Method for applying metal features onto metallized layers using electrochemical deposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
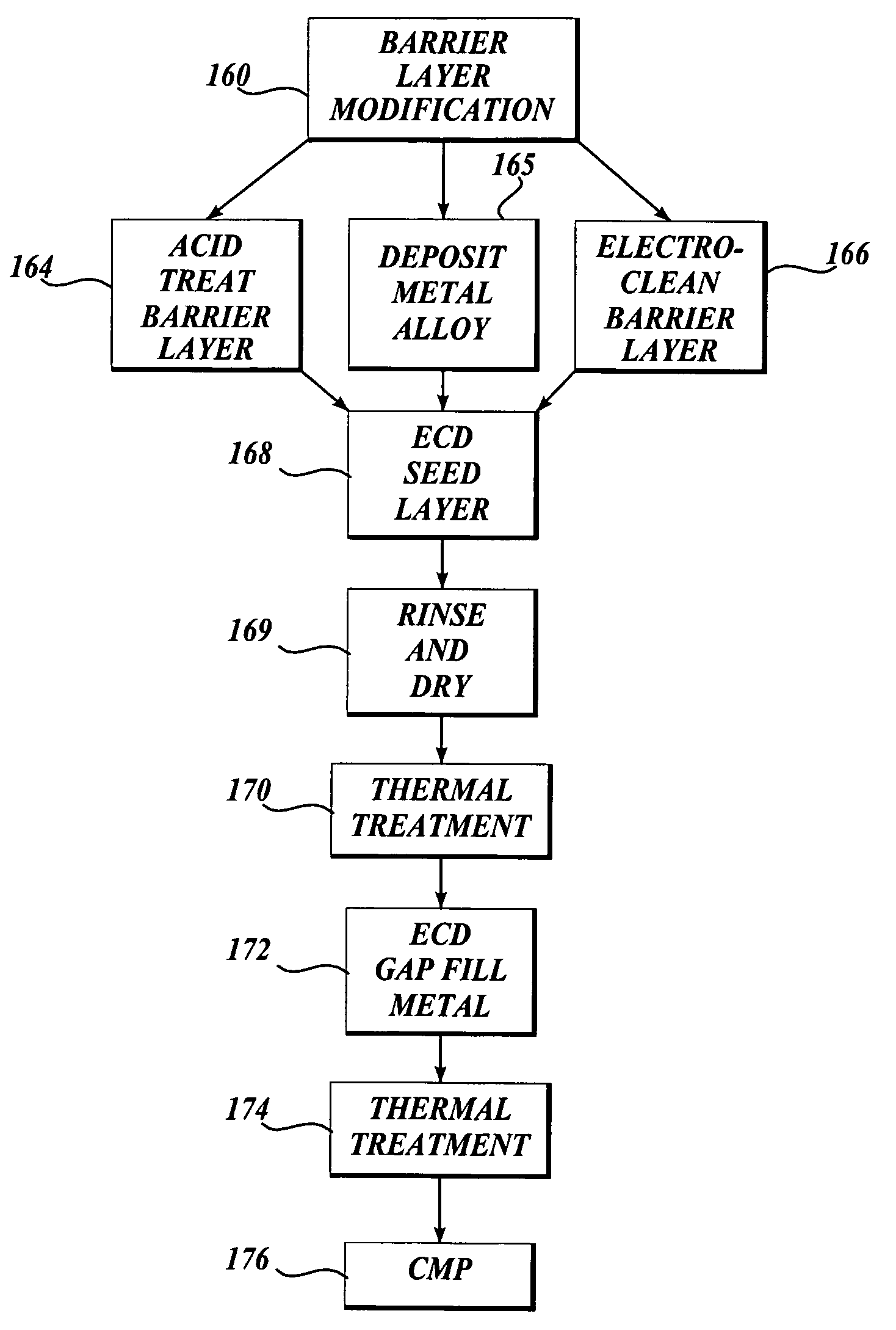
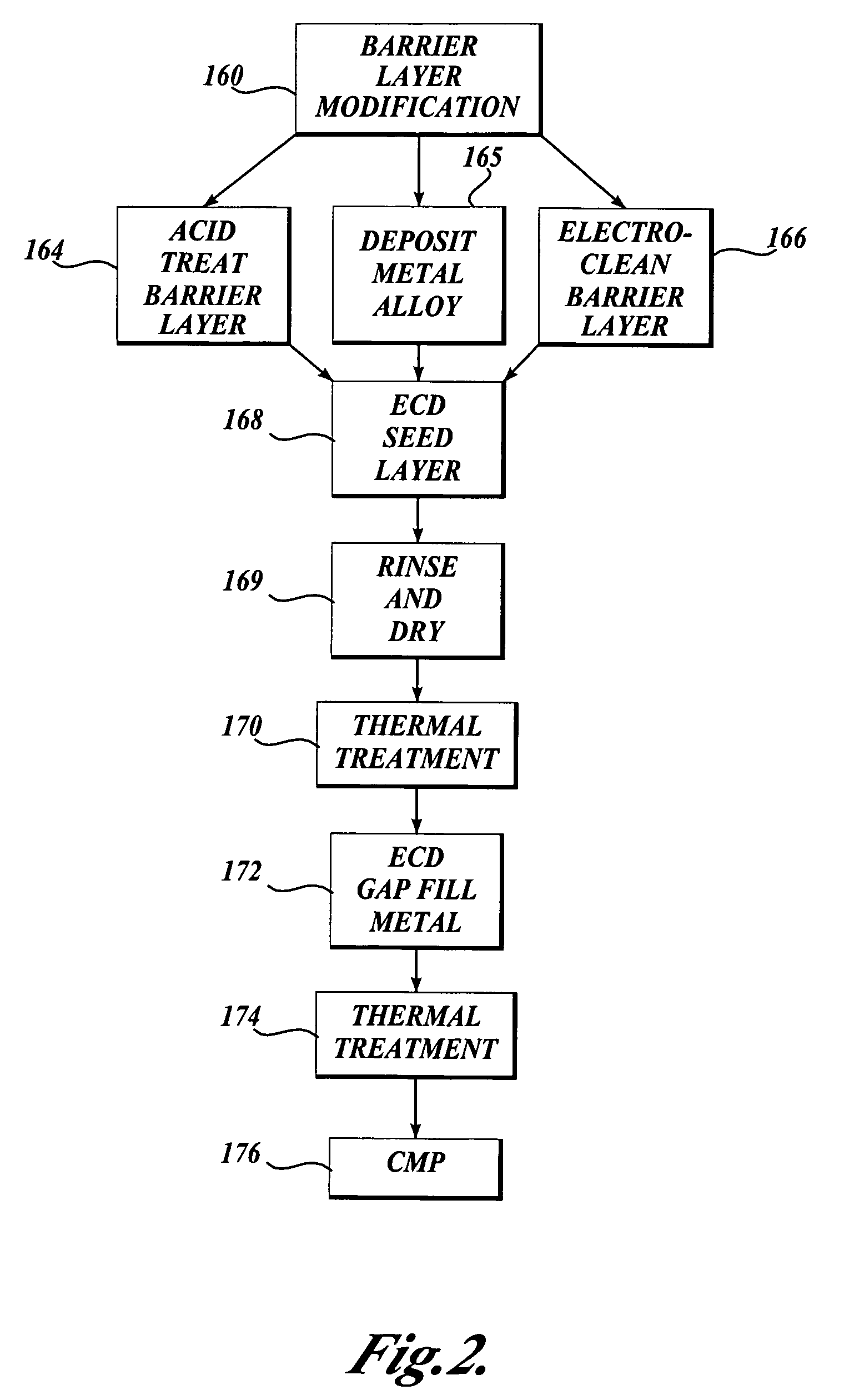
[0096] Acid Treatment of Barrier Layer.
