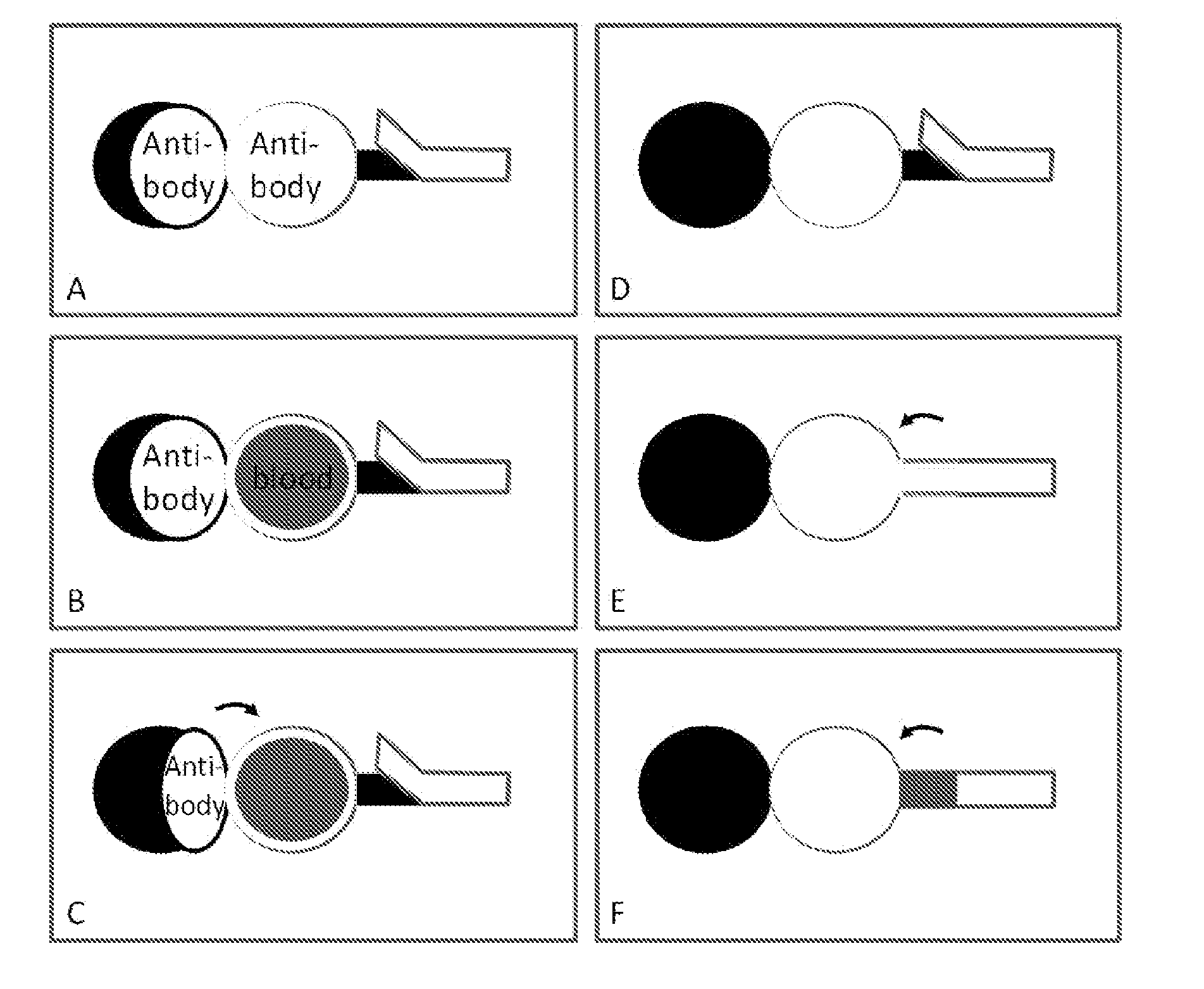
Testing device for identifying antigens and antibodies in biofluids
a biofluid and antigen technology, applied in the field of identification of antigens and antibodies within biofluids, can solve the problem of no convenient low cost disposable tests available for “on the spo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
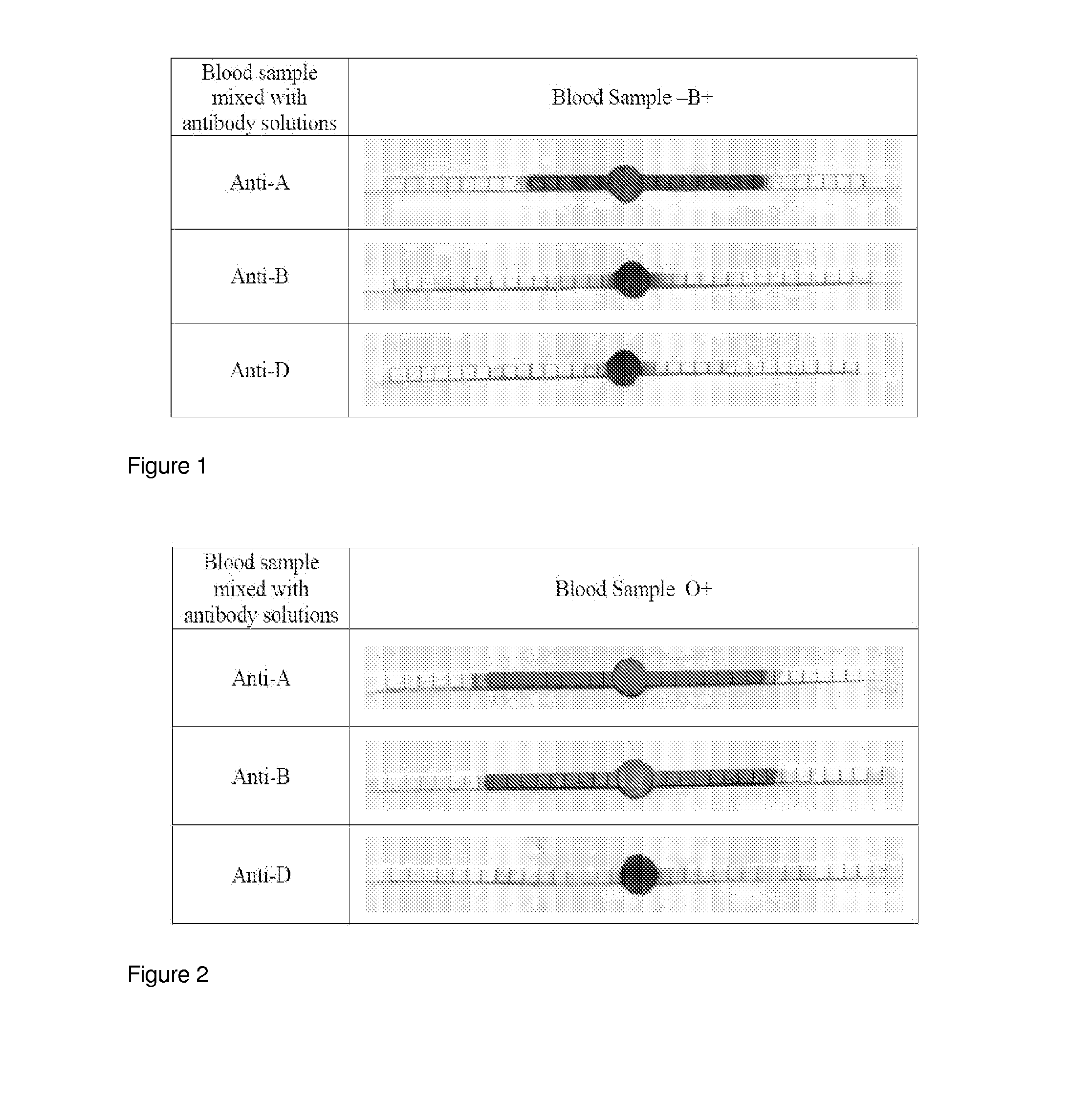
Sequential Agglutination / Coagulation of Blood Followed by Wicking on Paper: B+ (Two Step Process) (See FIG. 1)
[0044]Antibody A and B (Epiclone™ Anti-A, Anti-B, and Anti-D; CSL, Australia) solutions were used. Anti-A and Anti-B come as blue and yellow colour reagents, respectively. ‘B+’ blood was used in this study. The blood sample was supplied into plastic vials with anti-coagulant. ‘B+’ blood was separately mixed with pure Anti-A and Anti-B (as received) to prepare 100 μL solution. Paper strips (70 mm×2 mm) were made from Whatman#4 filter paper on which 2 mm unit marks were printed. The paper strips were soaked into phosphate buffer saline (PBS). Excess PBS was removed from the paper strips using standard blotting papers (Drink Coster Blotting, 280 GSM). The paper strips were then placed on Reflex Paper (80 GSM). 20 μL of every mixed solution was dispensed at the centre of paper strip using a calibrated micro-pipette. Pictures were taken after 4 minutes wicking.
[0045]It can be see...
example 2
Sequential Agglutination / Coagulation of Blood Followed by Wicking on Paper: O+ (Two Step Process) (See FIG. 2)
