Light-transmitting module capable of responding a high-frequency over 10GHz
a technology of light-transmitting modules and high-frequency response, which is applied in the direction of lasers, semiconductor laser structural details, semiconductor lasers, etc., can solve problems such as unstable operation of driving circuits, and achieve the effect of enhancing the high-frequency performance of light-transmitting modules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
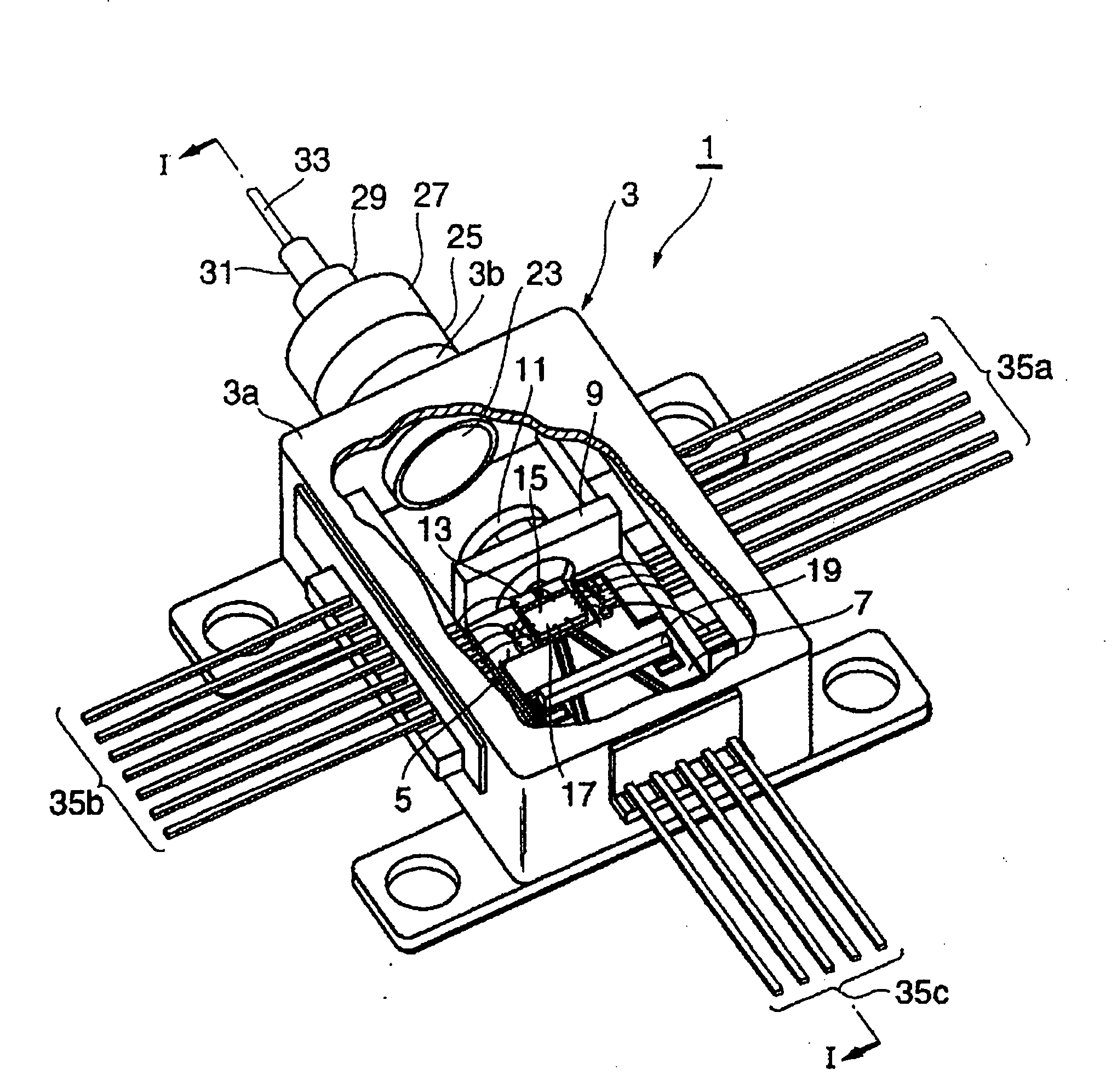
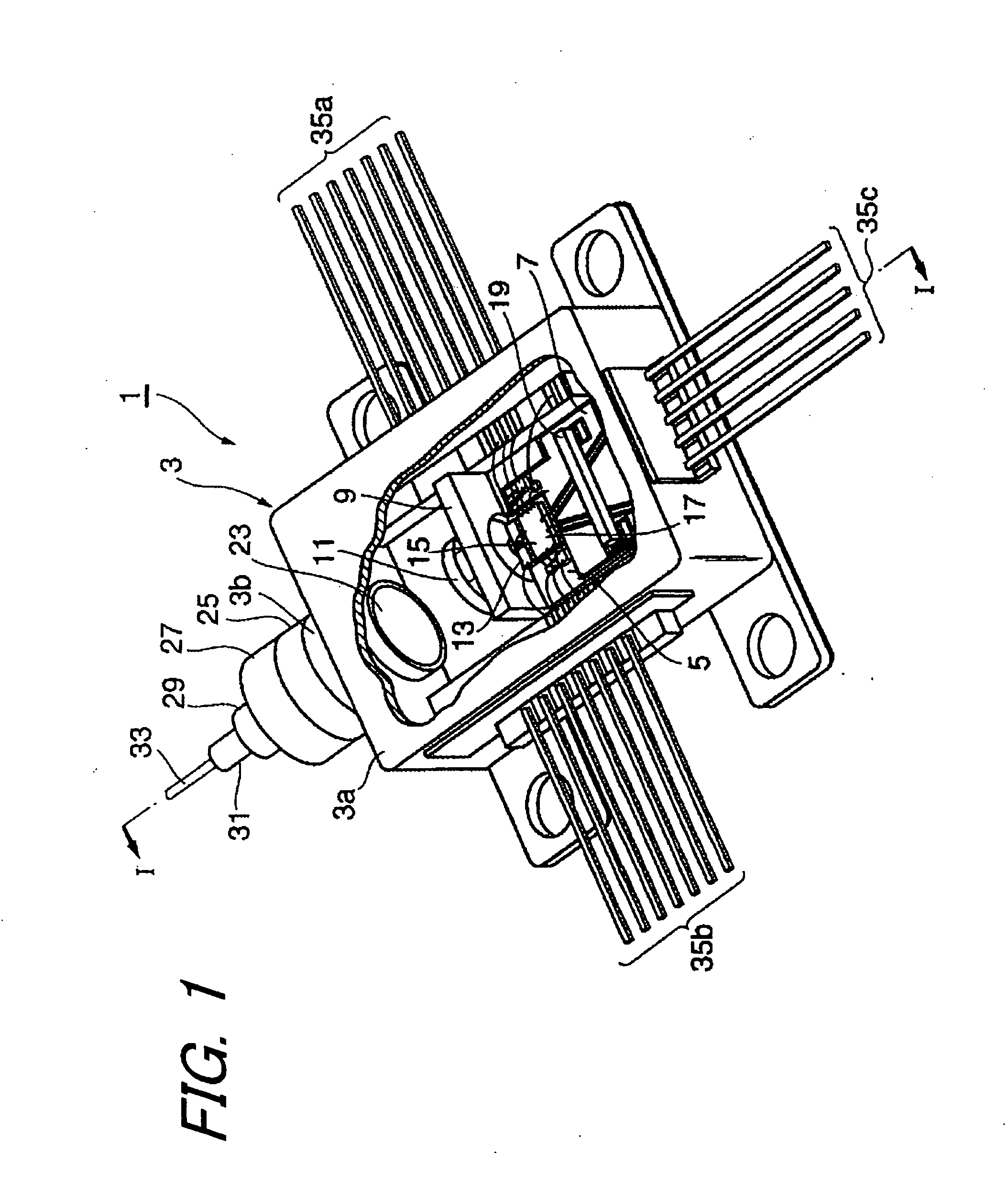
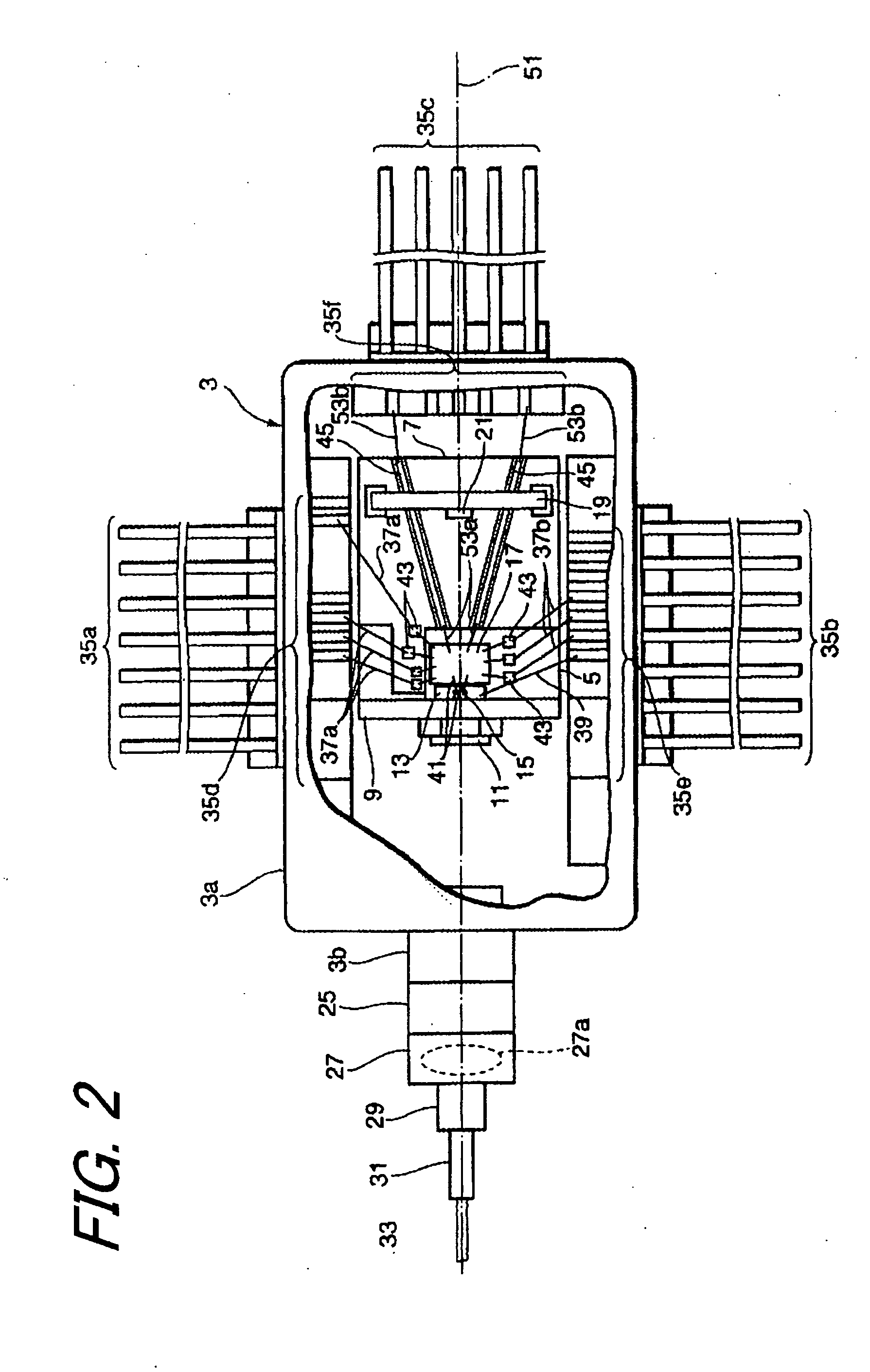
[0028]From FIG. 1 to FIG. 3 show a light-transmitting module 1 according to the first embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 1 is a perspective view, FIG. 2 is a plan view and FIG. 3 is a cross sectional view along the lint I-I in FIG. 1, respectively.
