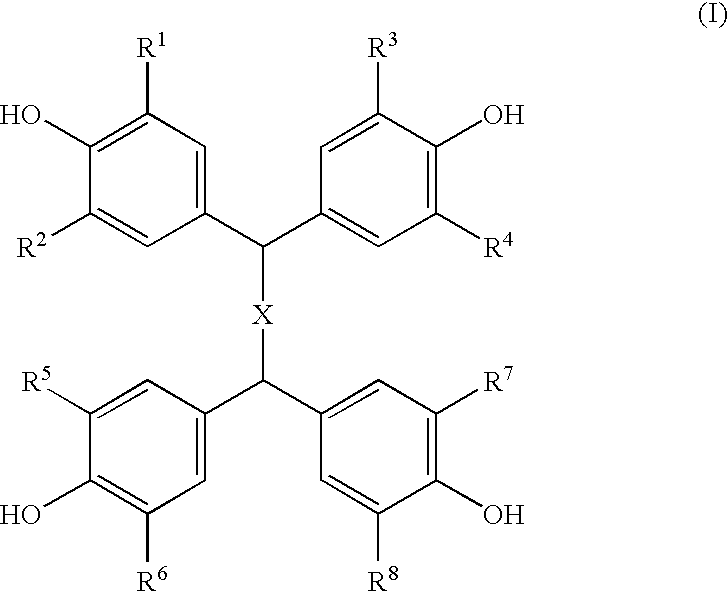
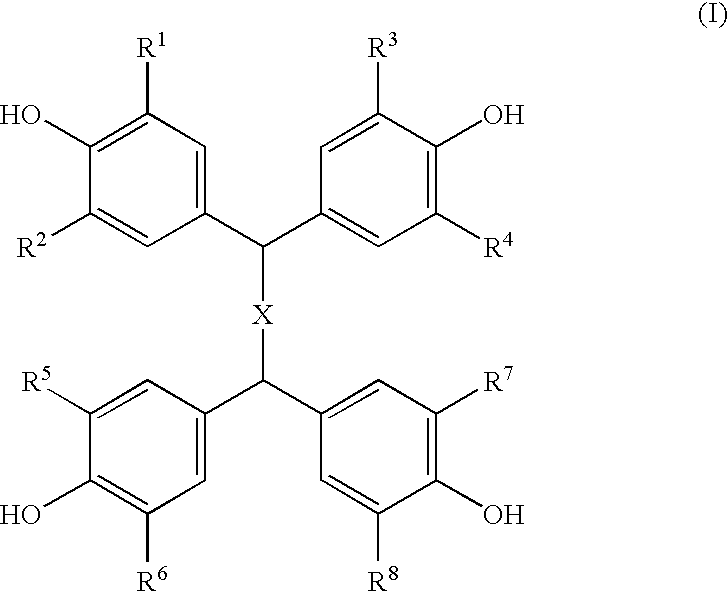
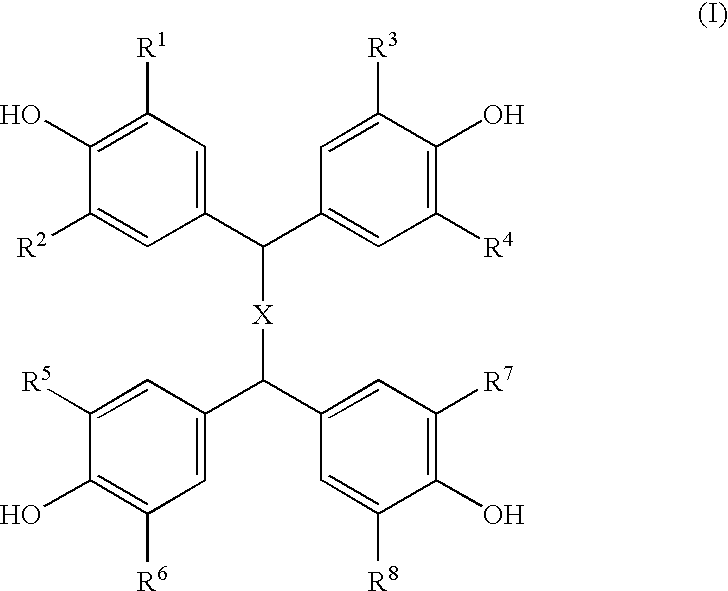
Composition of epoxy resin and clathrate of tetrakisphenol and epoxy-reactive curing compound
a technology of tetrakisphenol and epoxy resin, which is applied in the field of composition of epoxy resin and clathrate of tetrakisphenol and epoxyreactive curing compound, can solve the problems of increasing the viscosity of the composition, not being economical from operation, and not being easy to handle and operate economically
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Measurement of Prolonged Pot Life of Resin Compositions (Part 1)
To 100 parts of a base resin (uncured resin) UVR-6410 (Trade name, Manufactured by Union Carbide Co., Ltd.), was added 13.7 parts (corresponding to 4.0 parts by weight as 2MZ) of the inventive curative, sample No. 32, described in Table 1. The mixture was kneaded for 10 min. at 25.degree. C. and was further allowed to stand for 20 min. at 25.degree. C. Then, the initial viscosity of the resin composition prepared was measured. The resin composition was then placed under 25.degree. C., and periodical change in viscosity was measured. The viscosity measurement was accorded to JIS K-6833-1994, and B8R-type rotational viscosity meter (Manufactured by Tokyo Keiki) was used for the measurement. The results of the measurement are shown in Table 4 and FIG. 48. When prolonged pot life of the resin composition is defined as the time requiring for the viscosity of a resin to be the double value of the initial viscosity value, the ...
example 3
Measurement of Prolonged Pot Life of Resin Compositions (Part 2)
To 100 parts of a base resin (uncured resin) UVR-6410 (Trade name, Manufactured by Union Carbide Co., Ltd.), was added 11.2 parts by weight (corresponding to 4.0 parts by weight as 2B4MZ) of the inventive curative of sample No. 24 described in Table 1. Then, the viscosity of the resulting resin composition was measured according to the procedure as described in the example 2. The results of the measurement are shown in Table 5 and FIG. 49. When using the inventive curative of sample No. 24, the prolonged pot life, which is the time required for the viscosity of the resin composition to be a double value of the initial viscosity value, was found to be 180 hours.
example 4
Measurement of Prolonged Pot Life of Resin Compositions (Part 3)
To 100 parts by weight of a base resin (uncured resin) UVR-6410 (Trade name, Manufactured by Union Carbide Co., Ltd.), was added 30.5 parts by weight (corresponding to 4.0 parts by weight based on EDA) of the inventive curative of sample No. 10 described in Table 1. The viscosity of the resultant resin composition was measured according to the procedure described in the example 2. Similarly, the viscosity measurements were also done about a resin composition, in which 34.2 parts by weight (equivalent to 4.0 parts by weight based on EDA) of a curative of sample No. 11 described in Table 1 was used instead of the curative of sample No. 10. The results of the measurement are shown in Table 6 and FIG. 50. When using the curative of sample No. 10, the prolonged pot life, which is defined as time required for the viscosity of the resin to be a double value of the initial viscosity value, was found to be 180 hours. Whereas, wh...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com