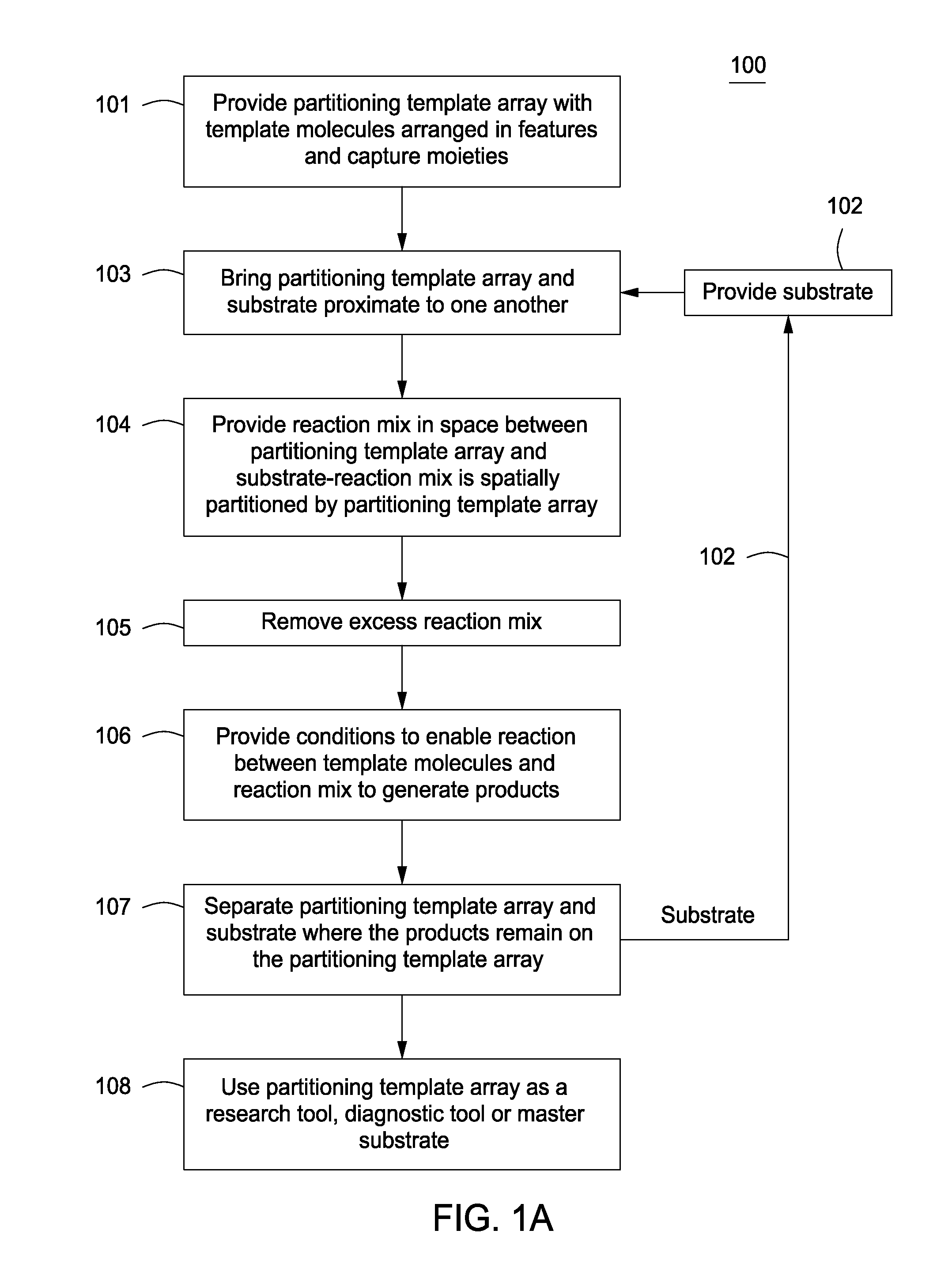
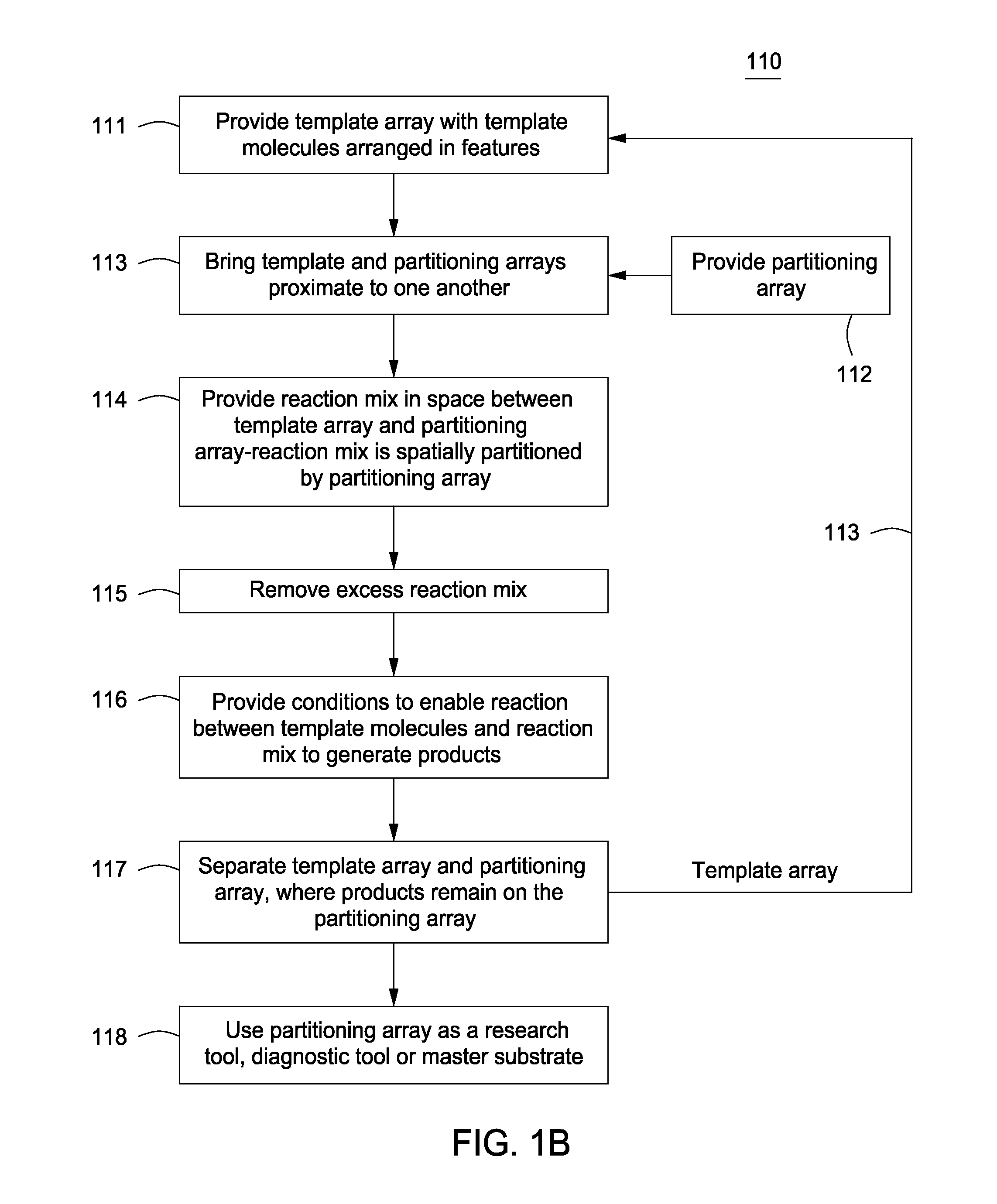
Methods for manufacturing molecular arrays
a manufacturing method and molecular array technology, applied in the field of molecular array manufacturing, can solve the problems of large variability in the quality of synthesized peptides, high cost of generating arrays with tens of thousands or more spotted peptides, and inefficient direct fabrication process,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Partitioning Array Fabrication
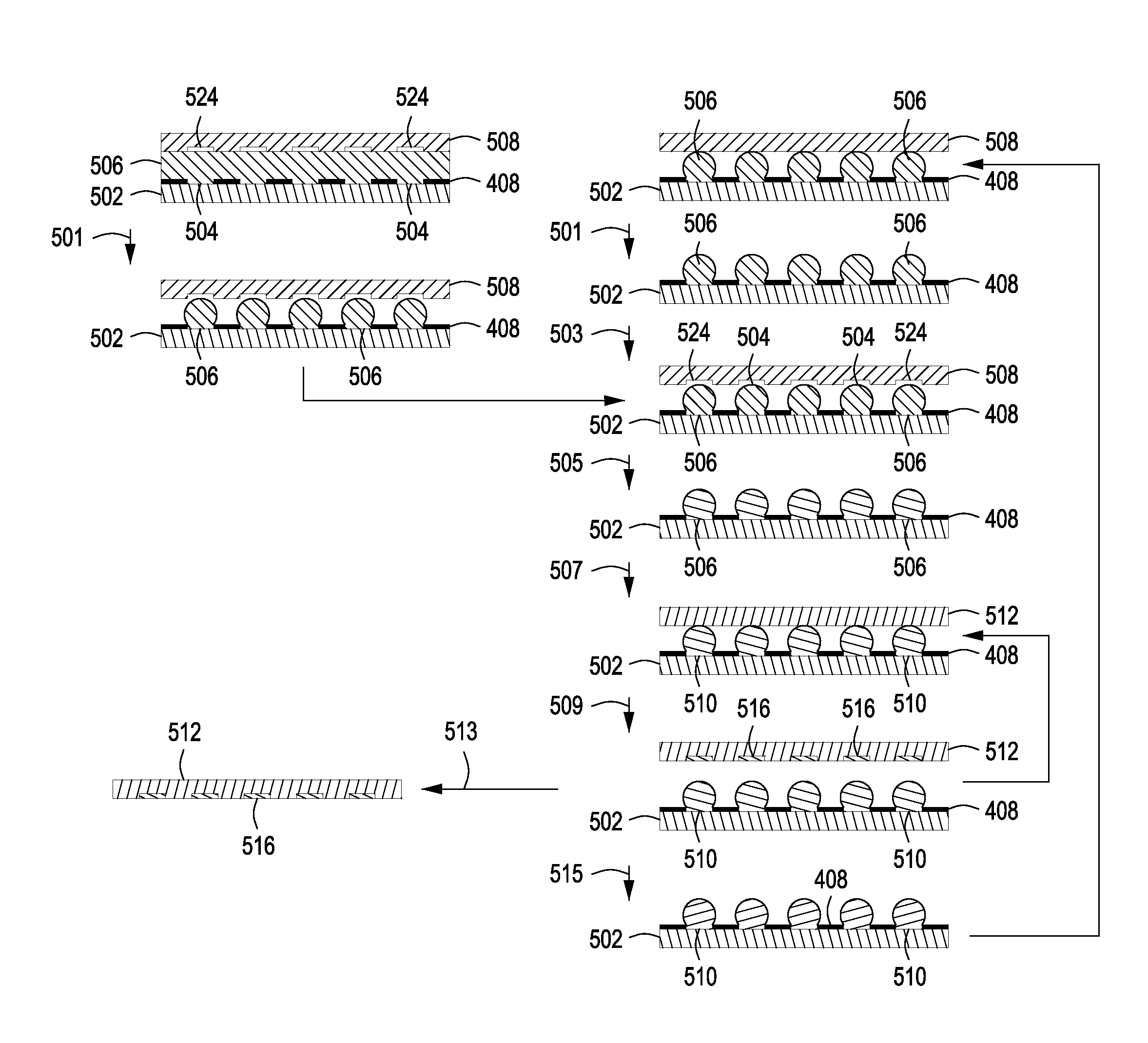
[0135]A partitioning array was fabricated from a standard silicon wafer. First, a patterned gasket comprising a boundary region surrounding the area to contain partitioning features was formed on the wafer by using UV lithography to pattern a 20 μm-thick layer of SU-8 epoxy-based negative photoresist on the wafer. The gasket was formed such that the partitioning array, when brought into proximity with another substrate (a dummy substrate, template array or capture substrate or replica array, for example), would form a flowcell. The