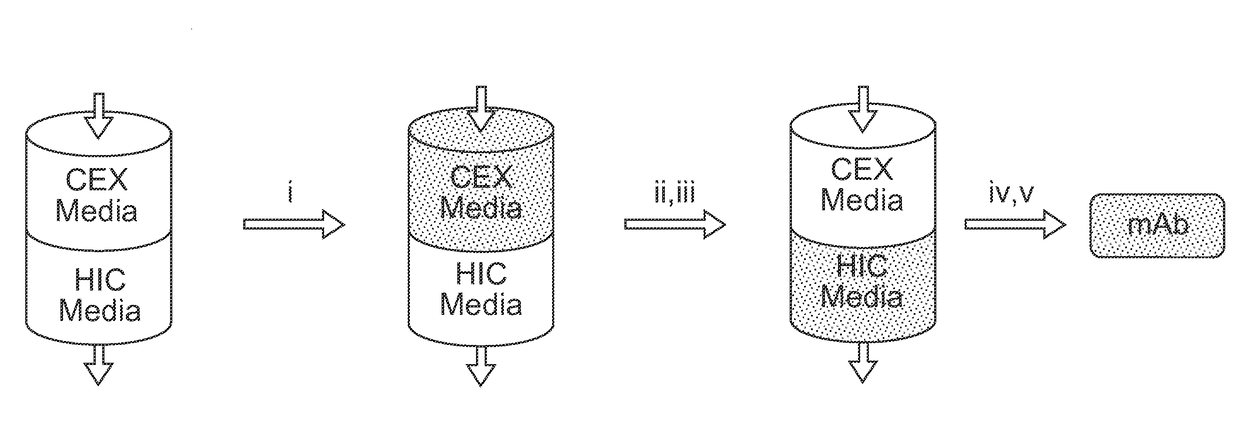
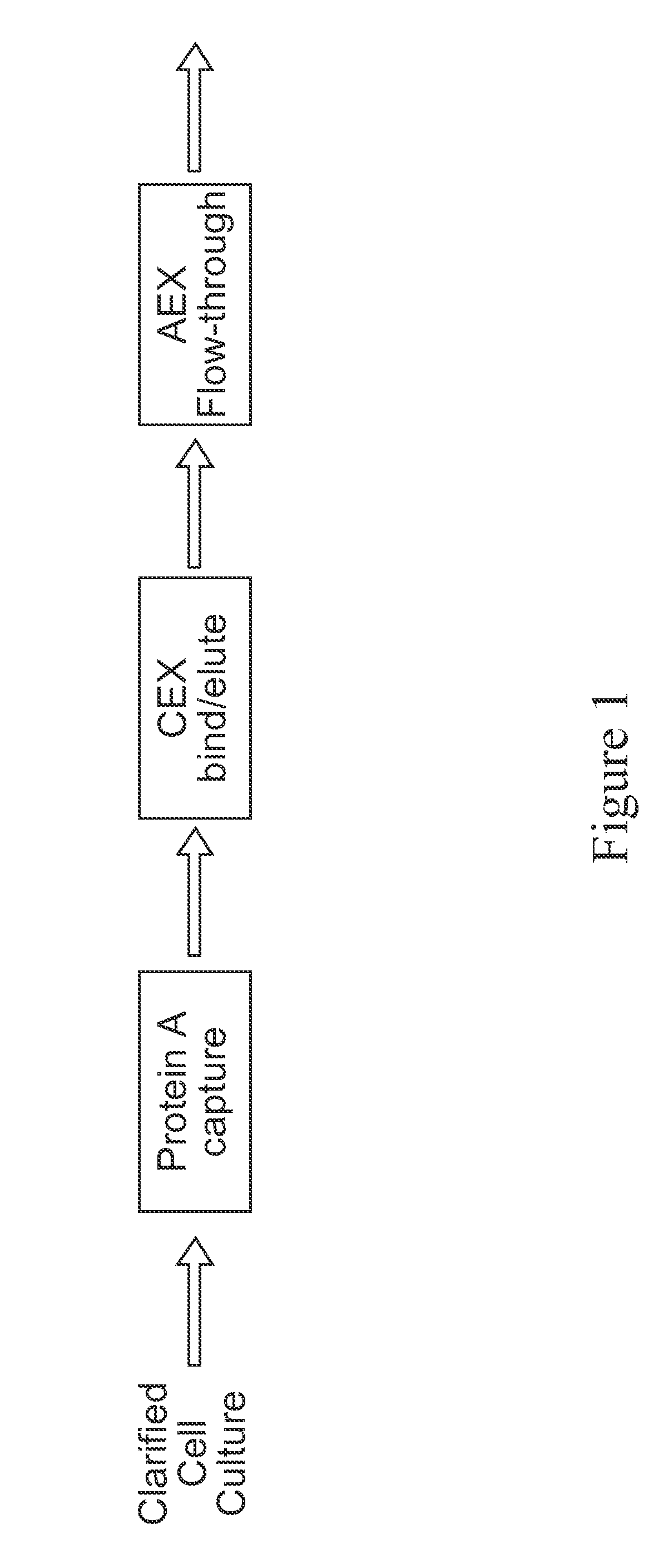
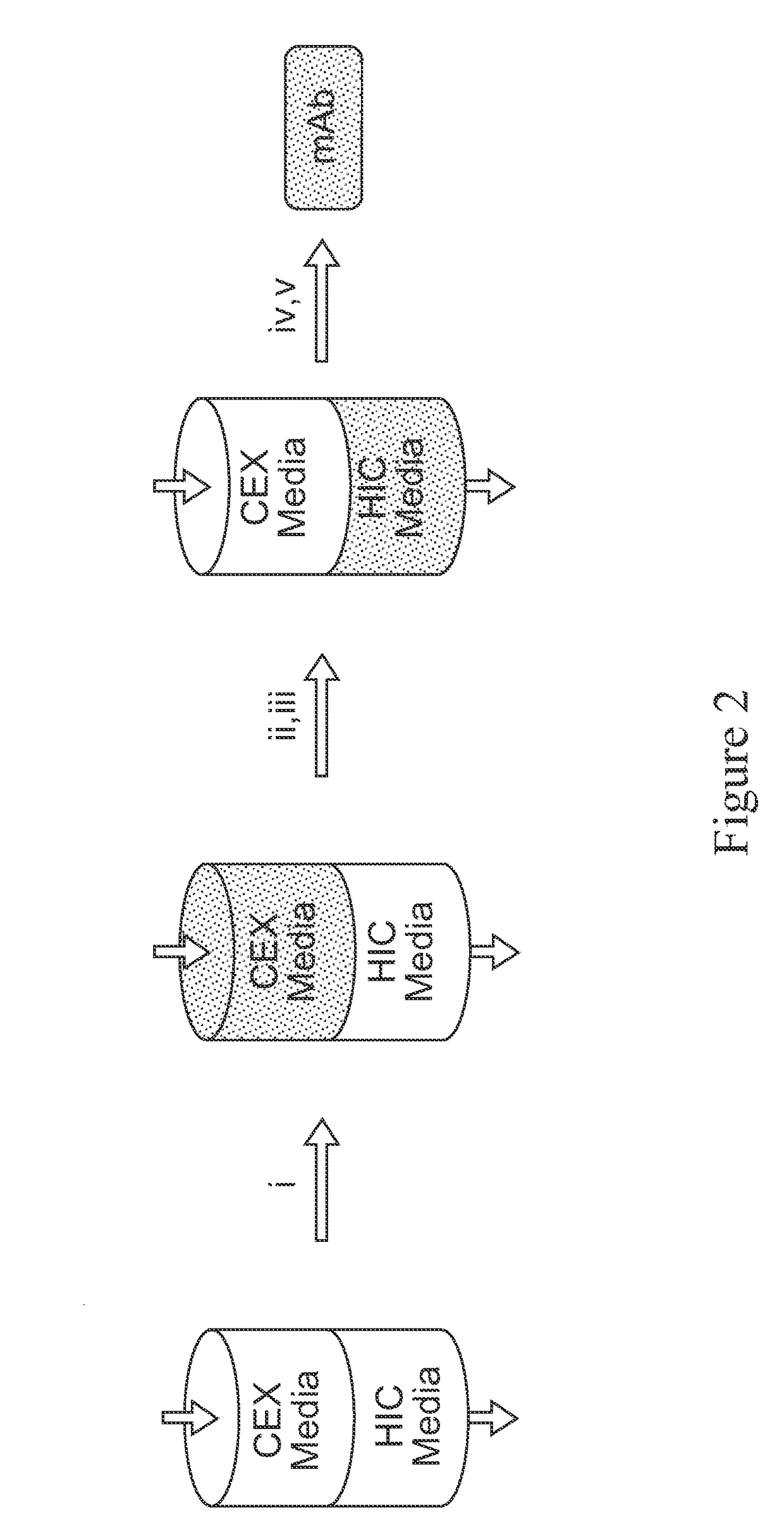
Mixed Bed Ion Exchange Adsorber
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Graft Polymerization of Un-Modified Nylon Fibers
[0207]10 g Allasso nylon fibers and water (466 ml) are added into a 500 ml bottle. 14 ml 1M HNO3 (14.4 mmol) are added to the reaction mixture, followed by the addition of 1.2 ml of a 0.4 M ammonium cerium(IV) nitrate solution in 1M HNO3 (0,480 mmol). The reaction mixture is agitated for 15 minutes. 3.39 g Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA, 24 mmol) are added. Now the agitated reaction mixture is heated to 35° C. for 1 hour. After cooling down to room temperature, the solids are washed with DI water (3×300 ml) and the damp material is used immediately in the following step.
