Smart cards having thin die
a technology of thin dies and smart cards, applied in the field of thin dies, can solve the problems of inability to use semiconductor dies of about 0.030 inches thick, failure of existing smart cards, and inability to meet the requirements of rf, so as to improve mechanical flexural resistance and enhance performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
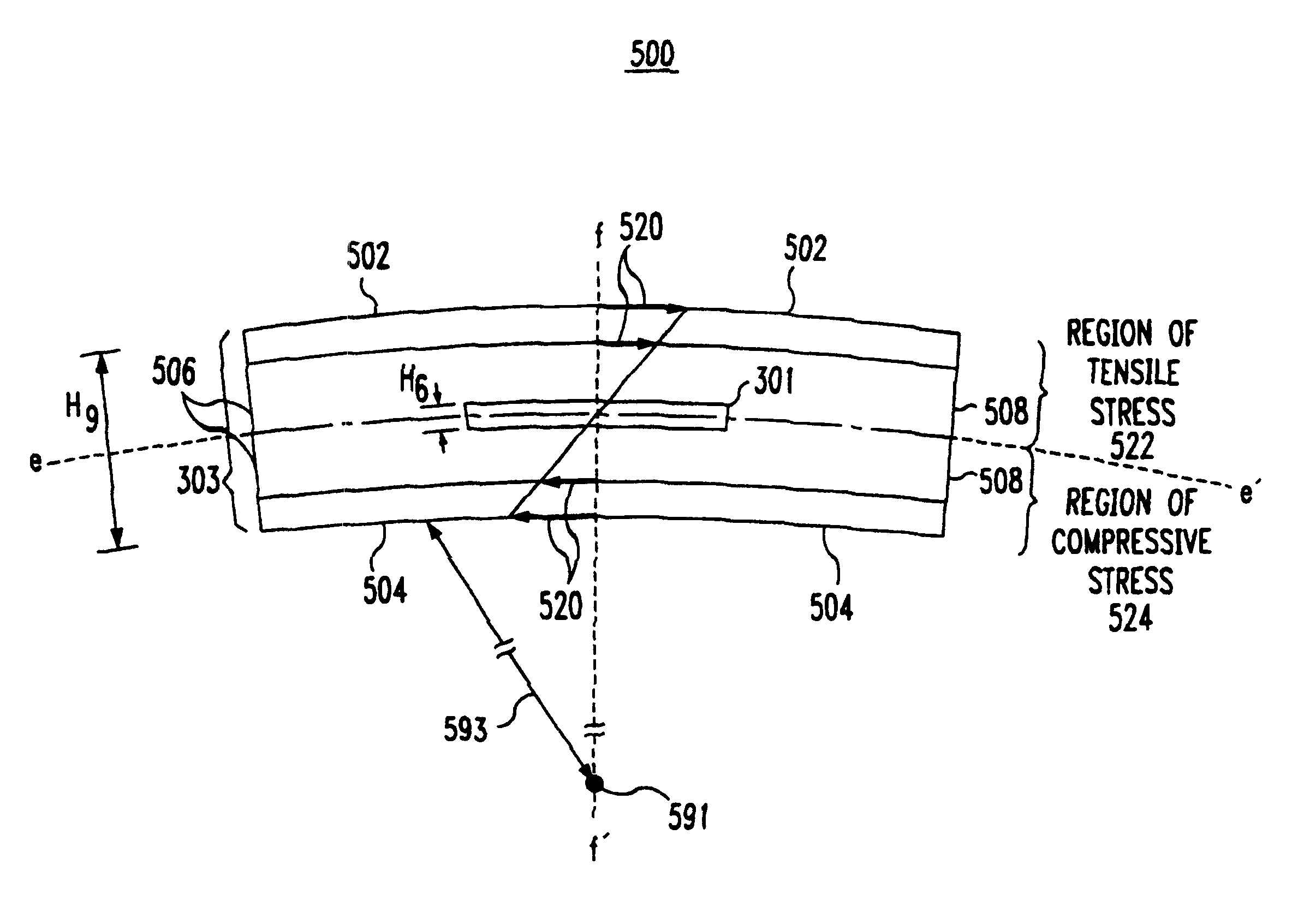
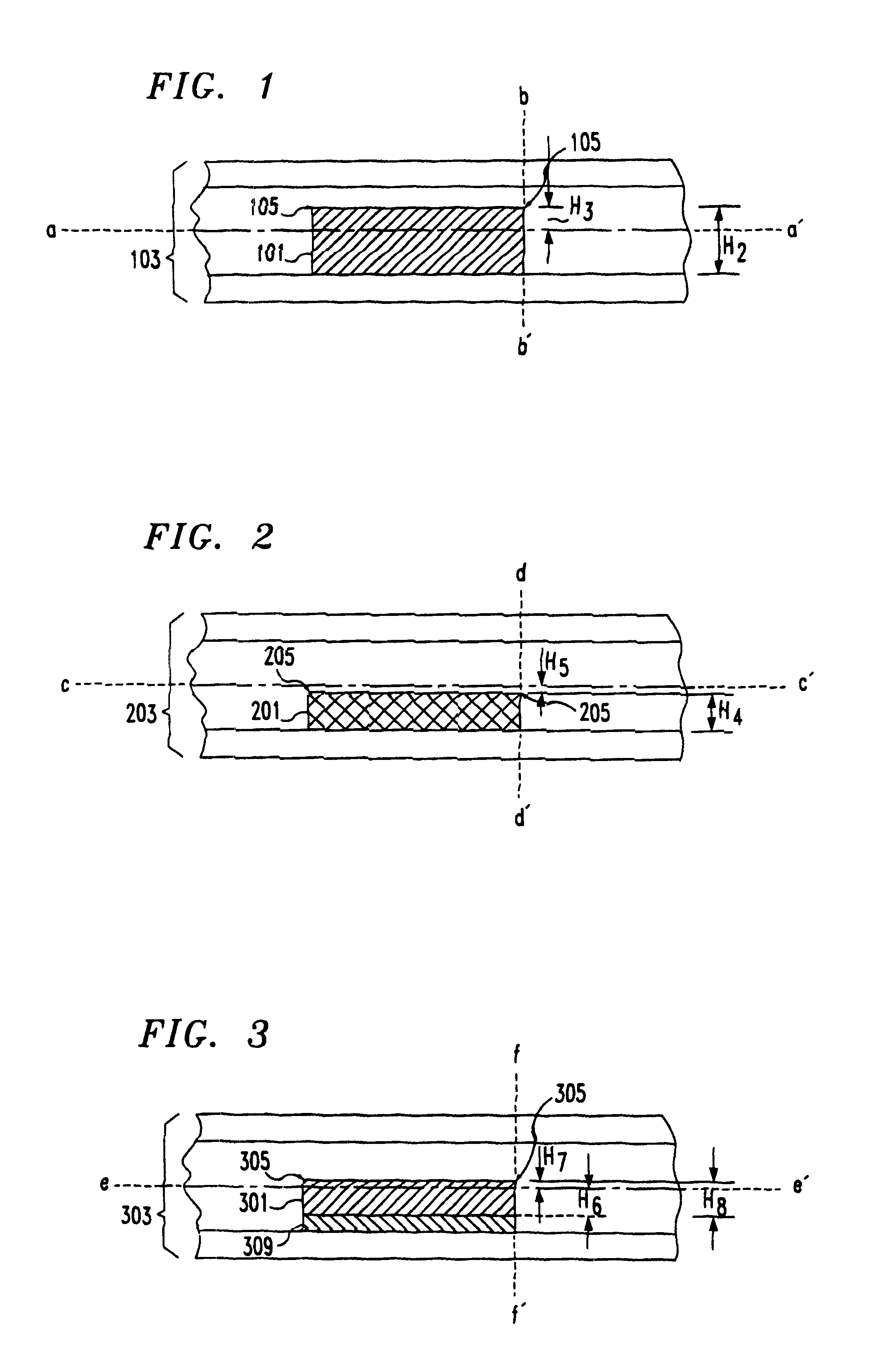
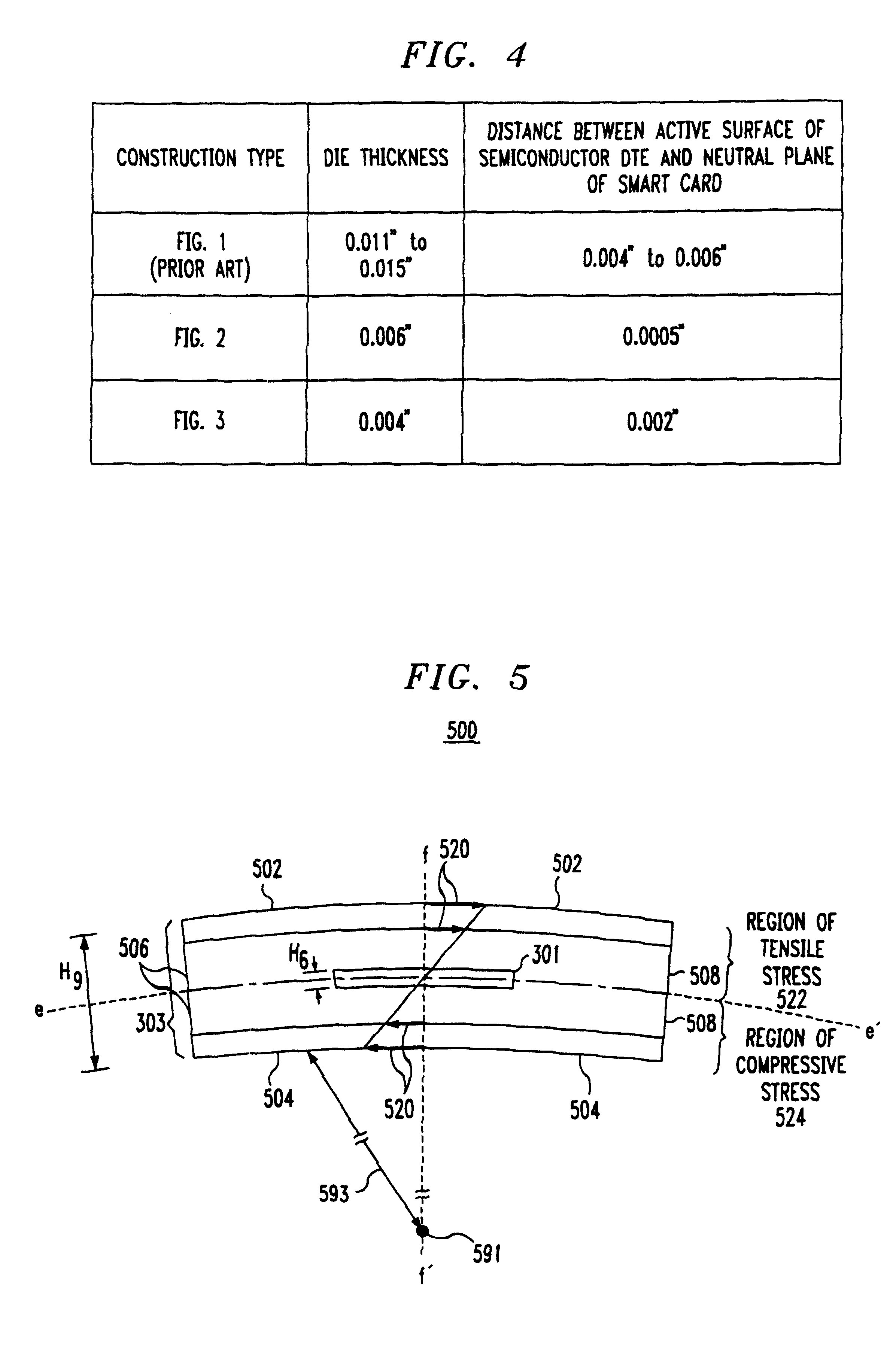
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of a smart card semiconductor die 201 fabricated in accordance with a first embodiment disclosed herein. Typically active devices, such as transistors and diodes, are fabricated near active surface 205 of semiconductor die 201. Smart card package 203 has a neutral plane which, in the cross sectional view