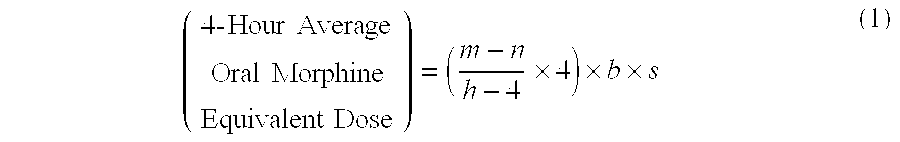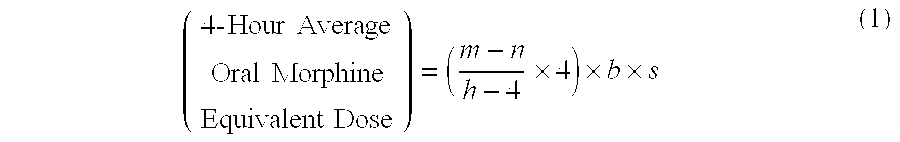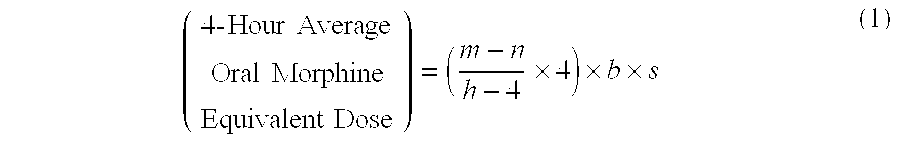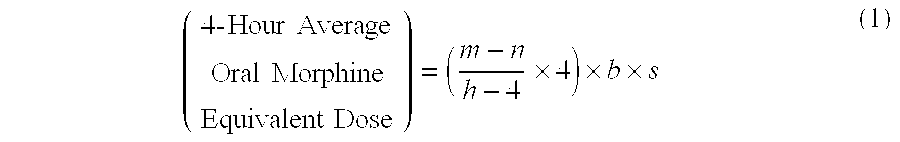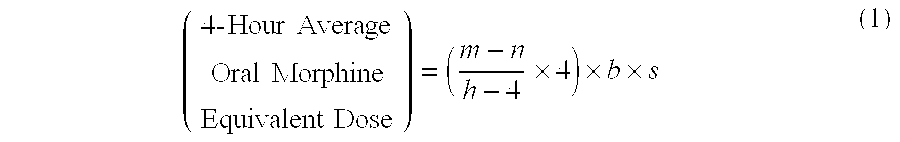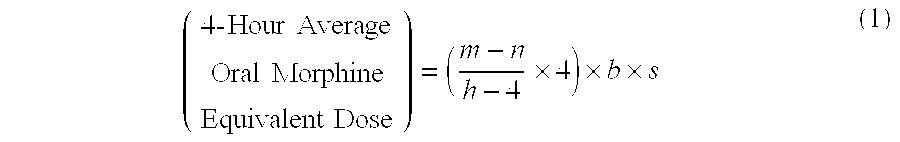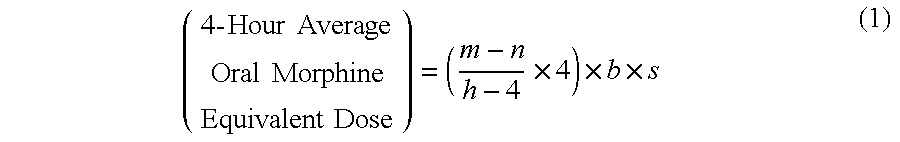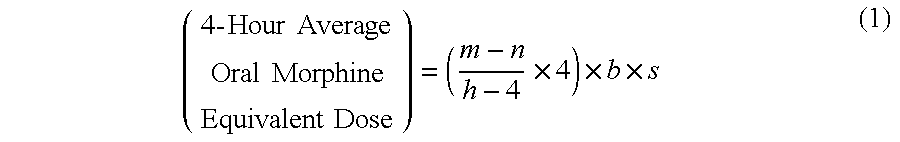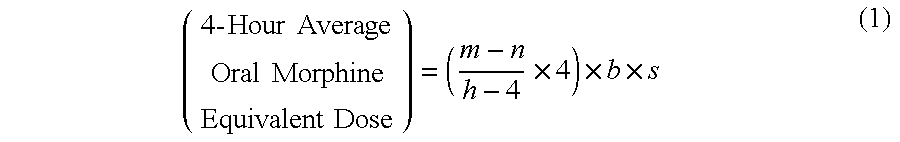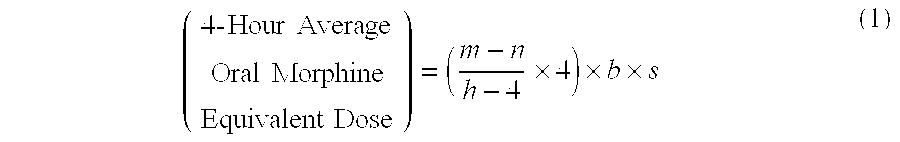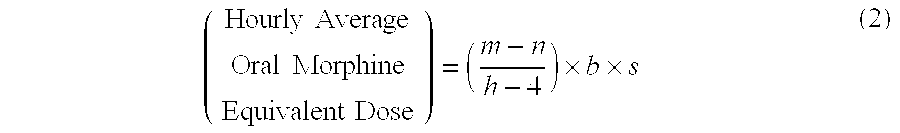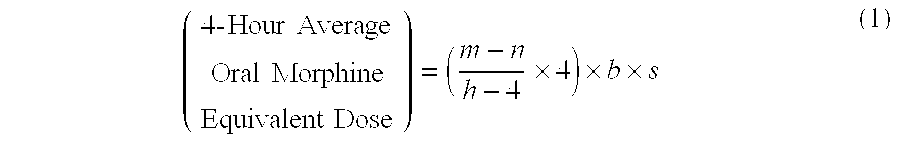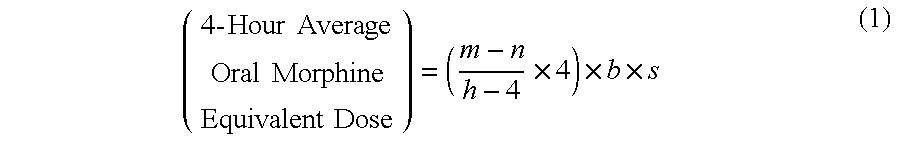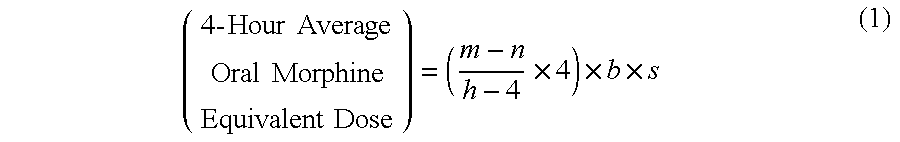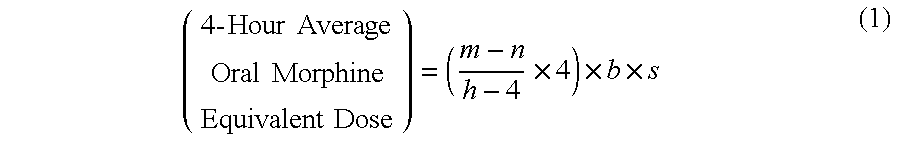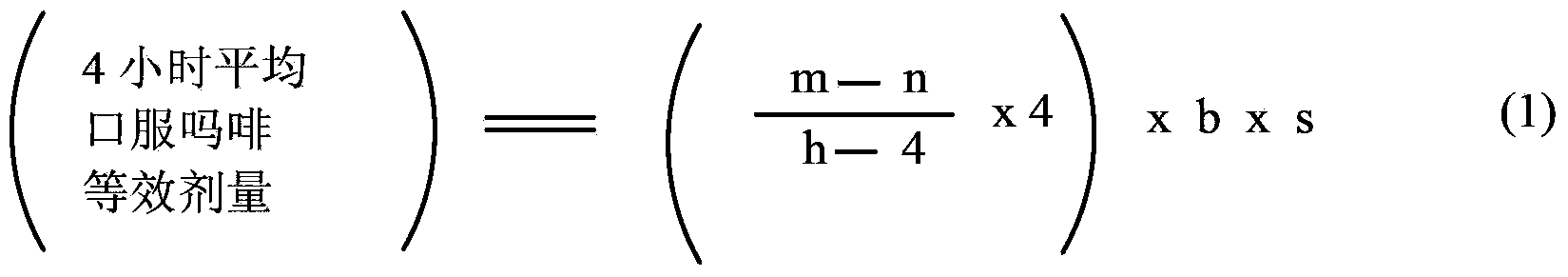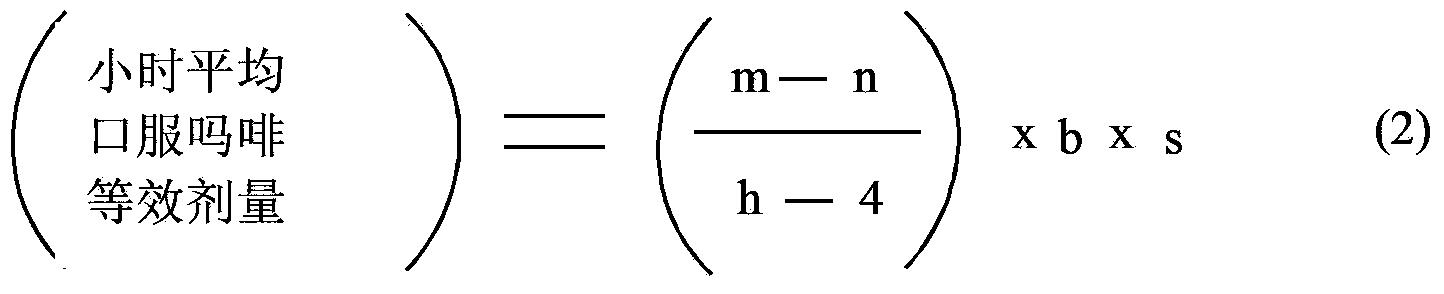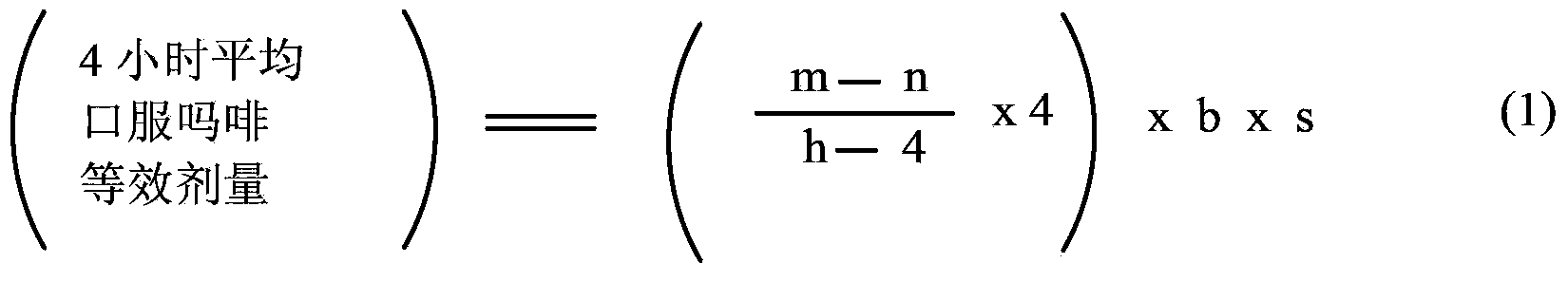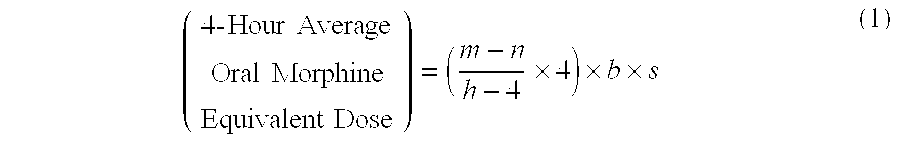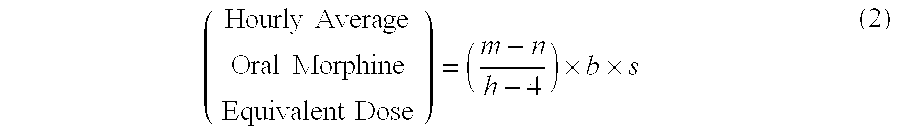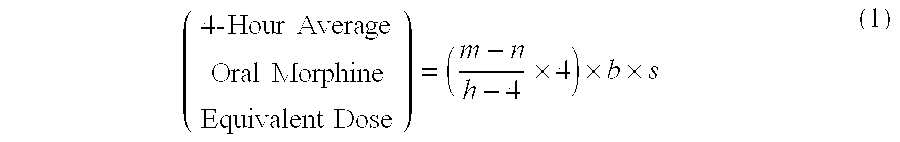Patents
Literature
30 results about "Intravenous dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and method for measuring and predicting insulin dosing rates
InactiveUS20070078314A1Efficient managementDrug and medicationsMedical automated diagnosisPatient dataGlucose polymers
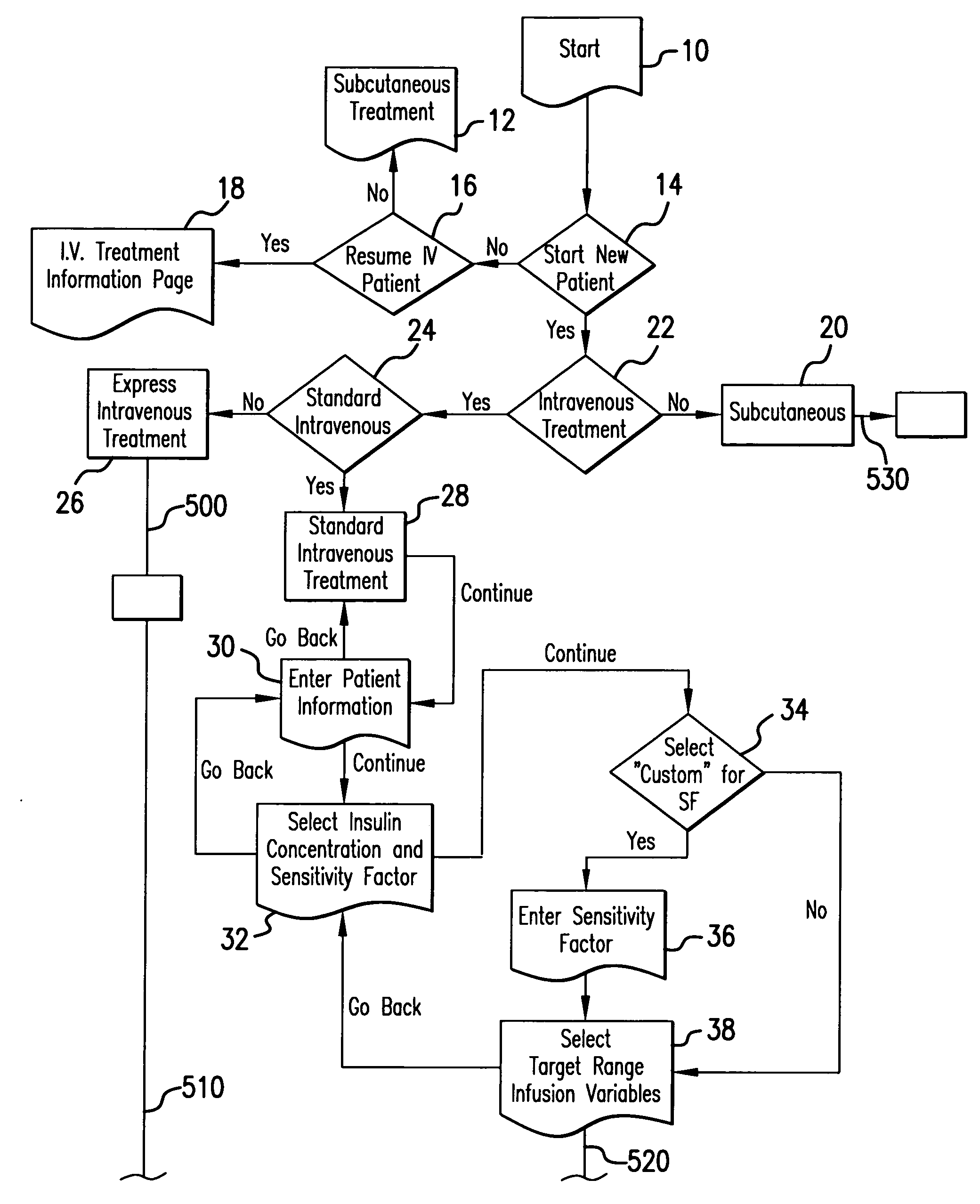
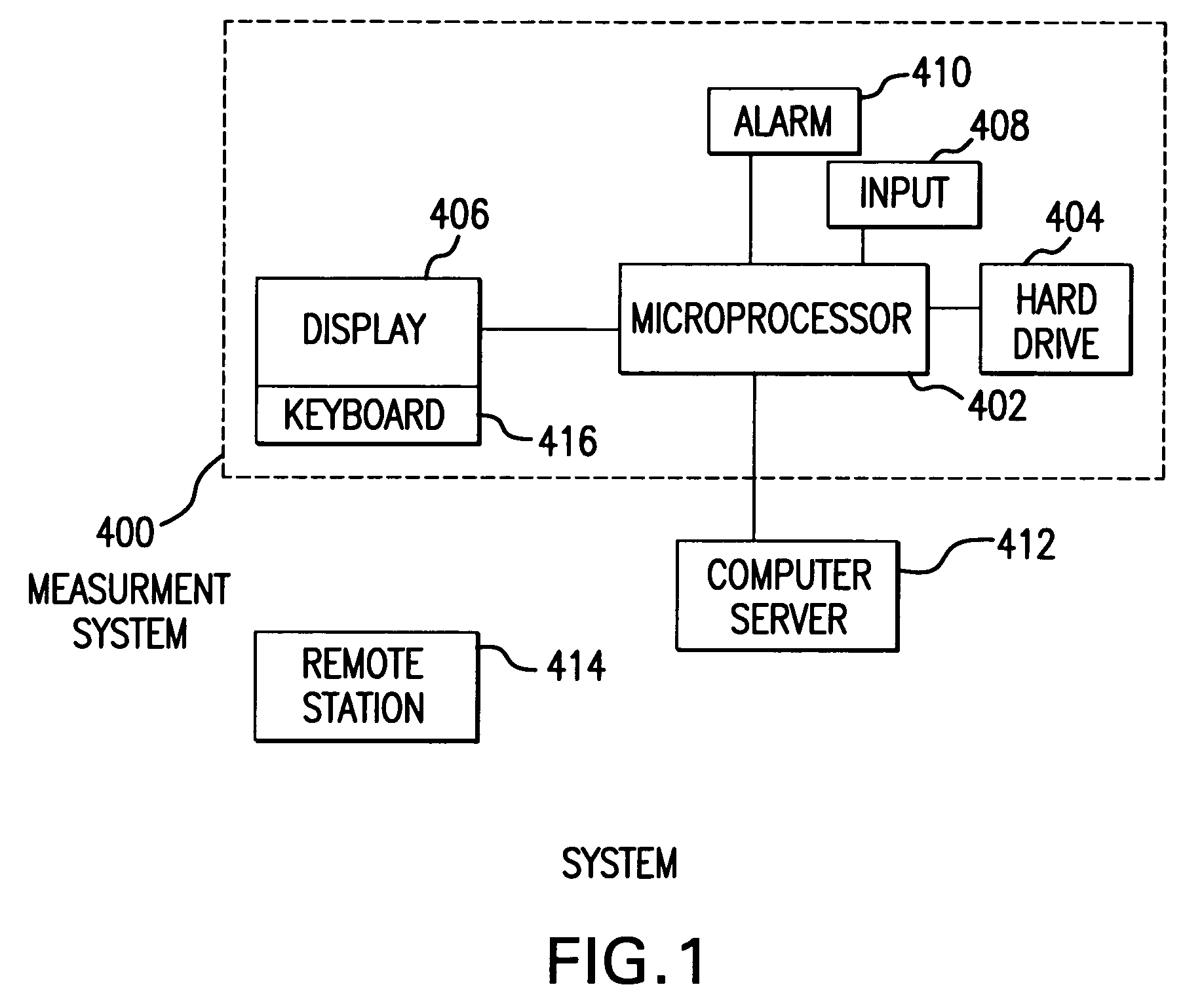
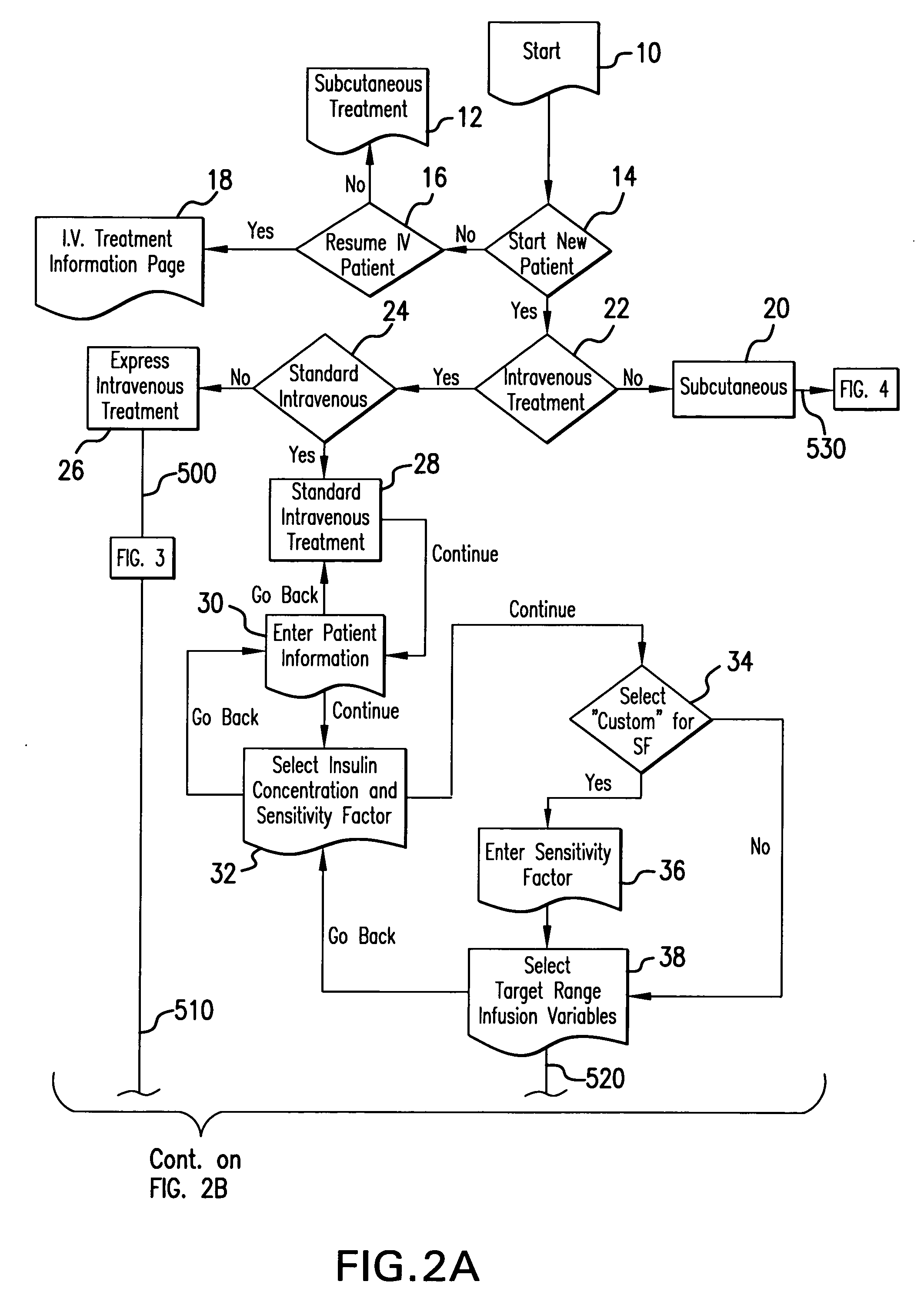
The method and system for managing a patient's blood glucose level predicts an insulin dosing rate to bring a patient's blood glucose level into a preferred target range within a predetermined time interval. The system includes a processor which actuates a blood glucose computer program to measure and predict the patient's blood glucose level. An input mechanism allows for insertion of a preferred target range of the patient's blood glucose level and further permits input of various patient data parameters. The processor calculates the optimum insulin dosing rate for the patient based upon the type of insulin dosing whether it be intravenous dosing and / or subcutaneous dosing. A display mechanism displays the patient dosing parameters and an alarm mechanism alerts a user when the patient's blood glucose level is outside of the preferred patient blood glucose target range.
