Mgf2 optical thin film including amorphous silicon oxide binder, optical element provided with the same, and method for producing mgf2 optical thin film
a technology of optical thin film and silicon oxide, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, coatings, magnesium halides, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient refractive index of the film, insufficient environmental resistance, insufficient mechanical strength of the film and the etc., to achieve excellent environmental resistance (durability), improve mechanical strength of the film and adhesive force between the film and the base material, and improve environmental resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
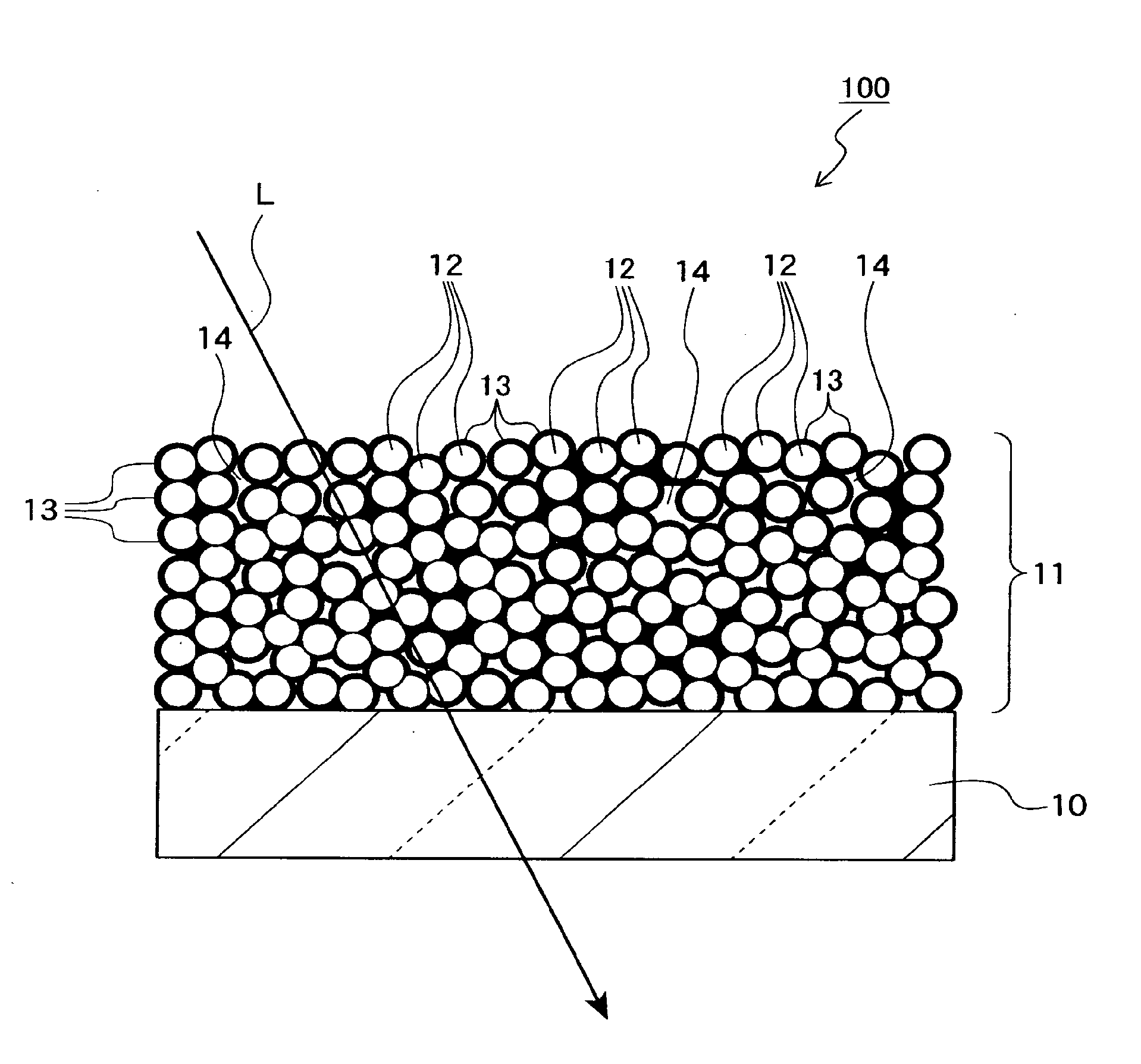
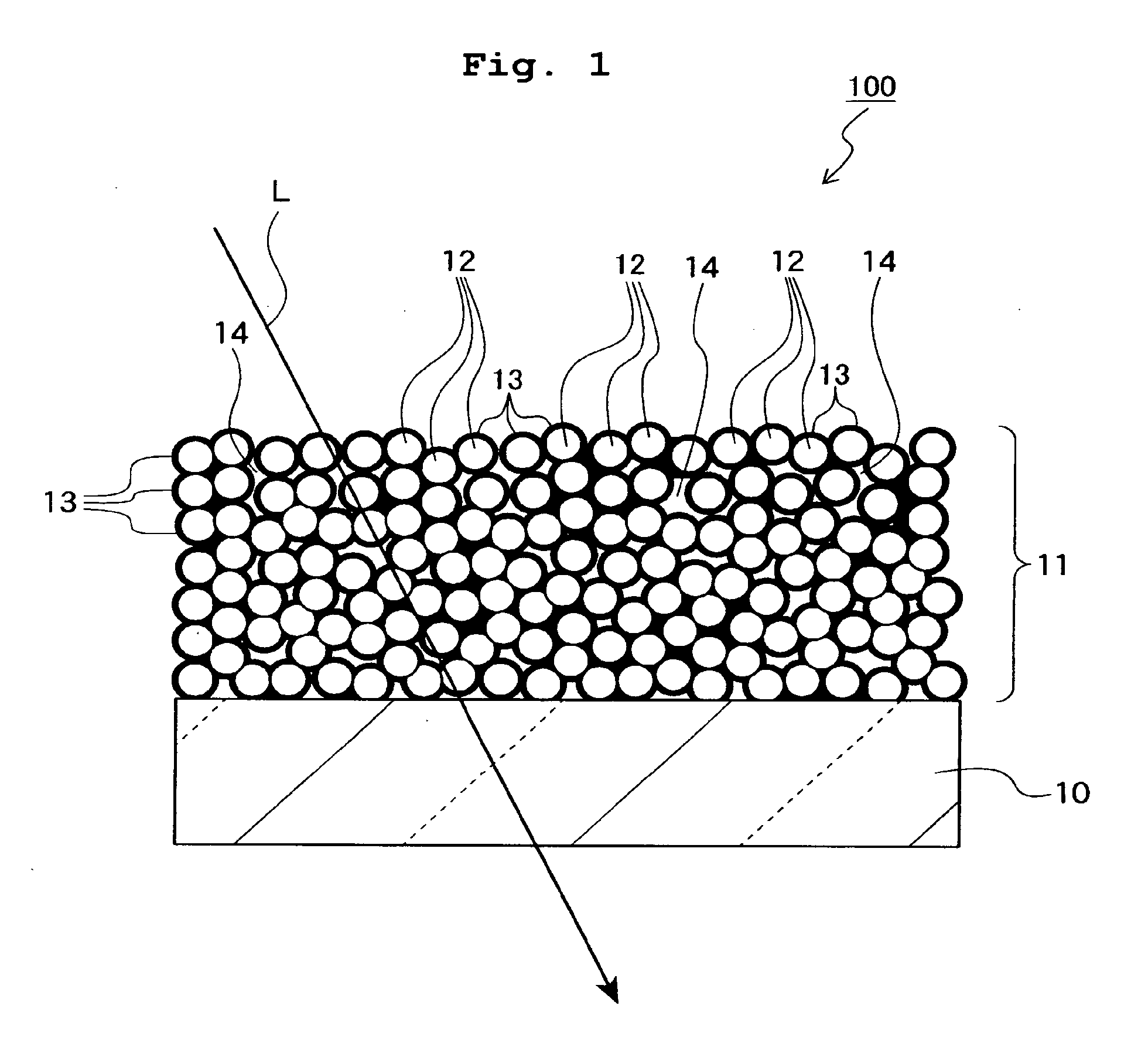
[0084]FIG. 1 shows an optical element in which an MgF2 optical thin film (MgF2—SiO2 film) of the first embodiment is formed. The optical element 100 includes a base material 10 and the MgF2 optical thin film 11 which is stacked on a flat optical surface of the base material 10. The base material 10 is formed of, for example, glass, plastic or the like having a refractive index of 1.4 to 2.1, and may be a plate member or a lens. The optical surface of the base material 10 may be formed to have a curved surface form.
[0085]The optical thin film 11 is an antireflection film which is stacked on at least one optical surface of the base material 10 onto which the light is radiated. In this embodiment, the optical thin film 11 is a singlelayered MgF2 antireflection film.
[0086]The optical thin film 11 includes MgF2 minute particles 12 and an amorphous silicon oxide-based binder 13. The connection is made by the amorphous silicon oxide-based binder 13 between a large number of the MgF2 minute...
examples 1 to 5
