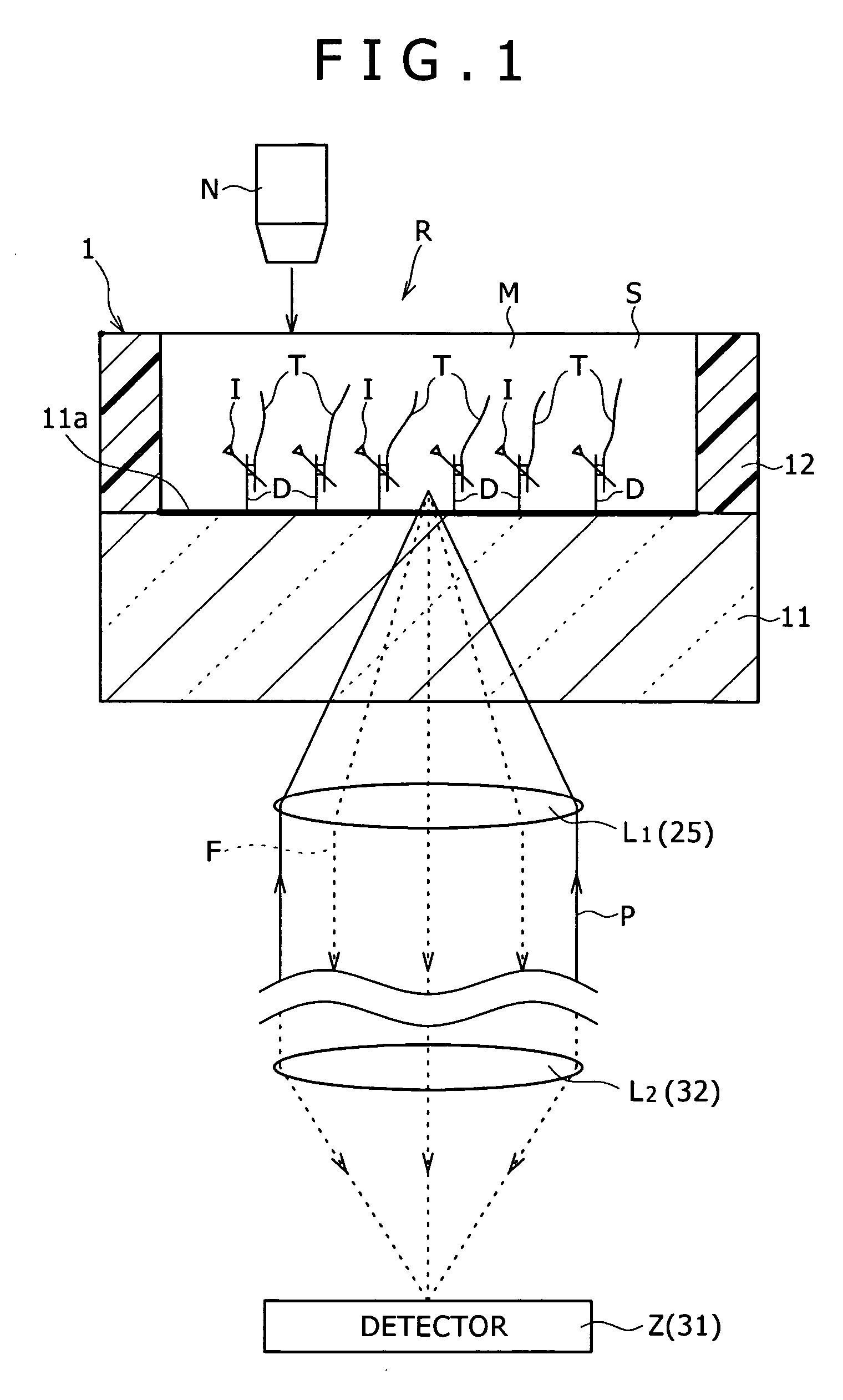
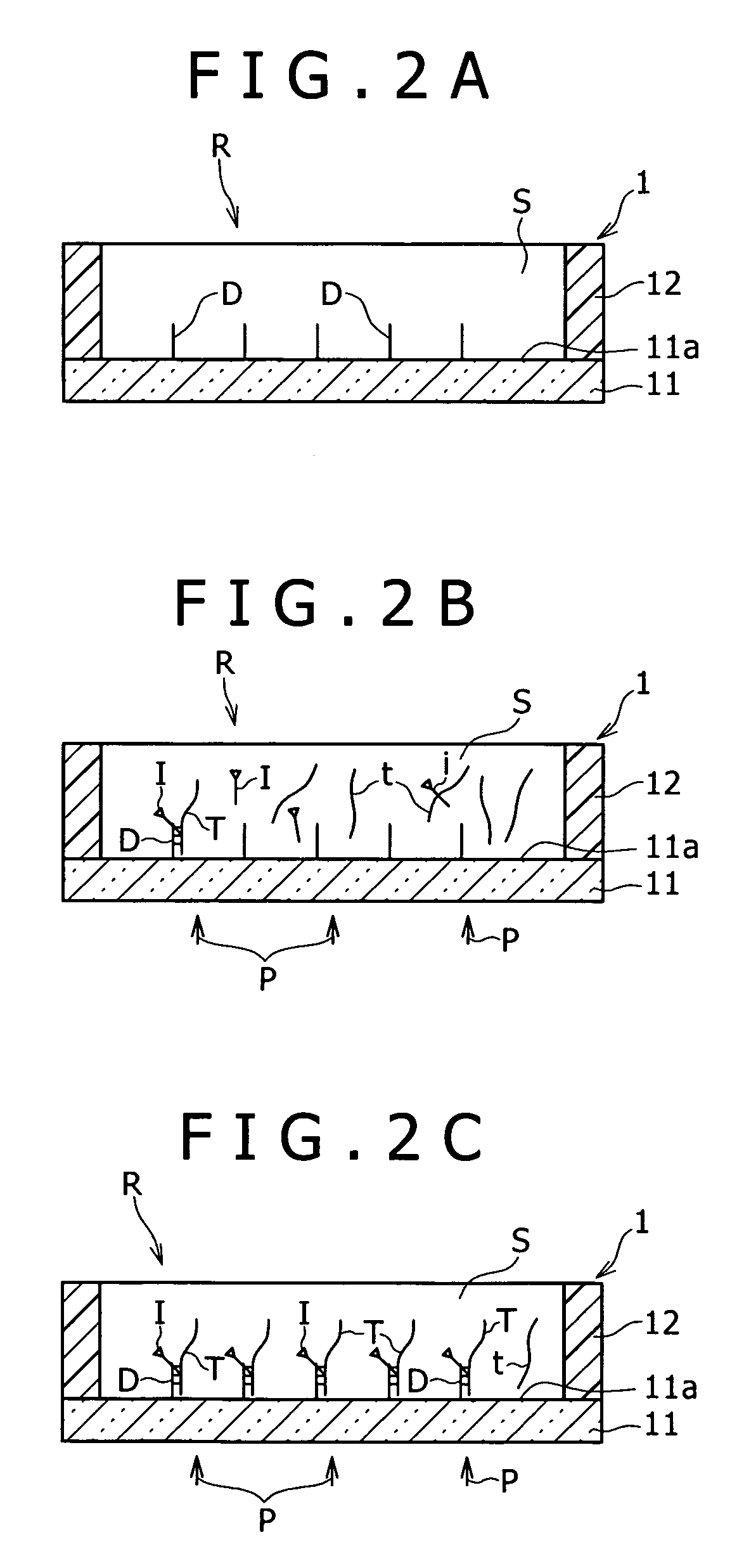
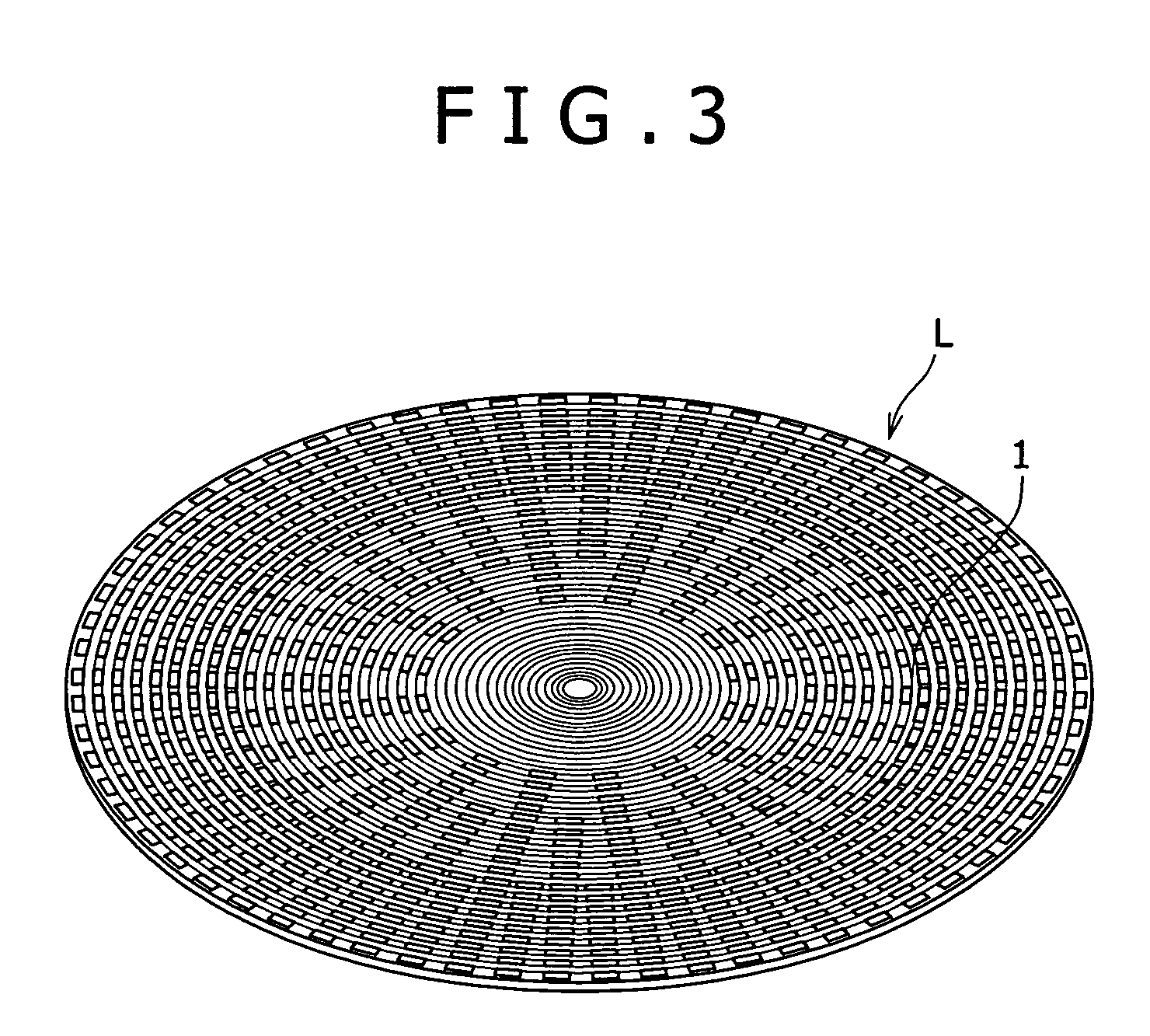
Method and unit for detecting an interaction such as hybridization, bioassay plate provided with a number of such detecting units, system for detecting an interaction such as hybridization, and reagent kit
a technology of intercalator and detecting unit, which is applied in the field of intercalator detection technique using salt-containing hepes buffer, can solve the problem that the binding characteristics of intercalator cannot be easily retained for a long time, and achieve the effects of improving the accuracy of hybridization detection, high general utility, and high utility valu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0107] Buffers suited for the structural stability of an intercalator were verified by thin-layer chromatography. As the intercalator, “SYBRGreen I Nucleic Acid Gel Stain” (trade name, product of Cambrex Corporation; “SYBR” is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc.; hereinafter referred to as “SYBRGreen I”) was used. “SYBRGreen I” is a high-sensitivity color-developing reagent useful for the detection of double-stranded nucleic acids. “SYBRGreen I” exhibits sensitivity as high as 25 to 100 times of ethidium bromide, it is a