Owner:GLUCOTEC
Method for assisting in differential diagnosis and treatment of autistic syndromes
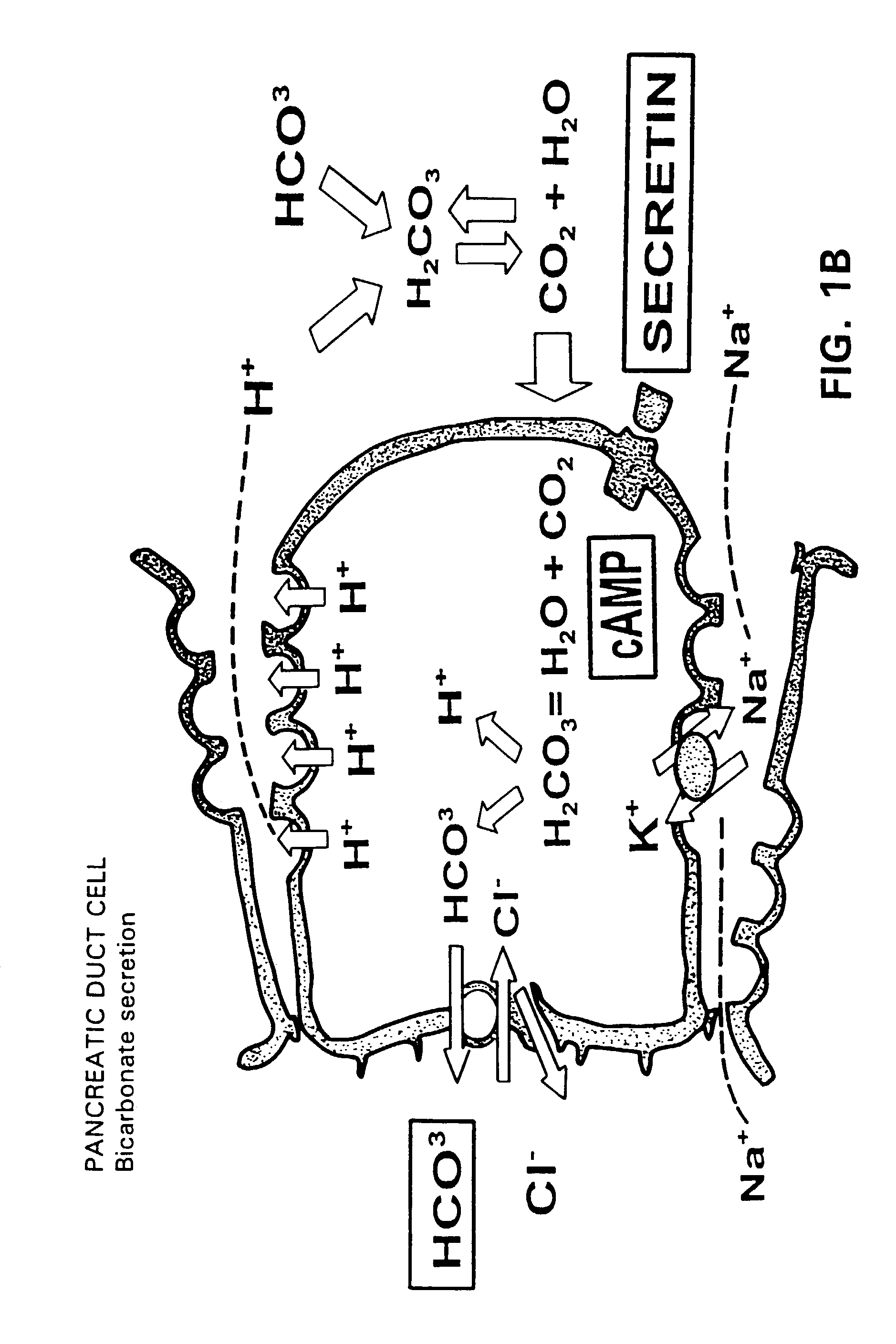
InactiveUS7091182B2EffectivenessContinued effectivenessNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiliary secretionVein
A novel relationship between pancreatico-biliary secretion and autistic syndrome is disclosed. This relationship enables a novel therapy for the treatment of the symptoms of autistic syndromes, comprising the administration of a therapeutically effective, preferably intravenous, dose of secretin to an individual with autistic syndrome. The relationship further enables a differential diagnosis for autistic syndrome, comprising an analysis of an individual's blood and / or intestinal tissue for the presence of secretin and comparison of the level of secretin to known norms.
Owner:REPLIGEN CORP
Methods for the treatment of a traumatic central nervous system injury
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
