Photoreduction method for metal complex ions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
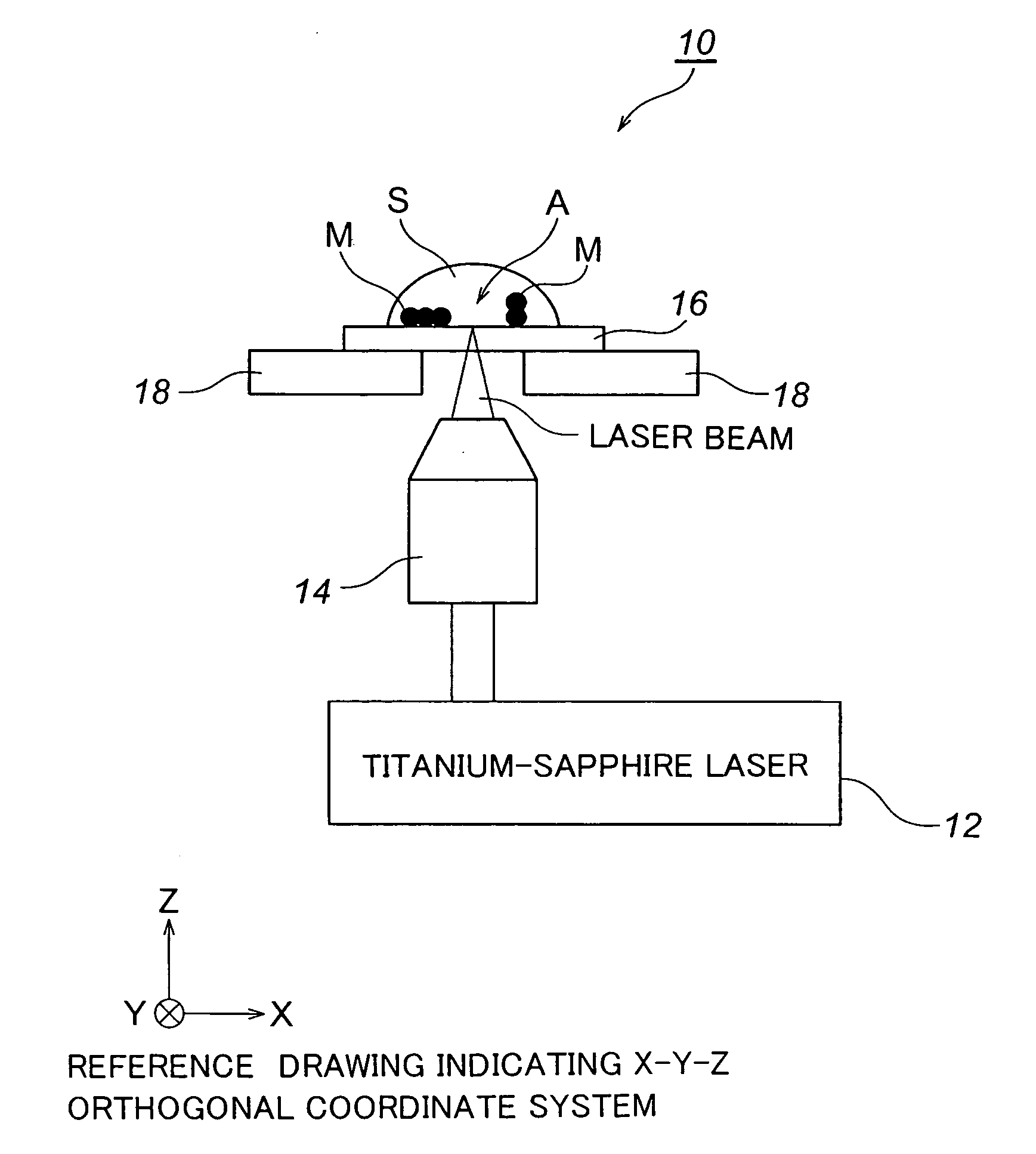
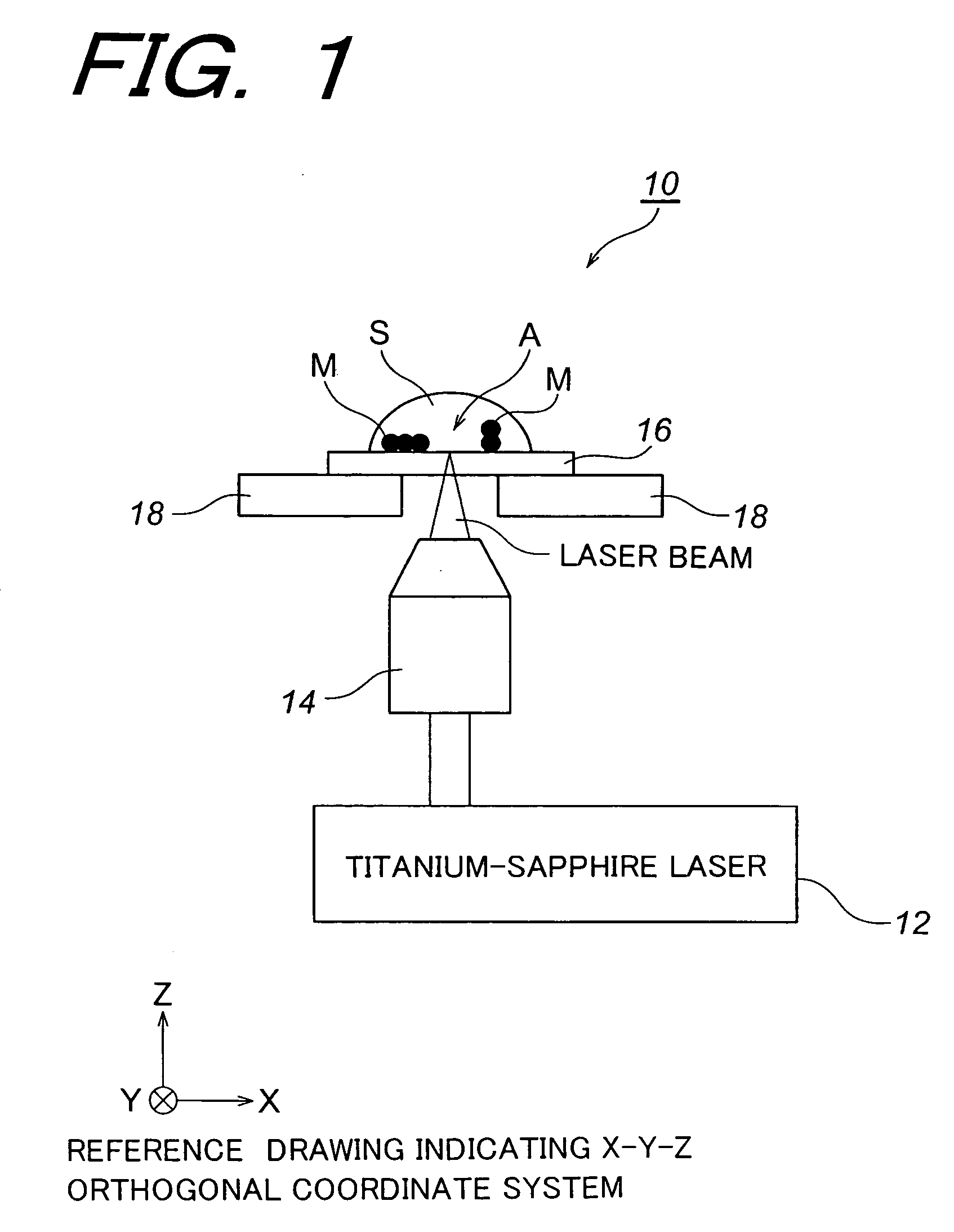
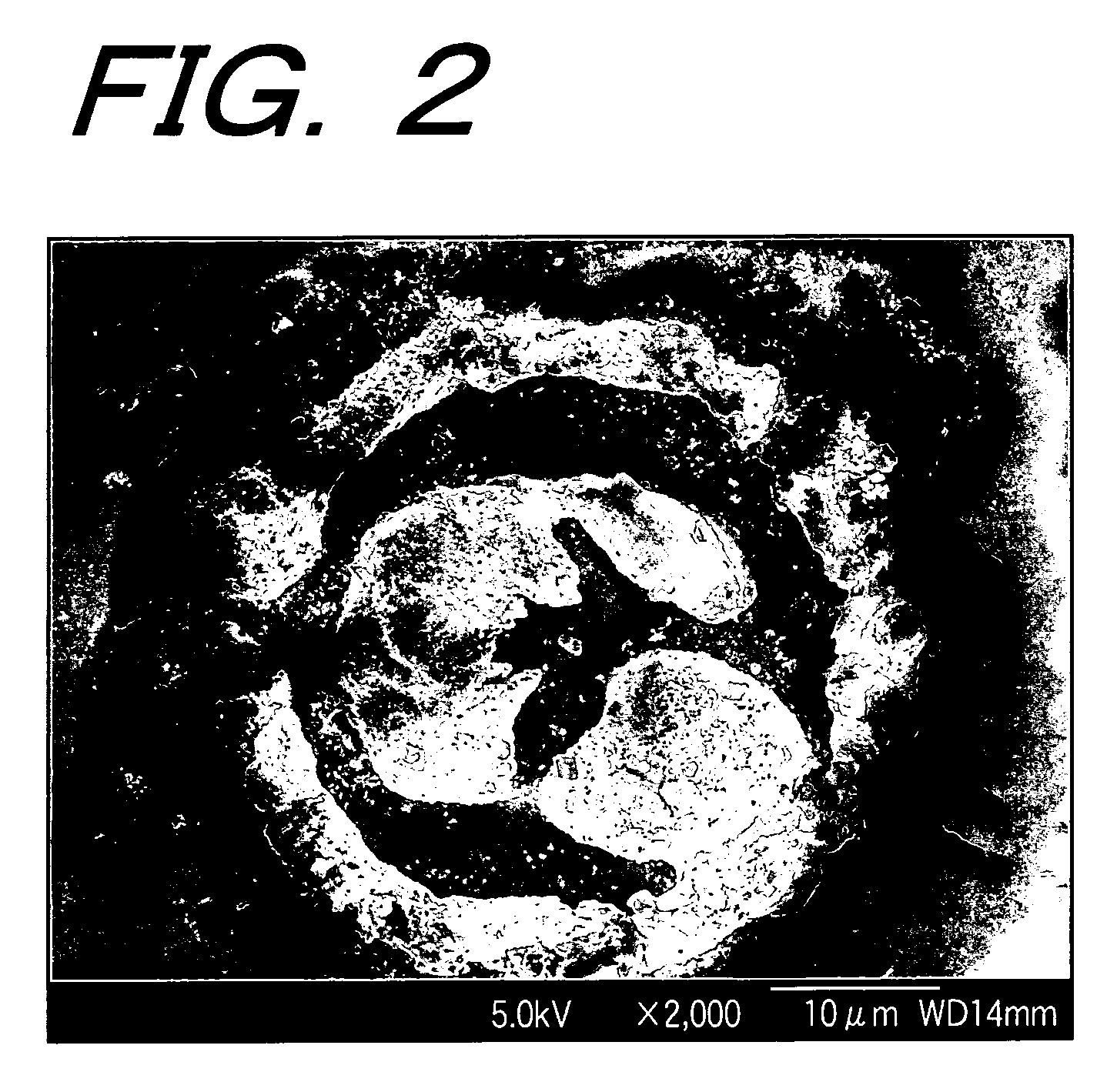
[0045]FIG. 2 is an electron micrograph showing the results of fabricating a silver structure in the case where a AgNO3 aqueous solution is used as the sample S, and the sample S is relatively scanned with the laser beam output from the titanium-sapphire laser 12 at a scanning speed 50 μm / s by means of the above-described optical system 10 wherein an illuminating radiation power is 78.5 mW with respect to the sample S.
[0046] On one hand, FIG. 3 is an electron micrograph showing the results of fabricating a silver structure in the case where a mixture prepared