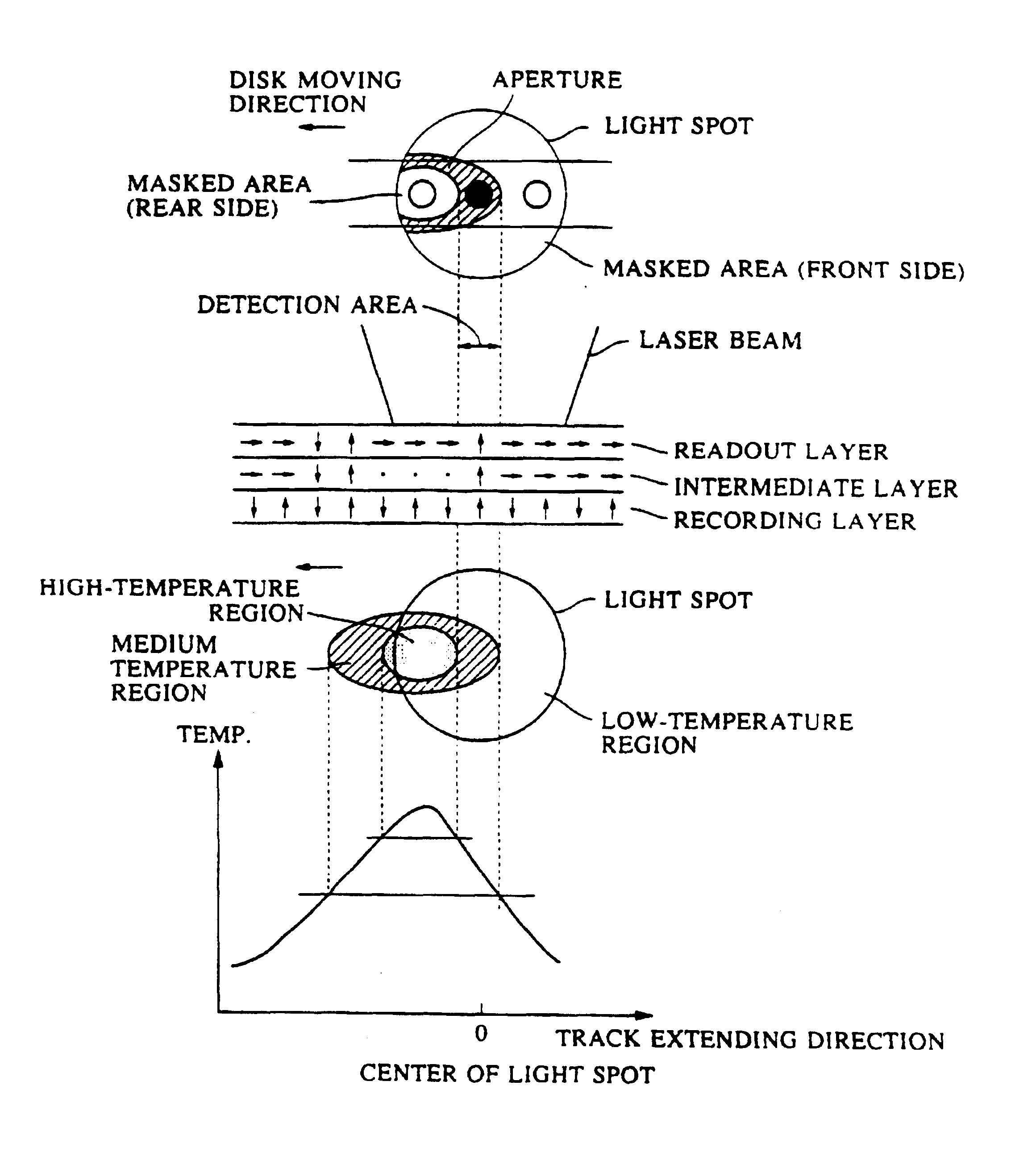
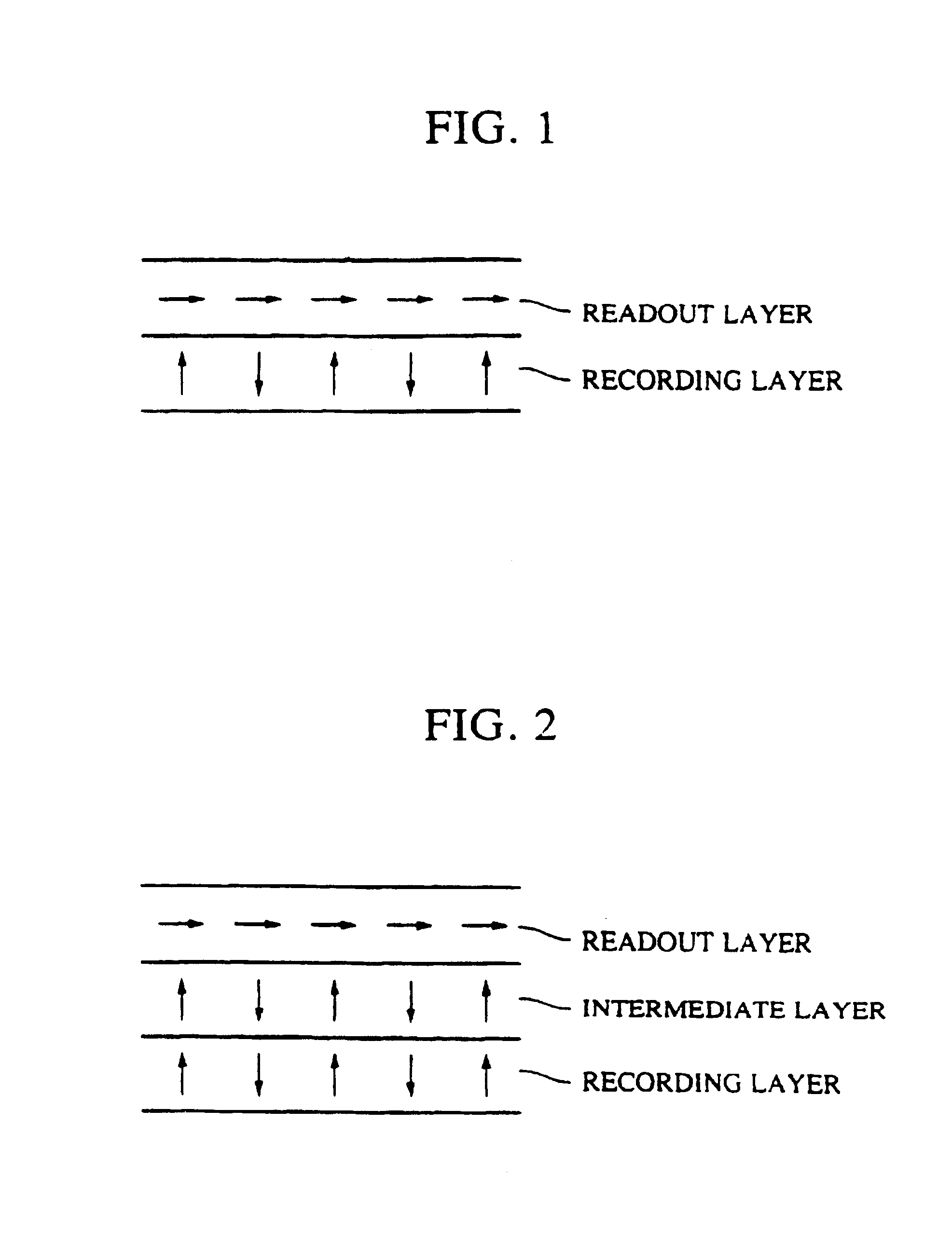
Magneto-optical recording medium and method for reproducing information from a magneto-optical recording medium having three layers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first experimental example
(First Experimental Example)
[0079]Targets Si, Tb, Gd, Fe, Co, Al and Cu were installed in a DC magnetron sputtering equipment, and a glass substrate was held on a holder. Thereafter, air was vacuum-exhausted from a chamber to establish a high vacuum level of less than 1×10−5 Pa by using a cryosorption pump.
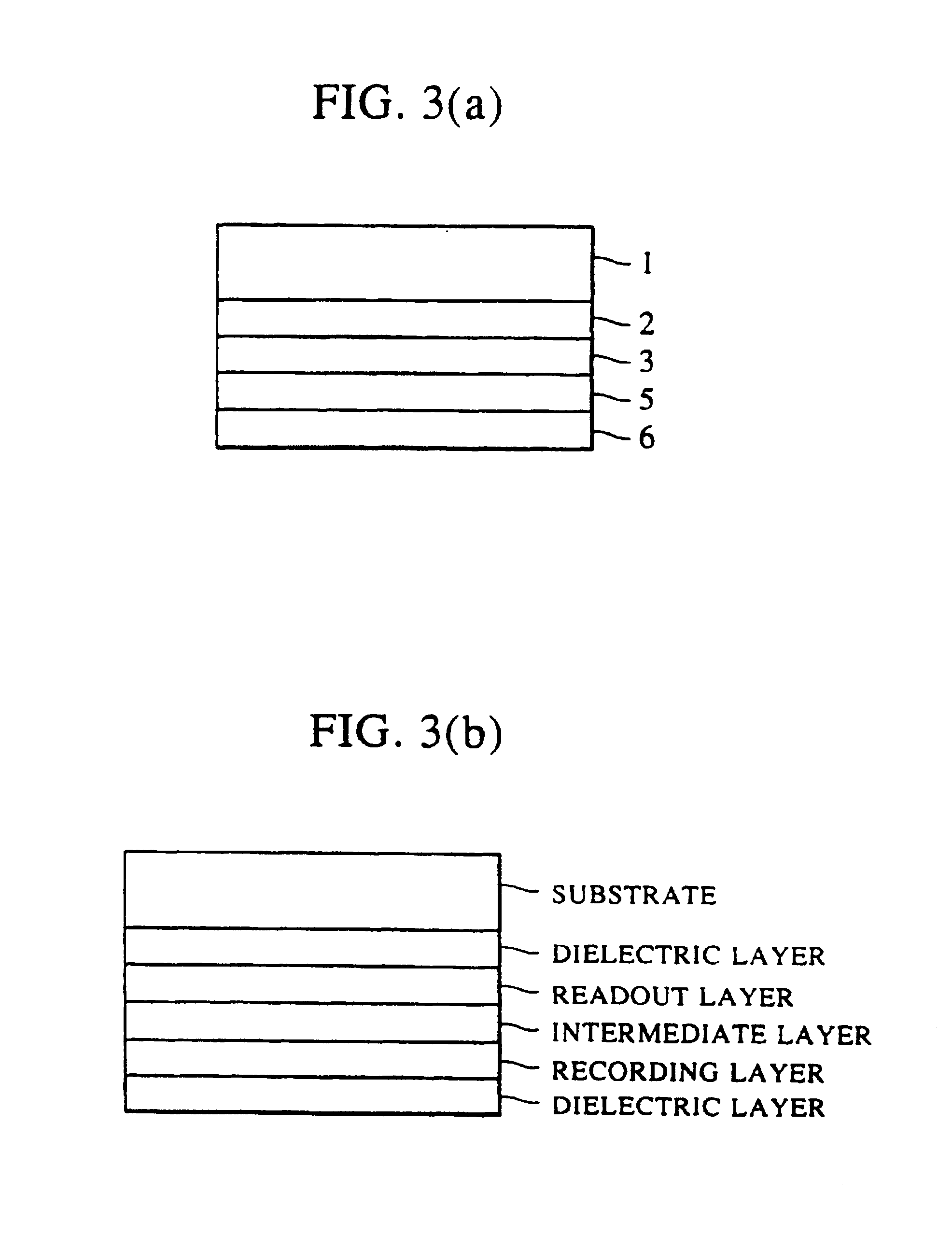
[0080]Ar gas was introduced into the chamber while vacuum-exhausting air, until the level of 0.3 Pa or Ar gas was reached. Then, a SiN layer, which functioned as an interference dielectric film, was deposited to a thickness of 700 Å on the surface of the substrate. A GdFeCo layer was (thickness: 400 Å) was deposited as a readout layer, and a TbFeCo layer (thickness: 400 Å) was deposited as a recording layer. Then, another SiN layer (thickness: 800 Å), which functioned as a protective dielectric film, was deposited to form a magnetooptical recording medium of the present invention having the two-layer structure shown in FIG. 3(a).