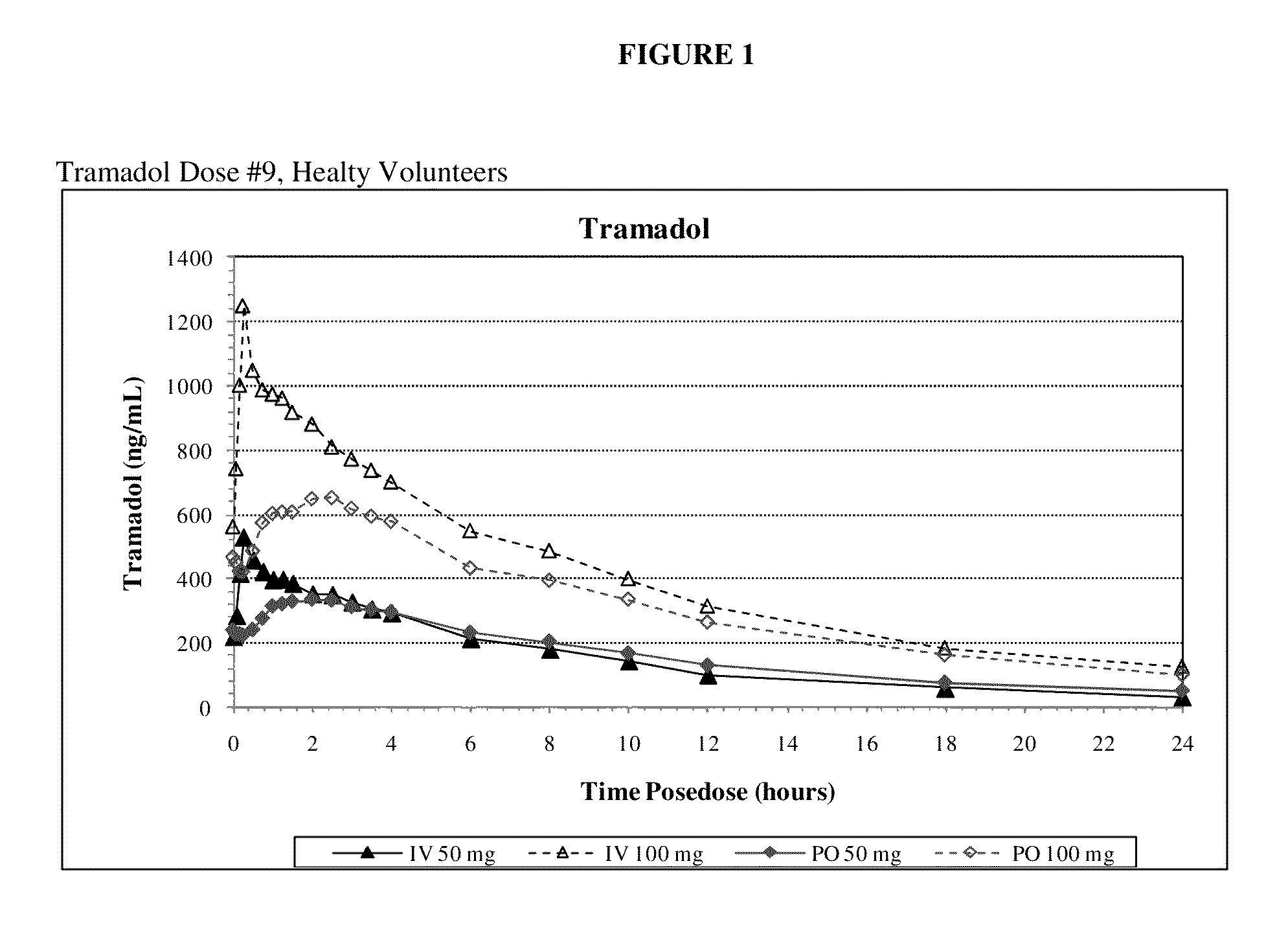
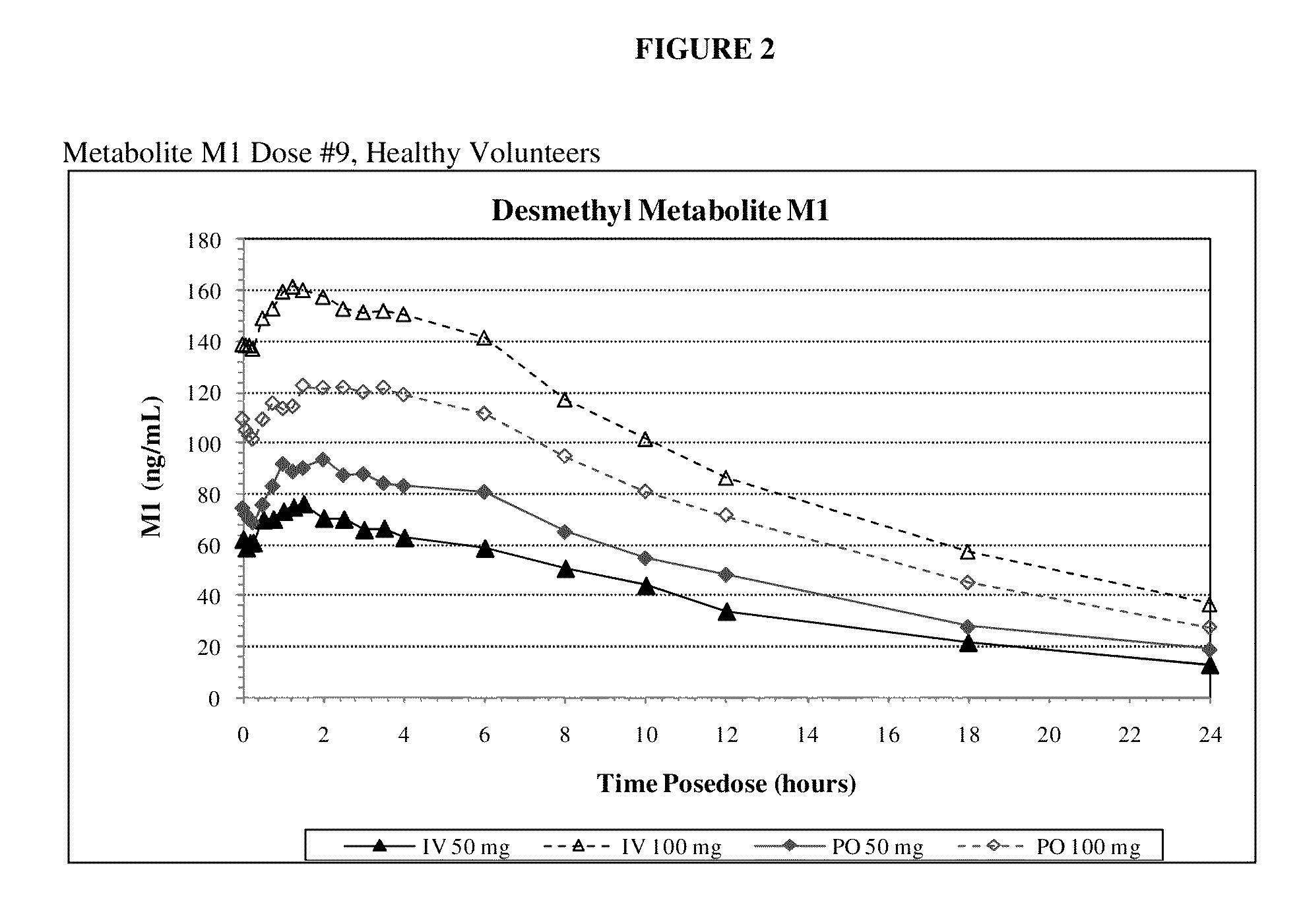
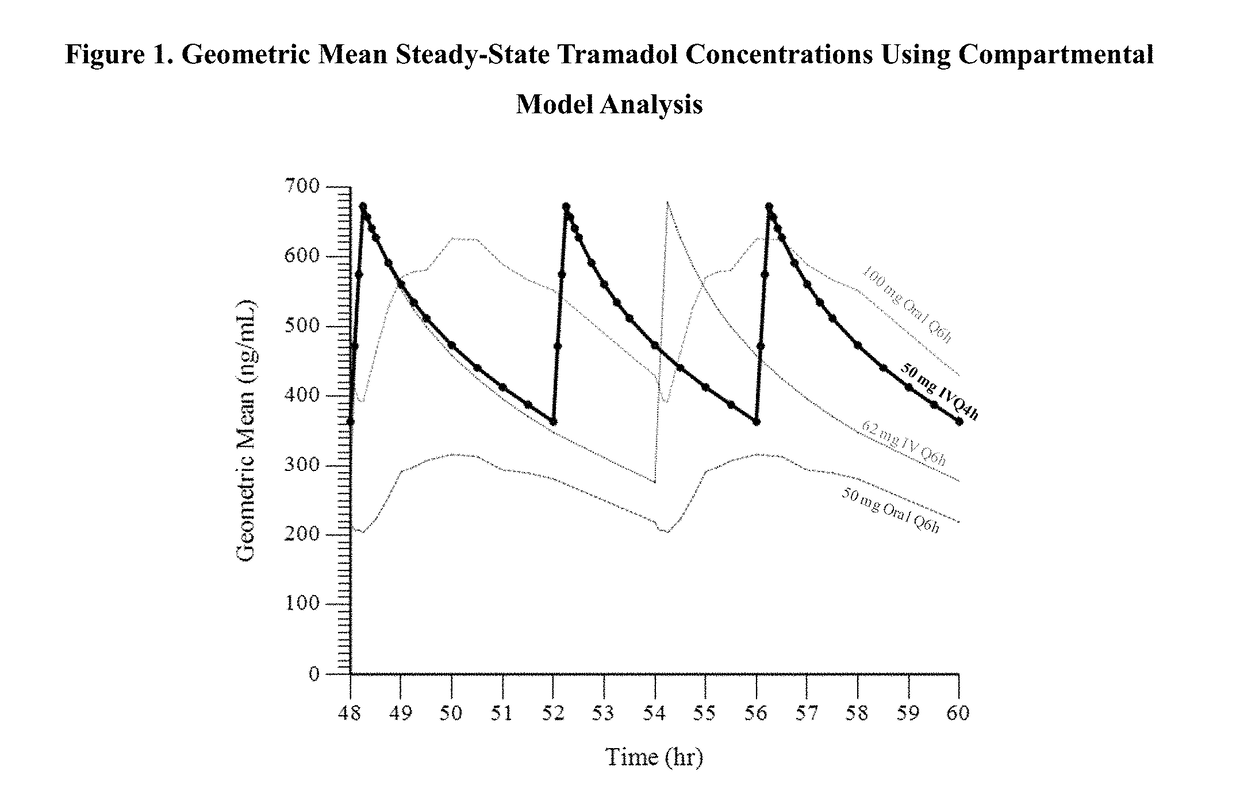
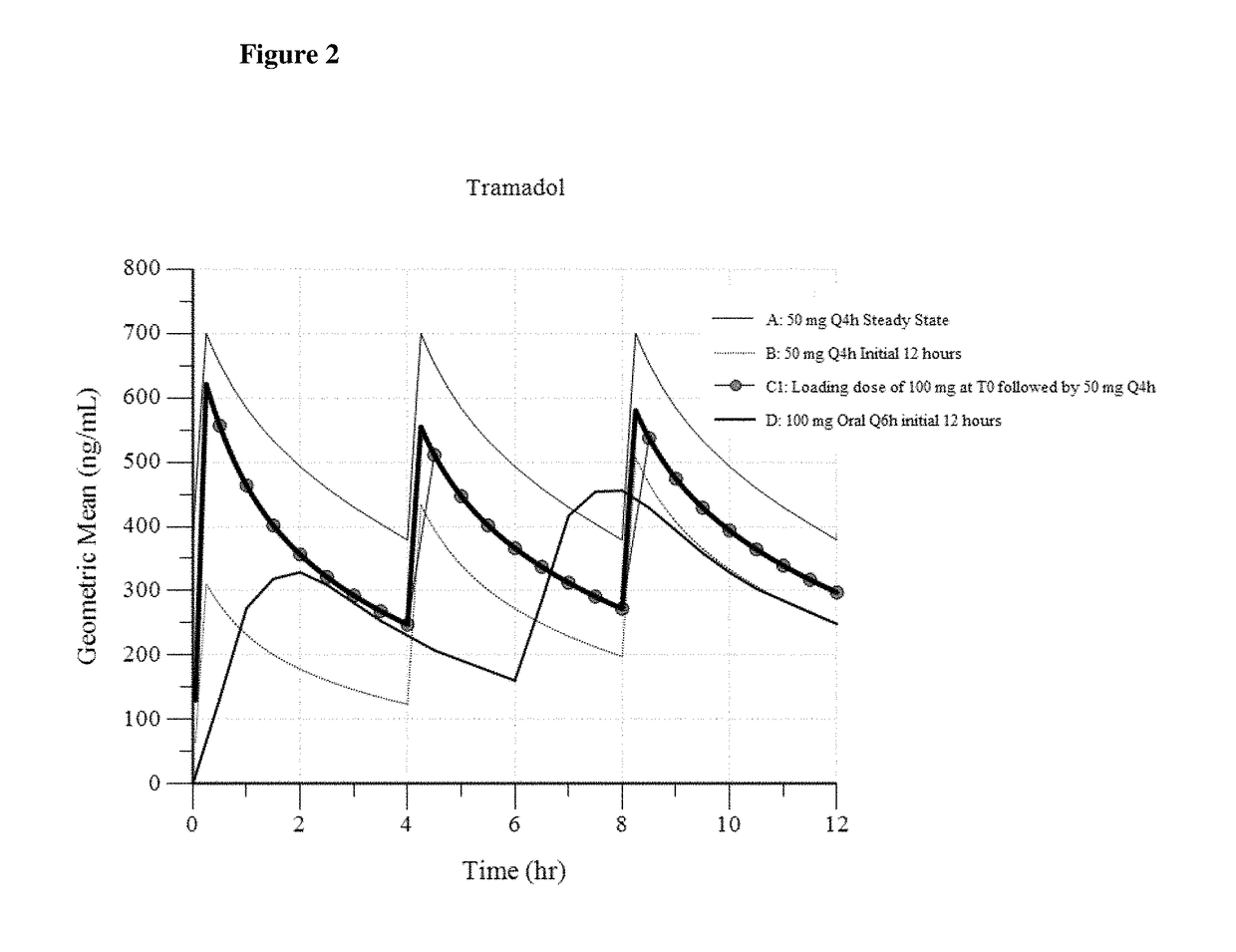
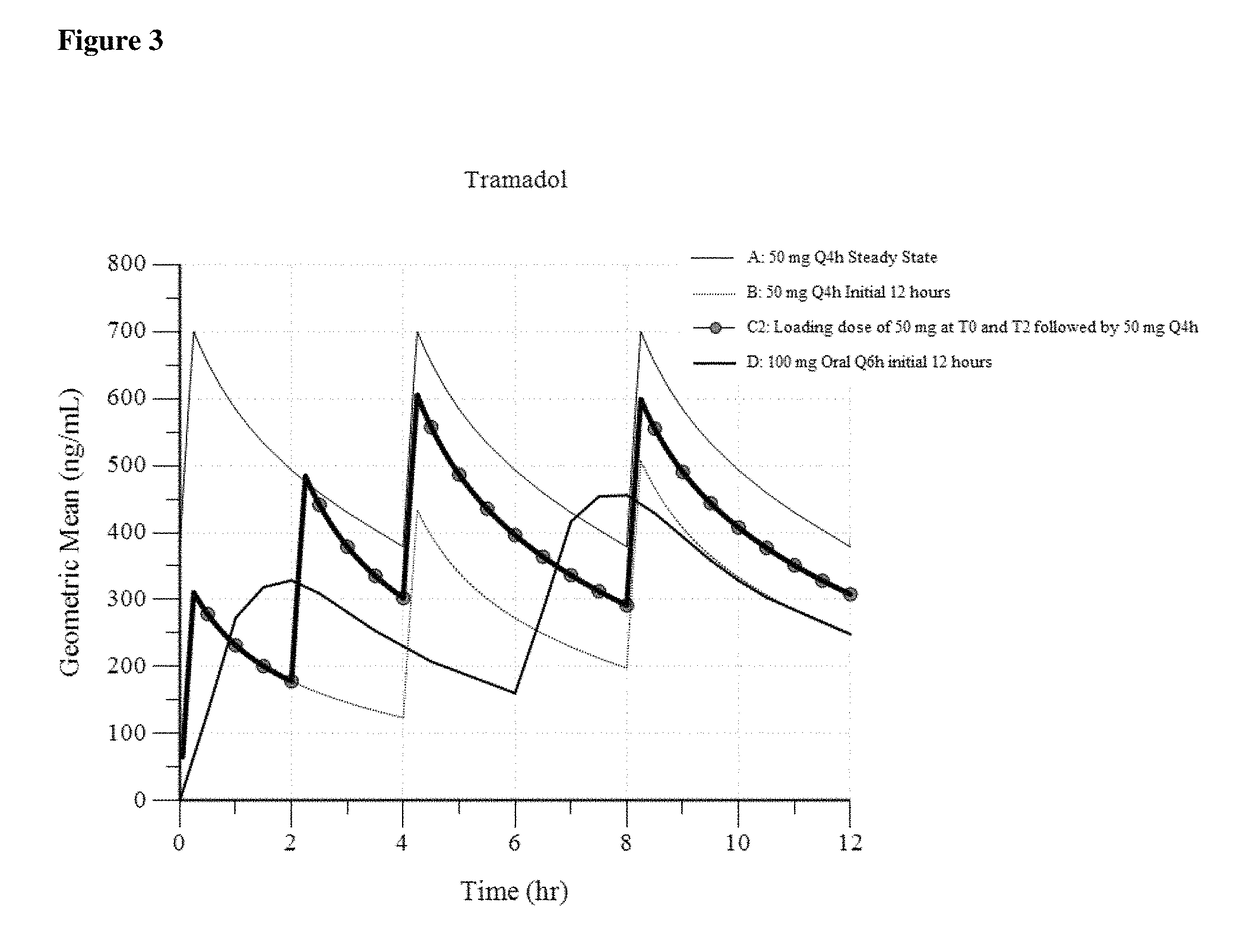
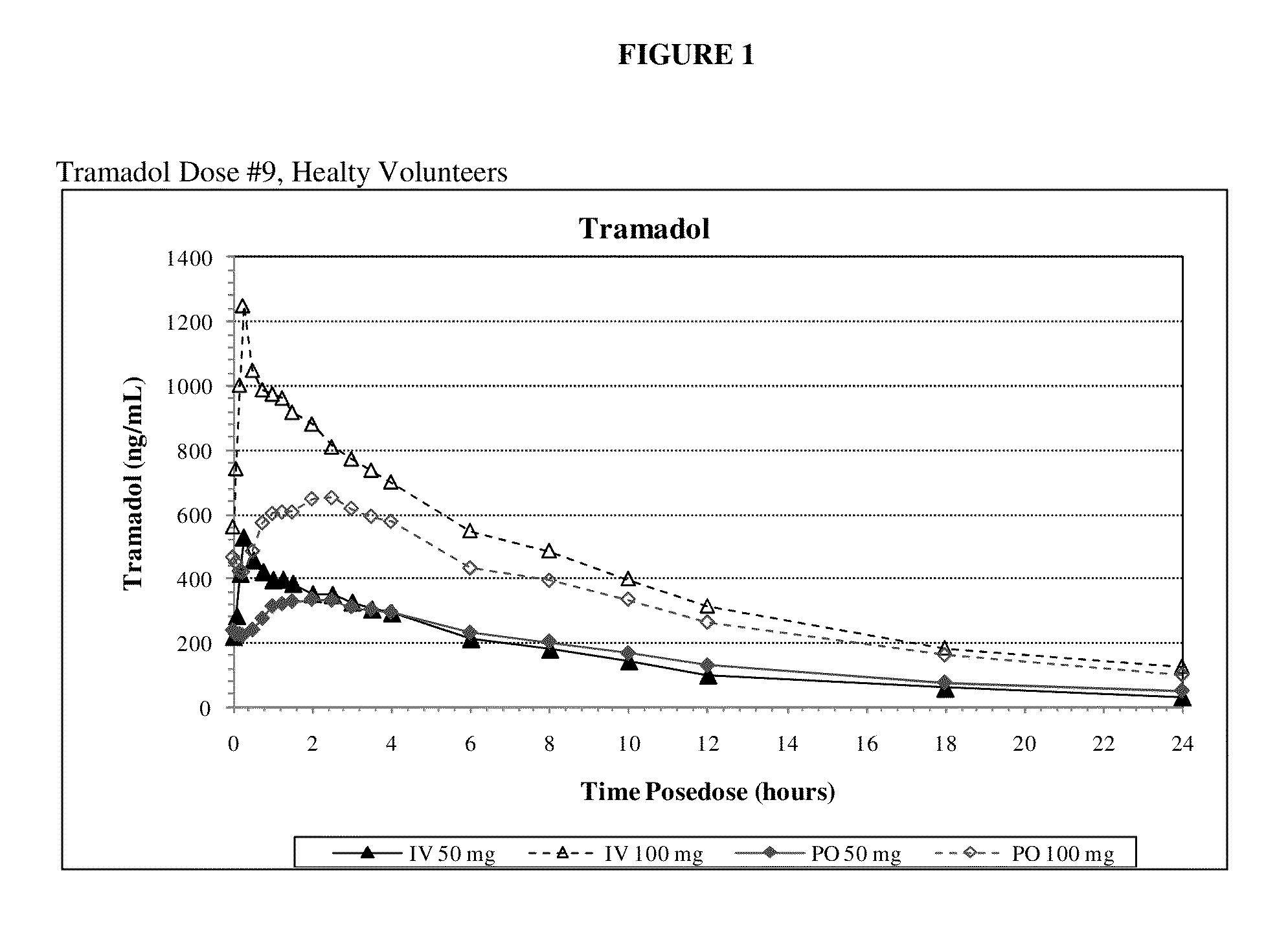
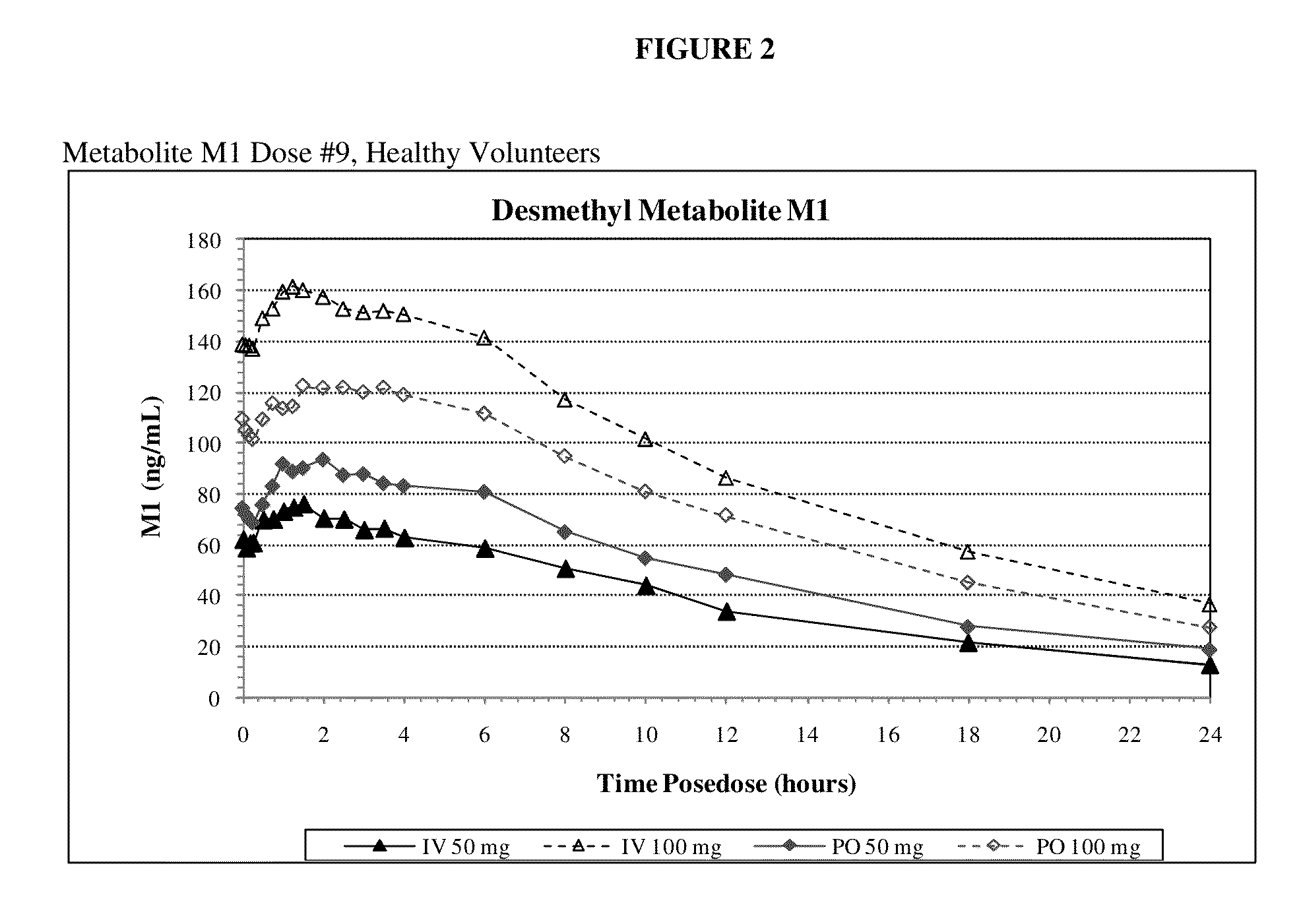
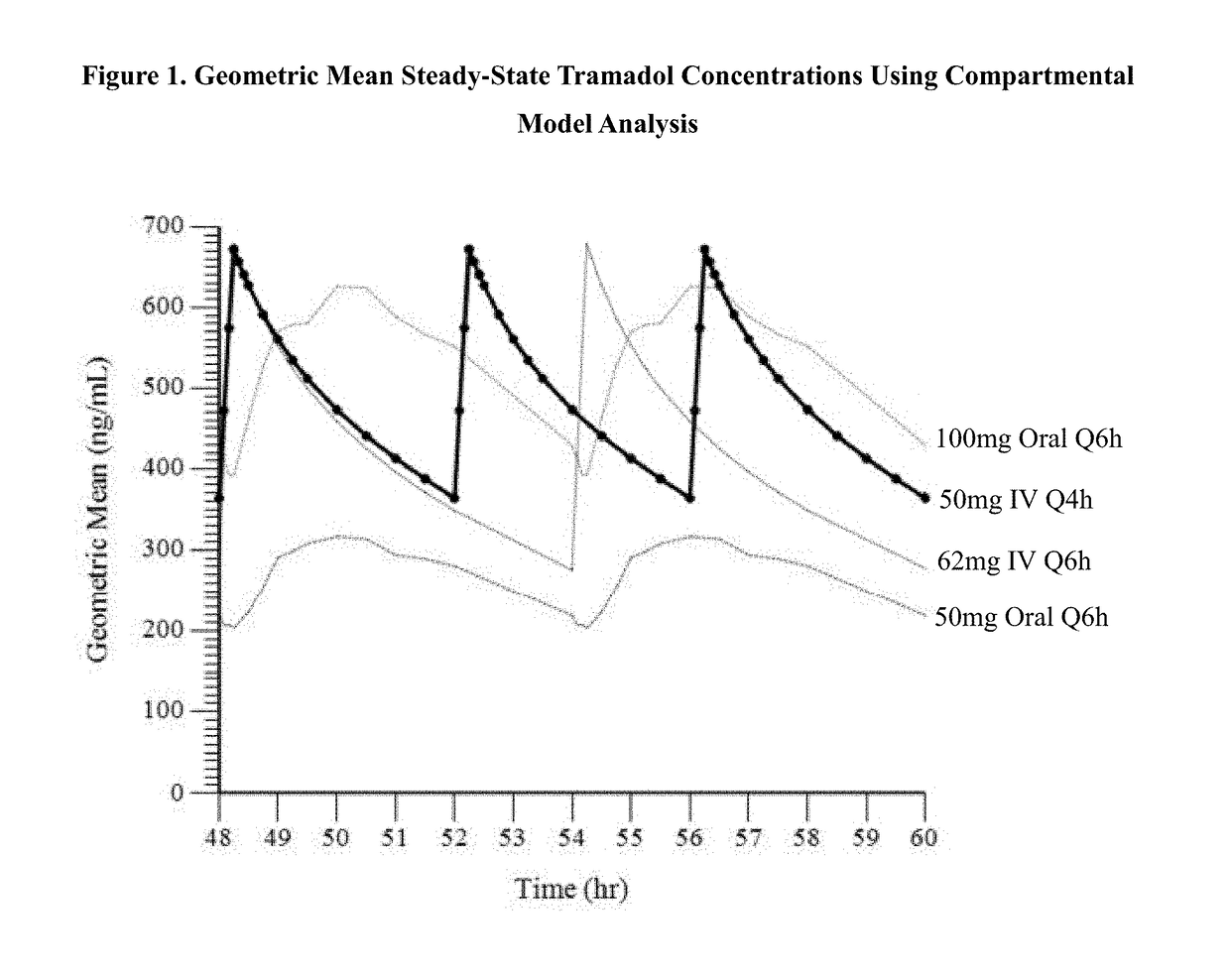
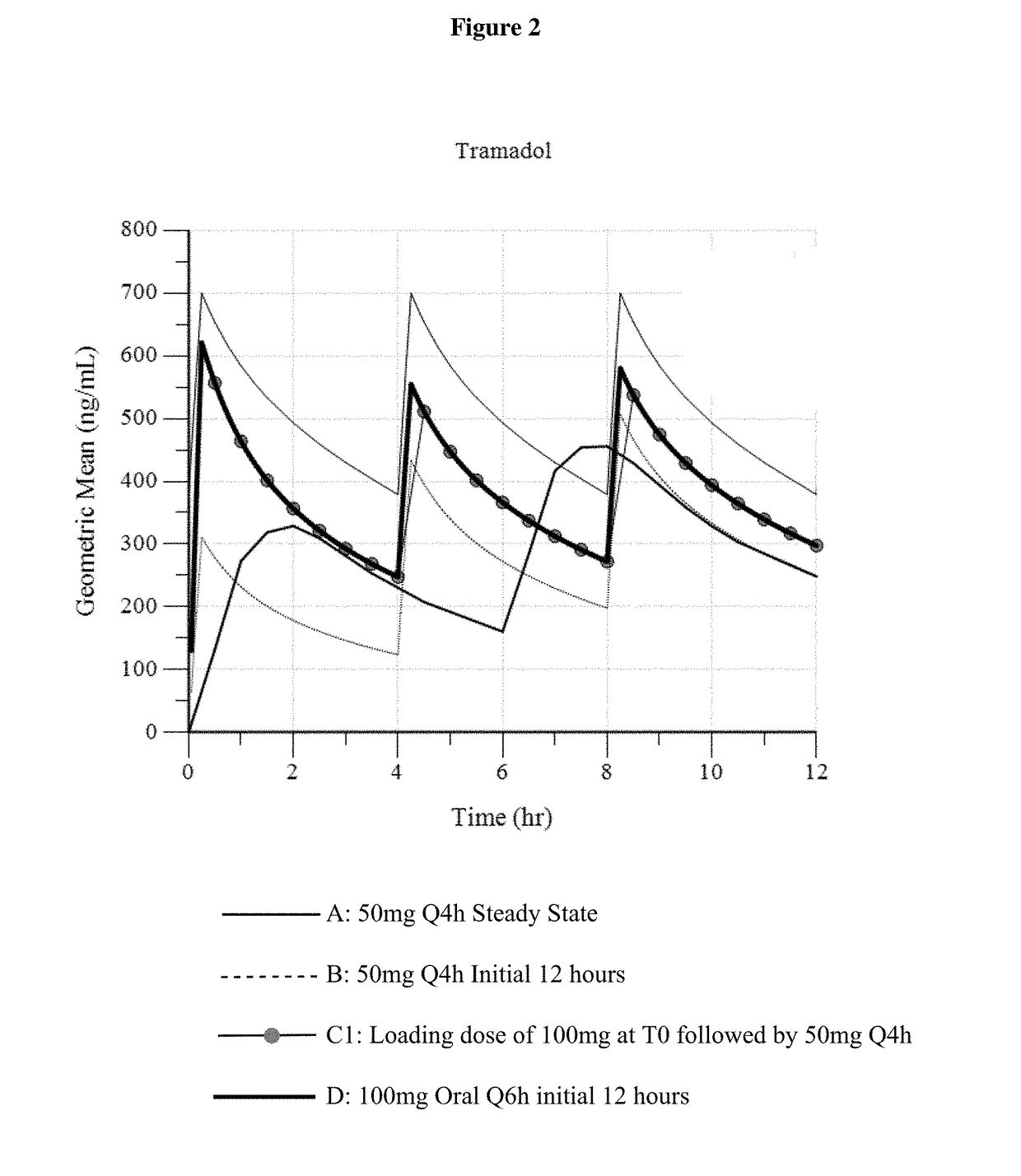
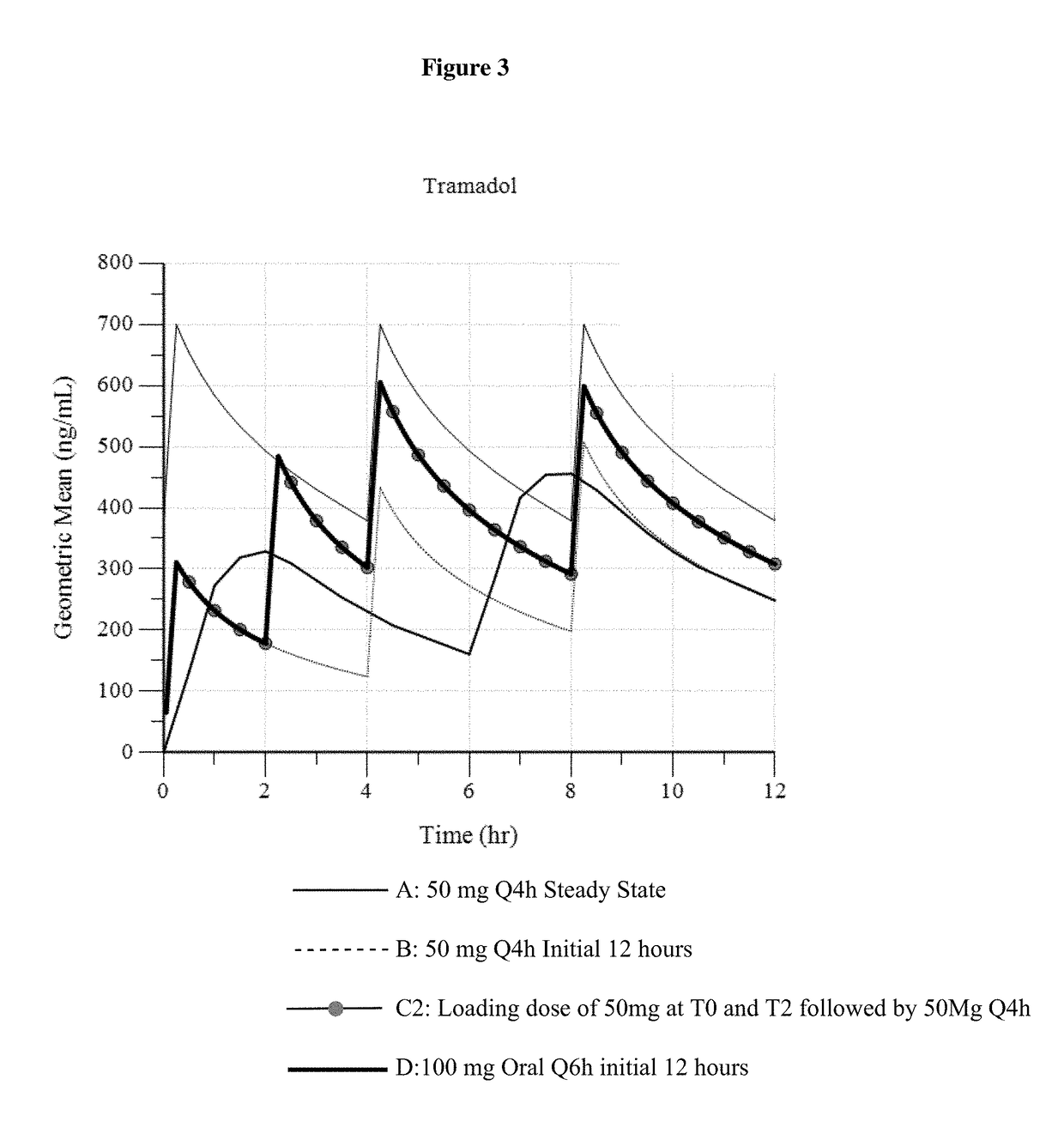
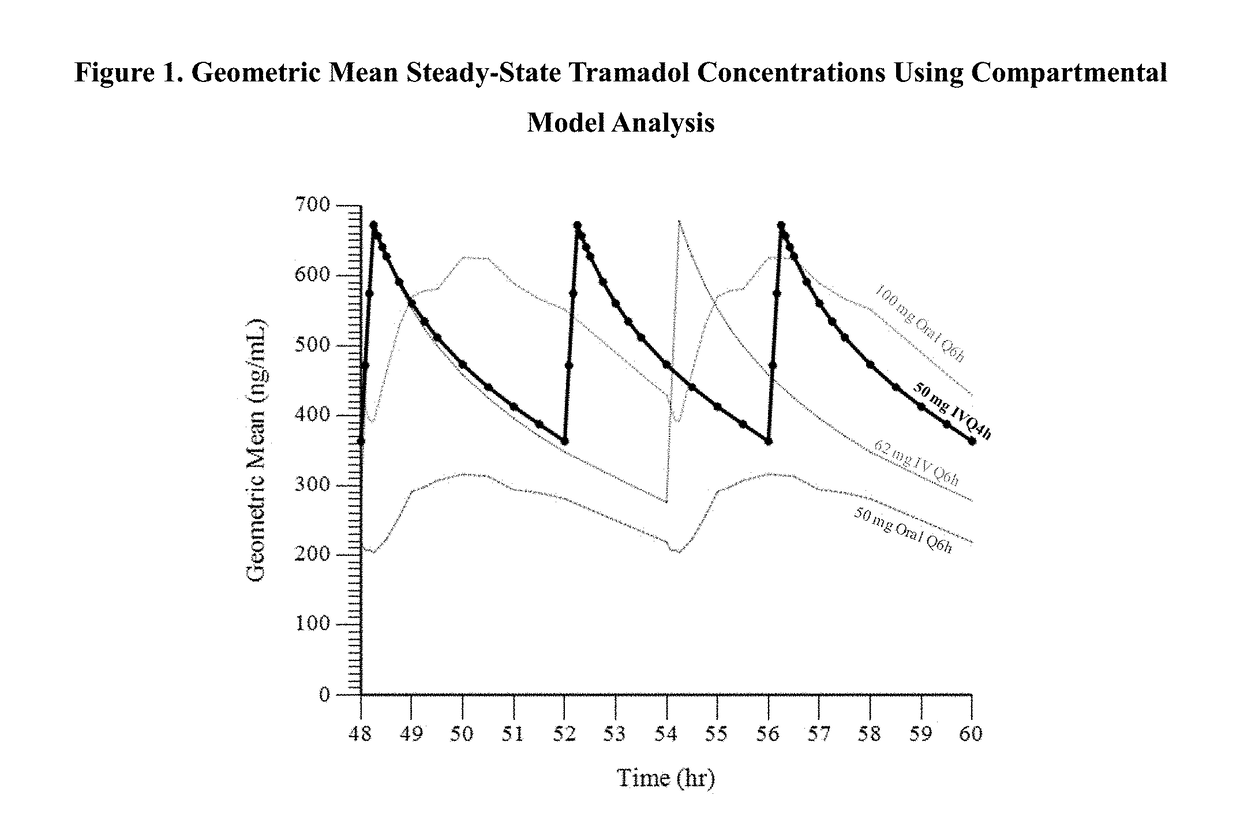
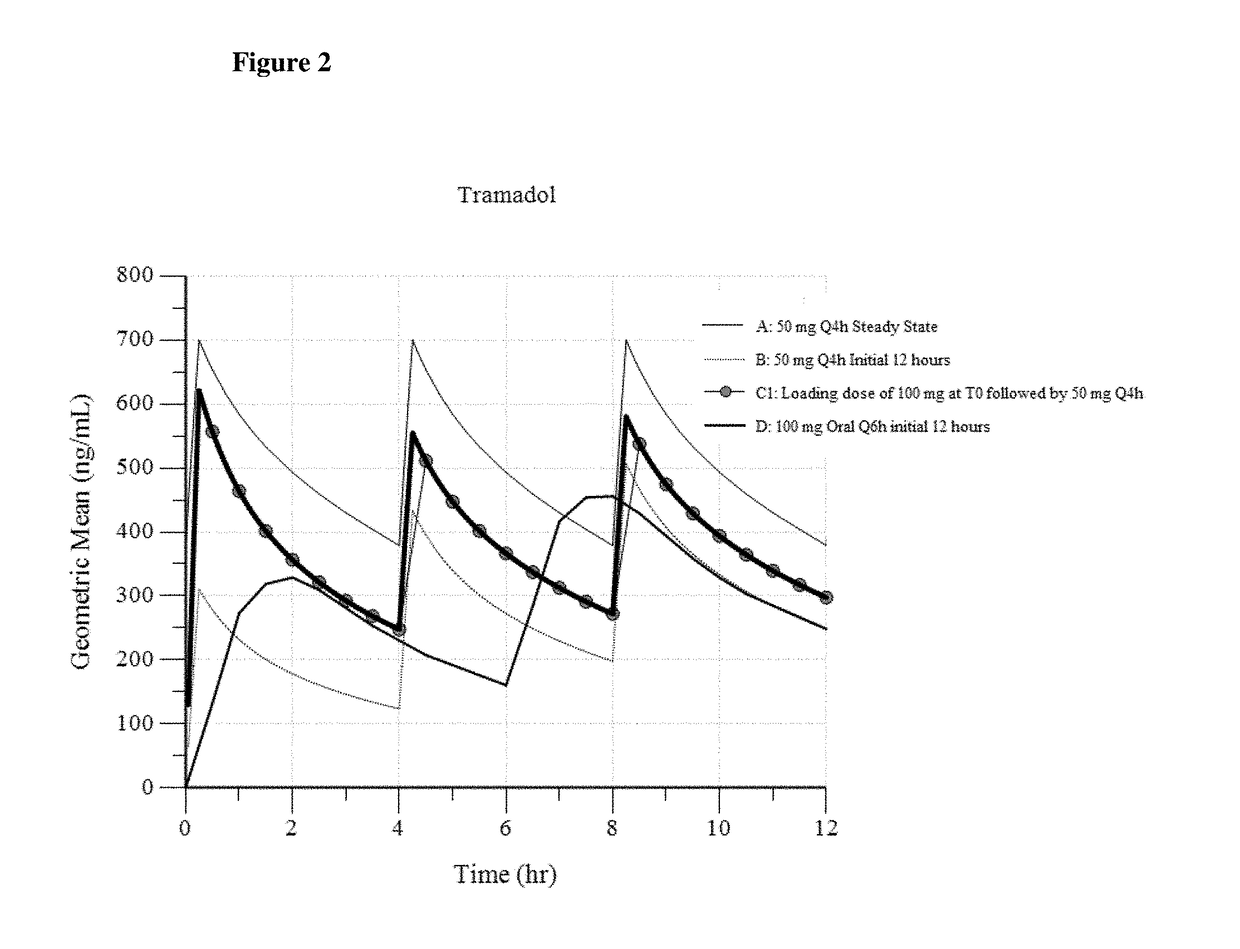
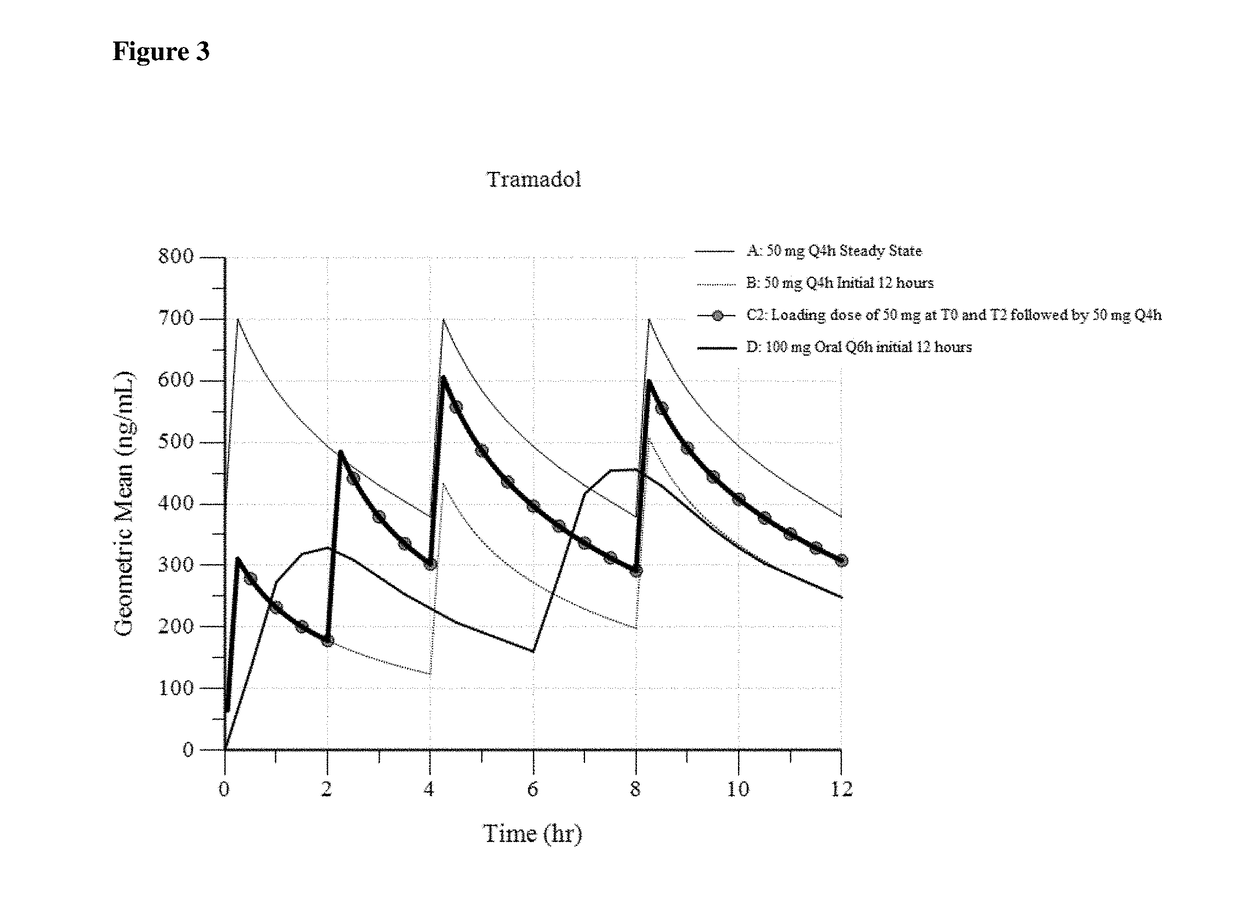
Intravenous administration of tramadol
ActiveUS9693949B1InhibitionRelieve painOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDosing regimenRegimen
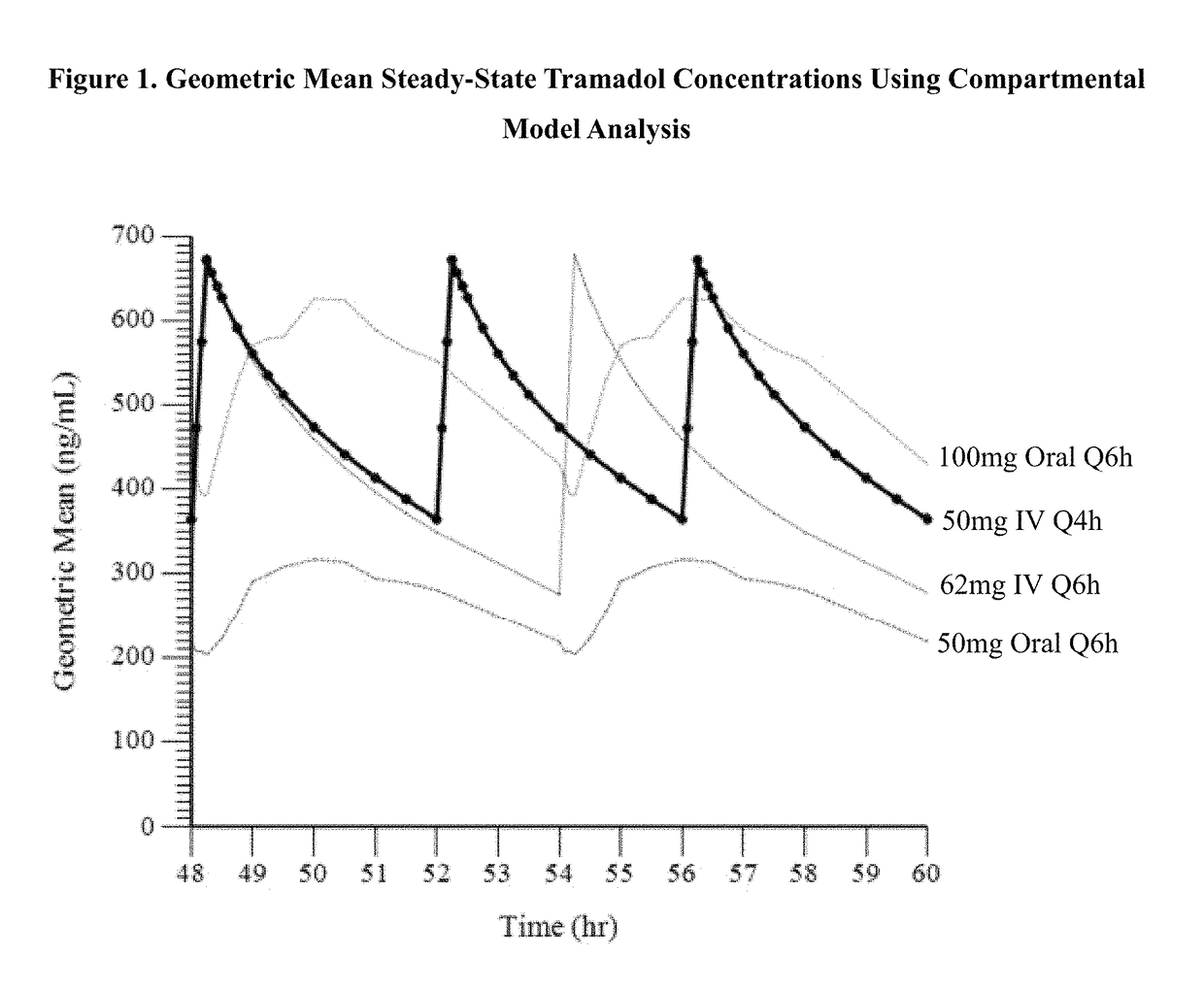
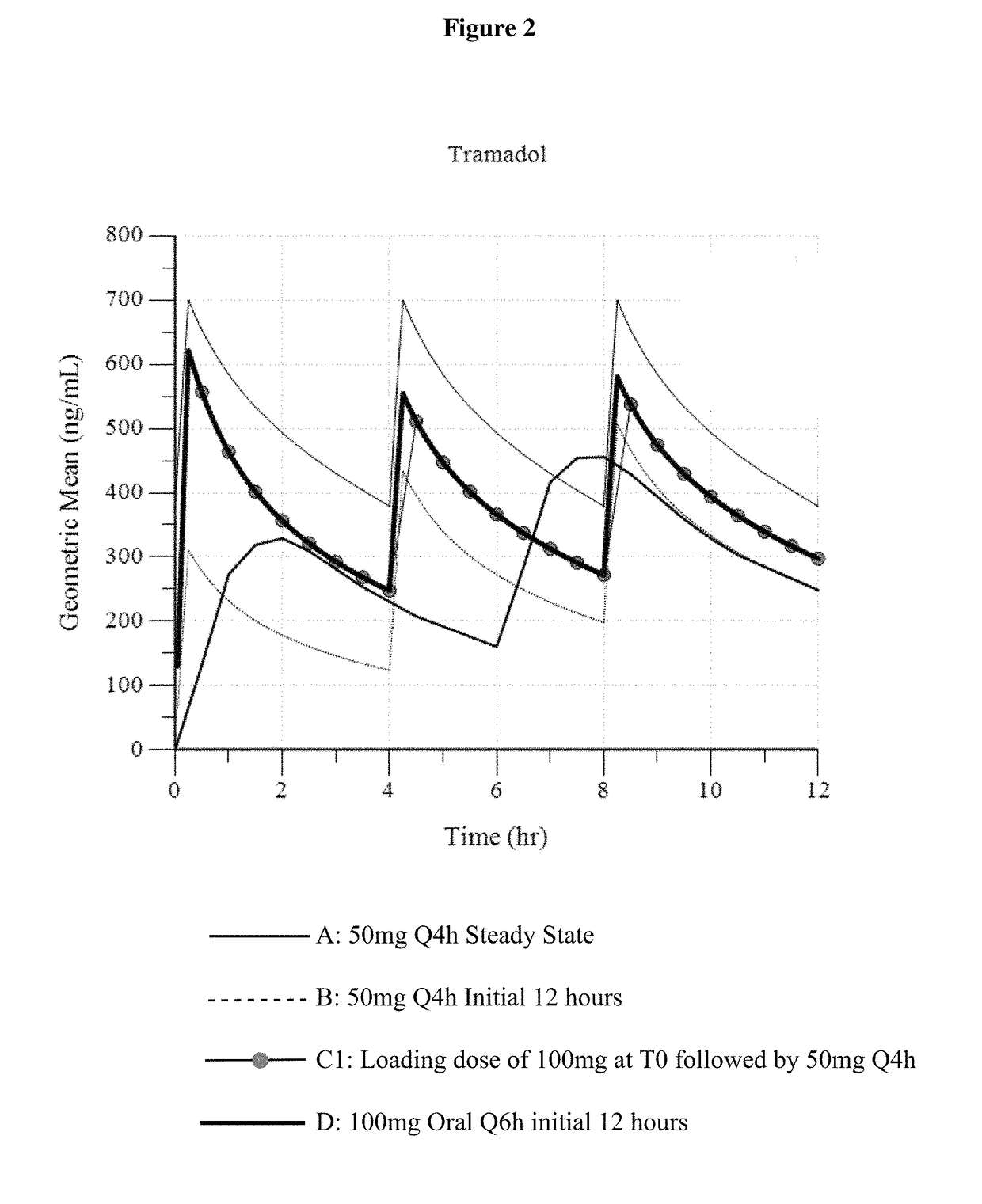
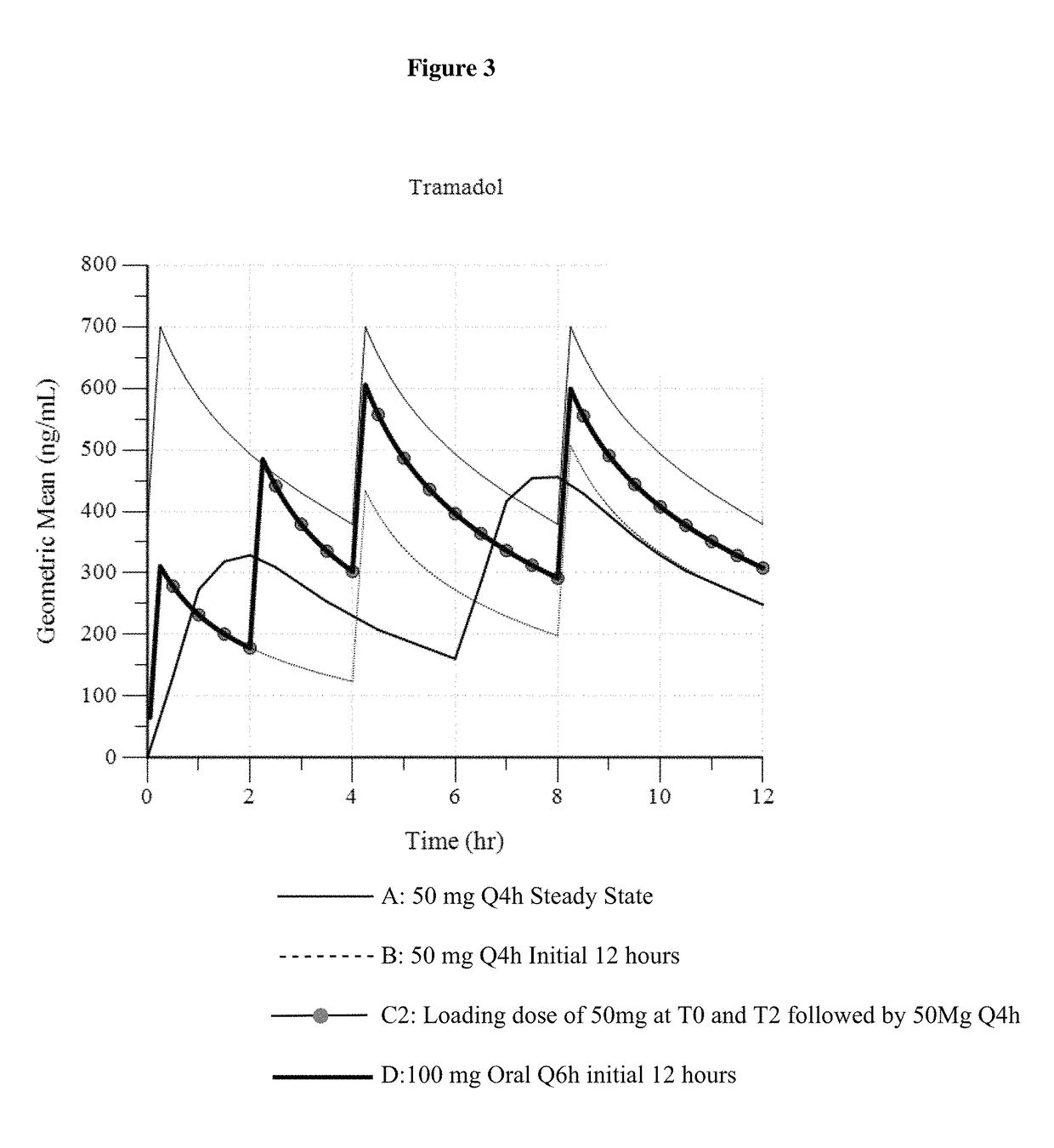
A method of treating pain, e.g., acute post-operative pain, by administering to a human patient(s) a therapeutically effective dose of tramadol intravenously in a dosing regimen which includes one or more loading doses administered at shortened intervals as compared to dosing at steady-state is disclosed. In certain embodiments, the dose of tramadol is from about 45 mg to about 80 mg and the second (and optionally) third doses are intravenously administered at intervals of from about 2 to about 3 hours, and thereafter the tramadol is intravenously administered at a dosing interval of about 4 to about 6 hours, until the patient no longer requires treatment with tramadol. In preferred embodiments, the intravenous dosing regimen provides a Cmax and AUC of tramadol is similar to the Cmax and AUC of an oral dose of 100 mg tramadol HCl given every 6 hours. In certain preferred embodiments, the dosing regimen comprises 50 mg IV tramadol at Hour 0, followed by 50 mg at Hour 2, 50 mg at hour 4, and 50 mg every 4 hours thereafter (e.g., until the patient no longer requires treatment with tramadol).
