Compositions and methods for the treatment of disorders of the central and peripheral nervous systems
a central and peripheral nervous system and composition technology, applied in the direction of drug compositions, biocide, heterocyclic compound active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of producing other, undesired effects, etc., to reduce the neurodegenerative effects of acute ethanol ingestion, reduce the activity of chloride-dependent cotransport systems, and relieve pain.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
The Effects of Furosemide on Epileptiform Discharges in Hippocampal Slices
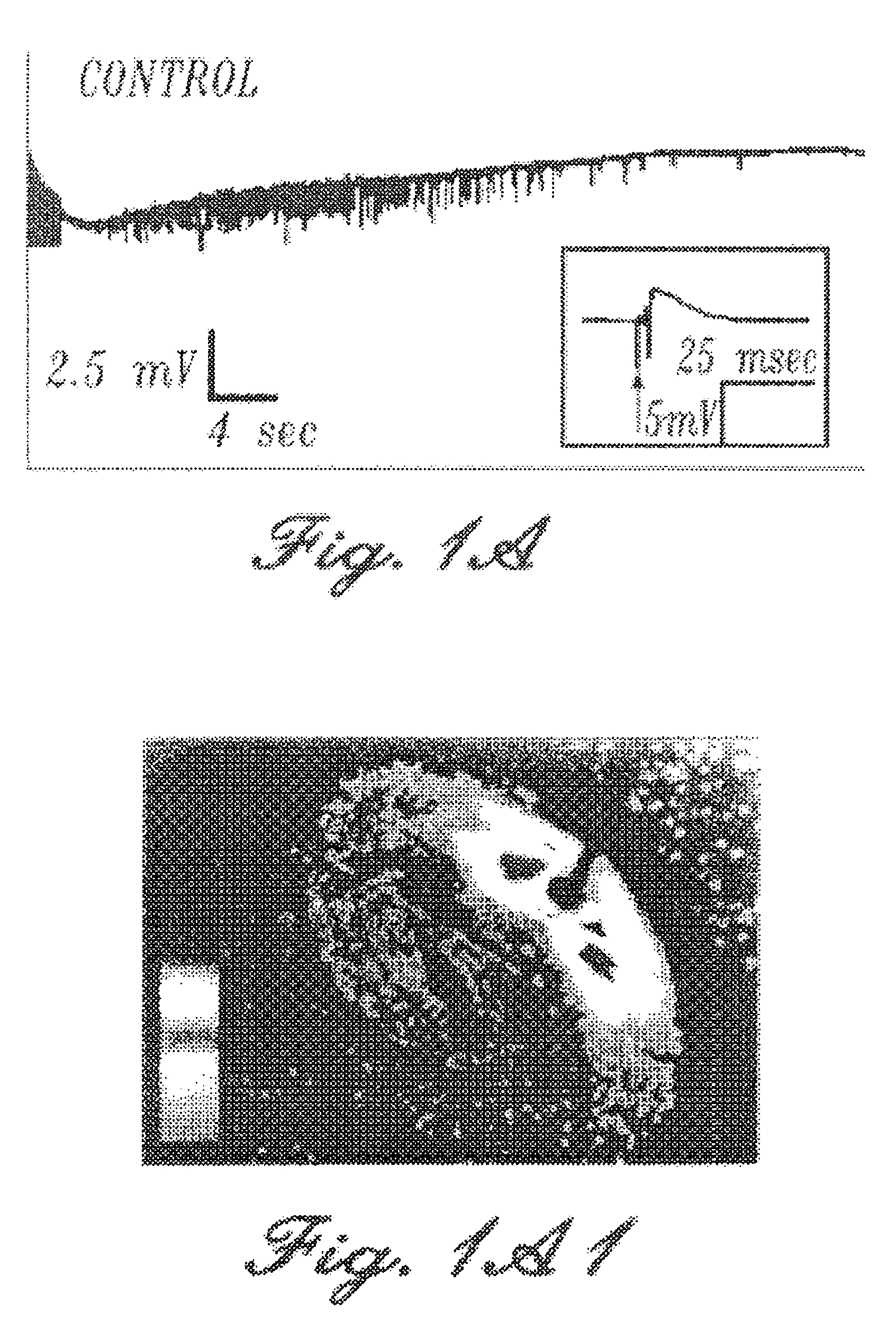
[0059] During these studies, spontaneous epileptiform activity was elicited by a variety of treatments. Sprague-Dawley rats (males and females; 25-35 days old) were decapitated, the top of the skull was rapidly removed, and the brain chilled with ice-cold oxygenated slicing medium. The slicing medium was a sucrose-based artificial cerebrospinal fluid (sACSF) consisting of 220 mM sucrose, 3 mM KCI, 1.25 mM NaH2PO4, 2 mM MgSO4, 26 mM NaHCO3, 2 mM CaCl2, and 10 mM dextrose (295-305 mOsm). A hemisphere of brain containing hippocampus was blocked and glued (cyanoacrylic adhesive) to the stage of a Vibroslicer (Frederick Haer, Brunsick, Me.). Horizontal or transverse slices 400 μm thick were cut in 4° C., oxygenated (95% O2; 5% CO2) slicing medium. The slices were immediately transferred to a holding chamber where they remained submerged in oxygenated bathing medium (ACSF) consisting of 124 mM NaCl, 3 mM KCl, 1.25 ...