[0168]The hydrofluoric acid methanol solution was mixed with the magnesium acetate methanol solution so that the MgF2 concentration was 1%, and that the hydrofluoric acid / magnesium acetate ratio was 1.95 to prepare an MgF2 sol solution. Subsequently, the sol solution was subjected to the high temperature high pressure treatment at 140° C. for 24 hours. The average particle diameter of MgF2 minute particles contained in the treated MgF2 sol solution was measured by the electron microscopic observation, which was 20 nm. The sol solution was concentrated by using the rotary evaporator, followed by being diluted with 1-propanol to substitute 67% of the methanol solvent. The MgF2 sol solution was allowed to have an MgF2 concentration of 2.5%, with which a silica glass substrate having a thickness of 3 mm was spin-coated at 2,000 rpm to form a porous MgF2 film.
[0169]The substrate was dried at 70° C. for 1 hour, and then the temperature was returned to room temperature. An undiluted soluti...
examples 6 to 8
[0172]MgF2—SiO2 films were formed by the double coating method in the same manner as in Examples 1 to 5 except that MgF2 sol solutions were prepared by mixing the hydrofluoric acid methanol solution with the magnesium acetate methanol solution so that the MgF2 concentration was 1%, and the ratio of hydrofluoric acid / magnesium acetate was 1.98, 1.99, and 2.0. Characteristics of the obtained films were measured. Results are shown in Table 1.
[0173]When the results are compared with each other with respect to Example 1, the following fact is appreciated. That is, there is such a tendency that as the ratio of hydrofluoric acid / magnesium acetate is higher, the refractive index of the MgF2—SiO2 film becomes lower. In order to make the refractive index of the MgF2—SiO2 film as low as possible, it is appreciated that the ratio of hydrofluoric acid / magnesium acetate is preferably allowed to approach 2.0. However, if the ratio of hydrofluoric acid / magnesium acetate exceeds 2.0, then the gelati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com