Owner:REVOGENEX IRELAND
Intravenous administration of tramadol
ActiveUS8895622B2Rapid onsetEliminate side effectsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsIntravenous therapyHuman patient
Owner:REVOGENEX IRELAND
Methods for the treatment of a traumatic central nervous system injury
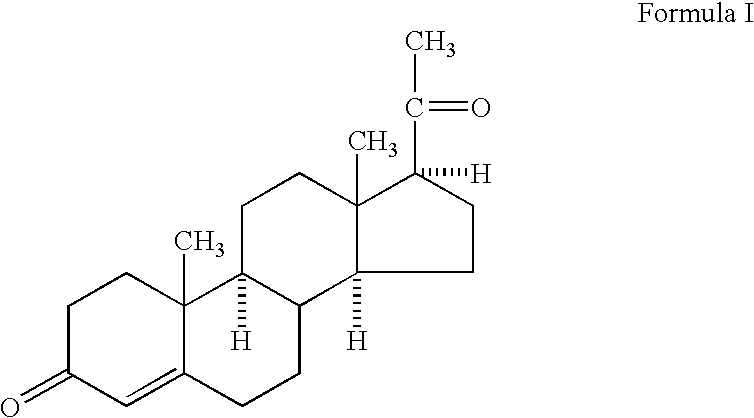
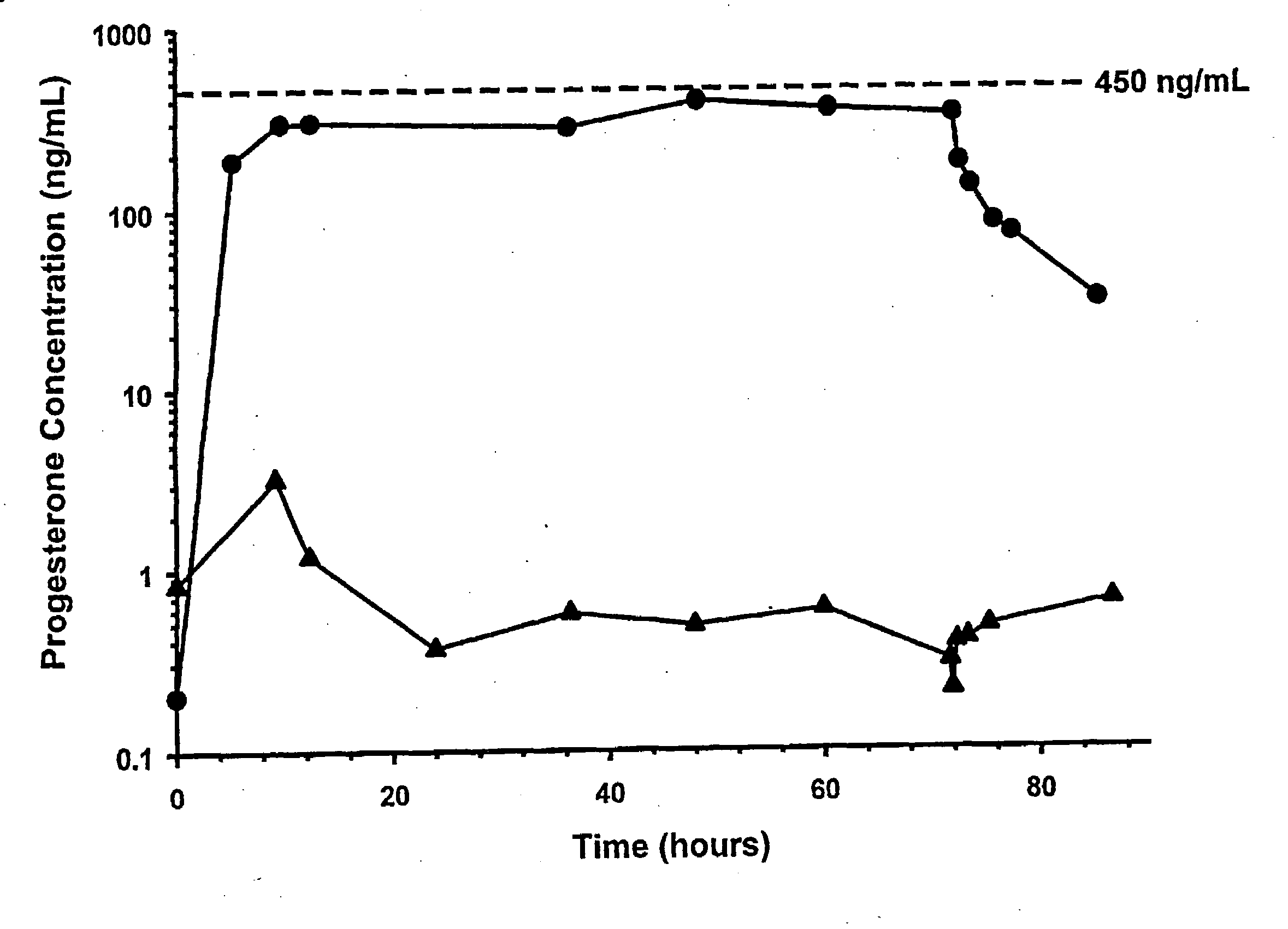
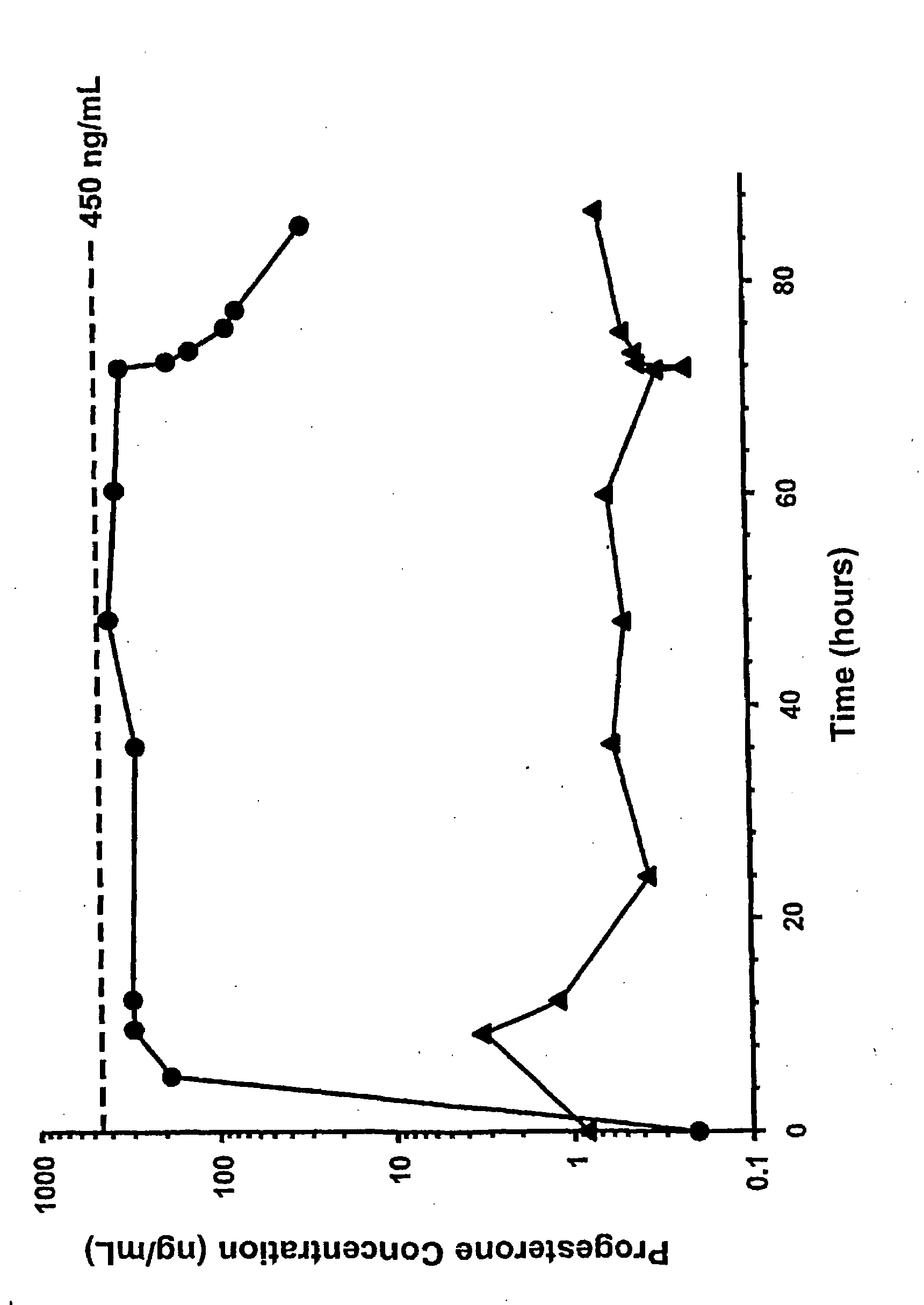
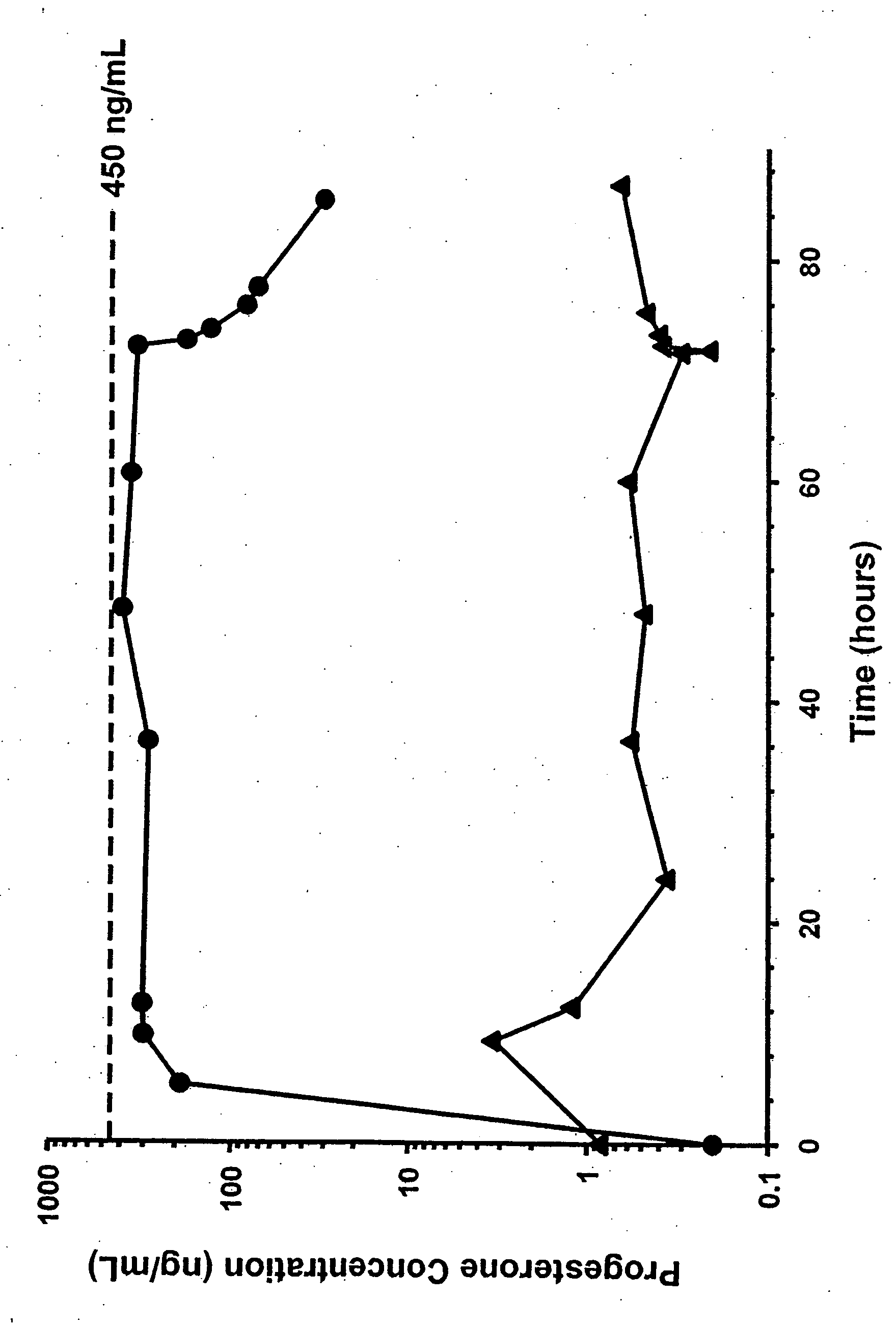
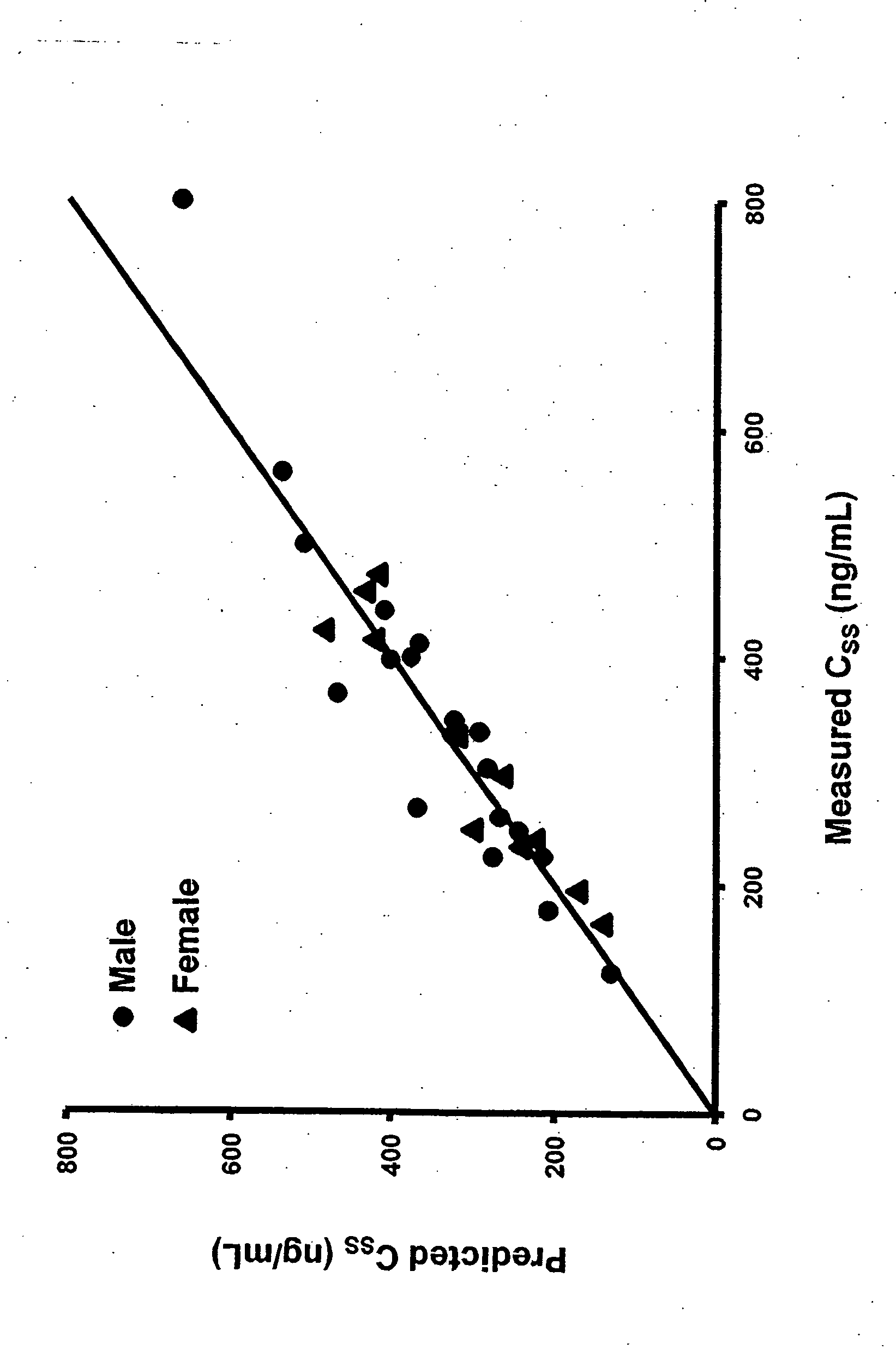
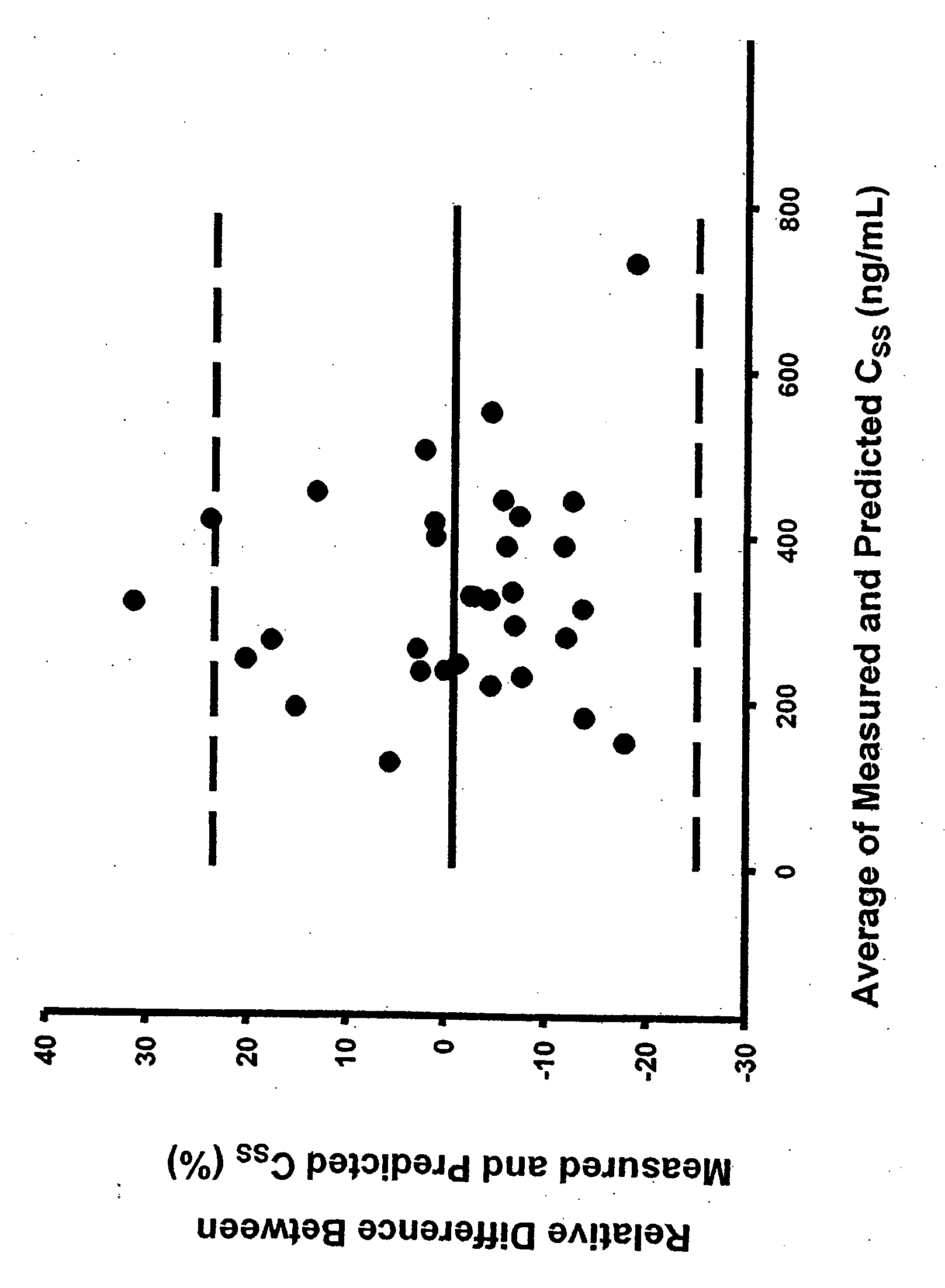
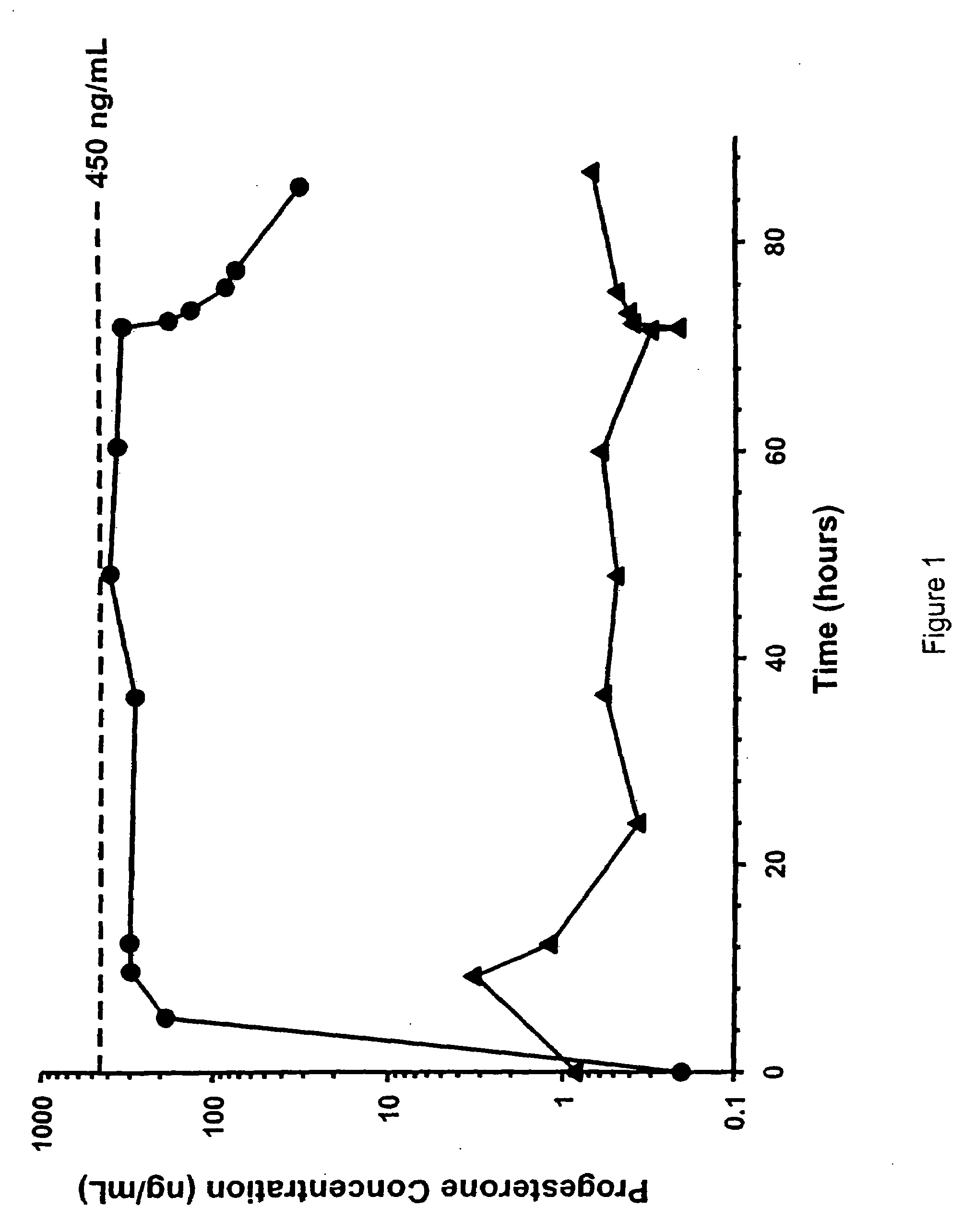
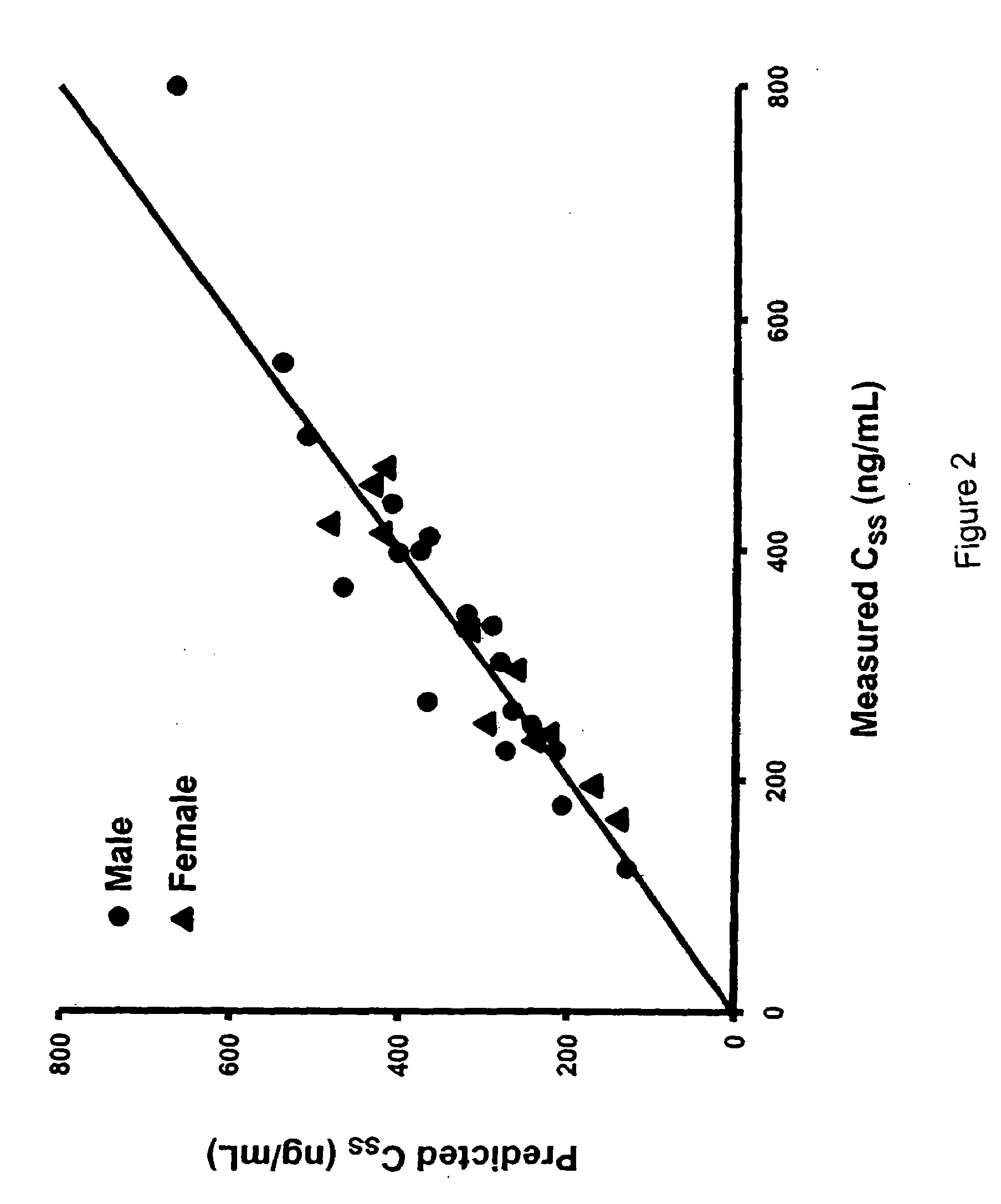
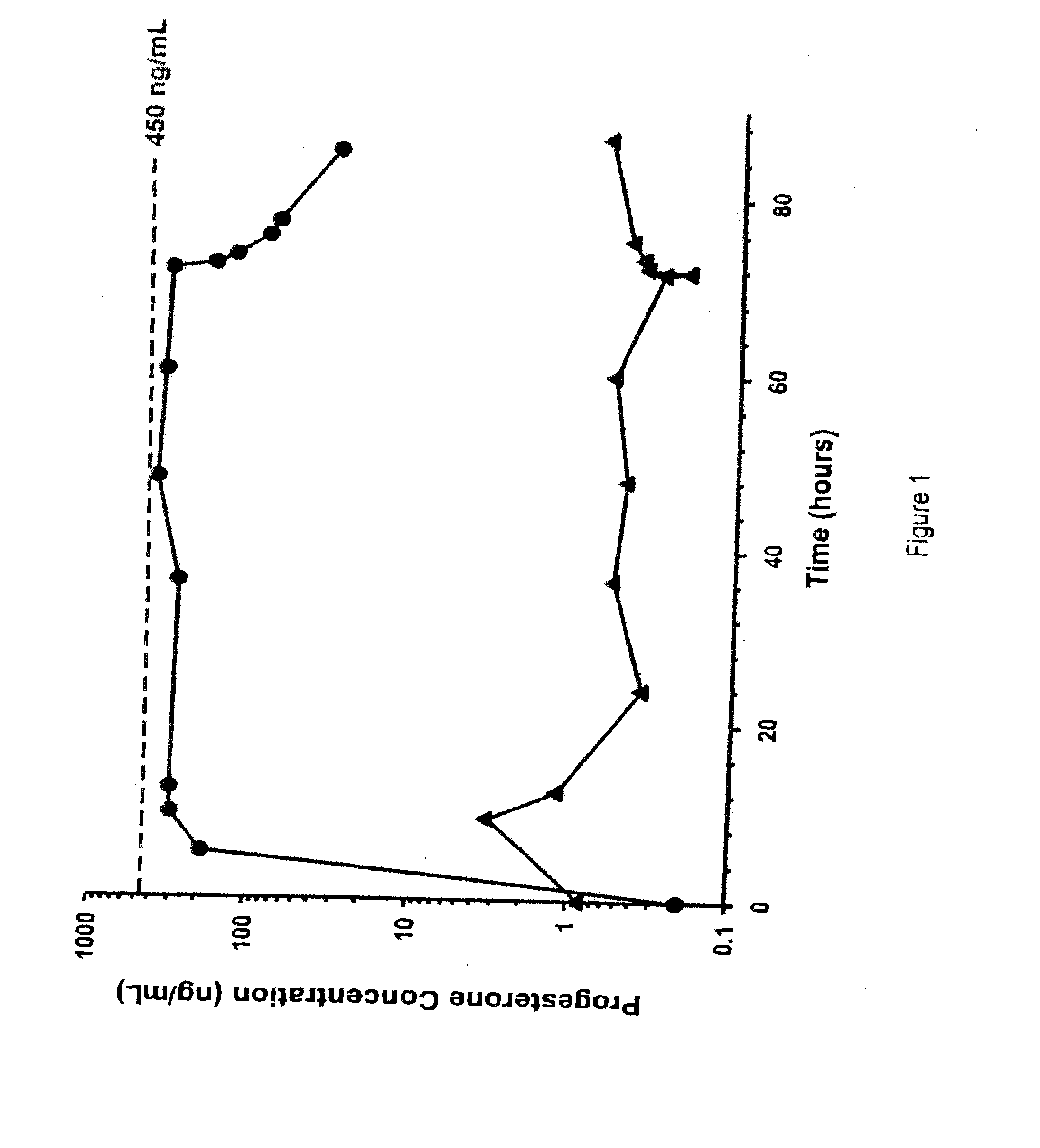
Methods of treating a subject with a traumatic central nervous system injury, more particularly, a traumatic brain injury, are provided. The methods comprise a therapy comprising a constant or a two-level dosing regime of progesterone. In one method, a subject in need thereof is administered at least one cycle of therapy, wherein the cycle of therapy comprises administering a therapeutically effective two-level intravenous dosing regime of progesterone. The two-level dosing regime comprises a first time period, wherein a higher hourly dose of progesterone is administered to the subject, followed by a second time period, wherein a lower hourly dose of progesterone is administered to the subject.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Methods for the treatment of a traumatic central nervous system injury
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Intravenous administration of tramadol
ActiveUS9980900B2Rapid onsetRelieve painOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDosing regimenRegimen
Owner:REVOGENEX IRELAND
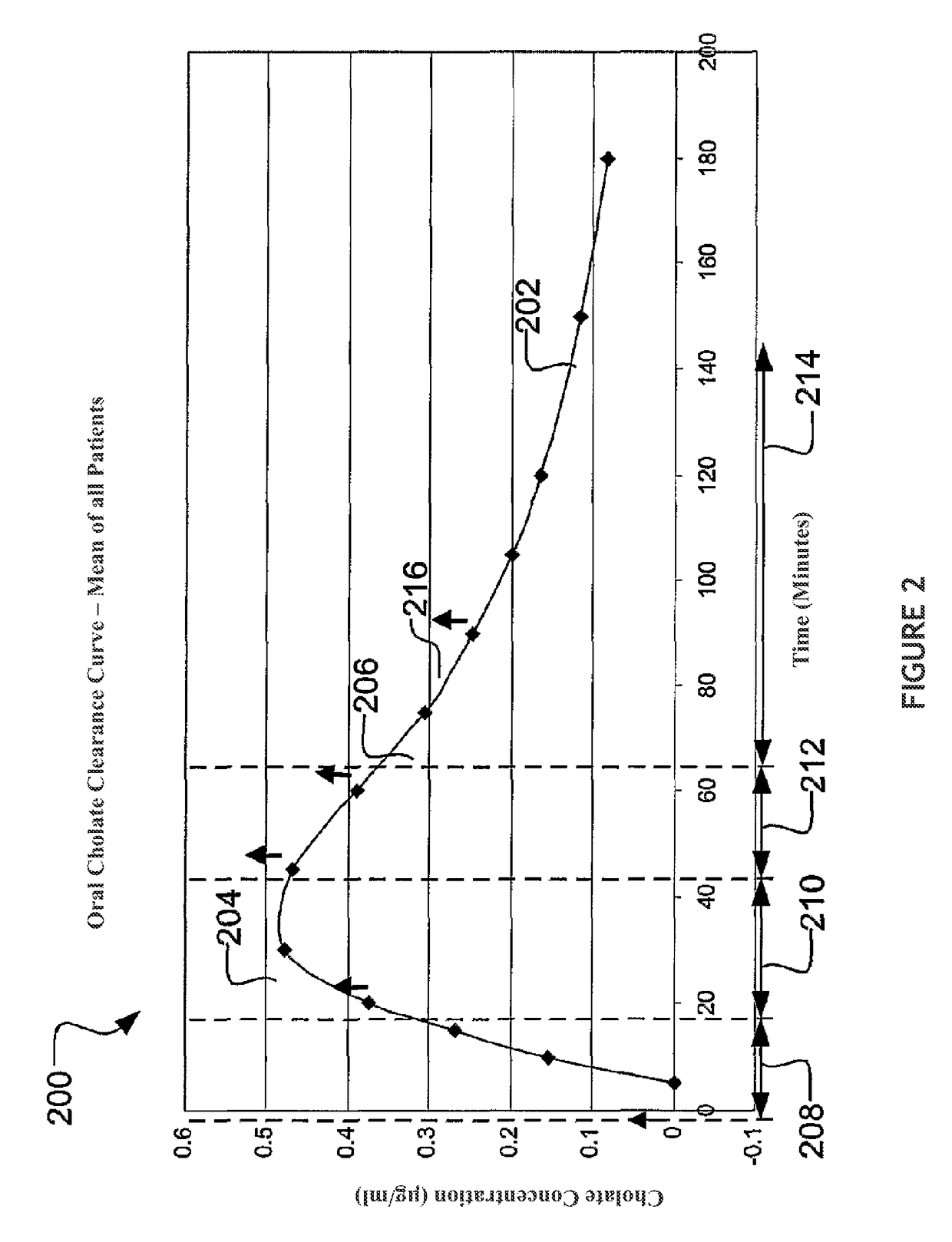
Methods for diagnosis and intervention of hepatic disorders
ActiveUS20140067276A1Rapid assessmentIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMedical automated diagnosisDiseaseChronic viral hepatitis C
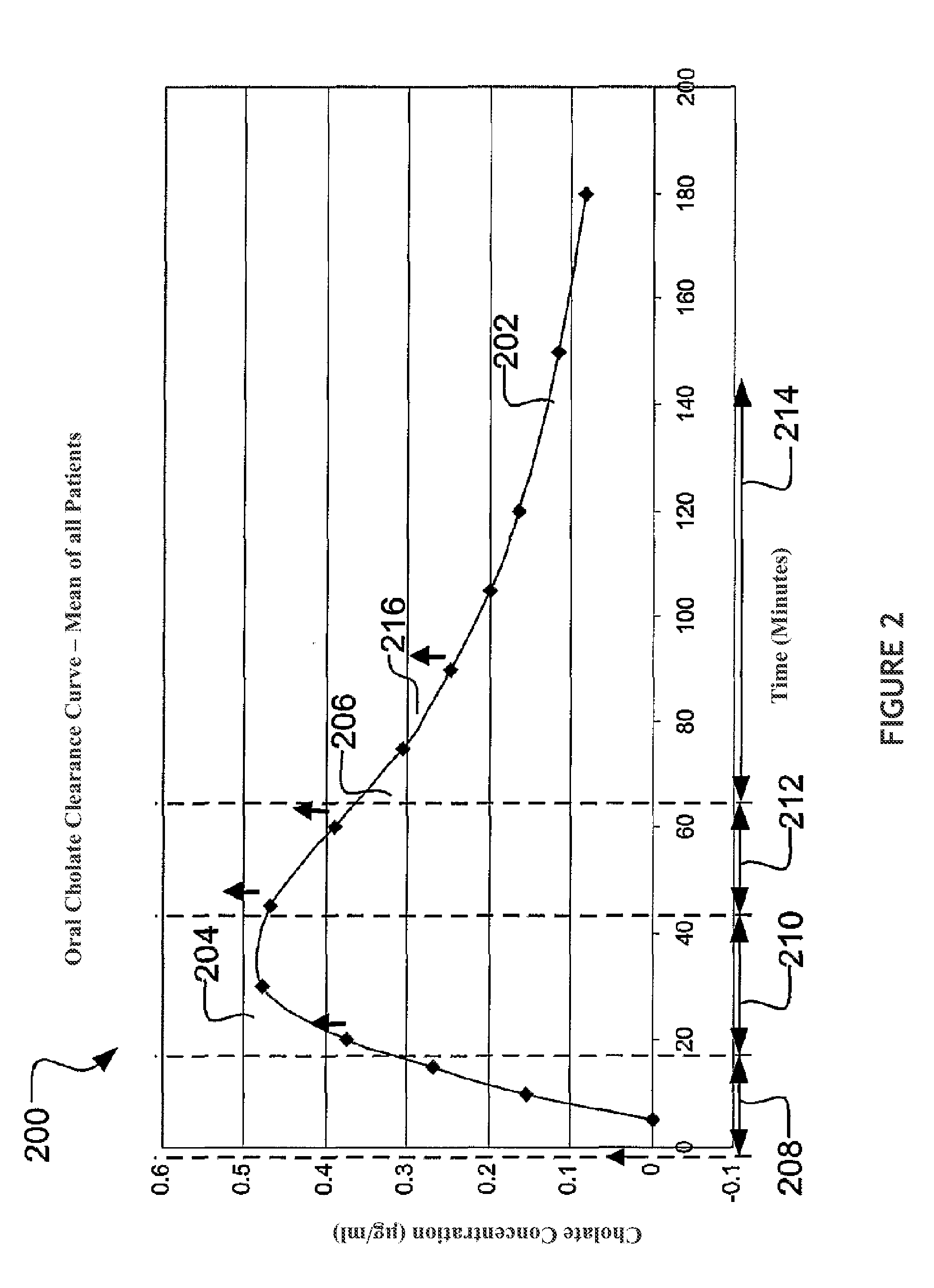
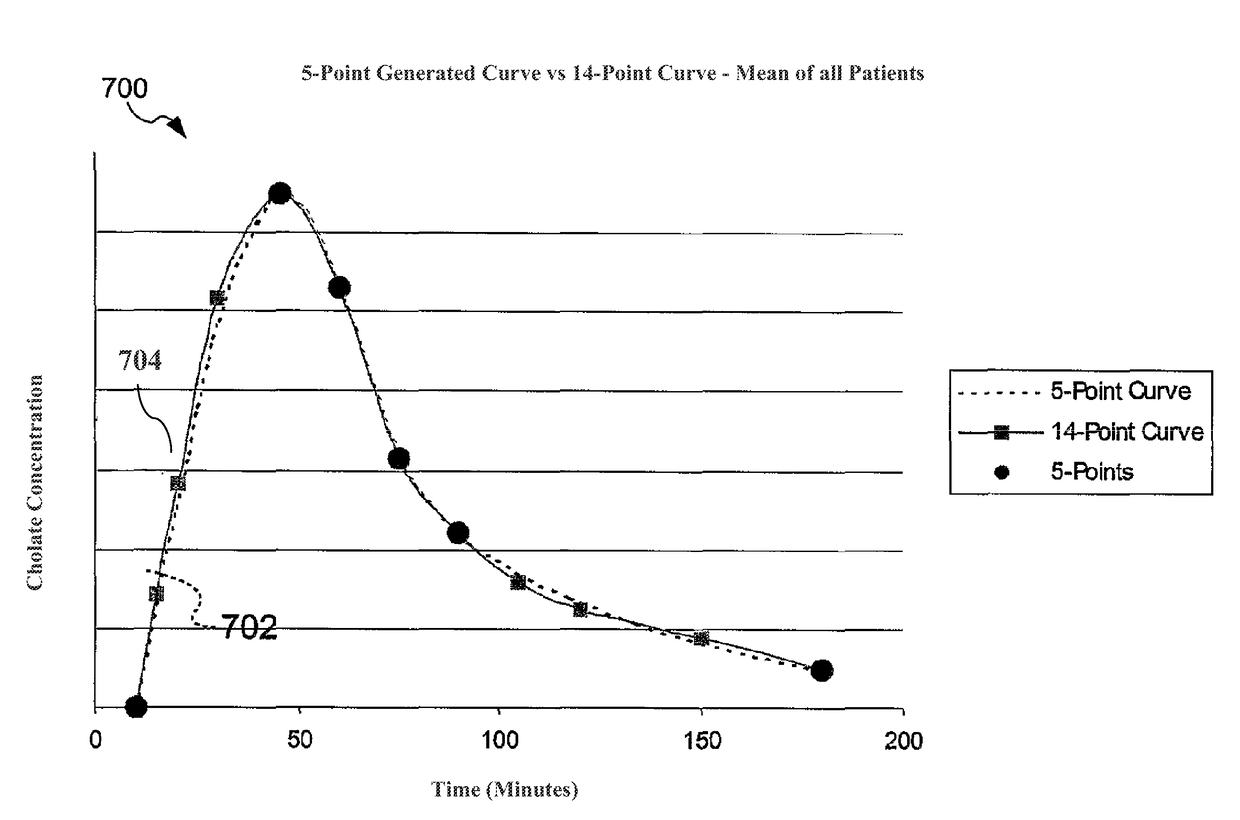
