Ophthalmic composition
a technology of ophthalmic composition and composition, which is applied in the field of ophthalmic composition, can solve the problems of general lack of symmetry in the structure of hyperbranched polymers, local irritation, etc., and achieve the effects of improving ophthalmic composition, corneal permeation of active agents, and solubility in water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experimental example 1
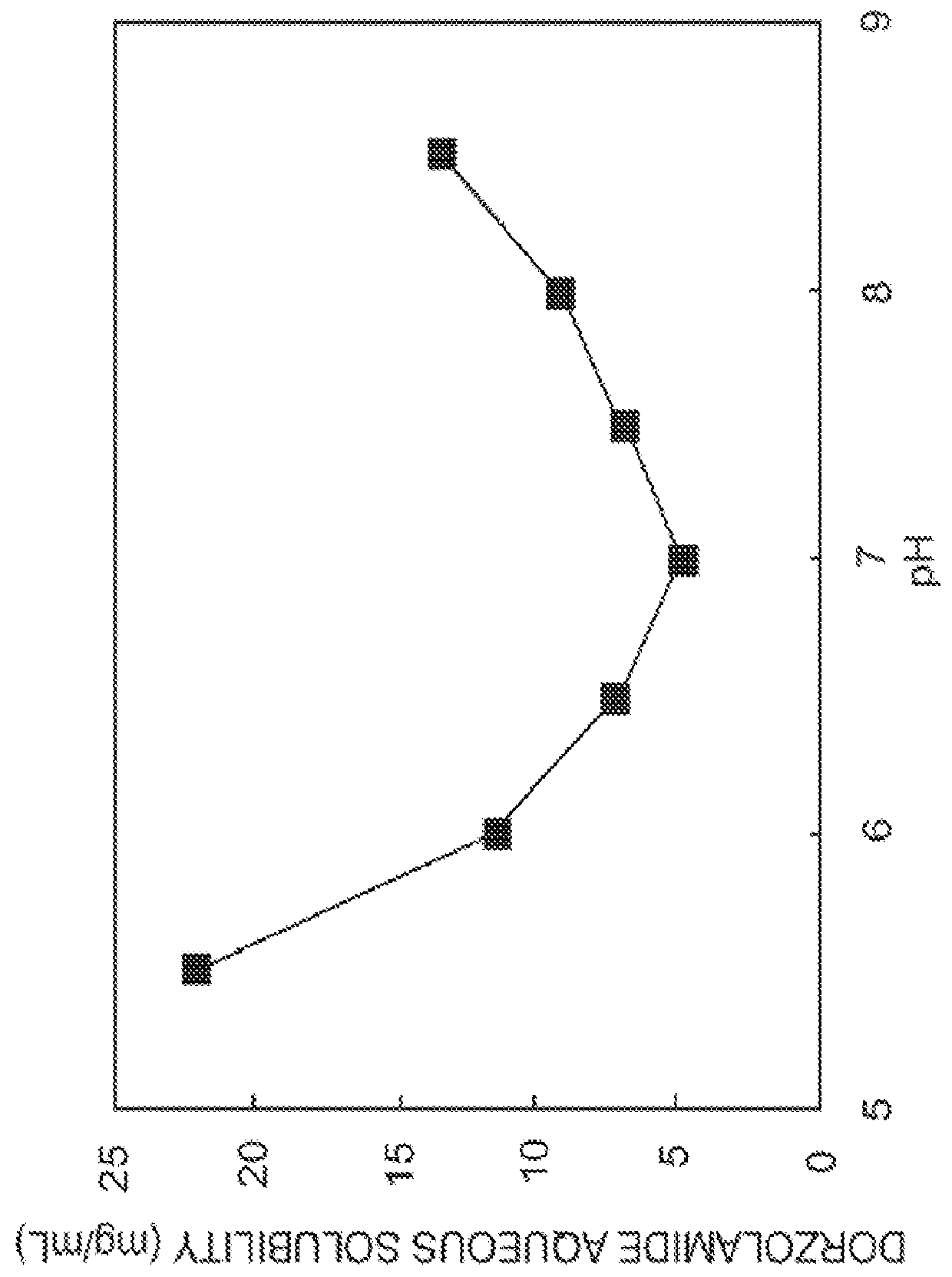
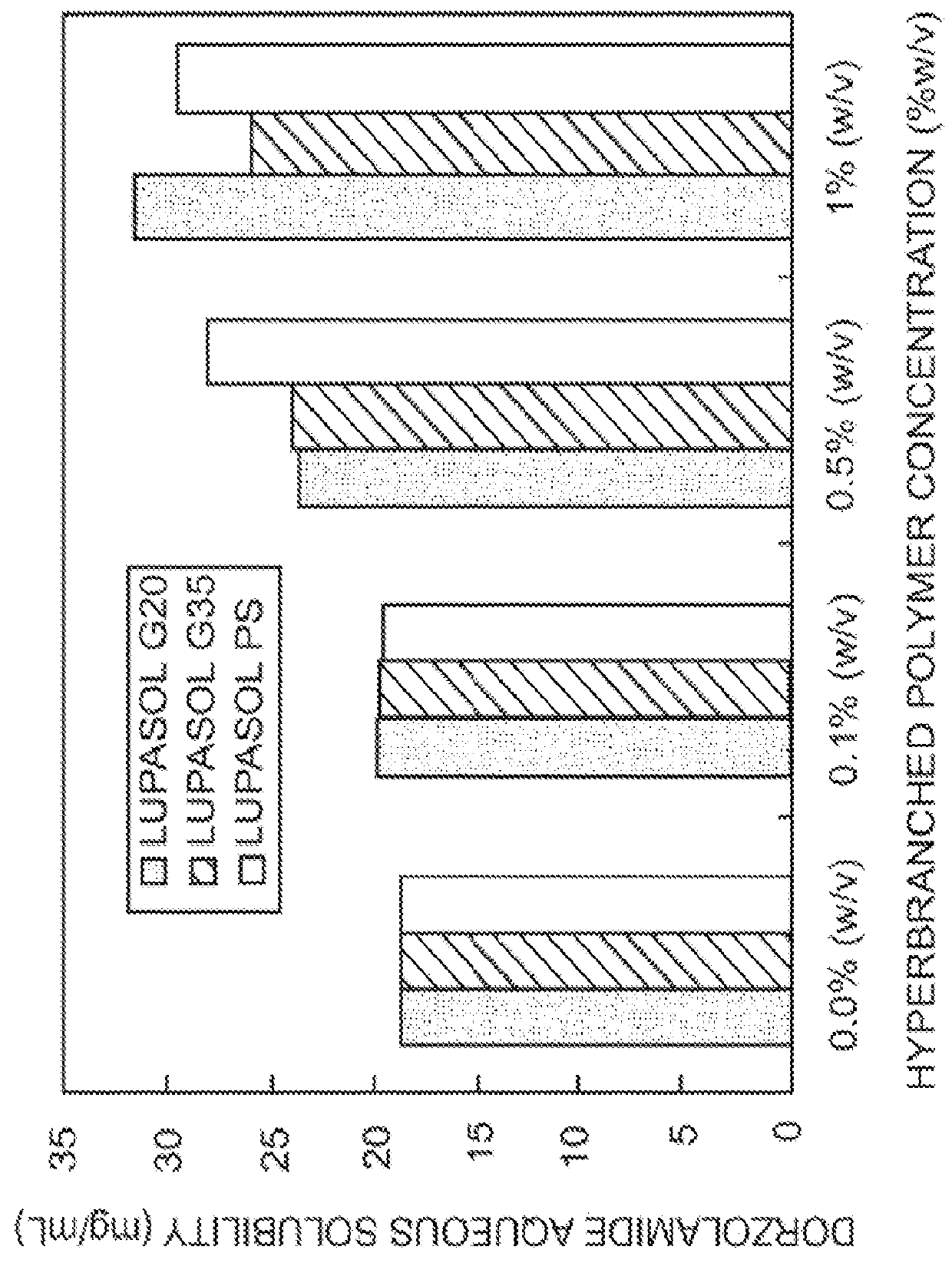
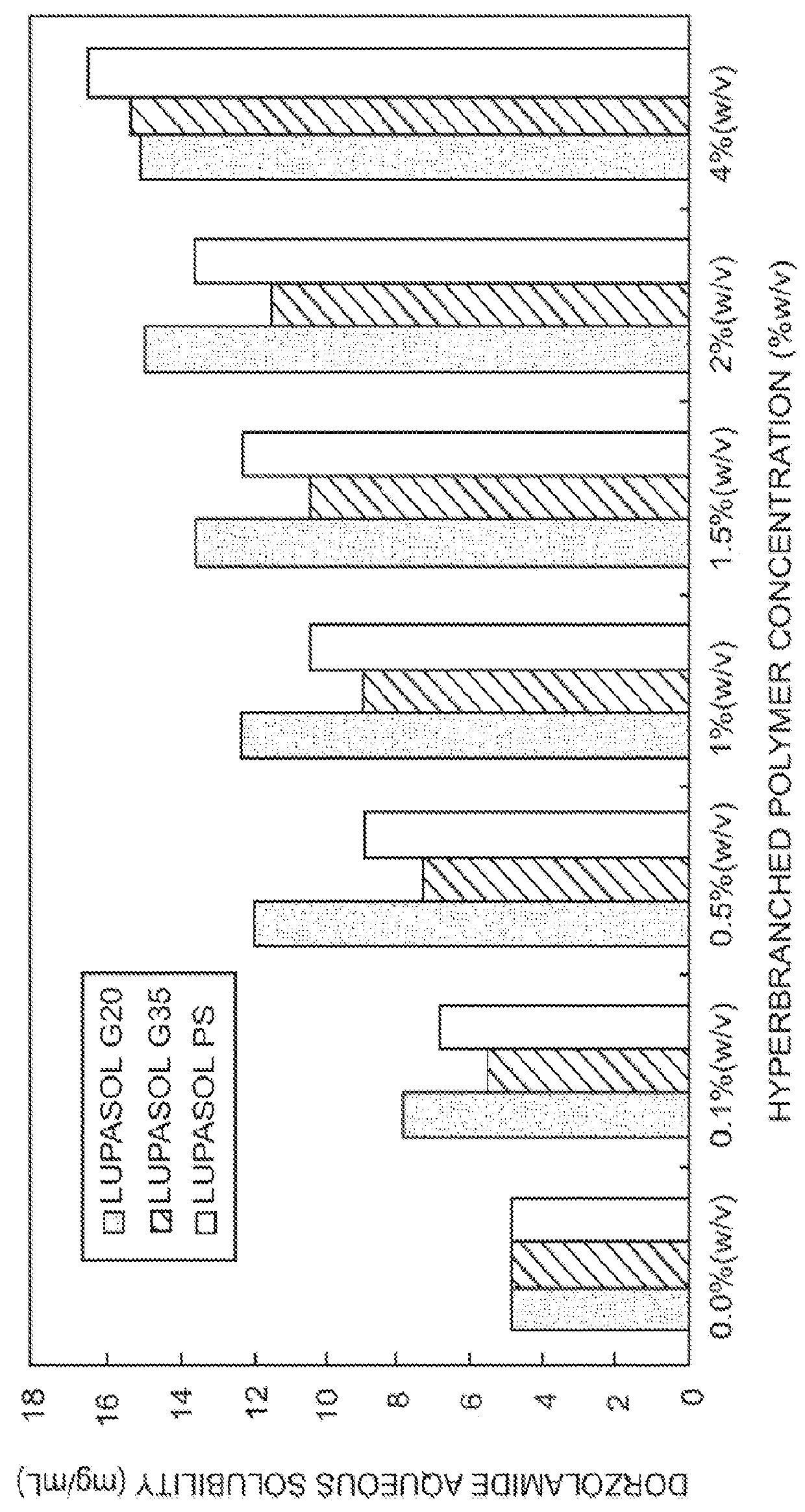
[0095]pH-solubility profile of Dorzolamide in aqueous solution containing different concentrations of Hyperbranched Polymer (HP) (Lupasol® G20, Lupasol® G 35, Lupasol® PS) and PEG.
Methods
[0096]Suspensions of Dorzolamide hydrochloride in 0.1% (w / v) phosphate buffer solution at pH 5.5, pH 6, pH 6.5, pH 7, pH 7, pH 8 and pH 8.5 were prepared. Similar suspensions were also prepared in aqueous solution containing different concentrations of different HP and PEG with a molecular weight of 8000. A combination of Polysorbate 80 and PEG 8000 was also attempted. The pH was measured accurately with micro-pH electrode (Thermo Scientific). The desired pH