Automated bioculture and bioculture experiments system
a cell culture and experiment system technology, applied in the field of automated cell culture systems, cell culture growth chambers and automated sampling systems, can solve the problems of cell culture methods that are labor-intensive, outbreaks of contamination in traditional cell culture laboratories, and common contamination, and achieve the effect of preventing contamination of cell cultur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] Reference will now be made in detail to the presently preferred embodiments of the invention which serve to explain the principles of the invention. It is to be understood that the application of the teachings of the present invention to a specific problem or environment will be within the capabilities of one having ordinary skill in the art in light of the teachings contained herein.
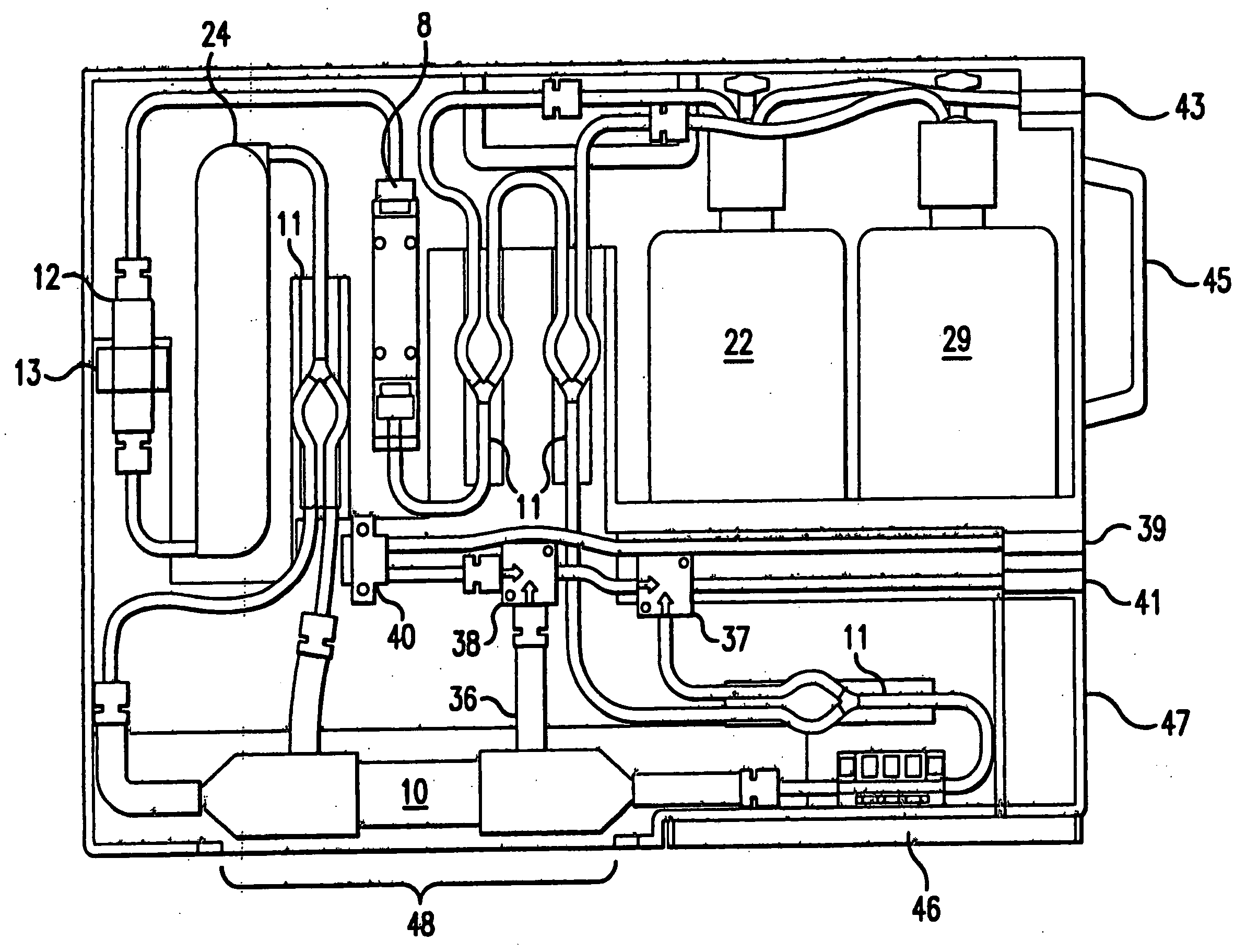
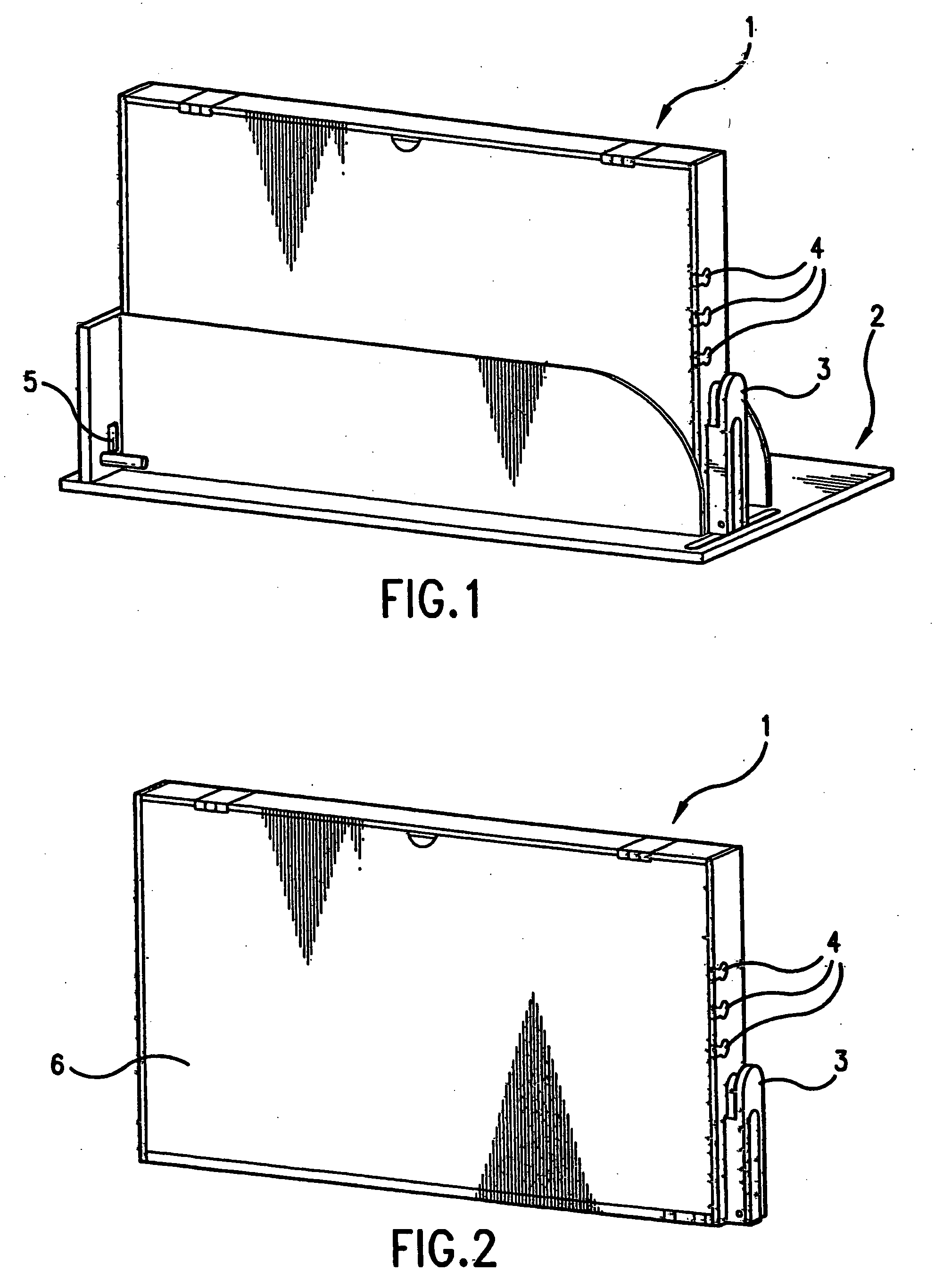
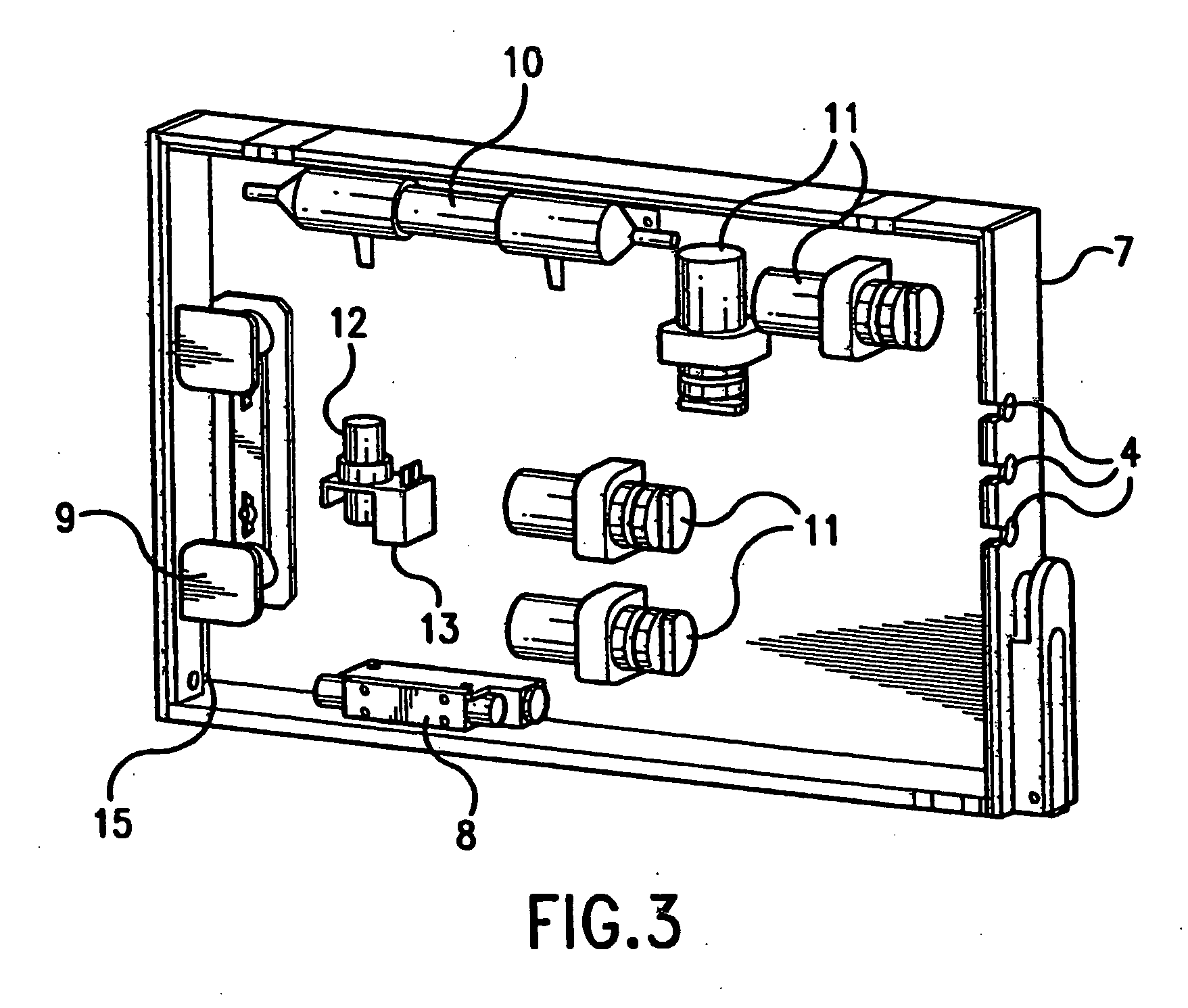
[0037] The present invention provides an automated precision cell culture system which includes one or a plurality of perfusion loop flowpath cartridges that can be placed in an optional rack or docking station which fits into an incubator. The incubator provides the appropriate gas and thermal environment for culturing the cells as each perfusion loop contains a means for passive diffusion of air from the incubator environment. The system provides for parallel processing and optimization through continuous set point maintenance of individual cell culture parameters as well as automated sampling...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| fluid flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com