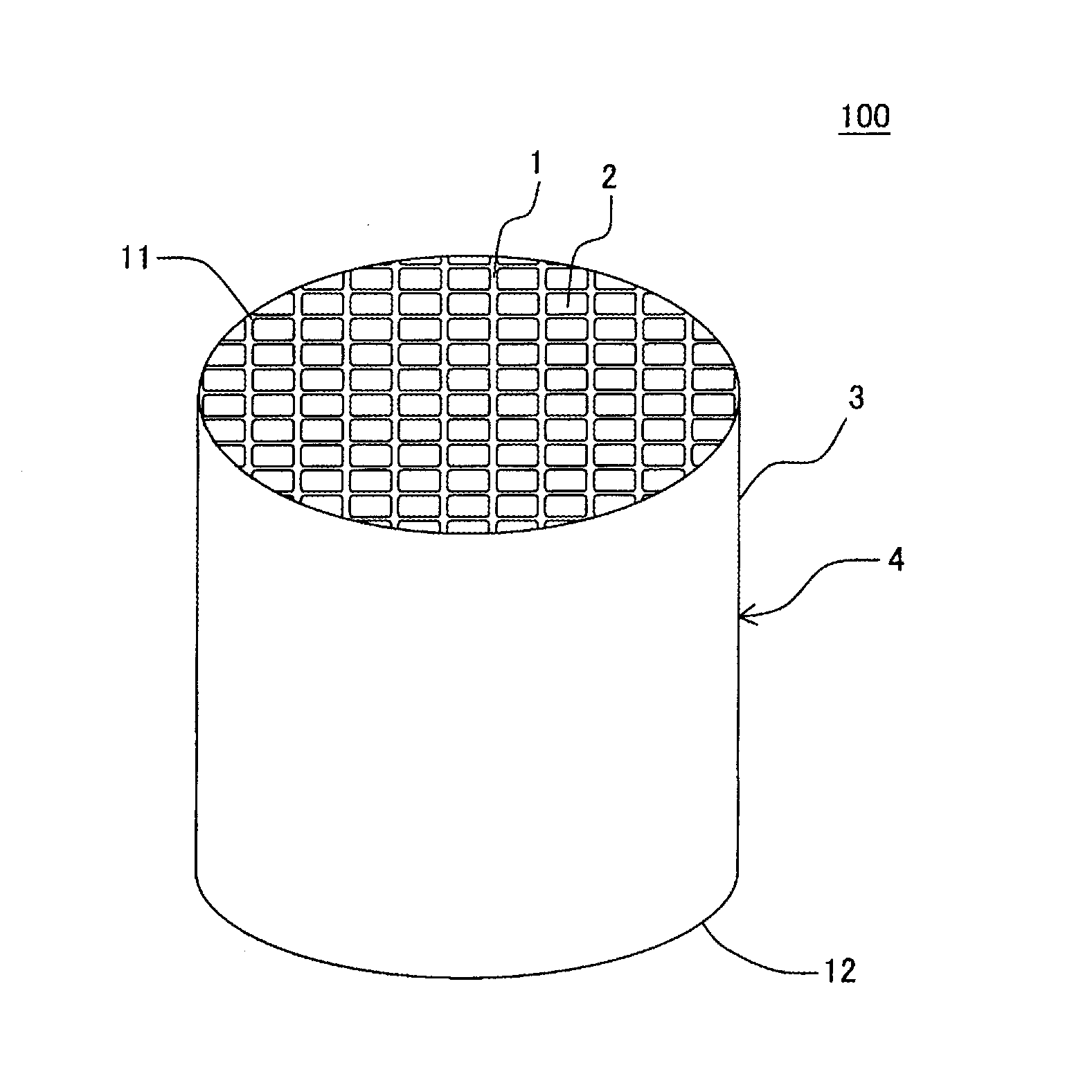
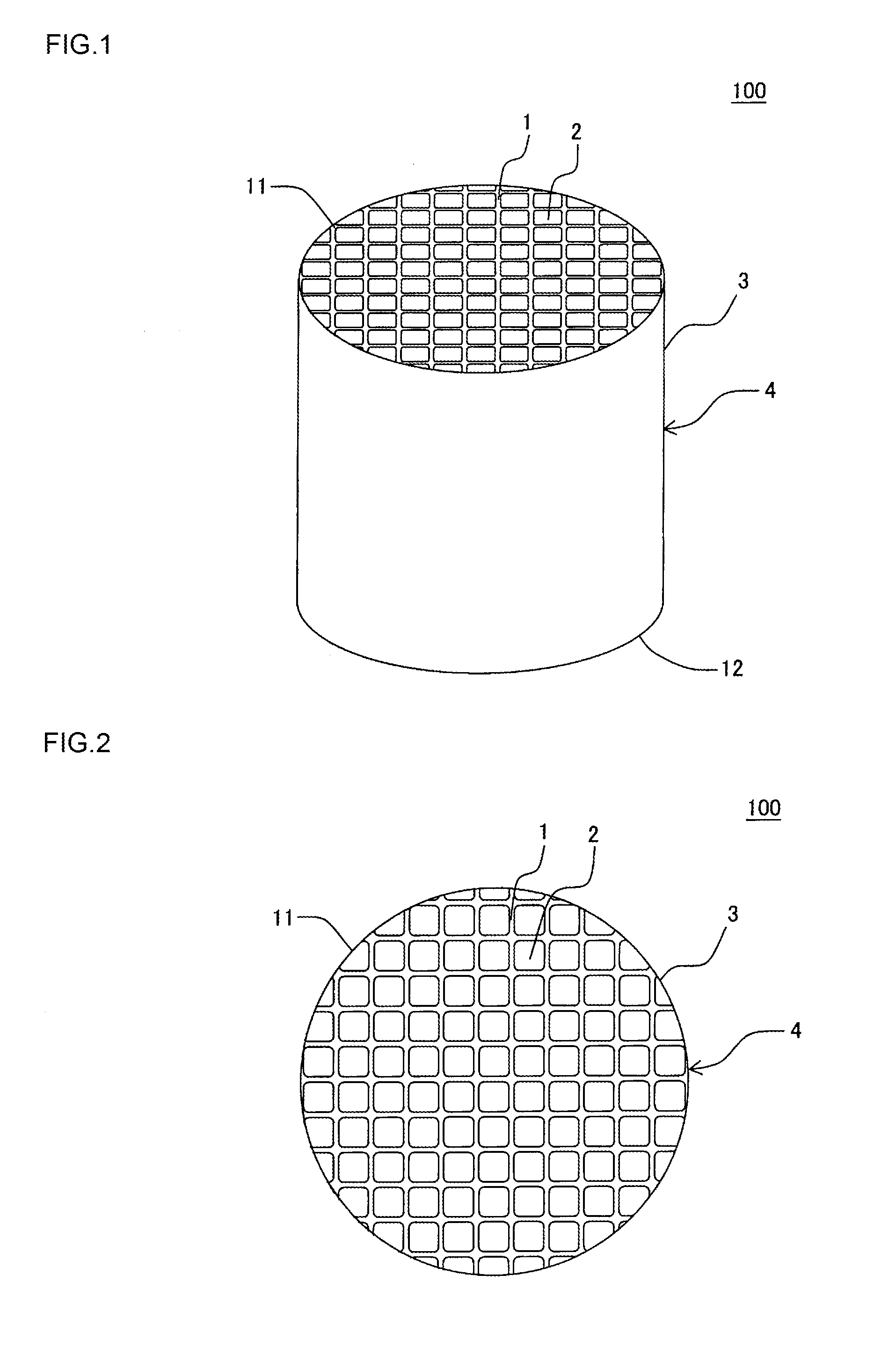
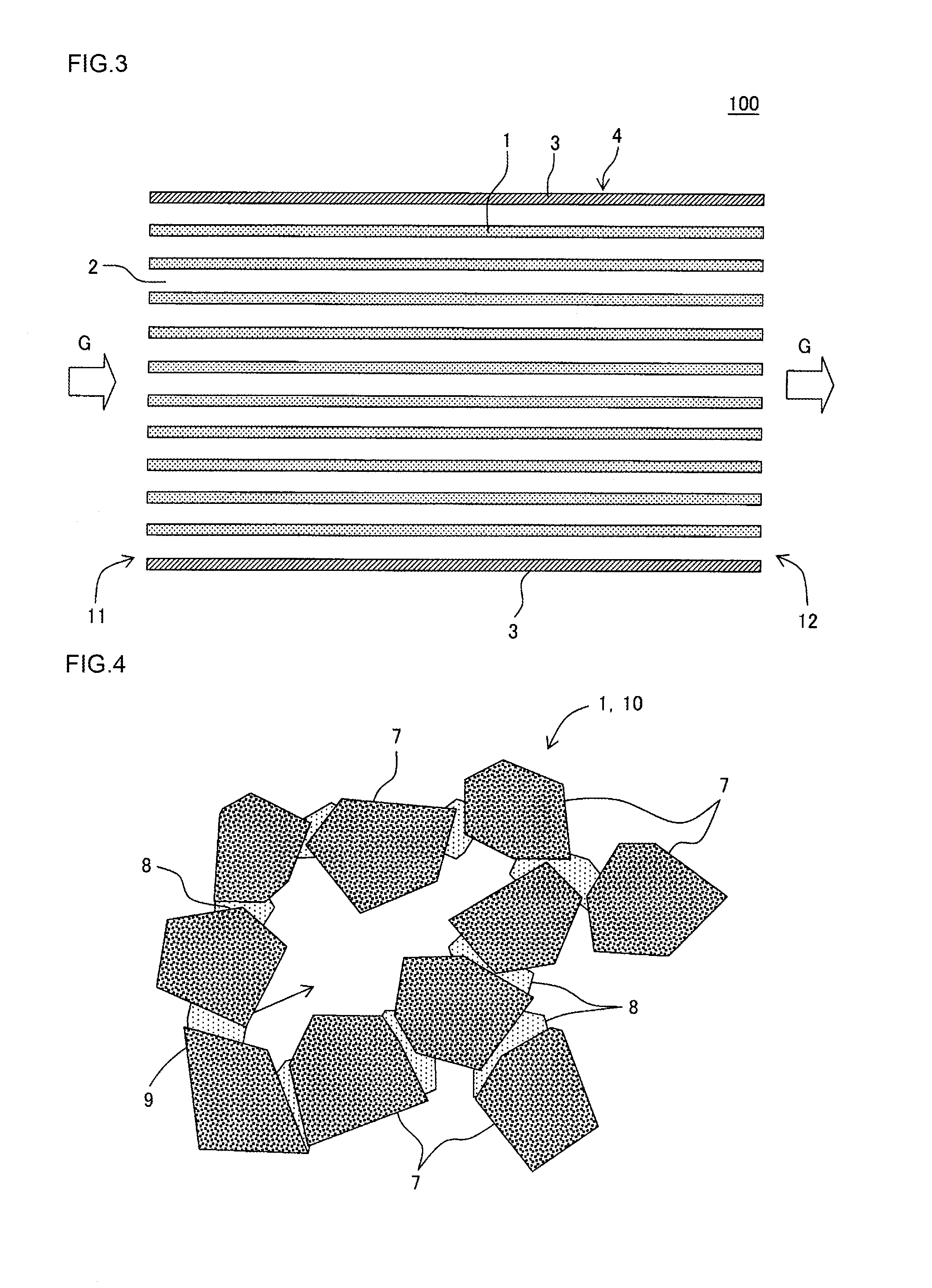
Honeycomb structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0067]In Example 1, first, a forming raw material was prepared by using molten silica particles, glass frit, and kaolin particles. As to blend ratios of the respective components in the forming raw material, the ratio of the molten silica particles was 50 mass %, the ratio of the glass frit was 30 mass %, and the ratio of the kaolin particles was 20 mass %. A median diameter of the molten silica particles was 15 μm, a median diameter of the glass frit was 10 μm, and a median diameter of the kaolin particles was 5 μm. As the glass frit, glass frit constituted of aluminosilicate glass was used. The glass frit used in Example 1 was “aluminosilicate glass A”. A column of “glass type” of Table 1 shows the type of glass frit used in preparing the forming raw material. Furthermore, a