Wind-heated molten salt as a thermal buffer for producing oil from unconventional resources
a technology of wind-heated molten salt and unconventional resources, which is applied in the direction of fluid removal, insulation, survey, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of finding and accessing new resources, the inherent intermittent nature of conventional crude oil, and the decline of conventional crude oil supply, so as to reduce the overall variability, reduce the need to burn fossil fuels, and facilitate the effect of couple wind
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
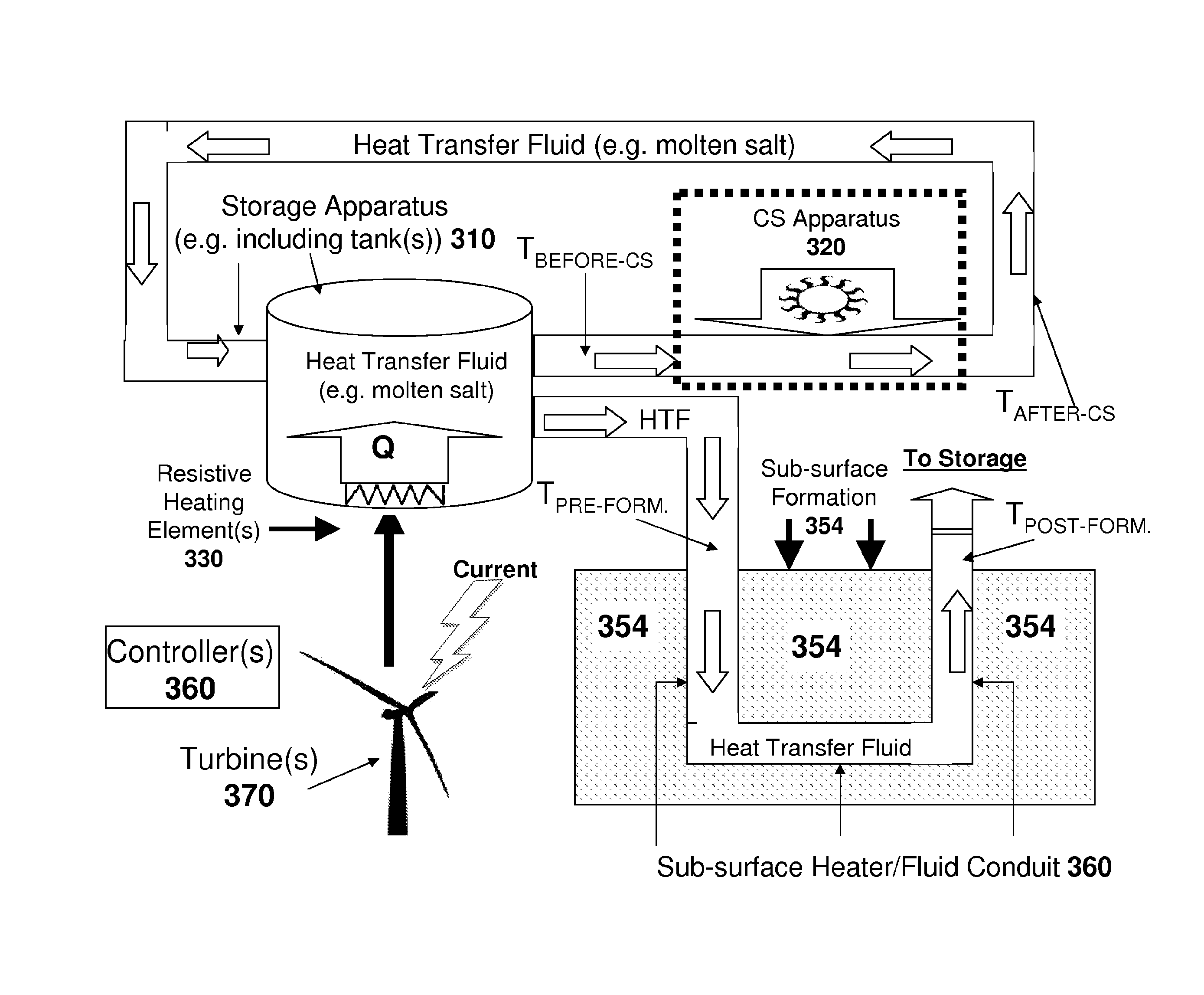
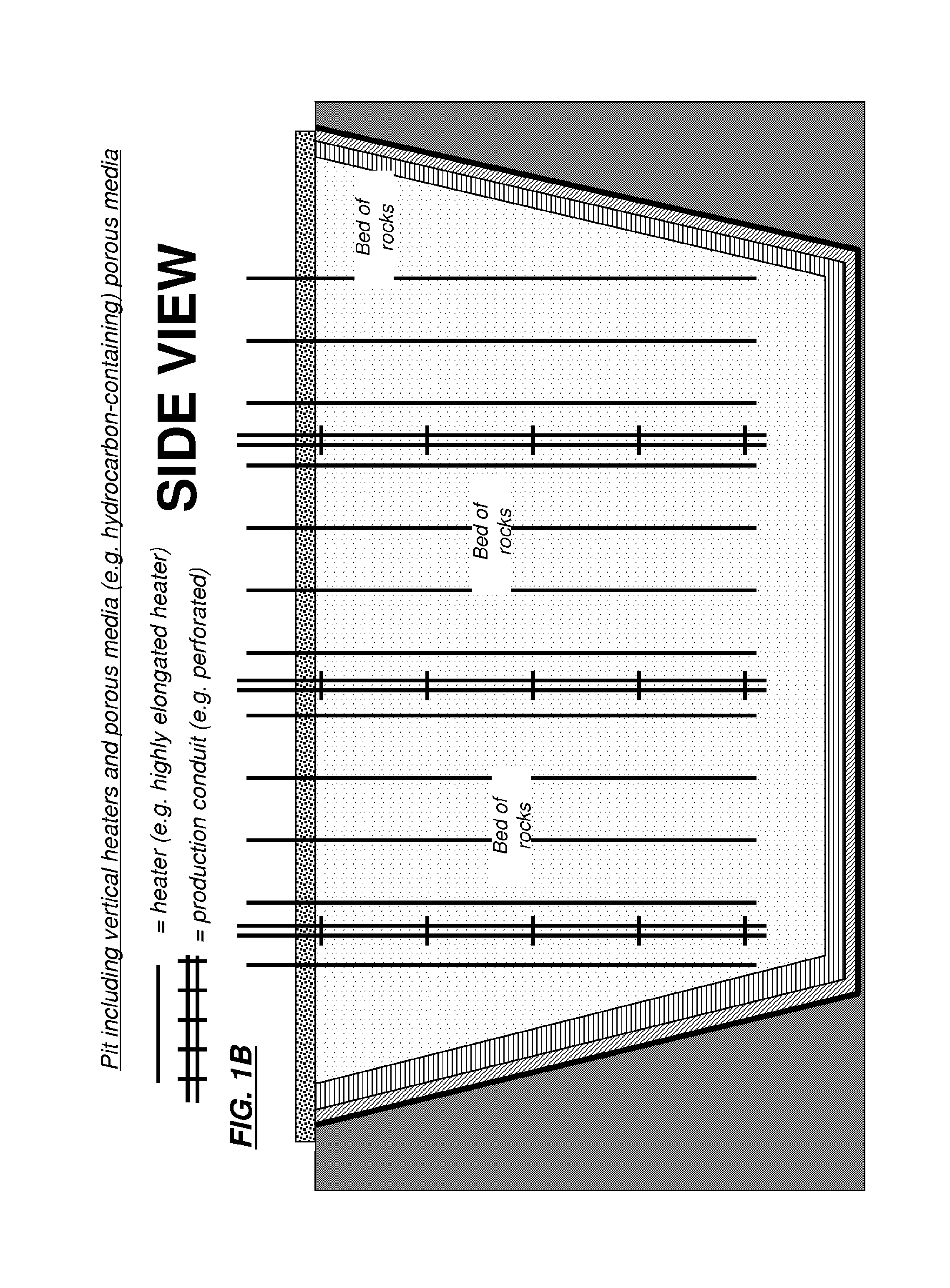
[0007]Some embodiments of the present invention relate to a system for production of hydrocarbon fluids comprising: a. an insulated storage tank and a quantity of heat transfer fluid disposed therein, at least one electrically resistive heater(s) situated within the storage tank and immersed within the heat transfer fluid; b. a bed of hydrocarbon-containing rocks situated within an enclosure, the storage tank being located outside of the enclosure; c. a source of wind electricity configured to supply electrical power to the immersed resistive heater(s) so as to heat the heat transfer fluid within the storage tank; and d. a flow system configured to force the wind-electricity-heated heat transfer fluid received from the storage tank: (i) to flow within conduits in thermal communication with the rocks of the bed so as to heat the rocks; and (ii) to return to the storage tank for reheating.
[0008]Examples of heat-transfer fluids include molten salt, synthetic oils and supercritical flui...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com