[0052]Antibody A and B (Epiclone™ Anti-A, Anti-B and Anti-D; CSL, Australia) solutions were used. Anti-A and Anti-B come as blue and yellow colour reagents, respectively. ‘O+’ blood was used in this study. The blood sample was supplied into plastic vials with anti-coagulant. ‘O+’ blood was separately mixed with Anti-A and Anti-B to prepare 100 μL solution. Paper strips (70 mm×2 mm) were made from Whatman#4 filter paper on which 2 mm unit marks were printed. The paper strips were soaked into phosphate buffer saline (PBS). Excess PBS was removed from the paper strips using standard blotting papers (Drink Coster Blotting, 280 GSM). The paper strips were then placed on Reflex Paper (80 GSM). 20 μL of every mixed solution was dispensed at the centre of paper strip using a calibrated micro-pipette. Pictures were taken after 4 minutes wicking.
[0053]It can be seen that:
[0054]O+ bloo...
example 3
Simultaneous Agglutination / Coagulation of Blood Followed by Wicking on Paper: Effect of Antigen Concentration (One Step Process) (See FIG. 3)
[0060]In another embodiment of the invention, the paper is first treated with specific antibodies, dried or conditioned before been exposed to a sample of pure blood. This example provides a single step treatment in which the only requirement is to deposit a drop of blood on the paper. This example also illustrates the effect of diluting the antibody solution on the wicking and separation performance of blood on paper. Antibody dilution affects the ratio blood (with its antigen) antibody.
[0061]Antibody A and B (Epiclone™ Anti-A and Anti-B; CSL, Australia) solutions were used. Anti-A and Anti-B come as blue and yellow colour reagents, respectively. “AB+” and ‘B+’ blood were used in this study. The blood sample was supplied into plastic vials with anti-coagulant. Paper strips (70 mm×2 mm) were made from Whatman#4 filter paper on which 2 mm unit m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com