The present disclosure concerns methods of administering and detecting a distinguishable agent in a sample from and assessing the condition of an organ in a subject. In a particular embodiment, the present invention concerns methods of detecting and comparing the cholate shunt, in a subject, preferably in a subject with chronic hepatitis C. In certain embodiments, the methods may comprise obtaining a sample from a subject such as a blood or saliva sample after administering an oral and intravenous dose of a distinguishable agent such as cholate and analyzing the sample clearance of the distinguishable agent from the subject and comparing the clearance levels in order to assess hepatic health. In another embodiment, the methods may comprise analyzing a sample from a subject for the presence of a distinguishable agent such as cholate and applying information obtained from analyzing the presence of the distinguishable agent to determine a treatment for a medical condition of the subject.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Methods for the treatment of a traumatic central nervous system injury
Methods of treating a subject with a traumatic central nervous system injury, more particularly, a traumatic brain injury, are provided. The methods comprise a therapy comprising a constant or a two-level dosing regime of progesterone. In one method, a subject in need thereof is administered at least one cycle of therapy, wherein the cycle of therapy comprises administering a therapeutically effective two-level intravenous dosing regime of progesterone. The two-level dosing regime comprises a first time period, wherein a higher hourly dose of progesterone is administered to the subject, followed by a second time period, wherein a lower hourly dose of progesterone is administered to the subject.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
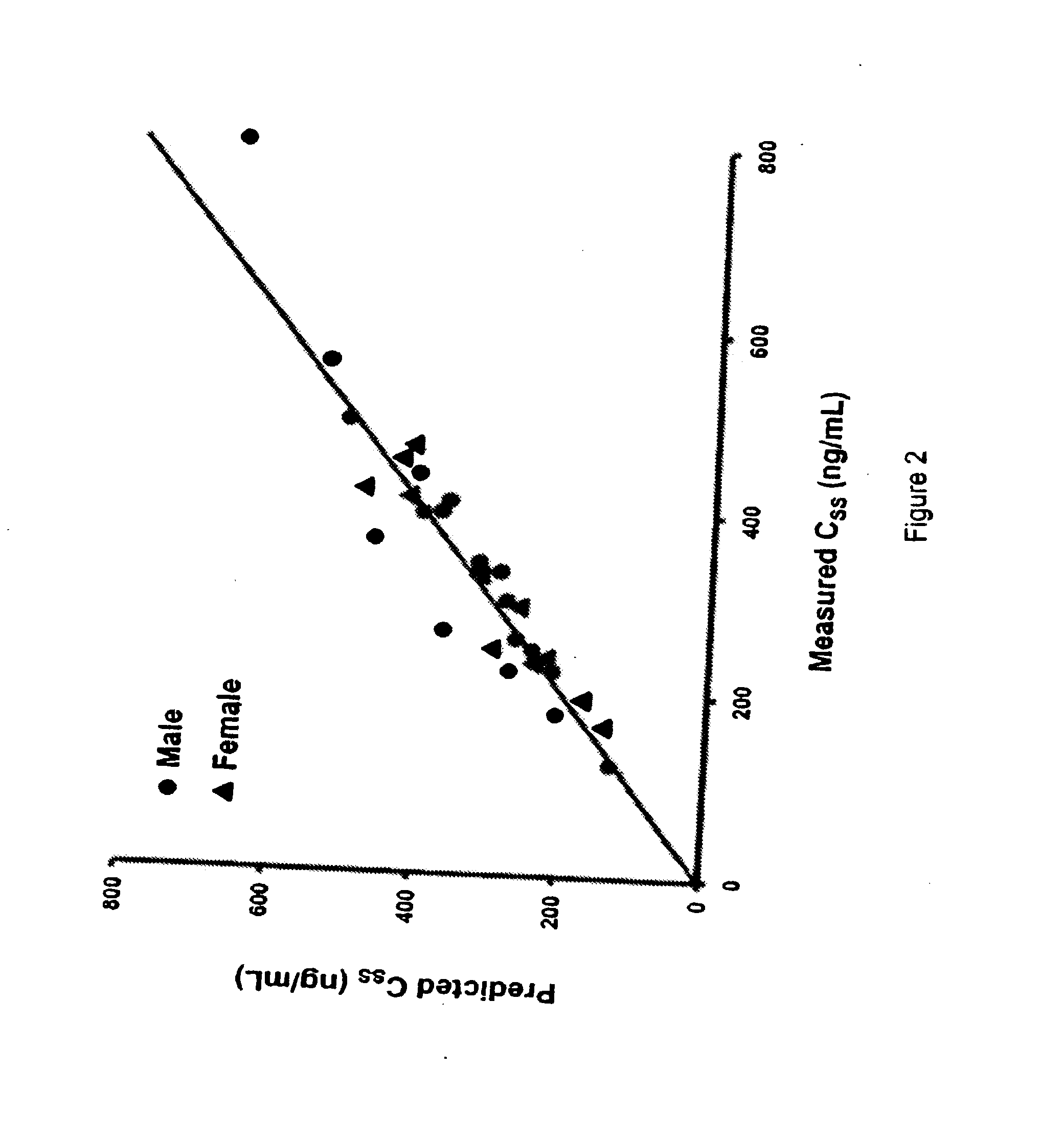
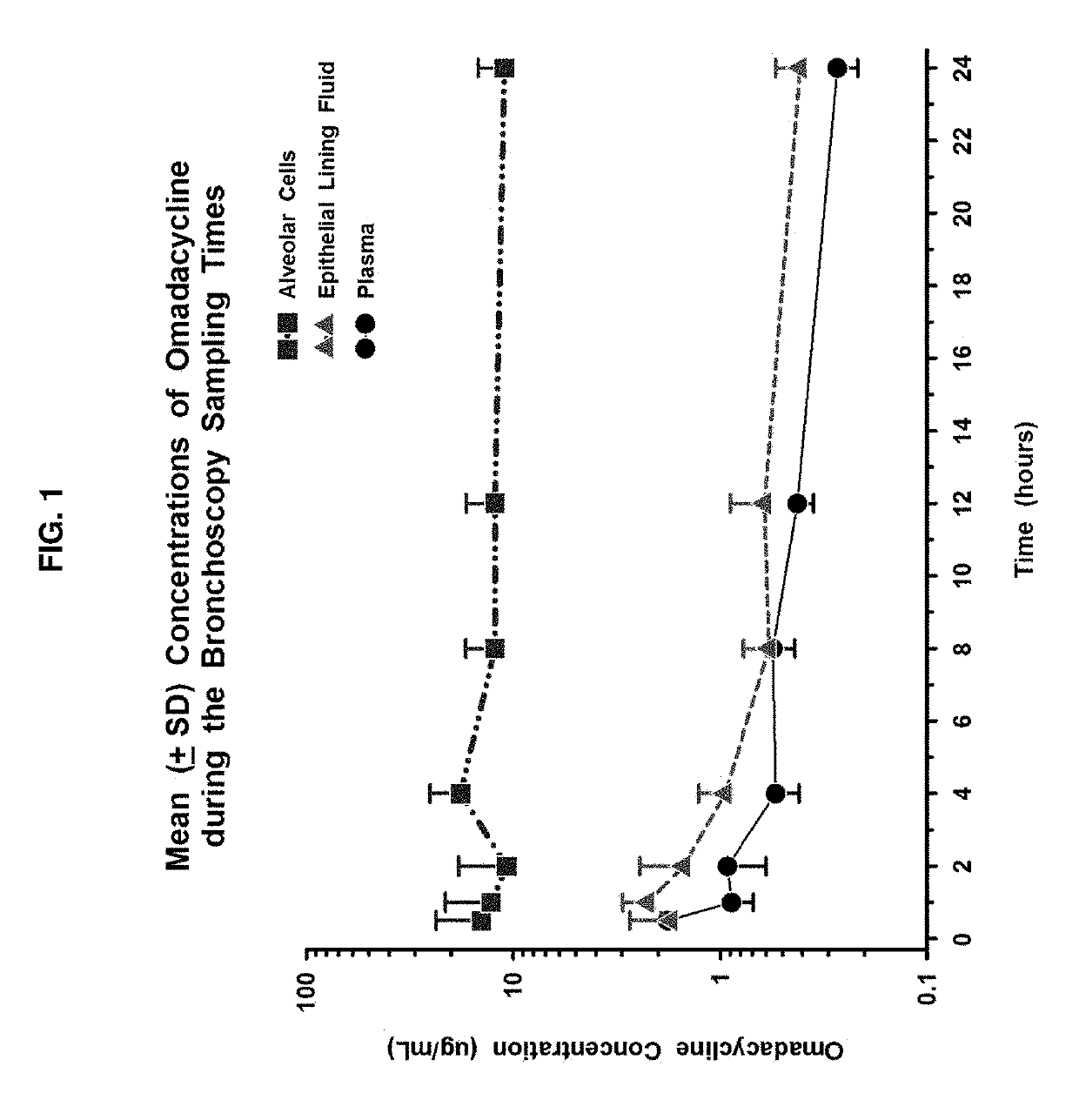
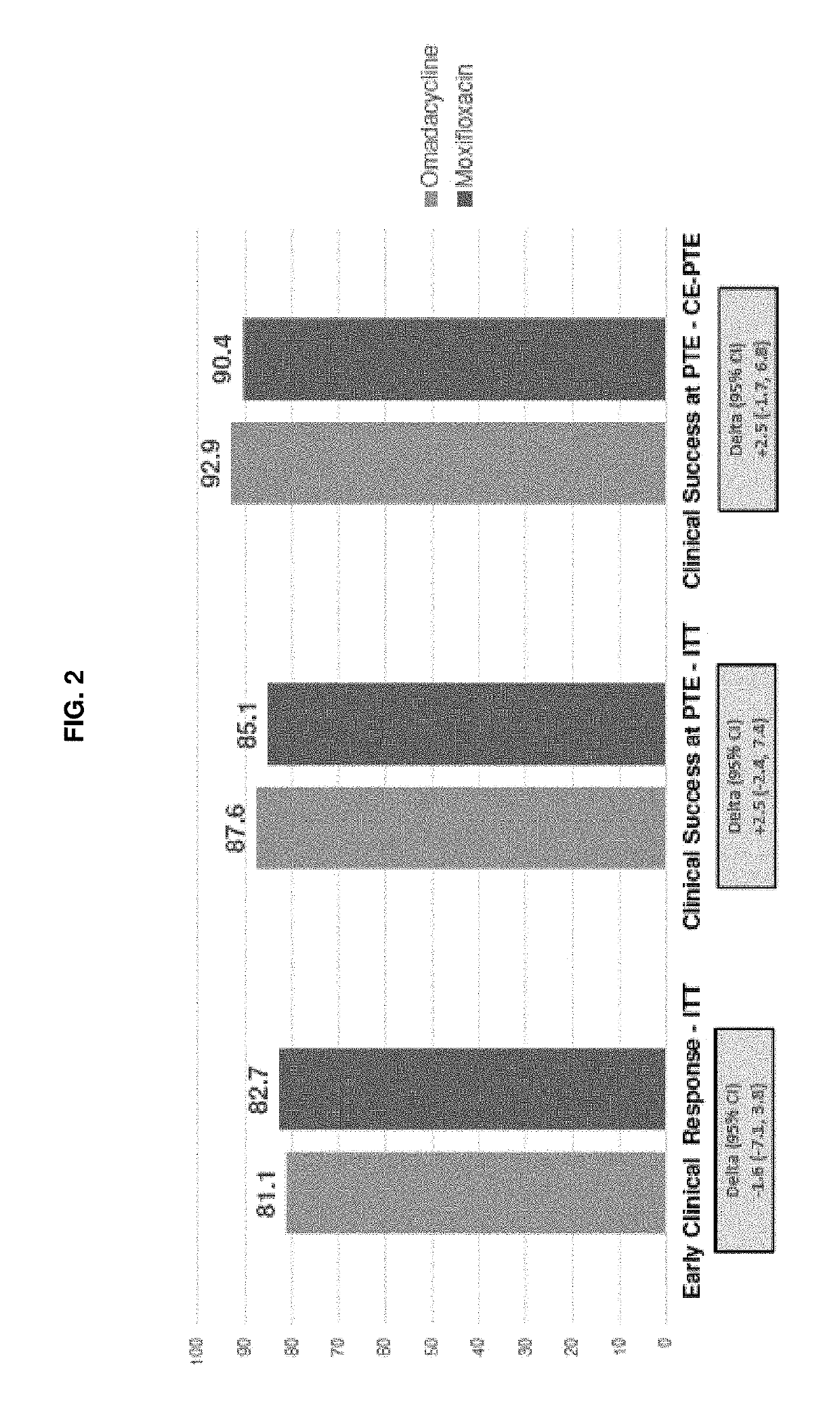
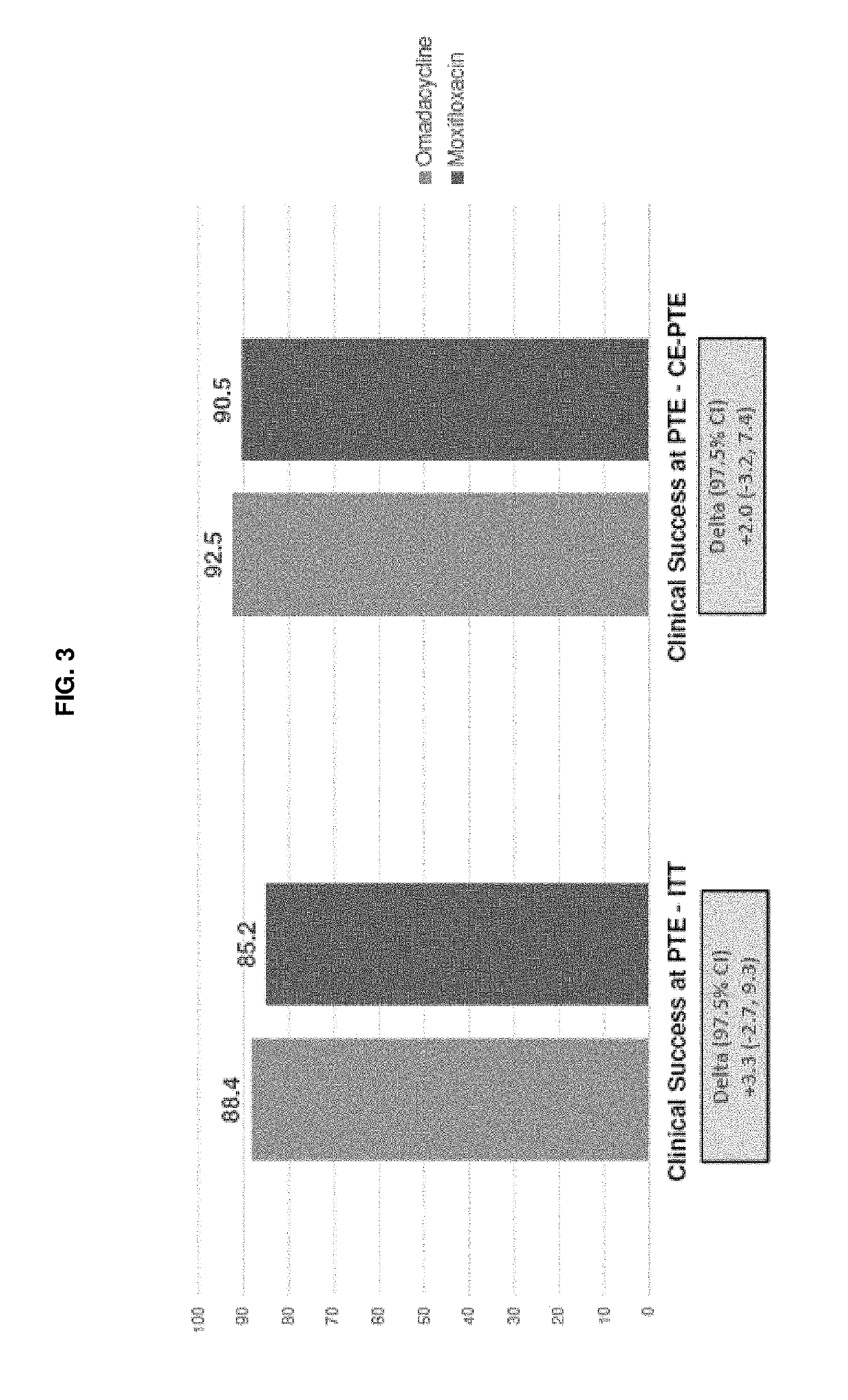
9-aminomethyl minocycline compounds and use thereof in treating community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP)
The invention disclosed herein provides a method for treating Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP) using 9-[(2,2-dimethyl-propyl amino)-methyl]-minocycline or a salt thereof, in either oral or IV doses or a combination of both.