was adjusted using either 1 M NaOH or 1 M HCl. The suspension solutions were first stirred for 10 min at room temperature (with heating up to 60° C. for 5 minutes). After allowing the suspensions to equilibrate at room temperature for an additional 30 minutes, the suspension solutions were then sonicated for 10 minutes and finally filtered throu...
experimental example 2
[0101]A simple rheological method for the in vitro assessment of mucin-hyperbranched polymer bioadhesive bond strength.
[0102]A simple viscometric method was adopted to quantify the mucin-polymer bioadhesive bond strength. In order to determine the muco-adhesive properties of commercially available HP called Lupasol® PS, the force of bioadhesion was calculated for different concentrations of HP with porcine gastric mucin at pH 7 in comparison with the market product COSOPT®. Porcine gastric mucin was used as a model mucin. However, since all mucins appear to share general physical, structural, and rheological properties, it is believed that porcine gastric mucin is a satisfactory model for primary evaluation of bioadhesive materials.
Methods
[0103]Brookfield Rotational L VDVE viscometer was employed for all measurements. Spindle with code number 18 was used for all viscosity measurements. A factor of 1.32 was used to convert rpm to shear rate (s−1) as per the manual. A solution of 15% ...
experimental example 3
[0110]Aqueous solubility of Dorzolamide in the presence of Timolol for a novel formulation containing HP (Lupasol® PS) and Polysorbate 80 or a combination of PEG and Polysorbate 80 at pH 5.65 and pH 7.
Methods
[0111]A suspension of Dorzolamide hydrochloride and 0.5% (w / v) Timolol in citrate buffer solution at pH 5.65 was prepared (Control sample). A similar suspension was also prepared in aqueous solution containing 2% (w / v) of HP in citrate buffer of pH 3. The final pH was adjusted to 5.65 with 1 M NaOH after addition of HP (sample 1). The combination of different molecular weight PEG and Polysorbate 80 at pH 5.65 as per Table 3 were also attempted. Table 3 shows all the different test samples suspensions to be prepared in 10 mM citrate buffer.
TABLE 3Different Test formulations prepared at pH 5.65 in citrate buffer, and at pH 7 in phosphate buffer.ContentControl(% v / w)SampleS #1S #2S #3S #4S #5S #6S #7S #8Dorzolamide>2.22>2.22>2.22>2.22>2.22>2.22>2.22>2.22>2.22HClTimolol0.6830.6830.6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com