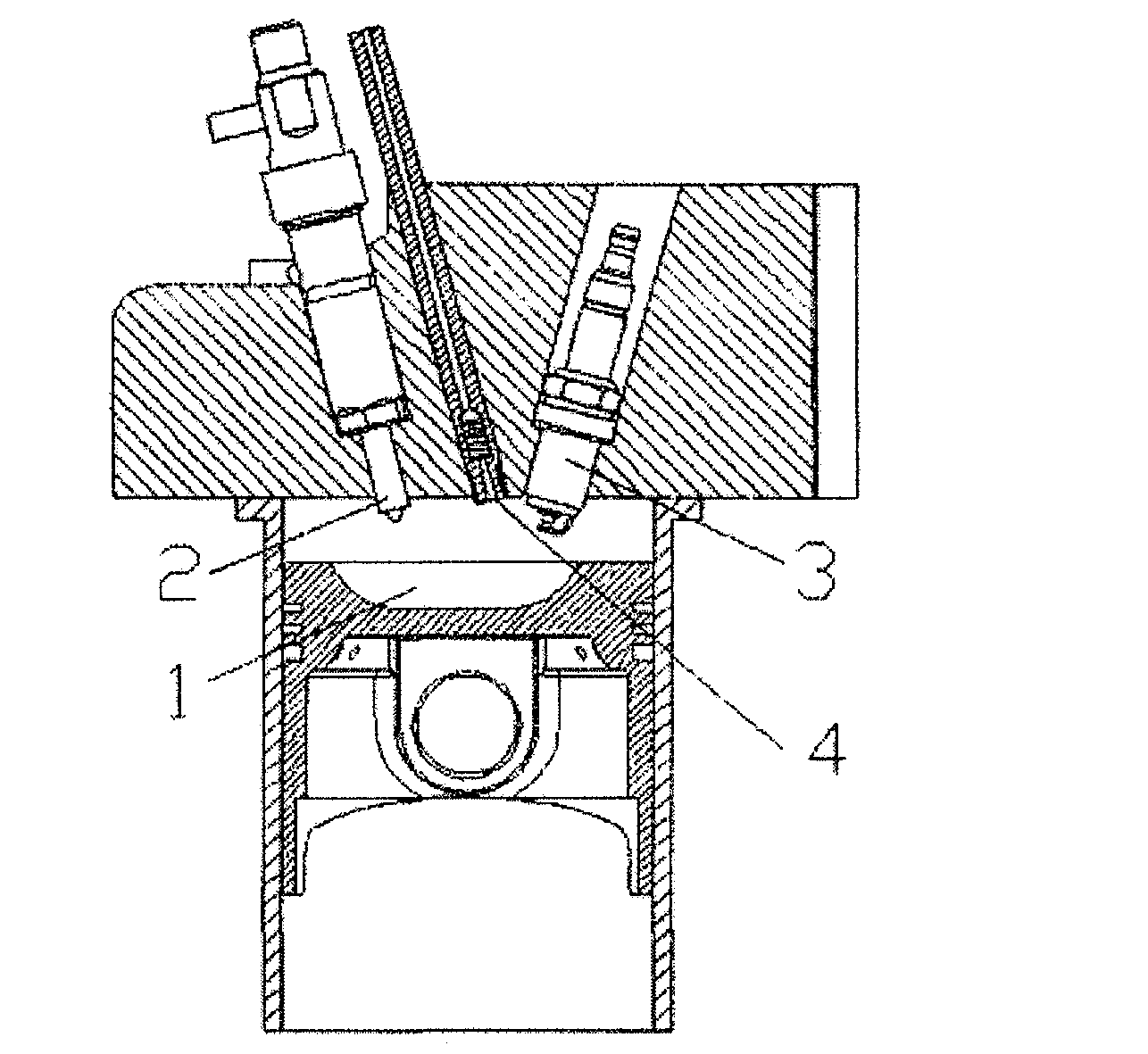
Multi-fuel pre-mixed combustion system of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20130104850A1Improve performanceLow costInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion systemSpray nozzle
A multi-fuel pre-mixed combustion system of an internal combustion engine includes a main fuel spray nozzle (2), which injects a mixed fuel of compression-ignition-suitable fuels, spark-ignition-suitable fuel, or a wide cut fuel to form a homogeneous primary pre-mixed gas. An auxiliary spray nozzle (4) injects a spark-ignition-suitable fuel to form a secondary mixed gas, which is ignited by the spark plug (3) by means of spray guiding or an ignition chamber (5), and the primary pre-mixed gas in the combustion chamber (1) is compression ignited. Consequently, the ignition