of FIG. 2, is represented by axis c-c'. However, unlike the semiconductor die 101 of FIG. 1, semiconductor die 201 has a thickness along axis d-d' of about 0.004 inches, represented as H.sub.4. Axis d-d' may be conceptualized as running parallel to the thinnest dimension of semiconductor 201, and / or running perpendicular to a plane including semiconductor die 201. The semiconductor die active surface 205 is situated at a distance H.sub.5 of 0.001 inches or less from the smart card neutral plane, represented as axis c-c' in FIG. 2.
Although the semiconductor die 201 of FIG. 2 is very thin compared to typical 0.011-inch die, the use of a thin die is adv...
second embodiment
FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view of a thin smart card semiconductor die 301 fabricated in accordance with a second embodiment disclosed herein. As in the case of semiconductor die 201 of FIG. 2, active devices, such as transistors and diodes, are fabricated near active surface 305 of semiconductor die 301. Smart card package 303 has a neutral plane which, in the cross sectional view of FIG. 3, is represented by axis e-e'. Unlike the semiconductor die 101 of FIG. 1, semiconductor die 301 has a thickness along axis f-f' of about 0.004 inches, represented as H.sub.8. The semiconductor die active surface 305 is situated at a distance H.sub.7 of 0.001 inches or less from the smart card neutral plane, represented as axis e-e' in FIG. 3. Unlike the semiconductor die 201 of FIG. 2, semiconductor 301 is mounted to smart card package 303 using a physical standoff 309. Physical standoff 309 functions as a mechanical spacer, holding the active semiconductor die 301 at a desired spatial relation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com