wafer was then baked at 300° C. to make the SU-8 substantially impervious to subsequent processing. The wafer was then cryo-etched using reactive-ion etching with inductively coupled plasma (RIE / ICP) at negative 140° C. using SF6 and O2 to form black silicon. The black silicon consisted of conical pillars, approximately 2 μm high and 100-200 nm wide.
[0136]A conformal layer of silicon dioxide approximately 50-200 nm in thickn...
example 2
Capture Substrate Fabrication
[0137]A borofloat glass microscope slide was used to prepare the capture substrate. First, the slide was cleaned using solvents and a strong acid / oxidizer bath, and were then cleaned further using a UV-Ozone cleaner (Jelight, Inc., Irvine, Calif.). The slides were functionalized using (3-aminopropyl)trimethozysilane (APTMS) in a vapor deposition system at 150° C. and 3 torr for 10 minutes. Amine functionality on the capture substrate (chip) was confirmed by labeling with Lissamine Rhomdamine B Sulfonyl Chloride, an amine-reactive fluorescent dye, and imaging with a microarray scanner.
example 3
Capture Substrate Printing
[0138]The flowcell was assembled by bringing the silicon partitioning array into contact with the capture substrate so that the SU-8 gasket surrounding the region of partitioning features contacted the edges of the capture substrate and the black silicon surface of the partitioning array was held at a distance equal to the thickness of the gasket. The partitioning array and capture substrate were then clamped together, and a tube was connected to the output port of the flowcell, where the output port was formed by one of the holes drilled into the partitioning array. The tube was then connected to a vacuum source.
[0139]A small volume of buffer containing reactive molecules, in this case fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), was pipetted into the input port formed by the second hole drilled into the partitioning array, where the FITC was pulled through the flow cell by the vacuum. The entire volume of the flow-cell was filled temporarily while the buffer trans...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volumes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com