example 2
The Effects of Furosemide on Epileptiform Discharges in Hippocampal Slices Perfused with High-K+ (10 mM) Bathing Medium
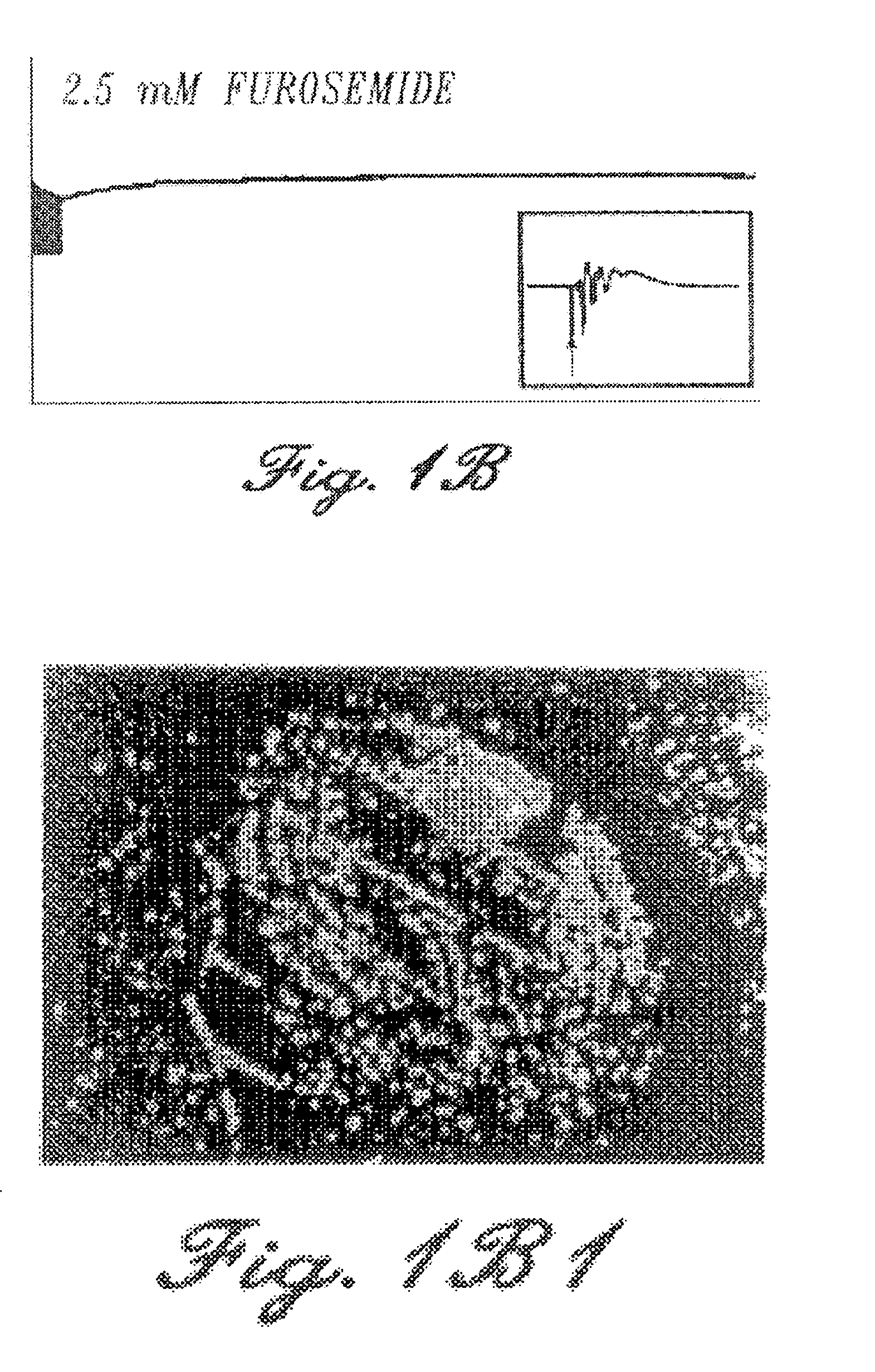
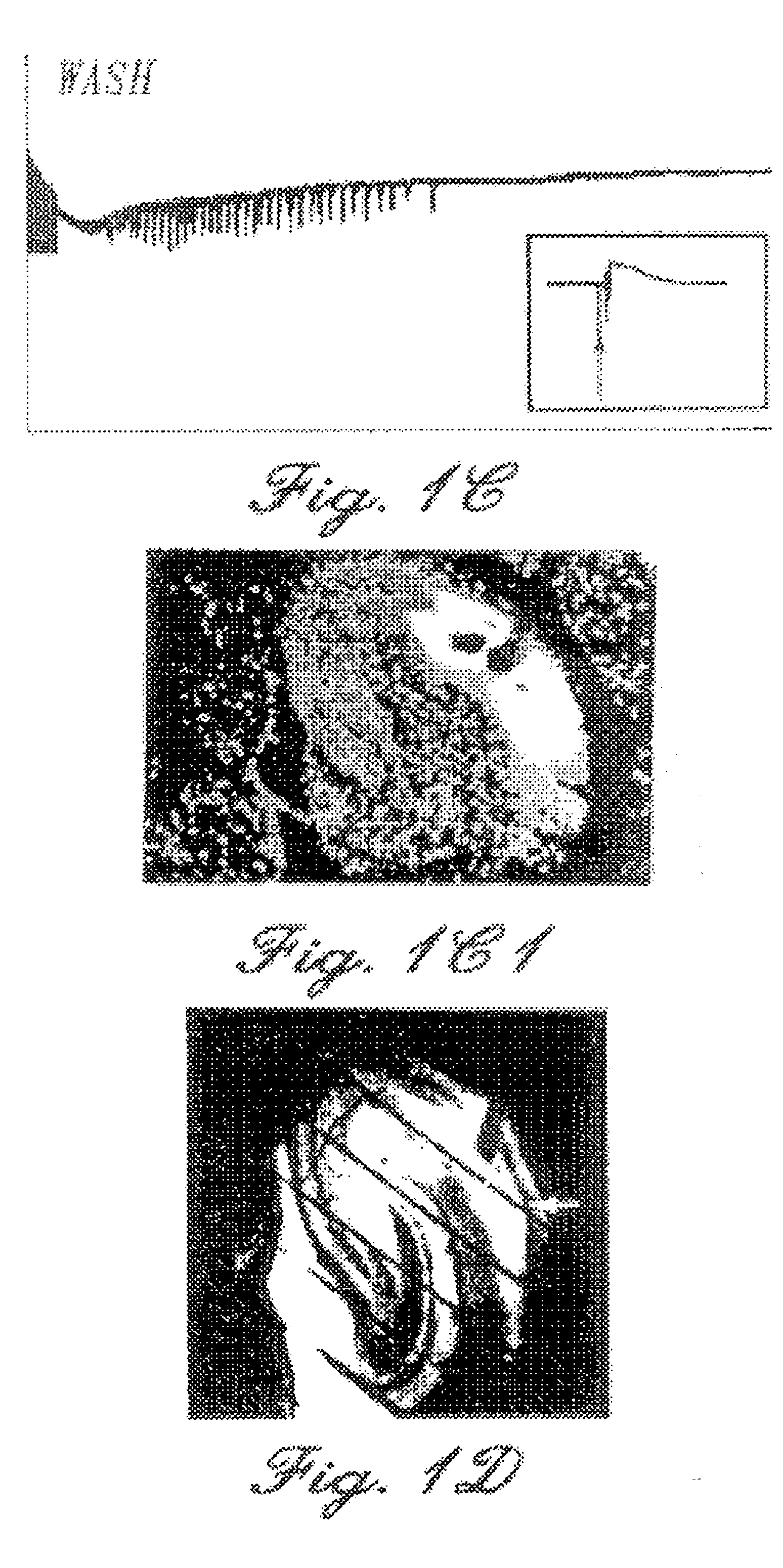
[0065] Rat hippocampal slices, prepared as described above, were perfused with a high-K+ solution until extended periods of spontaneous interictal-like bursting were recorded simultaneously in CA3 (top traces) and CA1 (lower traces) pyramidal cell regions (FIGS. 2A and 2B). After 15 minutes of perfusion with furosemide-containing medium (2.5 mM furosemide), the burst discharges increased in magnitude (FIGS. 2C and 2D). However, after 45 minutes of furosemide perfusion, the bursts were blocked in a reversible manner (FIGS. 2E, 2F, 2G and 2H). During this entire sequence of furosemide perfusion, the synaptic response to a single test pulse delivered to the Schaffer colalterals was either unchanged or enhanced (data not shown). It is possible that the initial increase in discharge amplitude reflected a furosemide-induced decrease in inhibition (Misgeld et al., Science...
example 3
The Effects of Furosemide on Epileptiform Activity Induced by i.v. Injection of Kainic Acid in Anesthetized Rats
[0067] This example illustrates an in vitro model in which epileptiform activity was induced by i.v. injection of kainic acid (KA) into anesthetized rats (Lothman et al., Neurology 31:806, 1981). The results are illustrated in FIGS. 3A-3H. Sprague-Dawley rats (4 animals; weights 250-270 g) were anesthetized with urethane (1.25 g / kg i.p.) and anesthesia maintained by additional urethane injections (0.25 g / kg i.p.) as needed. Body temperature was monitored using a rectal temperature probe and maintained at 35-37° C. with a heating pad; heart rate (EKG) was continuously monitored. The jugular vein was cannulated on one side for intravenous drug administration. Rats were placed in a Kopf stereotaxic device (with the top of the skull level), and a bipolar stainless-steel microelectrode insulated to 0.5 mm of the tip was inserted to a depth of 0.5-1.2 mm from the cortical surfa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Permeability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com