point of the primary mixed gas is effectively controlled and knock is avoided, and a homogeneous pre-mixed compression ignition is achieved over the whole range of operating conditions. The combustion rate is controlled by exhaust gas recirculation or spray of water into a cylinder or intake port, and high thermal efficiency is ensured by a high expansion ratio.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Supercharged internal combustion engine system
InactiveUS20090259388A1Weight increaseHigh densityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberMechanical energy
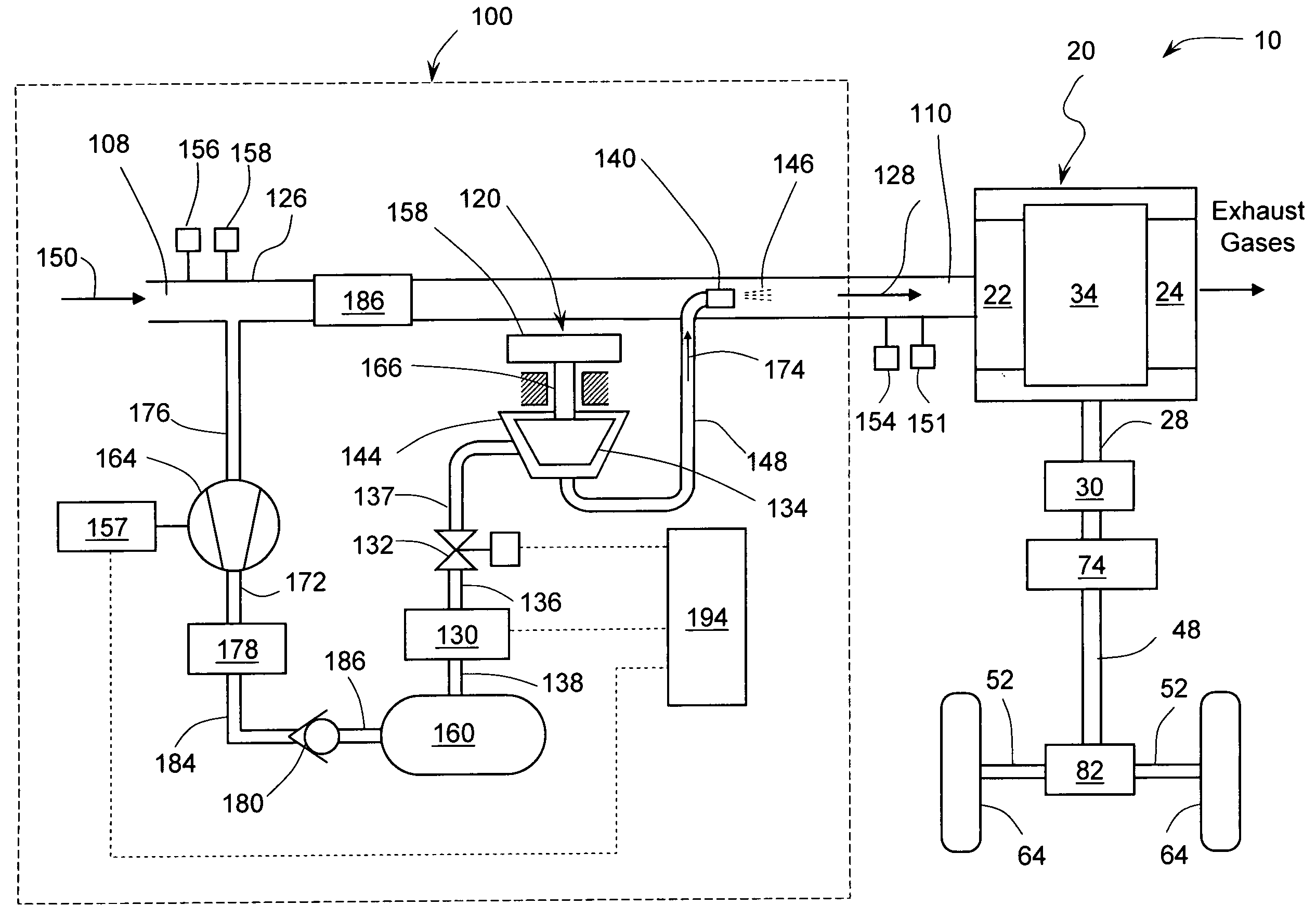
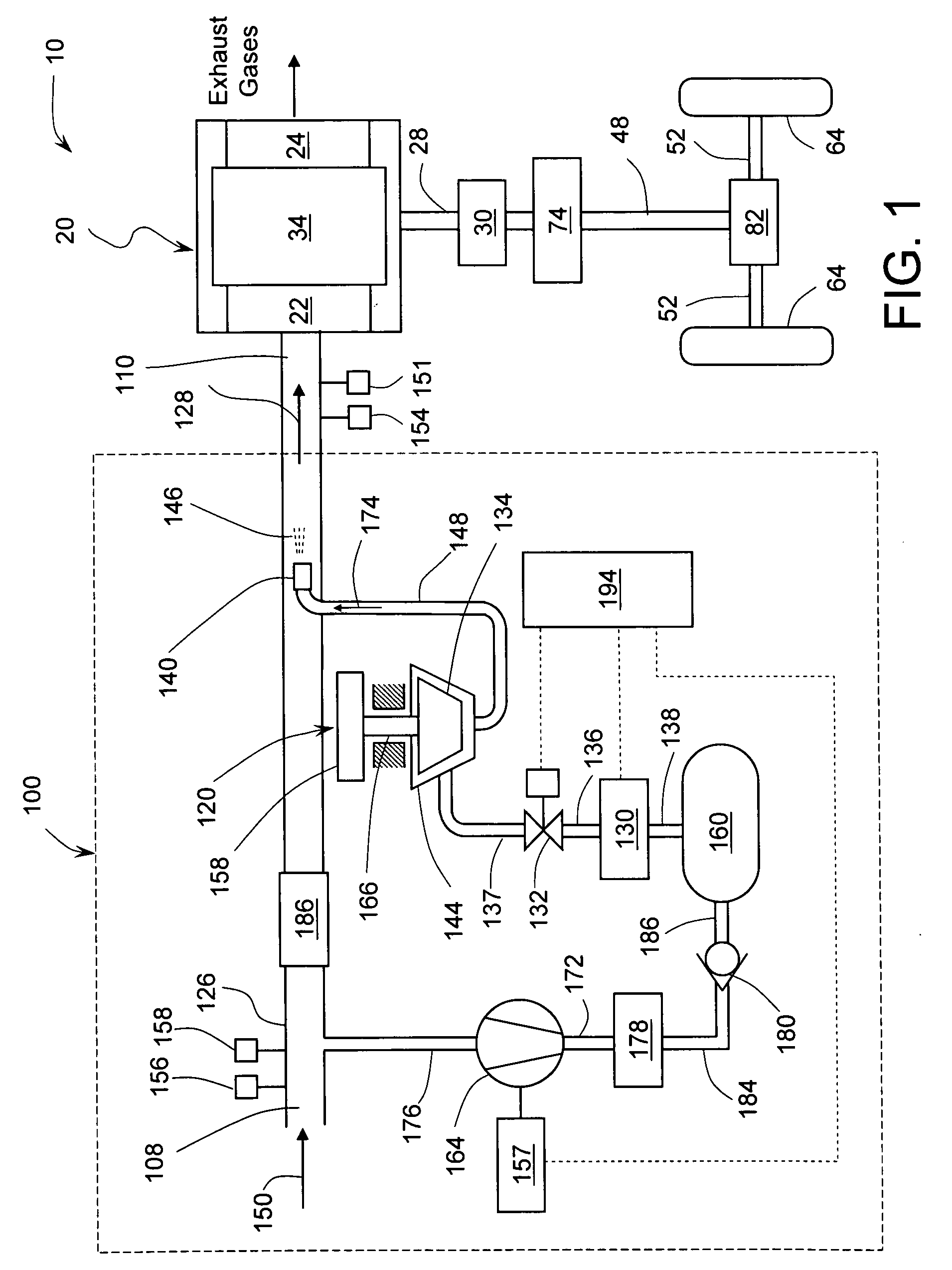
A supercharged internal combustion engine system wherein during periods of high power demand the weight of combustion chamber charge is increased by cooling a portion of intake air in a turboexpander using high-pressure air from a storage tank. In addition to increasing engine output power, cold air intake also reduces engine pre-ignition (knocking) thereby reducing emissions. Mechanical energy produced during expansion of high-pressure air may be used to operate a turbocompressor, which compresses intake air and further increases charge weight. Effective supercharging is achieved even at low engine speeds. One of the objects of the invention is to obtain more power from small displacement ICE and thus providing automotive vehicles with sufficient acceleration in addition to good fuel economy. Another object of the invention is to enhance turbocharged engines and reduce their response lag. Air storage tank may be recharged using energy recovered during vehicle deceleration.