[0029]The light-transmitting module 1 includes a package 3, a first block 5, a substrate 7, a heat sink 13, a laser diode 15 and a driver 17. The package 3, so-called a butterfly type package, has a box portion 3a enclosing the laser diode 15 and the driver 17 and a cylindrical portion 3b provided in the front side of the box portion 3a. Within the box portion 3a, an inert gas such as dry nitrogen is filled.
[0030]The first block 5 is a metallic slab disposed on the bottom surface of the box portion 3a. The heat sink 13 and the driver 17, arranged along a reference axis 51 in FIG. 2, are disposed on the first block 5. The heat sink is an insulator such as aluminum nitride (AlN), which dissipates heat generated by the laser diode 15 t...
second embodiment
[0057]Next, the second embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail. A light-emitting module 2 according to the second embodiment has a passive alignment arrangement. FIG. 12 is a perspective view, FIG. 13A is a cross sectional view taken along the line I-I in FIG. 12, FIG. 13B is a plan view, and FIG. 13C is a cross sectional view taken along the line II-II.
[0058]The light-emitting module 2 has a lead frame 75, a heat sink 61, a sub-mount 63, a driver 65, a plurality of lead terminals from 79a to 79d, and an optical fiber 71. The sub-mount 63 mounts the driver thereof. The optical fiber 71 is secured by a ferrule 77, which is also mounted on the heat sink 61. A resin 77 molds the light-emitting module 2.
[0059]On the lead frame 75 is mounted the sub-mount 63. The heat sink 61 made of conductive material such as copper tungsten (CuW) has receiving regions for the ferrule 61e, the optical fiber 61d and the laser diode 61a, formed integrally thereon and arranged alon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| capacitance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com