by dissolving Coumarin 440 into an ethanol solvent to a AgNO3 aqueous solution is used as the sample S, and the sample S is relatively scanned with the laser beam output from the titanium-sapphire laser 12 at a scanning speed 50 μm / s by means of the above-described optical system 10 wherein a concentration of Coumarin 440 is 0.02 wt % with respect to the ethanol solvent, while an illuminating radiation power is 14.3 mW with res...
example 2
[0049]FIG. 4 is an optical micrograph showing the results of fabricating a gold structure in the case where a HAuCl4 aqueous solution is used as the sample S, and the sample S is relatively scanned with the laser beam output from the titanium-sapphire laser 12 at a scanning speed 50 μm / s by means of the above-described optical system 10 wherein an illuminating radiation power is 142.9 mW with respect to the sample S.
[0050] On one hand, FIG. 5 is an optical micrograph showing the results of fabricating a gold structure in the case where a mixture prepared by dissolving Coumarin 481 into a dimethylformamide solvent to a HAuCl4 aqueous solution is used as the sample S, and the sample S is relatively scanned with the laser beam output from the titanium-sapphire laser 12 at a scanning speed 50 μm / s by means of the above-described optical system 10.
[0051] In this case, a concentration of Coumarin 481 is 0.1 wt % with respect to the dimethylformamide solvent, while an illuminating radiat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Metallic bond | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com