Owner:AGWEST
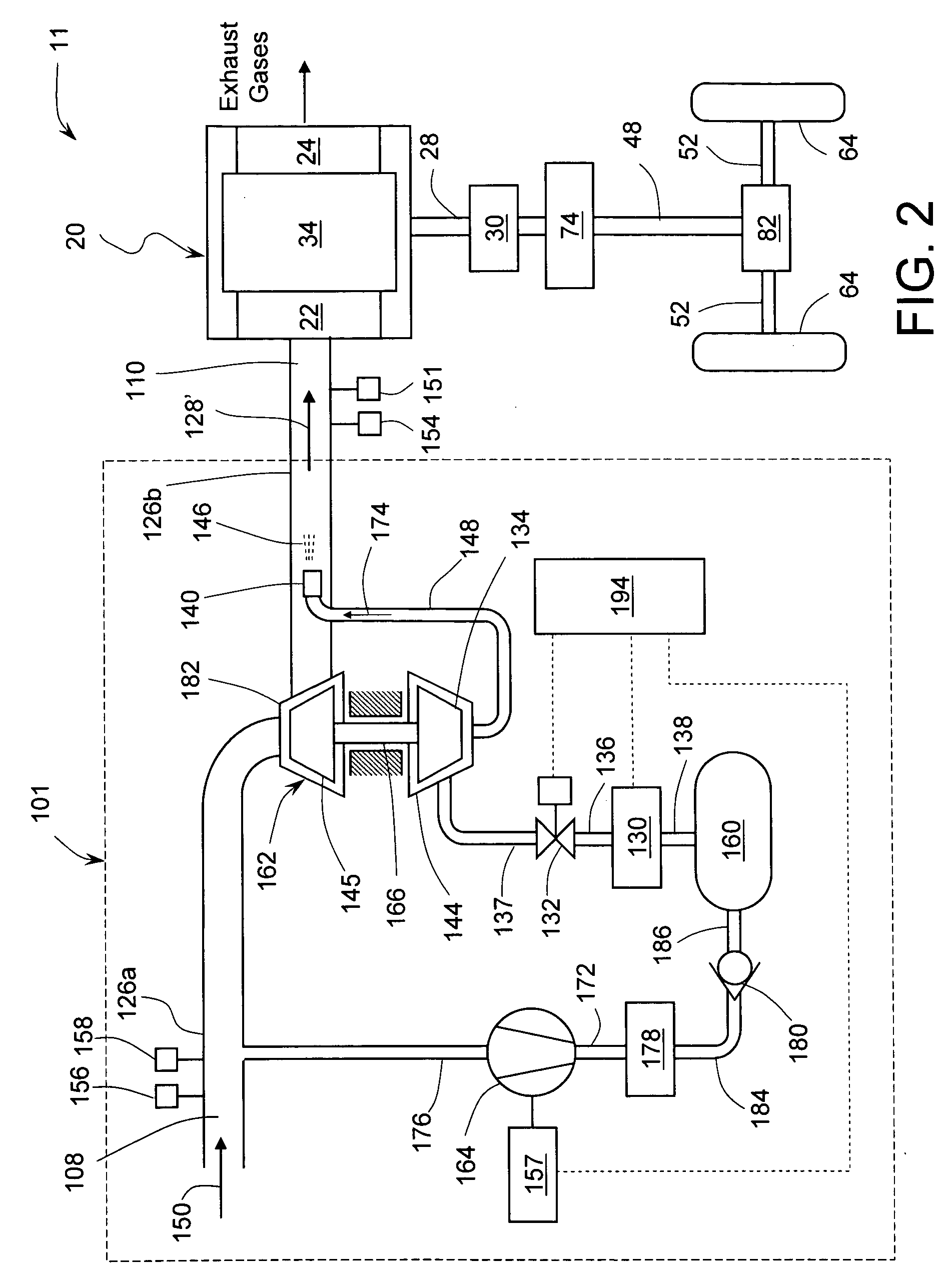
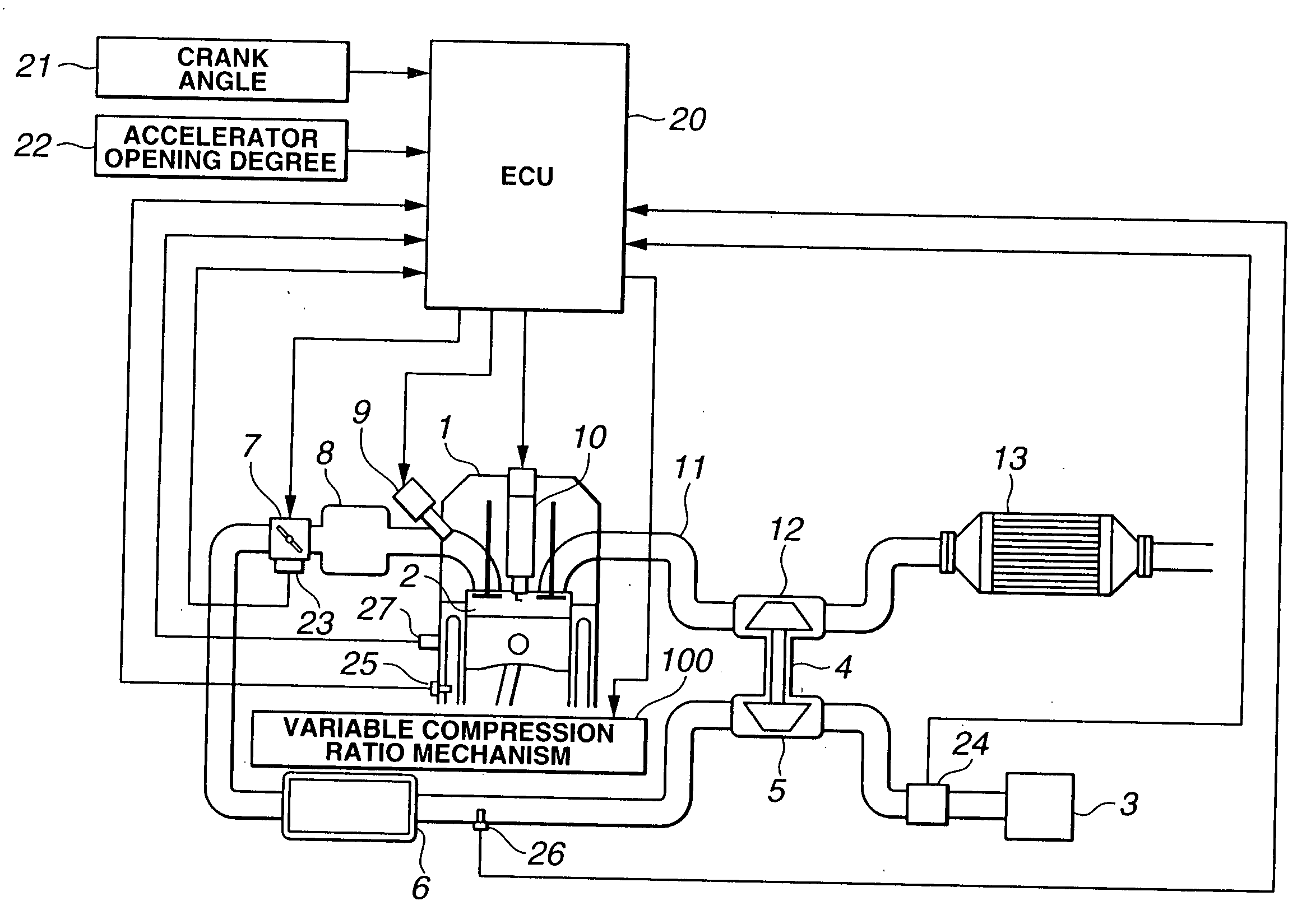
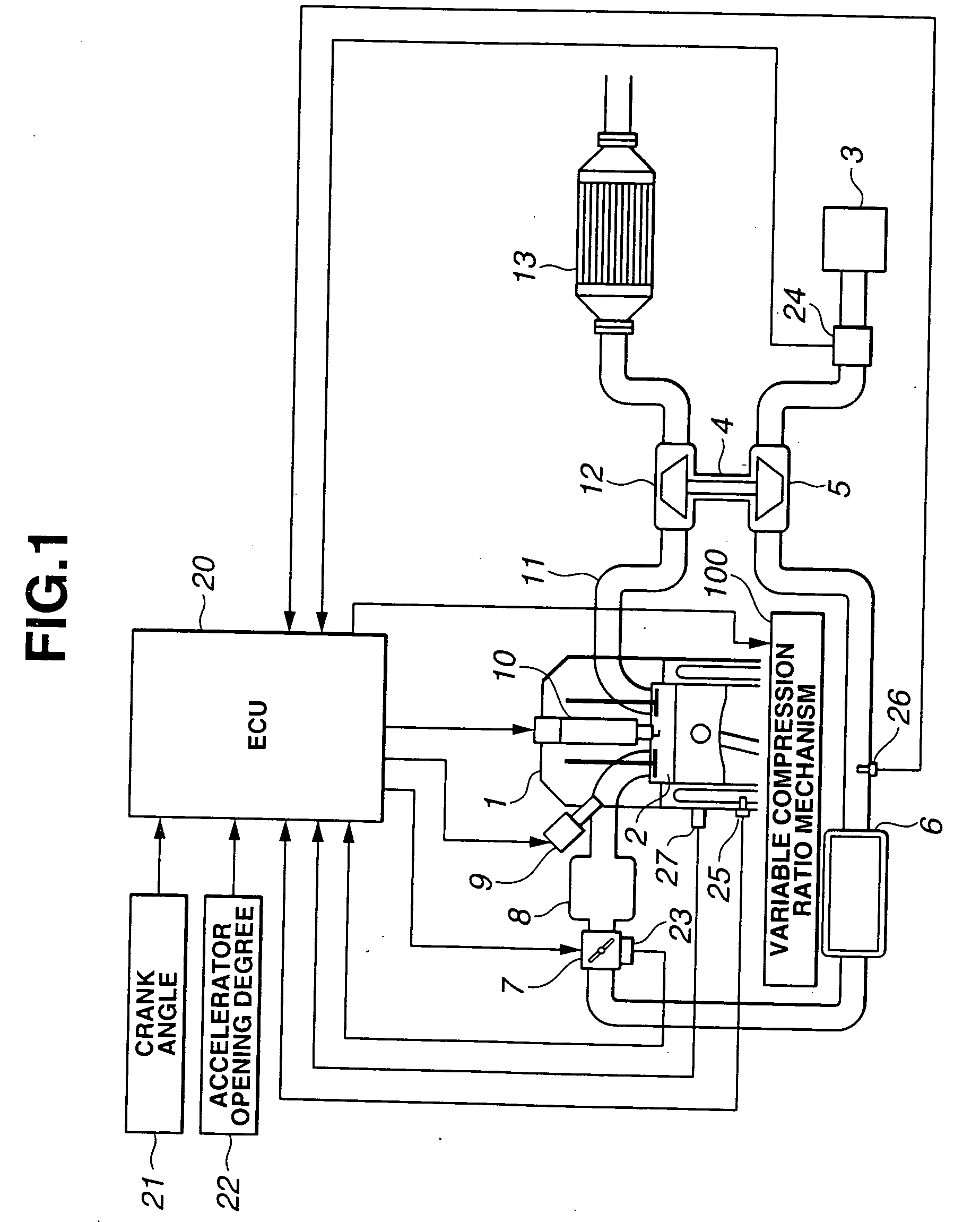
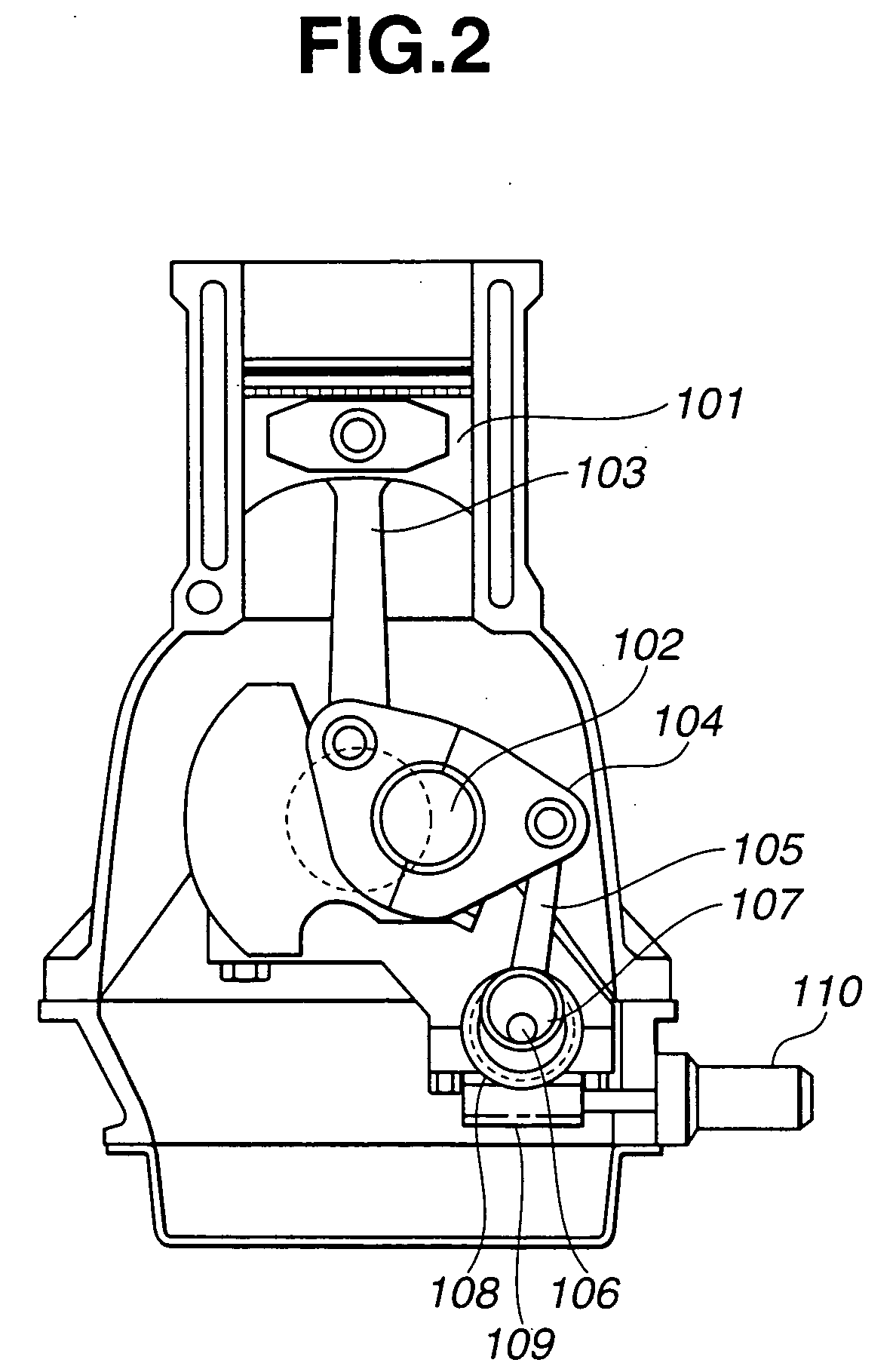
Control apparatus and method for internal combustion engine with variable compression ratio mechanism
ActiveUS20050056240A1Prevent deviationEasy to set upConnecting rodsInternal combustion piston enginesIgnition timingControl theory
A control apparatus for an internal combustion engine includes a variable compression ratio mechanism capable of varying a compression