Microorganisms Having Enhanced Resistance To Acetate And Related Compositions And Methods of Use
a technology of acetate and microorganisms, which is applied in the field of microorganisms and genetic modification thereof, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of ethanol, reducing the ethanol production rate and the total ethanol yield, and recalcitrance of biomass breakdown
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0064]This example describes the materials and methods used in the experiments described in the subsequent examples.
Strains and Culture Conditions
[0065]Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. E. coli strains were cultured on Luria-Bertani (LB) broth or agar plates for cloning and strain maintenance. Z. mobilis ZM4 was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC 31821). AcR is the Z. mobilis ZM4 acetate tolerant strain as described previously (Joachimstahl et al. 1998). ZM4 and AcR were cultured in RM medium at 30° C.
[0066]S. cerevisiae wild-type, deletion mutant and GST-fusion ORF over-expression strains were obtained through Open Biosystems (Huntsville, Ala.). S. cerevisiae strains were cultured in rich media (YPD media) and minimum complete medium (CM). CM media with 2% glucose was used for S. cerevisiae wild-type and S. cerevisiae deletion mutants. CM media with 2% glucose minus uracil was used for S. cerevisiae GST-over expressing st...
example 2
[0082]This example describes the results from the experiments conducted to determine the genetic basis for the acetate tolerance observed with the mutant Z. mobilis strain, AcR.
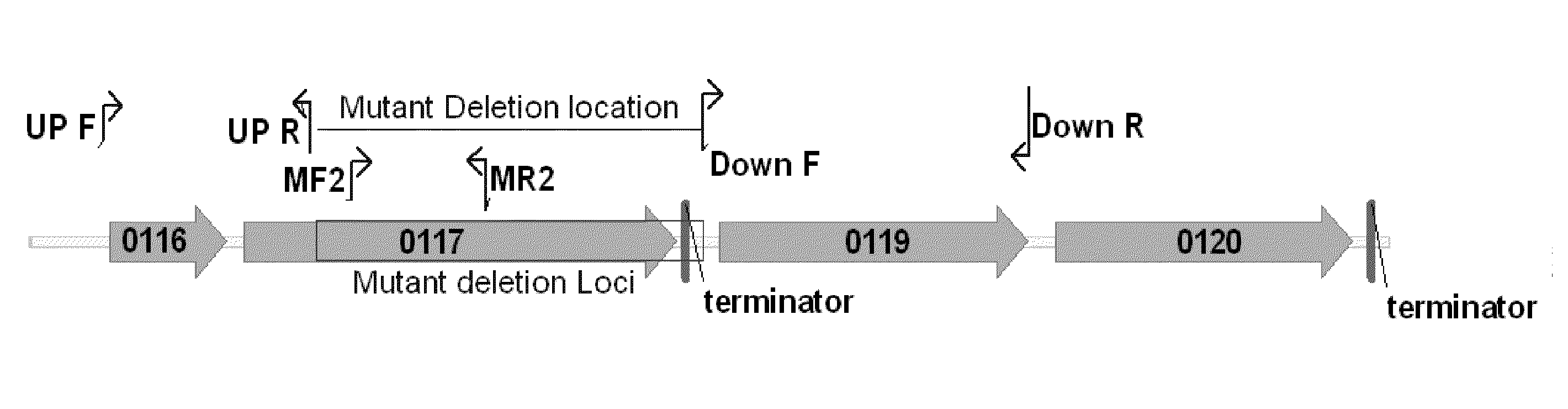
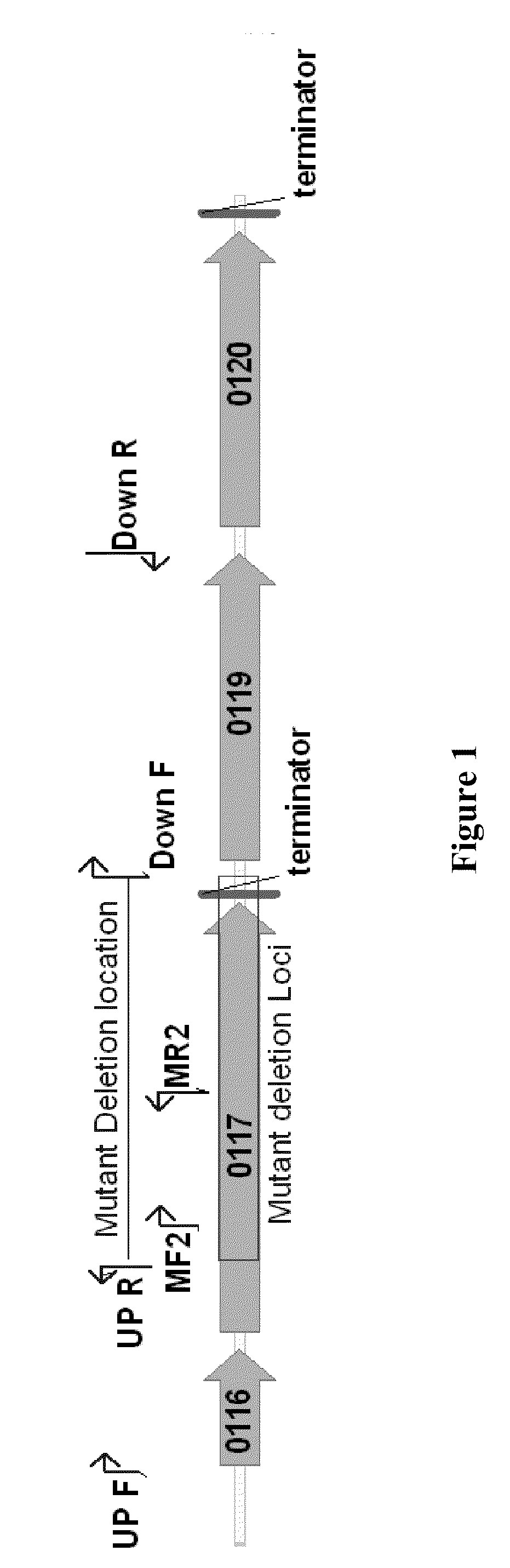
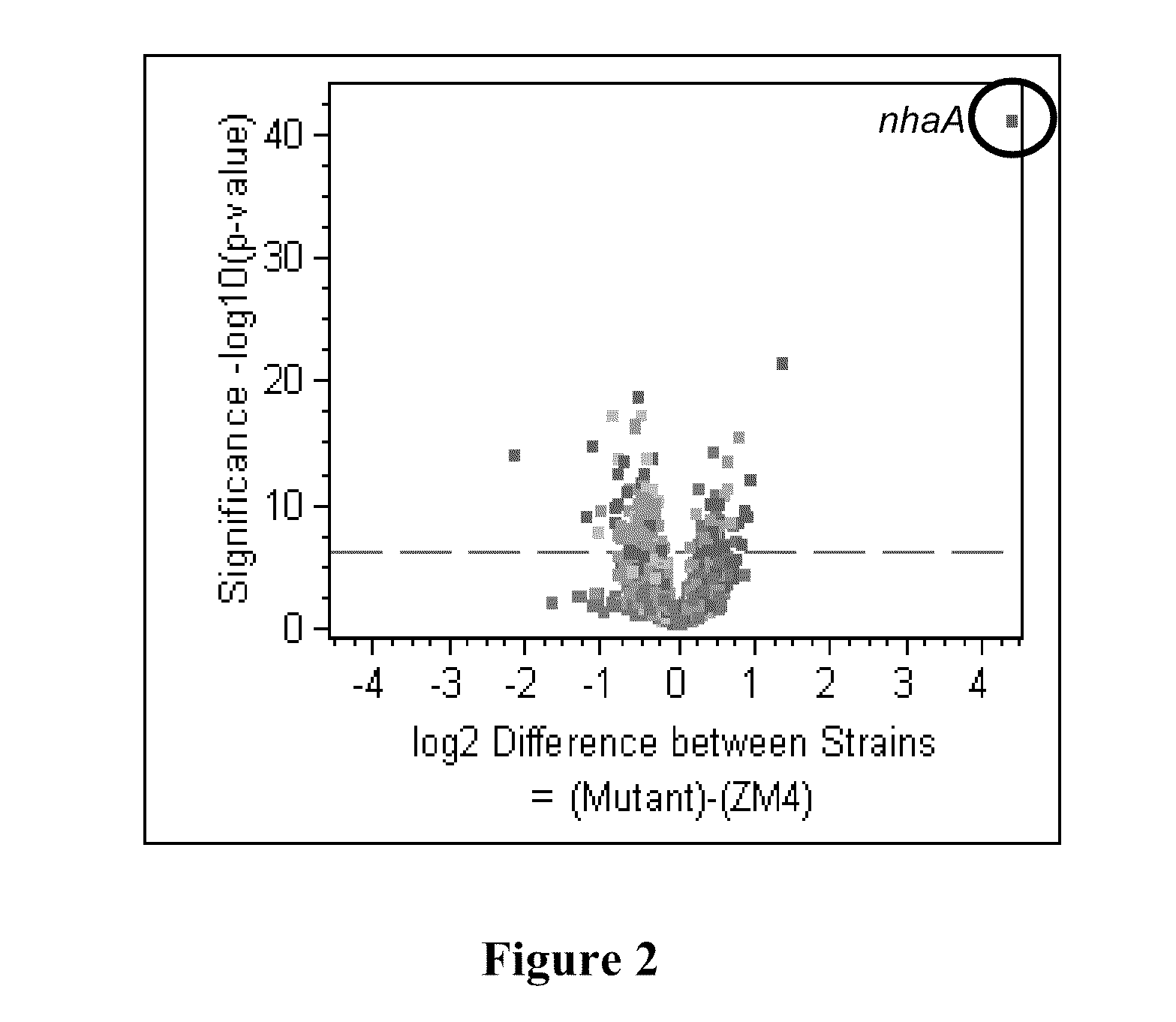
[0083]Using microarray comparative genome sequencing, next generation 454-pyroresequencing, and Sanger sequencing approaches, it was identified and confirmed that the genomic differences between the wild-type Z. mobilis strain, ZM4, and the acetate mutant AcR strain. The genetic changes in the mutant included a 1.5-kb deletion (FIG. 1) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Expression of the nhaA sodium proton anti-porter gene in AcR was found to be constitutive and significantly higher than in the wild-type strain under all the conditions tested (FIG. 2). Whole genome expression profiles were analyzed for mutant and wild-type exponential and stationary phase cells under sodium acetate and sodium chloride control conditions. A summary of these data is presented in FIG. 2 and Table 2.
TABLE 2Expression dat...
example 3
[0084]This example describes experiments conducted to test the hypothesis that the 1.5-kb deletion in the AcR genome resulted in increased nhaA expression that conferred increased acetate tolerance in the mutant.
[0085]A new Gateway® cloning compatible vector pBBR3-DEST42 was constructed. This vector contained the tetracycline resistance gene (FIG. 3) for candidate gene over-expression in ZM4 due to intrinsic, broad Z. mobilis antibiotic resistance. The anti-porter nhaA gene (FIG. 4) was cloned into the vector resulting in a nhaA over-expression vector p42-0119, which was then transformed into the wild-type ZM4 strain through conjugation to generate a strain over-expressing nhaA, which was named as “ZM4(p42-0119)”. In addition, a deletion mutant was constructed to mimic the 1.5-kb deletion region (FIG. 1) of the AcR acetate tolerant strain using the pJK100 system (Denef et al. 2006). Since the deletion covers most of the hypothetical protein ZMO0117 and the promoter region of ZMO0119...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com