Owner:PARATEK PHARM INC
Intravenous administration of tramadol
ActiveUS20130005821A1Rapid onsetEliminate side effectsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHuman patientIntravenous therapy
A method of treating pain, e.g., acute post-operative pain, by administering to a human patient(s) a therapeutically effective dose of tramadol intravenously over a prolonged time period is disclosed. In certain embodiments, the dose is intravenously administered in a time period from about 10 minutes to about 3 hours, preferably from about 10 minutes to about 30 minutes. In other embodiments, intravenous doses are administered at suitable time intervals over a time period from about 3 hours to 48 hours.
Owner:REVOGENEX IRELAND
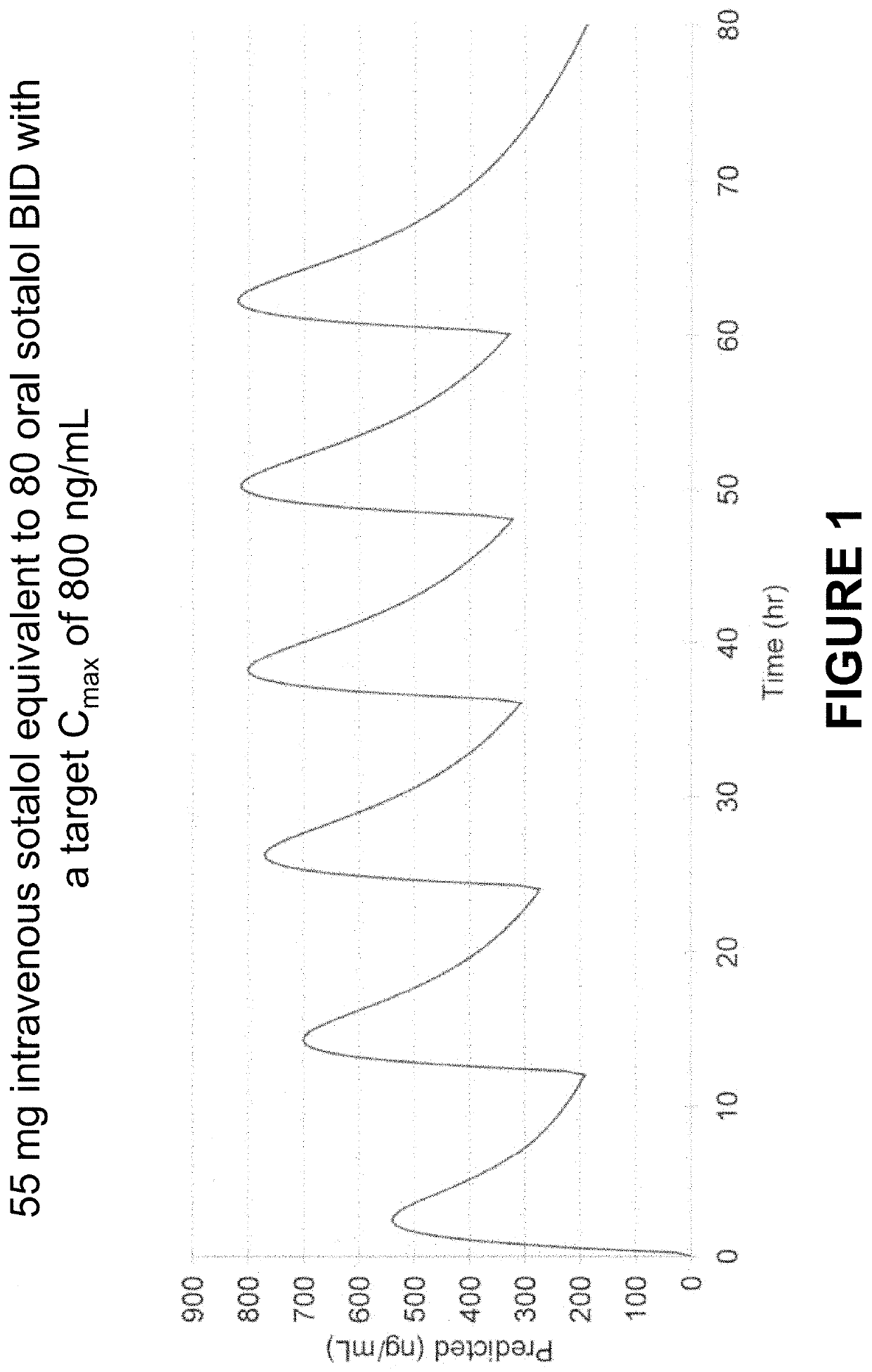
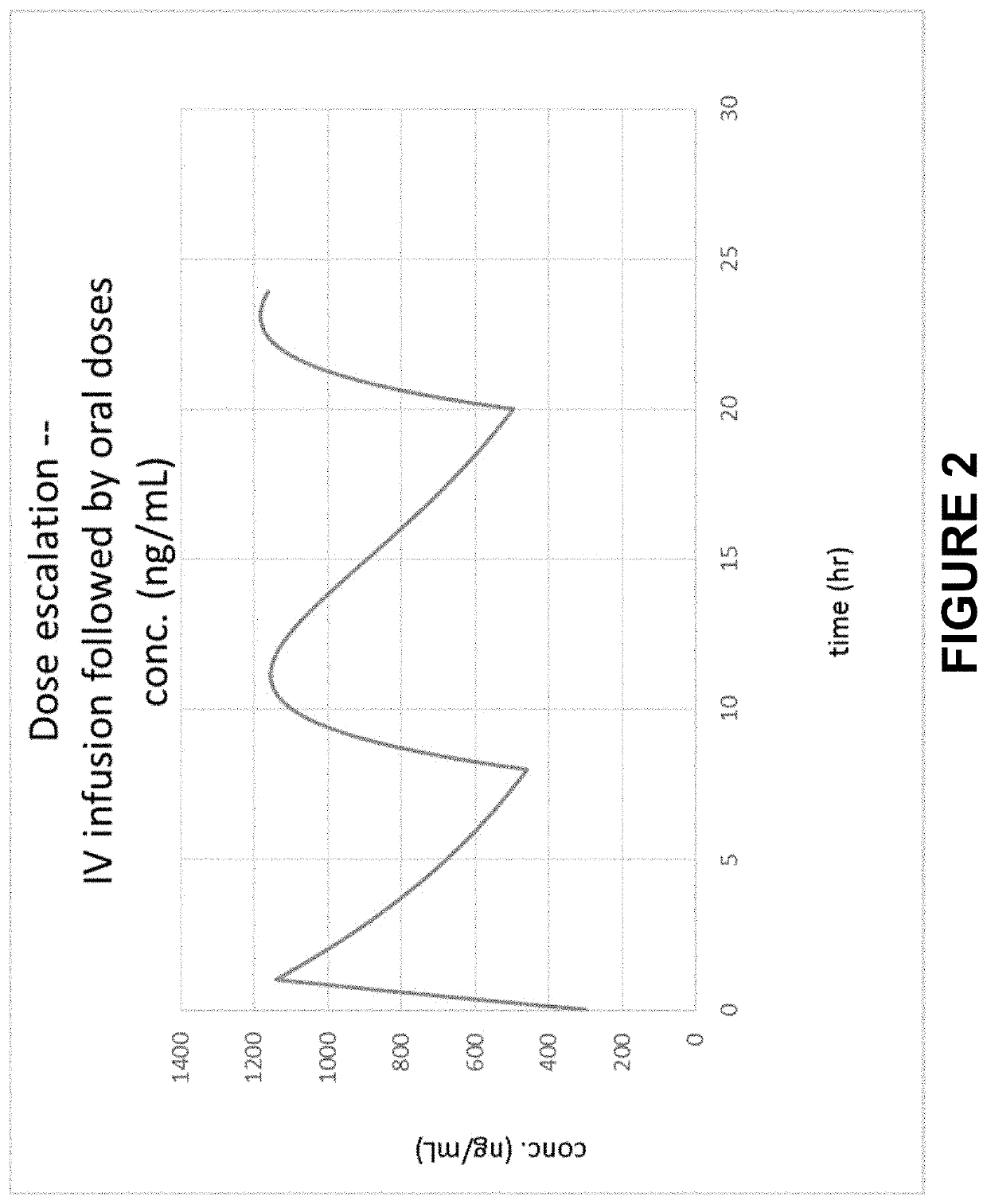
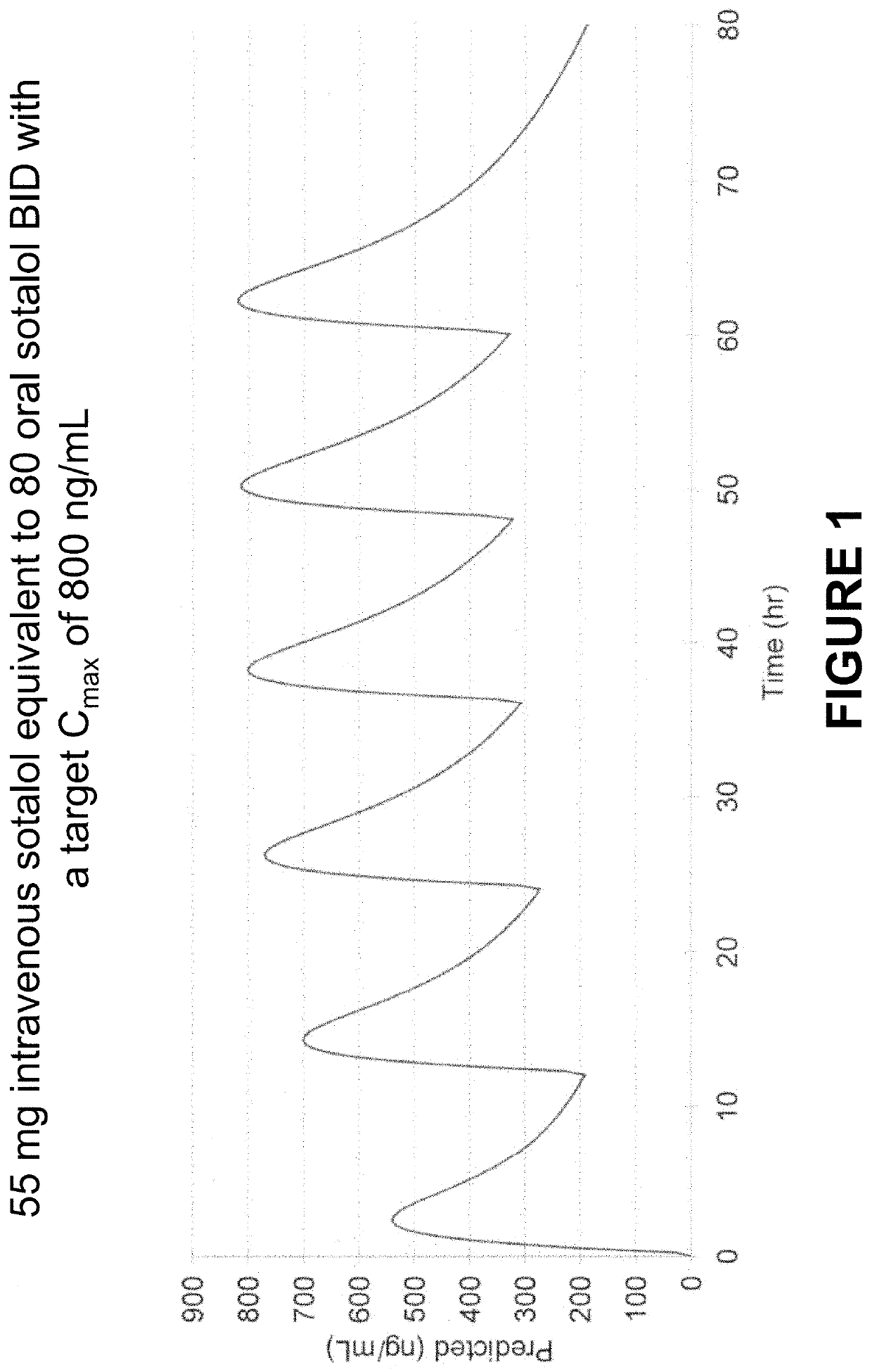
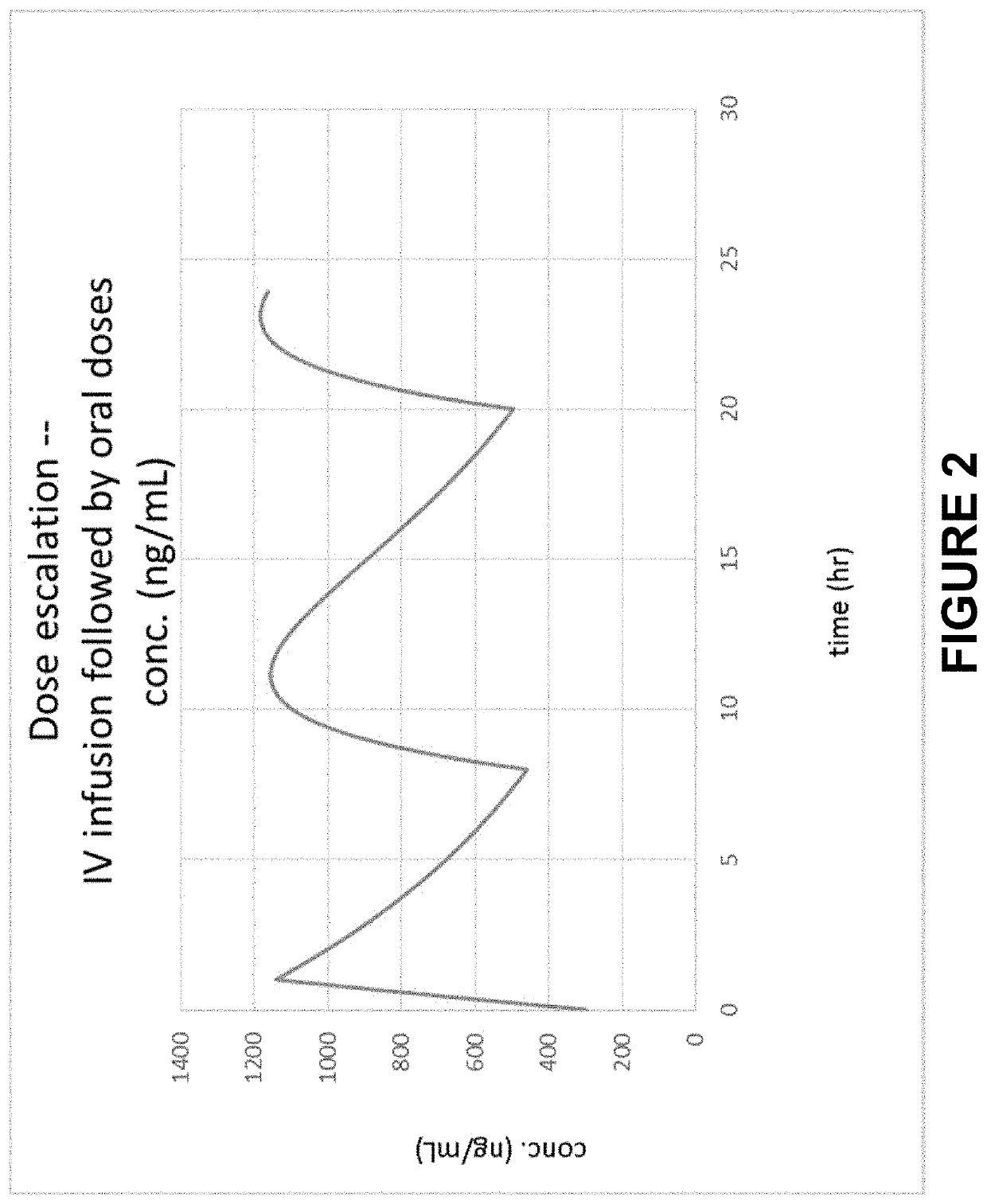
Method of Initiating and Escalating Sotalol Hydrochloride Dosing
PendingUS20200085771A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismAmide active ingredientsSotalol HydrochlorideOral administration
Owner:ALTATHERA PHARMA LLC
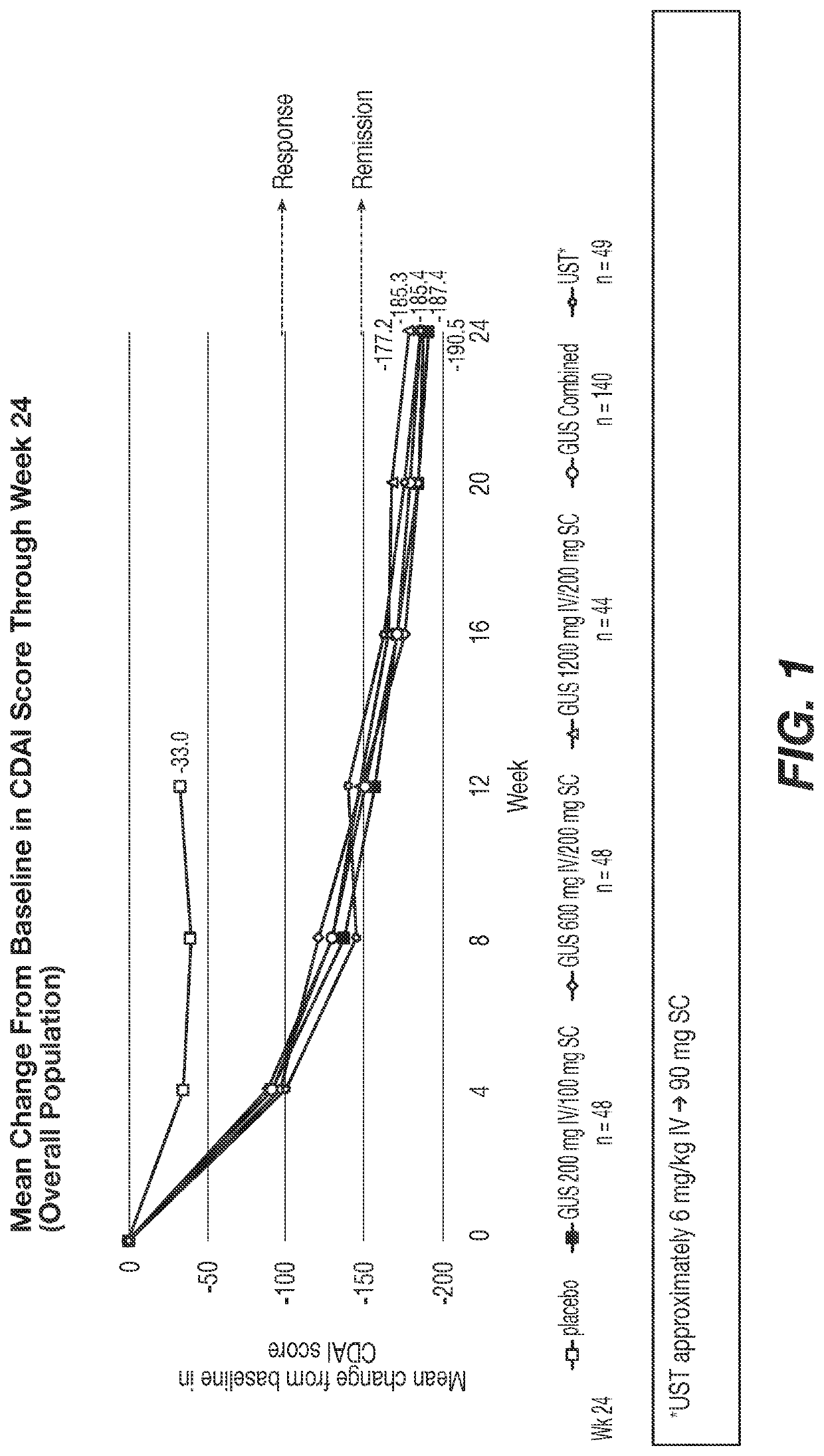
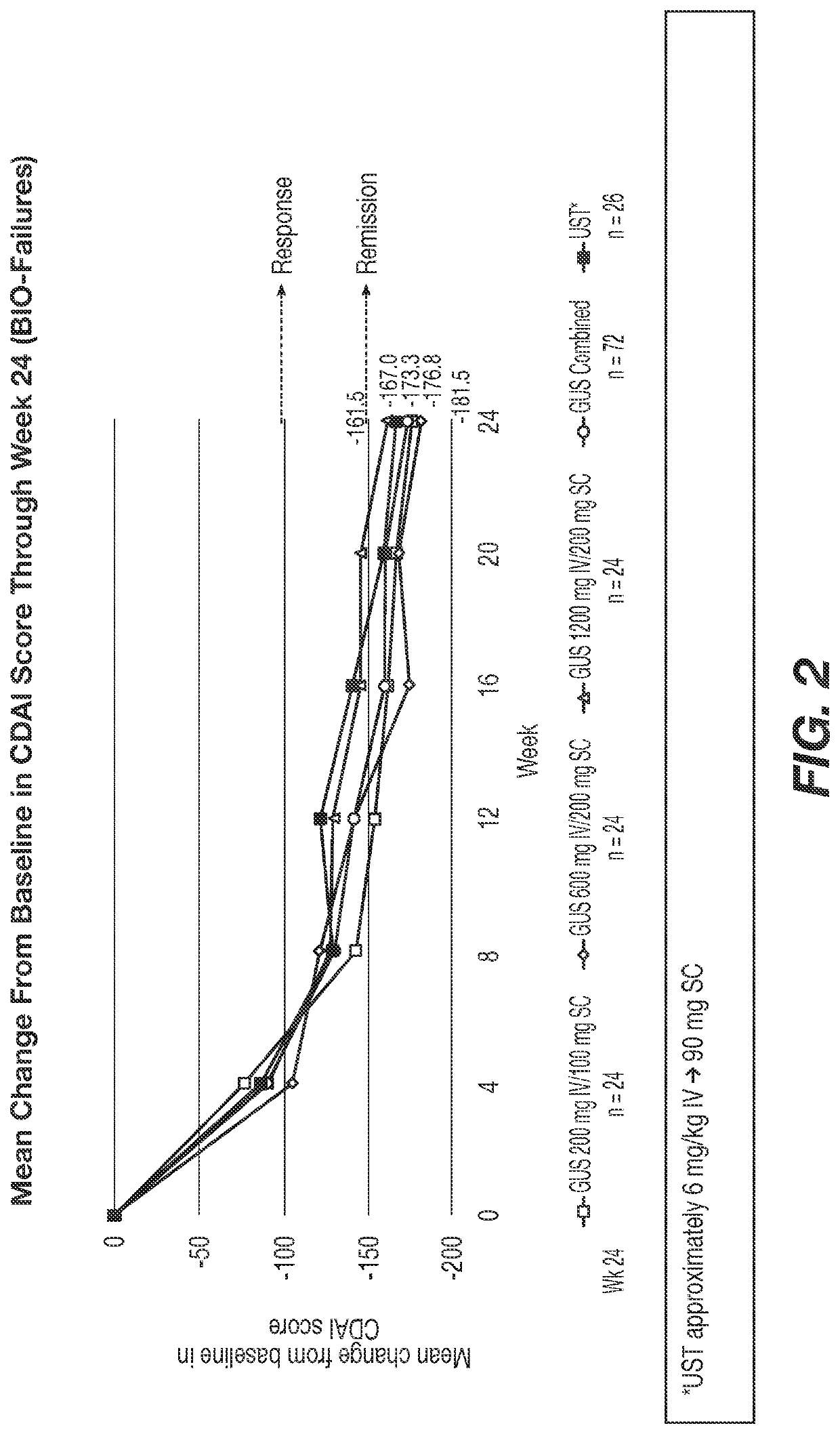
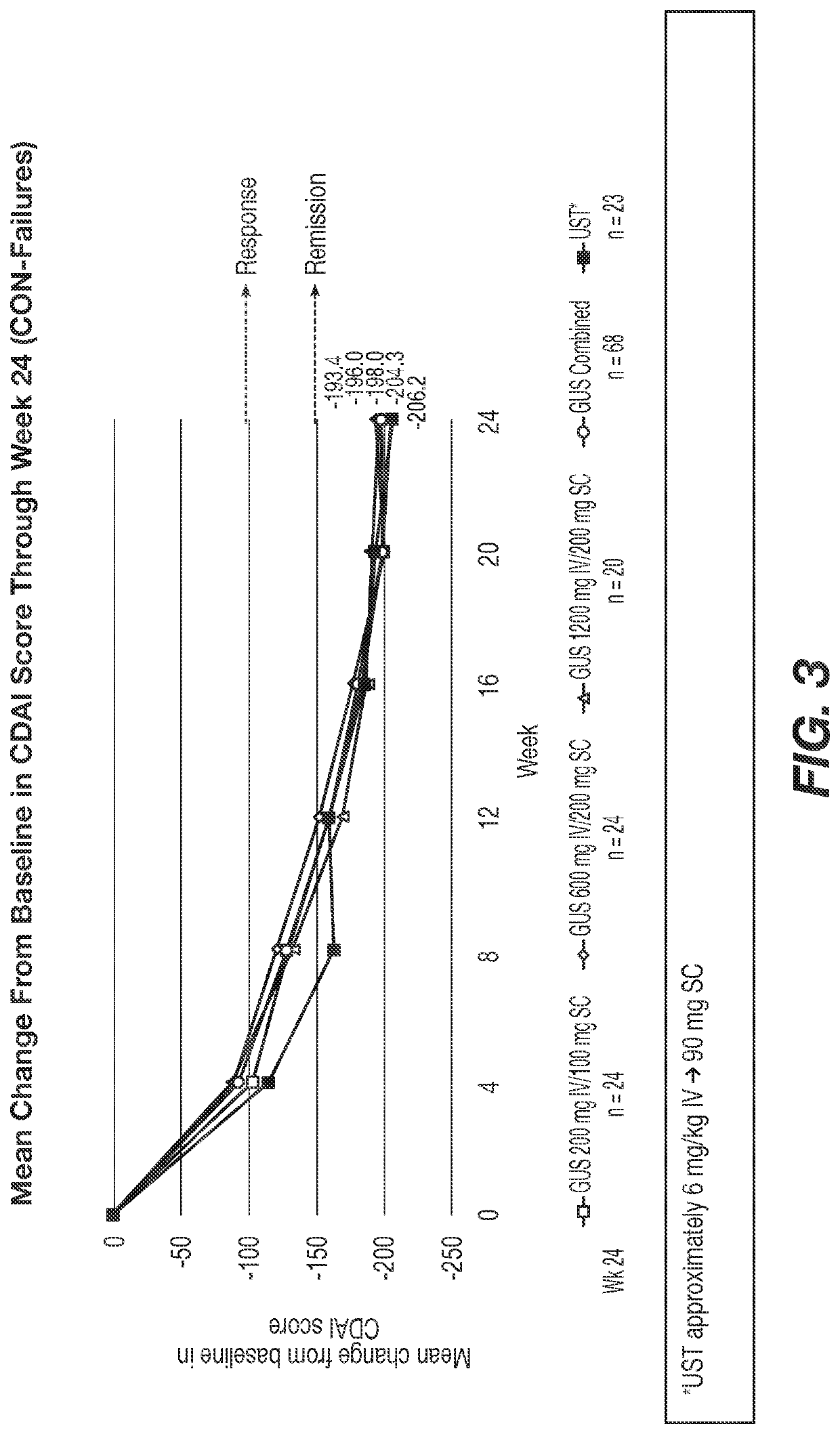
Methods of Treating Crohn's Disease with Anti-IL23 Specific Antibody
A method of treating Crohn's disease in a patient administers an IL-23 specific antibody, e.g., guselkumab, at an initial intravenous dose and subsequence subcutaneous doses.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Methods of Converting a Patient's Treatment Regimen from Intravenous Administration of an Opioid to Oral Co-Administration of Morphine and Oxycodone Using a Dosing Algorithm to Provide Analgesia
A method of converting a treatment for pain comprising intravenous administration of opioids, to a treatment for pain comprising oral administration of a first dose of an immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination in patients in need of analgesia. The method may comprise (1) determining a four-hour average oral morphine equivalents or determining a net average hourly intravenous dose, and (2) orally administering to the patient a first dose of a morphine-oxycodone combination in a 3:2 ratio by weight every four to six hours. Also, a method of treating pain in patients who had been administered opioids intravenously, comprising using a dosing algorithm to determine the first dose of the immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination.
Owner:QRXPHARMA
Methods of converting a patient's treatment regimen from intravenous administration of an opioid to oral co-administration of morphine and oxycodone using a dosing algorithm to provide analgesia
A method of converting a treatment for pain comprising intravenous administration of opioids, to a treatment for pain comprising oral administration of a first dose of an immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination in patients in need of analgesia. The method may comprise (1) determining a four-hour average oral morphine equivalents or determining a net average hourly intravenous dose, and (2) orally administering to the patient a first dose of a morphine-oxycodone combination in a 3:2 ratio by weight every four to six hours. Also, a method of treating pain in patients who had been administered opioids intravenously, comprising using a dosing algorithm to determine the first dose of the immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination.
Owner:QRXPHARMA
Methods for diagnosis and intervention of hepatic disorders
ActiveUS9639665B2Rapid assessmentMedical automated diagnosisDisease diagnosisChronic viral hepatitis CVein
The present disclosure concerns methods of administering and detecting a distinguishable agent in a sample from and assessing the condition of an organ in a subject. In a particular embodiment, the present invention concerns methods of detecting and comparing the cholate shunt, in a subject, preferably in a subject with chronic hepatitis C. In certain embodiments, the methods may comprise obtaining a sample from a subject such as a blood or saliva sample after administering an oral and intravenous dose of a distinguishable agent such as cholate and analyzing the sample clearance of the distinguishable agent from the subject and comparing the clearance levels in order to assess hepatic health. In another embodiment, the methods may comprise analyzing a sample from a subject for the presence of a distinguishable agent such as cholate and applying information obtained from analyzing the presence of the distinguishable agent to determine a treatment for a medical condition of the subject.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Method of Initiating and Escalating Sotalol Hydrochloride Dosing
PendingUS20200093759A1Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSotalol HydrochlorideOral administration
Owner:ALTATHERA PHARMA LLC
Methods of Converting a Patient's Treatment Regimen from Intravenous Administration of an Opioid to Oral Co-Administration of Morphine and Oxycodone Using a Dosing Algorithm to Provide Analgesia
A method of converting a treatment for pain comprising intravenous administration of opioids, to a treatment for pain comprising oral administration of a first dose of an immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination in patients in need of analgesia. The method may comprise (1) determining a four-hour average oral morphine equivalents or determining a net average hourly intravenous dose, and (2) orally administering to the patient a first dose of a morphine-oxycodone combination in a 3:2 ratio by weight every four to six hours. Also, a method of treating pain in patients who had been administered opioids intravenously, comprising using a dosing algorithm to determine the first dose of the immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination.
