Gene transfer into airway epithelial stem cell by using lentiviral vector pseudotyped with RNA virus or DNA virus spike protein
a technology of lentiviral vectors and spike proteins, which is applied in the direction of non-embryonic pluripotent stem cells, drug compositions, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of difficult gene transfer, hardly any vectors that can be efficiently transduced into intact airway epithelium, and difficult to adopt gene transfer approaches. achieve the effect of stable maintenance of gene expression and efficient introduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of Sendai Virus Envelope Protein Expression Plasmids
(1) Construction of Cytoplasmic Domain-Substituted HN Expression Plasmid
[0134]An HN expression plasmid was constructed, where the cytoplasmic domain of the HN protein was substituted with the cytoplasmic domain of the SIV envelope protein (FIG. 1). After annealing three sets of synthetic oligonucleotides (Xho+Xma / Xma-Xho, Xma+131 / 135-Xma, 132+Bam / Bam-136), they were incorporated in turn into the XhoI-BamHIF site of pBluescript KS+. A purified synthetic oligonucleotide-linked fragment obtained by digesting the aforementioned recombinant plasmid with XhoI and DraIII and a purified fragment comprising the 3′ side of the HN protein obtained by digesting the HN protein expression plasmid pCAGGS-HN with DraIII and Bsu36I were incorporated into the XhoI-Bsu36I site of pCAGGS (Gene, vol. 108, pp. 193-200, 1991). The plasmid obtained by the above-mentioned method was used as the SIV cytoplasmic domain-substituted HN expression ...
example 2
Gene Transfer into Mouse Nasal Cavity Epithelial Cells Using the F / HN Pseudotyped SIV Vector
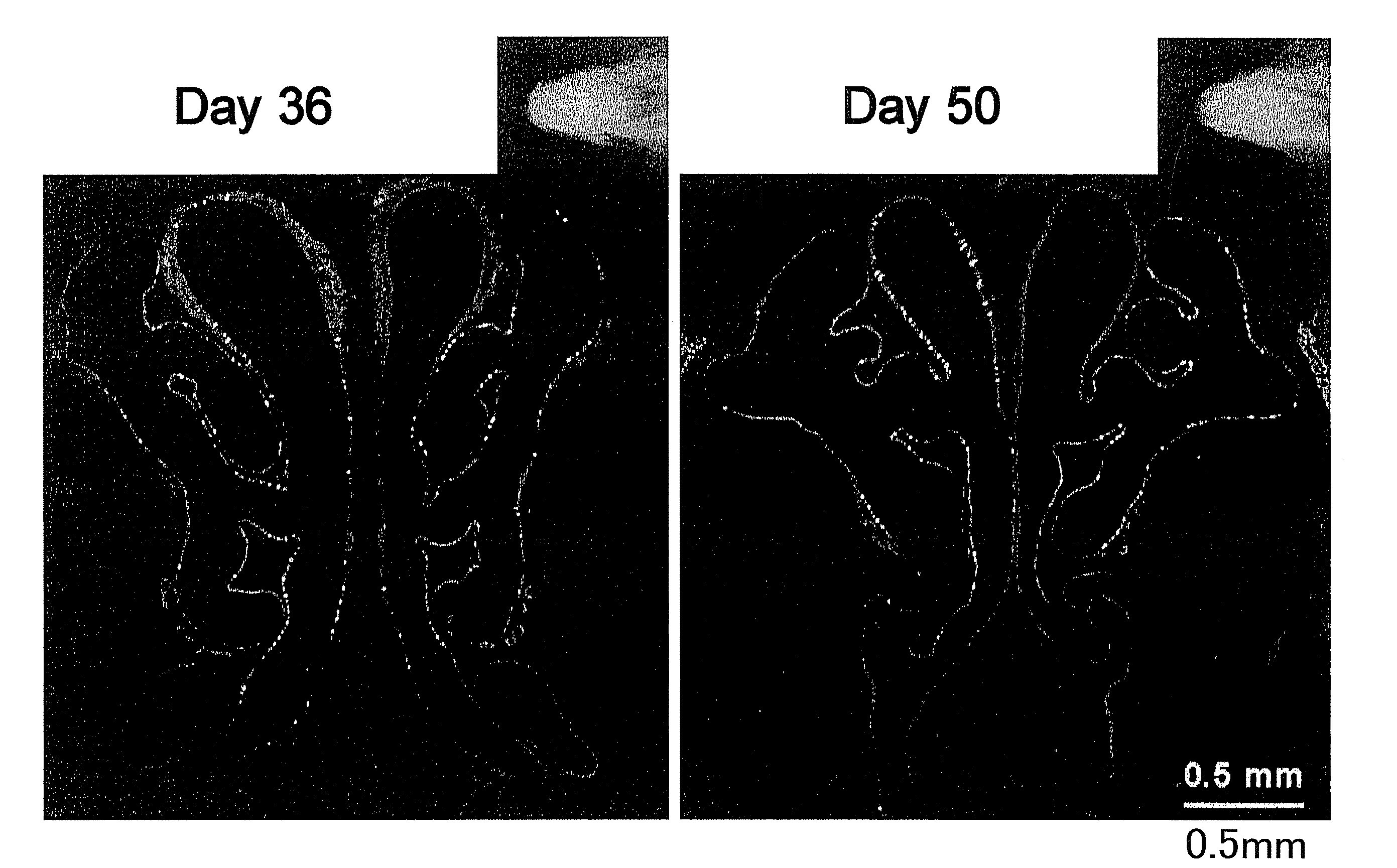
[0140]An F / HN pseudotyped SIV vector carrying eGFP was administered using a thin catheter to the mouse nasal cavity, the left nostril, without preconditioning (n=3, 4×10e8 TU per animal; 100 μl). The duration of expression of the transgenes was day 3 to day 360, and anatomical analysis of the mouse nasal cavity sections was performed according to the method of Mery et al. (Mery et al. Toxicol. Pathol. Vol. 22, p. 353-372, 1994). GFP expression was evaluated in the nasal cavity sections located 1 to 4 mm (sections corresponding to distances of 1, 2, 3, and 4 mm) from the tip of the mouse nasal bone.
[0141]As a result, without preconditioning in airway epithelial cells, efficient transfection and continuous GFP expression was observed for at least 160 days. Expression of eGFP was found to be maintained even on day 220 and day 360. Since the survival time of mouse nasal cavity epithelial cells is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strain point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com