composition considered to be adequate as an intercalator. It is to be noted that “SYBRGreen I” is labeled with a fluorescent colorant and permits the detection of its binding to a double-bonded nucleic acid on the basis of fluorescence. The experimental procedure will be described next.
[0108] Firstly, SYBRGreen I was diluted tenfold with the buffers shown in Table 1 to provide experimental samples (Sample 1 to Sample 7). For the preparation of the HEPE...
example 2
[0115] An investigation was conducted about the relationship between the temperature and pH of a buffer.
[0116] Provided were HEPES buffers, the pHs of which were 6.8, 7.1, 7.4 and 7.7, respectively, at room temperature (25° C.), and a Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 7.5). The pHs of the individual buffers were measured at temperatures of 35° C., 45° C., 55° C. and 65° C. The results are shown in FIG. 5.
[0117] As shown in FIG. 5, the Tris-EDTA buffer significantly varied in pH as the temperature changed. The HEPES buffers, on the other hand, underwent only small variations in pH even when their temperatures arose.
[0118] An intercalator may be impaired in its binding characteristics to a double-stranded nucleic acid and the quantity of fluorescence upon its binding to the double-stranded nucleic acid even by a very small change in the conditions. The above-described experimental results indicate that the use of a HEPES buffer makes it possible to control a pH change small even when conditions...
example 3
[0119] Verification was conducted on buffers capable of making greater the binding ratio of the binding between an intercalator and a double-stranded nucleic acid to the binding between the intercalator and a single-stranded nucleic acid. The following experimental procedure was followed.
[0120] Firstly, the buffers shown in Table 2 were provided.
TABLE 2SampleBuffer used for the dilution of SYBRGreen ISample 10.1 M HEPES, MgCl2 20 mM, pH 7.7Sample 2Phosphate buffer, NaCl 200 mM, pH 7.15Sample 3Tris-EDTA buffer, NaCl 200 mM, pH 7.8Sample 4Tris-EDTA buffer, MgCl2 20 mM, pH 7.5
[0121] Next, SYBRGreen I was diluted 10,000-fold with the buffers, respectively. A single-stranded or double-stranded nucleic acid of 30 mer was added at 100 nM and, after having been left over at room temperature for 10 minutes or 30 minutes, fluorometry was performed. The fluorometric results of those left over at room temperature for 10 minutes are shown in Table 3, and the fluorometric results of those left...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ionic strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com