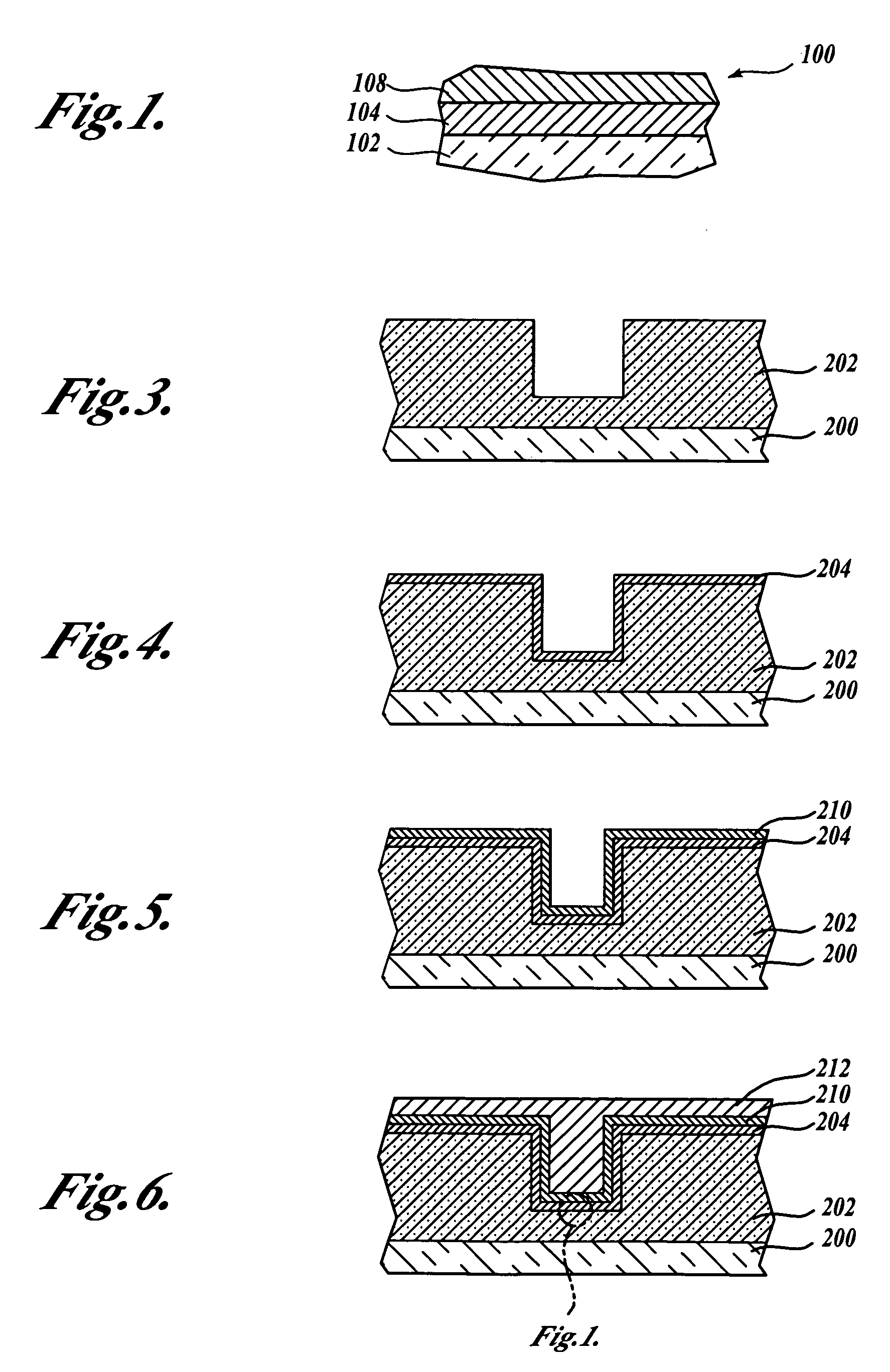
[0097] Acid treatment of a tantalum barrier was performed using 2% by weight aqueous solution of hydrofluoric acid. A 200 mm blanket wafer deposited with 25 nanometers of PVD tantalum barrier was used. This rotating wafer was subjected to a water spray treatment for 15 seconds followed by an acid spray treatment for 15 seconds. Then the rotating wafer was cleaned by spraying de-ionized water for another 15 seconds to remove the excess acid from its surface. For an additional 5 seconds, the wafer was rotated to sling off large water droplets. The wafer was then wet-transferred to a plating chamber. In the plating chamber, the wafer was plated with copper up to a thickness of ˜80 nanometers. After plating, the wafer was cleaned insitu with de-ionized water and the wafer was transferred to a SRD (Spin, Rinse, and Dry) chamber. In this SRD chamber, the spinning wafer was once again cleaned with de-ionized water thoroughly to remove any plating che...
example 2
[0098] Electrolytic Treatment of Barrier Layer.
[0099] Electrolytic treatment of a tantalum barrier was performed using 2% by weight of potassium hydroxide aqueous solution. A 200 mm blanket wafer with 25 nanometers of PVD tantalum barrier was treated. This rotating wafer was used as a cathode and subjected to a current of 1 A (˜3 mA / cm2) for one minute while an inert platinum electrode was the anode. The wafer was then wet-transferred to a SRD chamber where the spinning wafer was rinsed with de-ionized water and then once again wet transferred to a plating chamber. In the plating chamber, the wafer was plated with copper up to a thickness of about 80 nanometers. After plating, the wafer was cleaned insitu with de-ionized water and the wafer was transferred to a SRD chamber. In this SRD chamber, the spinning wafer was once again cleaned with de-ionized water thoroughly to remove any plating chemistry left on its surface. After rinsing, the wafer was dried by spinning it in the chamb...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adhesion strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com