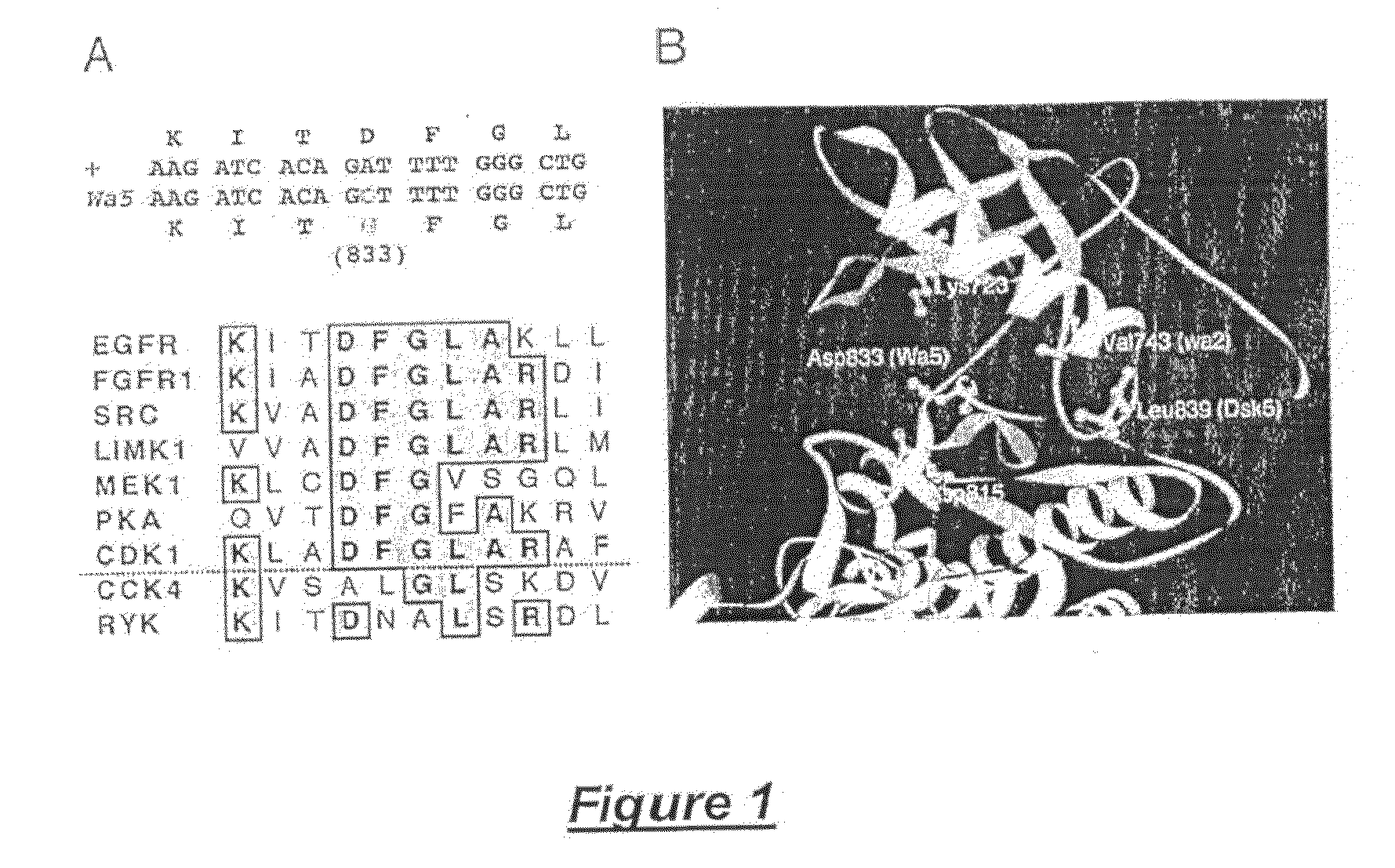
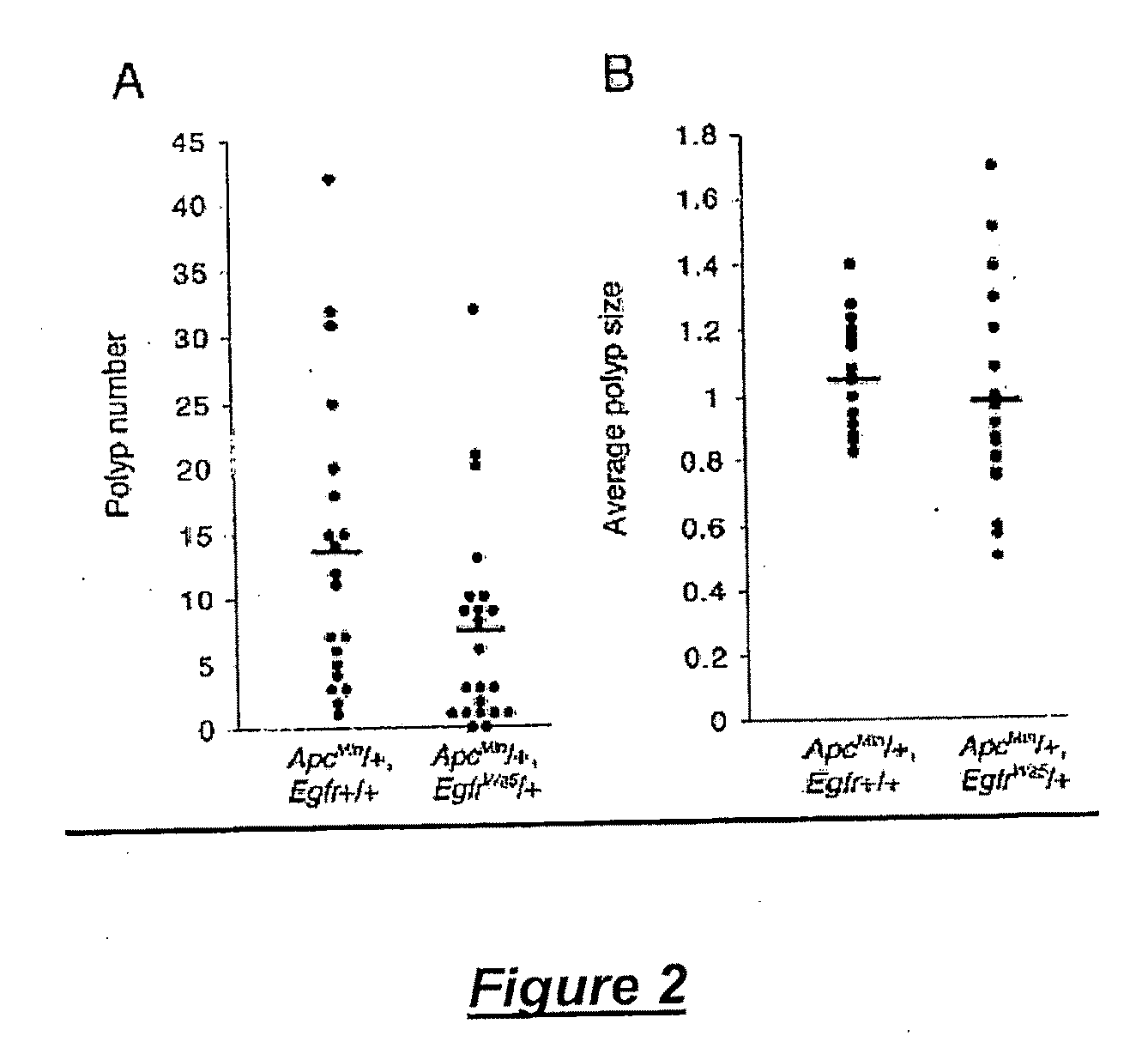
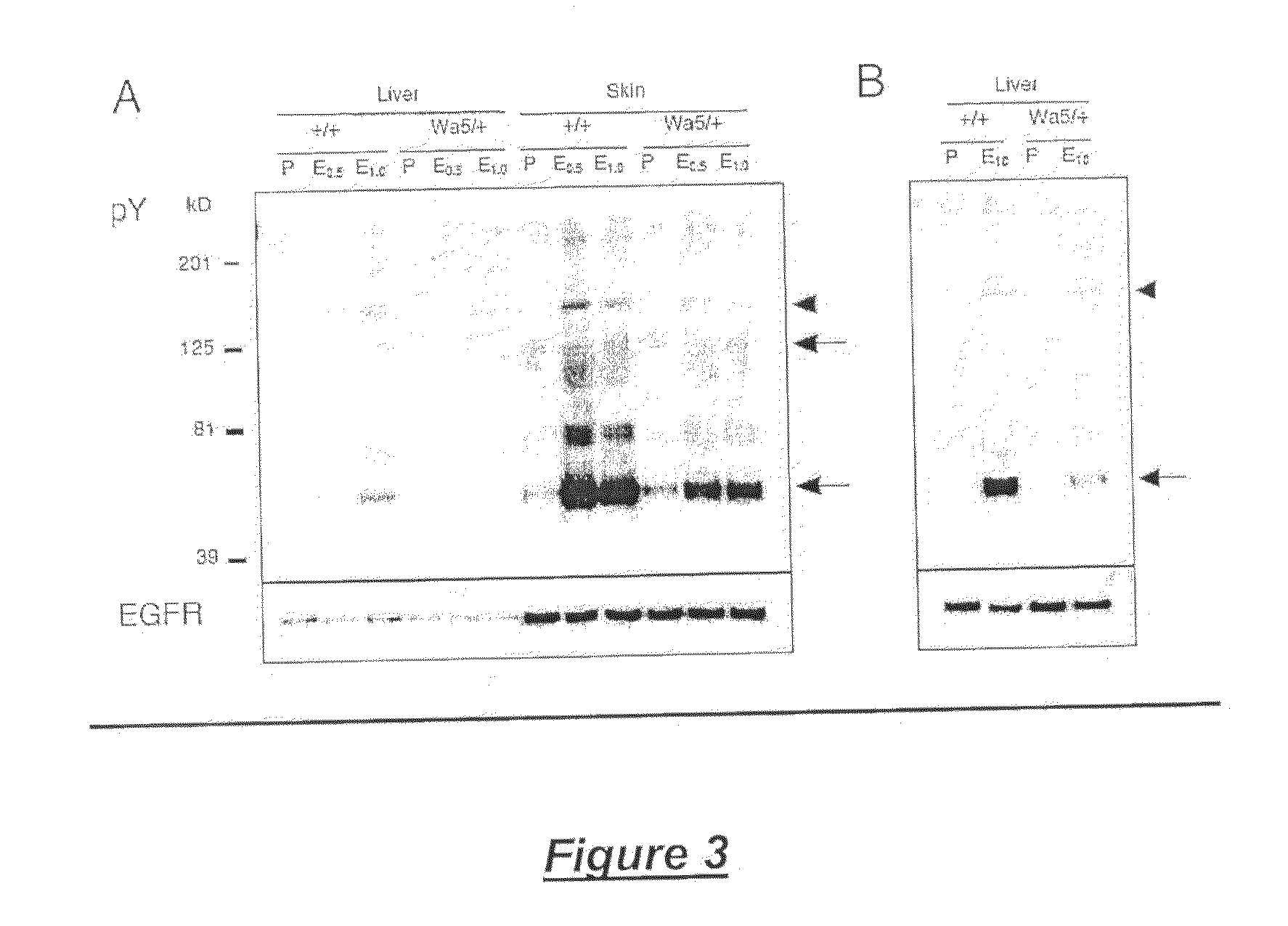
Modulation of epidermal growth factor heterodimer activity
a growth factor and heterodimer technology, applied in the field of epidermal growth factor heterodimer activity modulation, can solve the problems of insufficient expression and/or activity of the erbb receptor, limiting its availability to become activated by ligand binding, and being likely non-specific, so as to suppress the growth of tumors, inhibit the formation of heterodimers, and suppress tumor growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
EgfrWa5 Mutation Identification
[0165]All exons (Reiter et al., 2001), along with immediate flanking regions, of Egfr were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) from Egfrwa5 / +, BALB / c, C3H, and C57BL / 6 genomic DNA using intronic primers that were also used for subsequent sequence analysis. PCR products were purified using the multiscreen PCR 96-well filtration system (Millipore Corp., Billerica, Mass., United States of America) on a BIOMEK® 2000 robotic platform (Beckman Coulter, Inc., Fullerton, Calif., United States of America) and sequenced