[0081]When the SiN layer was formed, N2 gas was intr...
second experimental example
(Second Experimental Example)
[0085]A magnetooptical recording medium was fabricated, which had the same layer structure as the above first example except that a polycarbonate substrate having a diameter of 130 mm and pregrooves was used.
[0086]Results of measurement of recording-reproducing characteristics of the magnetooptical recording medium were as follows. A measuring instrument comprised an objective lens of 0.55 N.A. and a projector for outputting a laser beam of 780 mm wavelength. Power for recording was preset at 8 mW, and linear velocity was 9 m / sec. Then, 6-15 MHz carrier signal was recorded in the recording layer by using a field modulation system in which a magnetic field of ±2000 e was applied stepwise. The dependency of C / N ratio on the recorded mark length was measured. The reproducing power was set to a value (2.5 to 3.5 mW) so that C / N ratio is maximized.
[0087]Table 1 shows the C / N ratios of the carrier signals recorded at 15 MHz (mark length: 30 μm), 11.25 MHz (mar...
third experimental example
(Third Experimental Example)
[0089]A magnetooptical recording medium of the present invention comprising a readout layer, a recording layer and an intermediate layer with low Curie temperature provided therebetween was fabricated and evaluated.
[0090]The same film forming instrument and film forming method as those employed in the second experiment example were used. A SiN layer as an interference dielectric layer was deposited to a thickness of 830 Å on the surface of a polycarbonate substrate having a diameter of 130 mm and pregrooves. A GdFeCo layer (thickness: 400 Å) was deposited as a readout layer, a TbFeCoAl layer (thickness: 100 Å) was deposited as an intermediate layer, a TbFeCo layer (thickness: 300 Å) was deposited as a recording layer. Then, another SiN layer (thickness: 700 Å) was deposited as a protective dielectric layer to form a magnetooptical recording medium having the structure shown in FIG. 3(b).
[0091]When the SiN layer was formed, N2 gas was introduced in additio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com