Owner:QRXPHARMA
Methods of Treating Crohn's Disease with Anti-IL23 Specific Antibody
PendingUS20210347880A1Digestive systemImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsCrohn's diseaseGuselkumab
A method of treating Crohn's disease in a patient administers an IL-23 specific antibody, e.g., guselkumab, at an initial intravenous dose and subsequent subcutaneous doses in order for the patient to respond to the antibody and meet one or more of the clinical endpoints.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Treatment of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
ActiveCN105899219AVertebrate antigen ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismRegimenImmunodeficiency virus
Methods of treating a patient with human immunodeficiency virus are disclosed. The method includes a providing intradermal and intravenous doses of a aThl composition that can increase the CD4+ cells in a patient that are resistant to HIV. The description includes a method for viral load reduction and a viral purge method. The regimen leads to a spike in the viral load and a then a return to baseline or lower levels of the virus and can lead to reduction and / or elimination of the latent viral reservoirs. Kits configured to provide intradermal doses and intravenous doses according to the regimen are also included.
Owner:IMMUNOVATIVE THERAPIES
Intravenous administration of tramadol
ActiveUS20170172914A1Improve securityImproving tolerabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDosing regimenRegimen
A method of treating pain, e.g., acute post-operative pain, by administering to a human patient(s) a therapeutically effective dose of tramadol intravenously in a dosing regimen which includes one or more loading doses administered at shortened intervals as compared to dosing at steady-state is disclosed. In certain embodiments, the dose of tramadol is from about 45 mg to about 80 mg and the second (and optionally) third doses are intravenously administered at intervals of from about 2 to about 3 hours, and thereafter the tramadol is intravenously administered at a dosing interval of about 4 to about 6 hours, until the patient no longer requires treatment with tramadol. In preferred embodiments, the intravenous dosing regimen provides a Cmax and AUC of tramadol is similar to the Cmax and AUC of an oral dose of 100 mg tramadol HCl given every 6 hours. In certain preferred embodiments, the dosing regimen comprises 50 mg IV tramadol at Hour 0, followed by 50 mg at Hour 2, 50 mg at hour 4, and 50 mg every 4 hours thereafter (e.g., until the patient no longer requires treatment with tramadol).
Owner:REVOGENEX IRELAND
Intravenous injection dosing room and its automatic control system
ActiveCN104548240BReduce volumeReduce investmentPharmaceutical containersPharmaceutical product form changeAutomatic controlPositive pressure
Owner:SICHUAN CHUANJING CLEAN TECH HLDG
Intravenous administration of tramadol
ActiveUS20170281533A1Improve securityImproving tolerabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDosing regimenRegimen
Owner:REVOGENEX IRELAND
Treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
ActiveCN105899219BGenetic material ingredientsVertebrate antigen ingredientsRegimenImmune deficiency syndrome
Owner:IMMUNOVATIVE THERAPIES
Methods of converting a patient's treatment regimen from intravenous administration of an opioid to oral co-administration of morphine and oxycodone using a dosing algorithm to provide analgesia
A method of converting a treatment for pain comprising intravenous administration of opioids, to a treatment for pain comprising oral administration of a first dose of an immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination in patients in need of analgesia. The method may comprise (1) determining a four-hour average oral morphine equivalents or determining a net average hourly intravenous dose, and (2) orally administering to the patient a first dose of a morphine-oxycodone combination in a 3:2 ratio by weight every four to six hours. Also, a method of treating pain in patients who had been administered opioids intravenously, comprising using a dosing algorithm to determine the first dose of the immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination.
Owner:QRXPHARMA
Methods of converting a patient's treatment regimen from intravenous administration of an opioid to oral co-administration of morphine and oxycodone by using a dosing algorithm to provide analgesia
InactiveCN103415291ANervous disorderPharmaceutical active ingredientsCo administrationImmediate release
A method of converting a treatment for pain comprising intravenous administration of opioids, to a treatment for pain comprising oral administration of a first dose of an immediate release mgrphine-oxycodone combination in patients in need of analgesia. The method may comprise (1) determining a four-hour average oral morphine equivalents, a one-hour average oral morphine equivalents, or determining a net average hourly inlravenous dose, and (2) orally administering to the patient a first dose of a morphine-oxycodone combination in a 3:2 ratio by weight every four to six hours. Also, a method of treating pain in patients who had been administered opioids intravenously, comprising using a dosing algorithm lo determine the first dose of the immediate release morphine-oxycodone combination.
Owner:QRXPHARMA
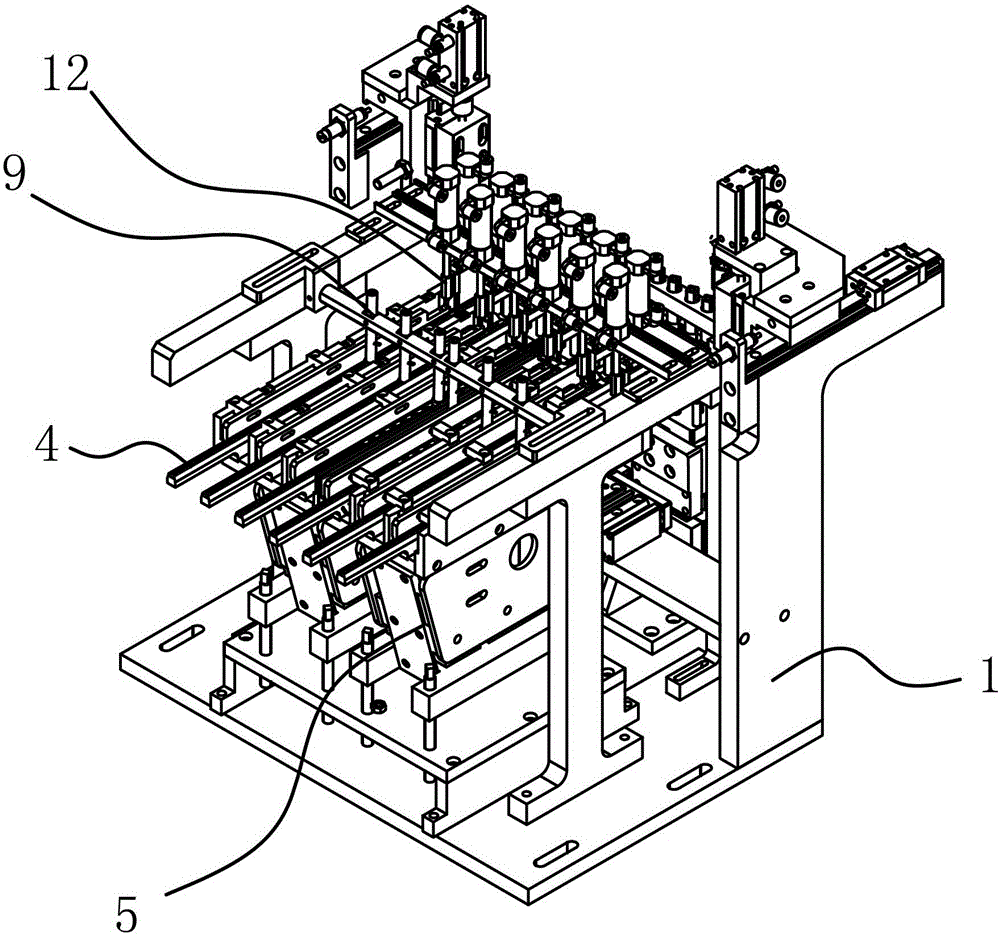
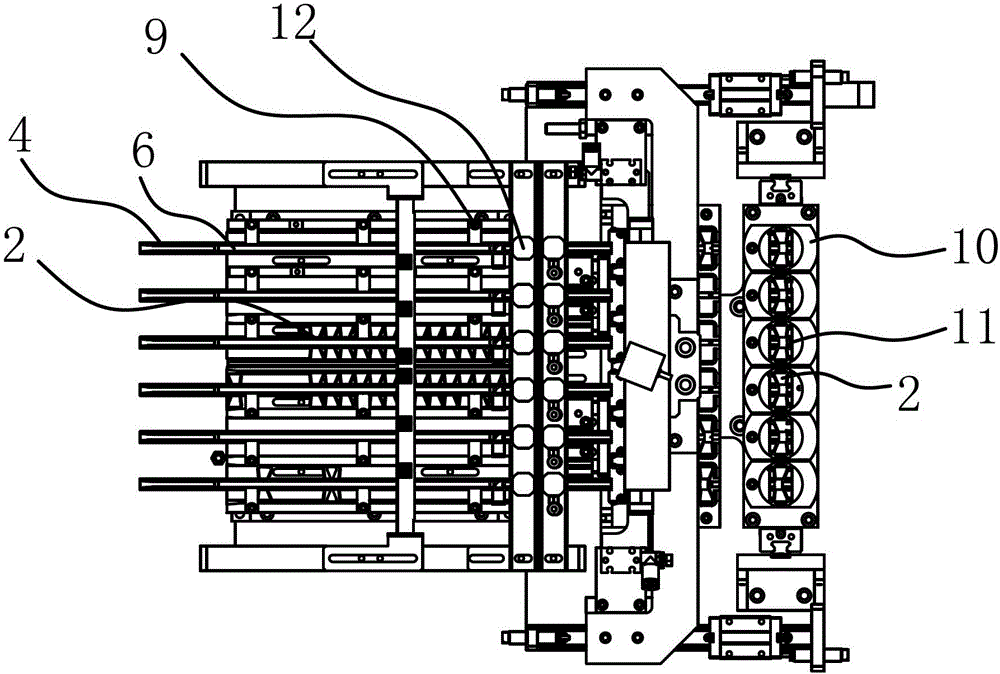
Method and device for distributing materials of a needle seat assembly of a double-needle-handle medical venous needle
ActiveCN103241540BRealize automatic feeding processBarriers preventing subsequent assemblyConveyor partsVeinMedical device
Owner:MAIDER MEDICAL IND EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com