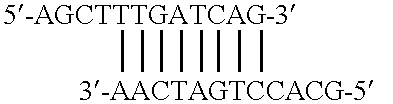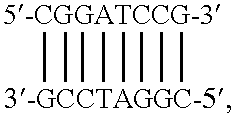Method of using eukaryotic expression vectors comprising the BK virus enhancer
a technology of bk virus and enhancer, which is applied in the field of using eukaryotic expression vectors comprising bk virus enhancer, can solve the problems that eukaryotic expression vectors that utilized enhancers to increase the transcription of recombinant genes were not expected to work better than vectors without enhancers in e1a-containing host cells, and achieves the effect of increasing the transcription and expression of recombinant genes and being easily transferred to other vector
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of BK Virus DNA
BK virus is obtained from the American Type Culture Collection under the accession number ATCC VR-837. The virus is delivered in freeze-dried form and resuspended in Hank's balanced salts (Gibco, 3175 Staley Road, Brand Island, N.Y. 14072) to a titer of about 10.sup.5 .Iadd.plaque-forming .Iaddend.units (pfu) / ml. The host of choice for the preparation of BK virus DNA is primary human embryonic kidney (PHEK) cells, which can be obtained from Flow Laboratories, Inc., 7655 Old Springhouse Road, McLean, Va. 22101, under catalogue number 0-100 or from M.A. Bioproducts under catalogue number 70-151.
About five 75 mm.sup.2 polystyrene flasks comprising confluent monolayers of about 10.sup.6 PHEK cells are used to prepare the virus. About 1 ml of BK virus at a titer of 10.sup.5 pfu / ml is added to each flask, which is then incubated at 37.degree. C. for one hour, and then, fresh culture medium (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium, Gibco, supplemented with 10% fetal b...
example 2
Construction of Plasmids pBKE1 and pBKE2
About one .mu.g of the BK virus DNA prepared in Example 1 in one .mu.l of TE buffer was dissolved in 2 .mu.l of 10.times. EcoRI buffer (1.0M Tris-HCl, pH=7.5; 0.5M NaCl; 50 mM MgCl.sub.2 ; and 1 mg / ml BSA) and 15 .mu.l of H.sub.2 O. About 2 .mu.l (.about.10 units; all enzyme units referred to herein, unless otherwise indicated, refer to the unit definitions of New England Biolabs, 32 Tozer Road, Beverly, Mass. 01915-9990, although the actual source of the enzymes may have been different) of restriction enzyme EcoRI were added to the solution of DNA, and the resulting reaction was incubated at 37.degree. C. for two hours.
About 1 .mu.g of plasmid pUC8 (available from Pharmacia P-L Biochemicals, 800 Centennial Ave., Piscataway, N.J. 08854) in 1 .mu.l of TE buffer was digested with EcoRI in substantial accordance with the procedure used to prepare the EcoRI-digested BK virus DNA. The EcoRI-digested plasmid pUC8 DNA was diluted to 100 .mu.l in TE b...
example 3
Construction of Plasmids pBKneo1 and pBKneo2
E. coli K12 HB101 / pdBPV-MMTneo cells are obtained in lyophil form from the American Type Culture Collection under the accession number ATCC 37224. The lyophilized cells are plated on L-agar plates containing 100 .mu.g / ml ampicillin and incubated at 37.degree. C. to obtain single colony isolates.
One liter of L broth (10 g tryptone, 10 g NaCl, and 5 g yeast extract per liter) containing 50 .mu.g / ml ampicillin was inoculated with a colony of E. coli K12 HB101 / pdBPV-MMTneo and incubated in an air-shaker at 37.degree. C. until the O.D..sub.590 was .about.1 absorbance unit, at which time 150 mg of chloramphenicol were added to the culture. The incubation was continued for about 16 hours; the chloramphenicol addition inhibits protein synthesis, and thus inhibits further cell division, but allows plasmid replication to continue.
The culture was centrifuged in a Sorvall GSA rotor (DuPont Co., Instrument Products, Biomedical Division, Newtown, Conn. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com