column of “clay” of Table 1 shows components other than the molten silica particles and glass frit used in preparing the forming raw material. In Example 1, the abovementioned kaolin particles corresponded to ...
example 2
[0081]In Example 2, a forming raw material was first prepared by using molten silica particles, glass frit and clay. As to blend ratios of the respective components in the forming raw material, the ratio of the molten silica particles was 50 mass %, the ratio of the glass frit was 30 mass %, and the ratio of the clay was 20 mass %. As the clay, Kibushi clay was used. In Example 2, the procedures of Example 1 were repeated except that the forming raw material was prepared as described above, to prepare a honeycomb structure of Example 2. As to the obtained honeycomb structure, “porosity (%)”, a “thermal expansion coefficient (×10−6 / ° C.)”, “A-axis compressive strength (MPa)” and a “median diameter (μm)” were measured in the same manner as in Example 1. Table 3 shows the measurement results. Furthermore, chemical components of the honeycomb structure of Example 2 were measured in the same manner as in Example 1. Table 3 shows the chemical components of the honeycomb structure of Examp...
example 3
[0082]The procedures of Example 1 were repeated except that as glass frit, “aluminosilicate glass B” of such a chemical composition as shown in Table 2 was used, to prepare a honeycomb structure of Example 3. As to the obtained honeycomb structure, “porosity (%)”, a “thermal expansion coefficient (×10−6 / ° C.)”, “A-axis compressive strength (MPa)” and a “median diameter (μm)” were measured in the same manner as in Example 1. Table 3 shows the measurement results. Furthermore, chemical components of the honeycomb structure of Example 3 were measured in the same manner as in Example 1. Table 3 shows the chemical components of the honeycomb structure of Example 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com