directly using BIG DYE™ terminator cycle sequencing (Applied Biosystems, Inc., Foster City, Calif., United States of America). Sequences were analyzed using the SEQUENCER™ program (Gene Codes Corp., Ann Arbor, Mich., United States of America) to identify the causative mutation in EgfrWa5.
example 2
Mouse Strains, Crosses, and Genotyping
[0166]The EgfrWa5 mutation was maintained by intercrossing EgfrWA5 / + mice on a mixed genetic background containing contributions from BALB / c, C3H, and C57BL / 6J. The Egfrwa2 / + and Egfrtm1Mag / + (Threadgill et al., 1995) mutations were maintained on C57BL / 6J congenic or 129S6 / SvEvTAC isogenic backgrounds, respectively. Tgfatm1Dcl null mice were maintained on a mixed genetic background of 129S6 / SvEvTAC and C57BL / 6J (Luetteke et al., 1993). The Apcmin mutation (Moser et al., 1993) was maintained as congenic on a C57BL / 6J background.
[0167]Complementation studies were performed by crossing Egfrtm1Mag / + females with EgfrWa5 / +males. EgfrWa5 / + female mice were bred to ApcMin / + male mice, producing ApcMin / + mice on wild type and EgfrWa5 / + backgrounds. To generate Tgfatm1Dcl / tm1Dcl, EgfrWa5 / + double-mutant mice, Tgfatm1Dcl / tm1Dcl females were mated to Tgfatm1 / Dcl / +, EgfrWa5 / + males. In order to generate compound heterozygous animals, Egfrwa2 / + females were ...
example 3
In Vivo Phosphorylation Assays
[0169]Neonatal pups were injected subcutaneously with 10 μl / g body weight of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or 0.5, 1.0, or 10 μg / g body weight of EGF (R&D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, Minn., United States of America) in PBS. After 10 minutes, liver and skin were harvested, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80° C. The frozen tissues were homogenized in 5-10 volumes (5-10 ml / g tissue) of homogenization buffer consisting of 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1% Triton X-100, 1 mM PMSF, 10 μg / ml of leupeptin, 10 μg / ml of aprotinin, 1 mM sodium vanadate, and 10 mM β-glycerophosphate at 4° C. The tissue lysates were cleared by centrifugation for 10 minutes at 4° C. and protein concentrations were determined by the Bradford assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, Calif., United States of America). An equal amount of protein lysate (15 μg) was separated by denaturing 7.5% sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com