ratio of the engine, a compression ratio setting section that sets a compression ratio to be attained by the variable compression ratio mechanism in accordance with an operating condition of the engine, a knock detecting section that detects a knock occurrence state, an ignition timing learning correcting section that determines a learning correction value of an ignition timing in accordance with the knock occurrence sate, and a compression ratio correcting section that corrects the compression ratio set by the compression ratio setting section in accordance with the learning correction value of the ignition timing. A control method is also provided.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
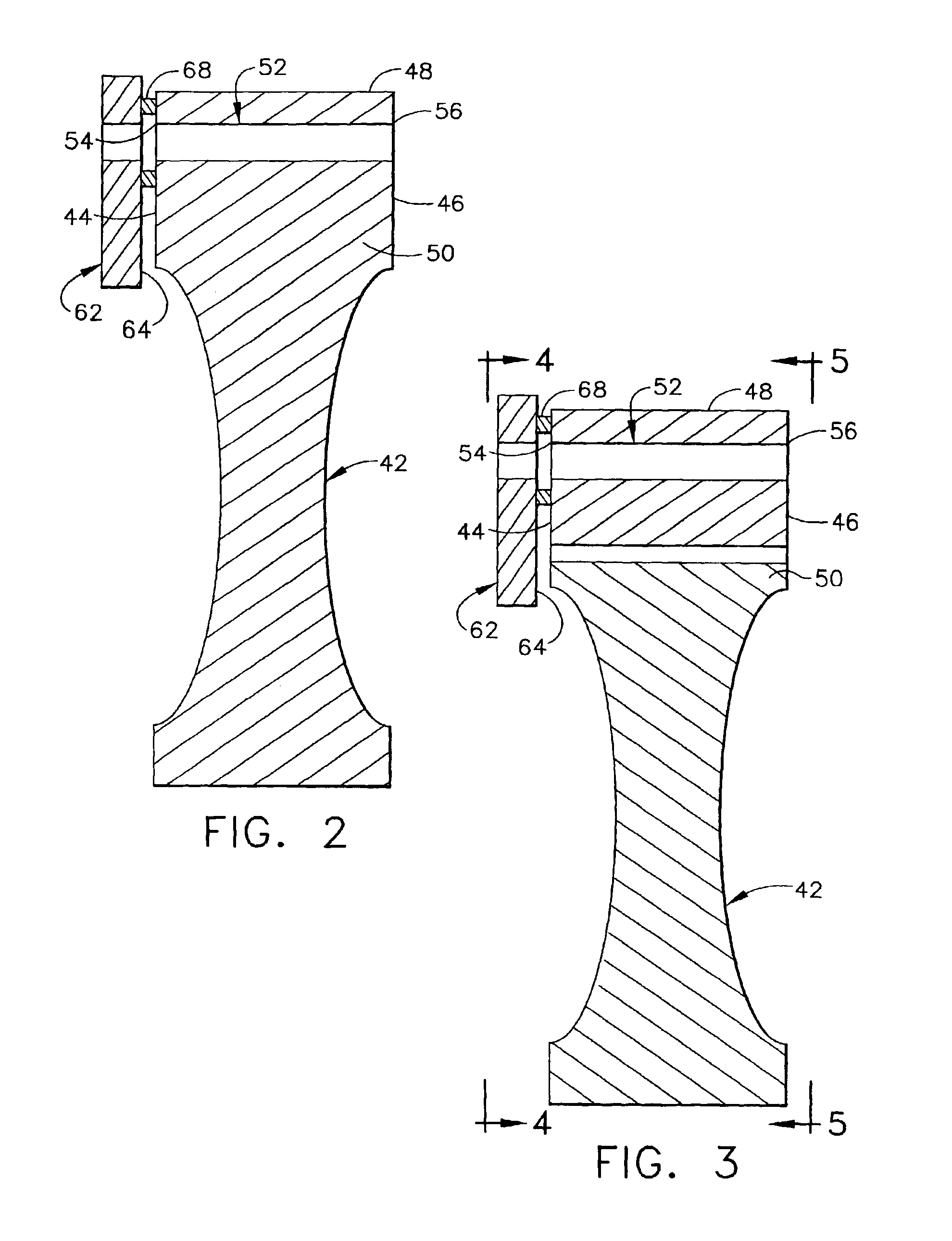
Pulse detonation system for a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS6889505B2Turbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionDetonationGas turbines
A pulse detonation system for a gas turbine engine having a longitudinal centerline axis extending therethrough includes a rotatable cylindrical member having a forward surface, an aft surface, and an outer circumferential surface, where at least one stage of circumferentially spaced detonation chambers is disposed therein. The pulse detonation system further includes a shaft rotatably connected to the cylindrical member and a stator configured in spaced arrangement around the forward surface, the aft surface, and the outer circumferential surface of the cylindrical member and a portion of the shaft. The stator has at least one group of ports formed therein which sequentially align with the detonation chambers as the cylindrical member rotates. In this way, detonation cycles are performed in the detonation chambers of each detonation stage so that reaction forces induced by the detonation cycles create a torque which causes the cylindrical member to rotate. Each detonation chamber includes a first open end located adjacent the outer circumferential surface of the cylindrical member and a second closed end located within a middle portion of the cylindrical member.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com