example 2
Q-Functionalization of Epoxy-Functionalized Fibers (AEX Fiber Media)
[0208]The damp GMA functionalized fibers from example 1 are added into a 2 L bottle together with water (500 ml) and a solution of 50 wt % trimethylamine (aq.) in methanol (500 ml). The mixture is agitated for 18 hours at room temperature. Then the fiber solids are subsequently washed with a solution of 0.2 M ascorbic acid in 0.5 M sulphuric acid (3×400 ml), DI water (3×400 ml), 1M sodium hydroxide solution (3×400 ml), DI water (3×400 ml) and ethanol (1×400 ml). Subsequently, the material is placed in an oven to dry at 40° C. for 48 hours.
Yield: 11.74 g of a white fibrous solid
example 3
Graft Polymerization of Un-Modified Nylon Fibers (CEX Fiber Media)
[0209]10 g Allasso nylon fibers and water (460 ml) are added into a 1000 ml bottle. 29.8 ml 1M HNO3 solution (30 mmol) are added to the reaction mixture, followed by the addition of a solution 7.46 ml of a 0.4 M ammonium cerium(IV) nitrate solution in 1M HNO3 (3.00 mmol). The reaction mixture is agitated for 15 minutes. Then 61.5 g 3-sulfopropylmethacrylate potassium salt (3-SPMA, 250 mmol) are added and the resulting agitated reaction mixture is heated to 35° C. for 18 hours. After cooling to room temperature, the fiber solids from each bottle are washed with DI water (3×300 ml), 0.2 M ascorbic acid in 0.5 M sulphuric acid (3×300 ml), DI water (3×300 ml), 1M sodium hydroxide solution (3×300 ml), DI water 3×300 ml) and ethanol (1×300 ml). The prepared material is then placed in an oven to dry at 40° C.
Yield: 11.38 g of a white fibrous solid
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Interaction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com