Method for non-vacuum melting and casting Cu-Cr-Zr alloy
A non-vacuum smelting, cu-cr-zr technology, used in the processing, smelting and casting of Cu-Cr-Zr alloys, can solve the problem of inability to measure components, adjust components, raw material components and impurities High content requirements, high requirements for furnace body sealing and other problems, to achieve the effects of large-scale production, high cost, and difficult large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
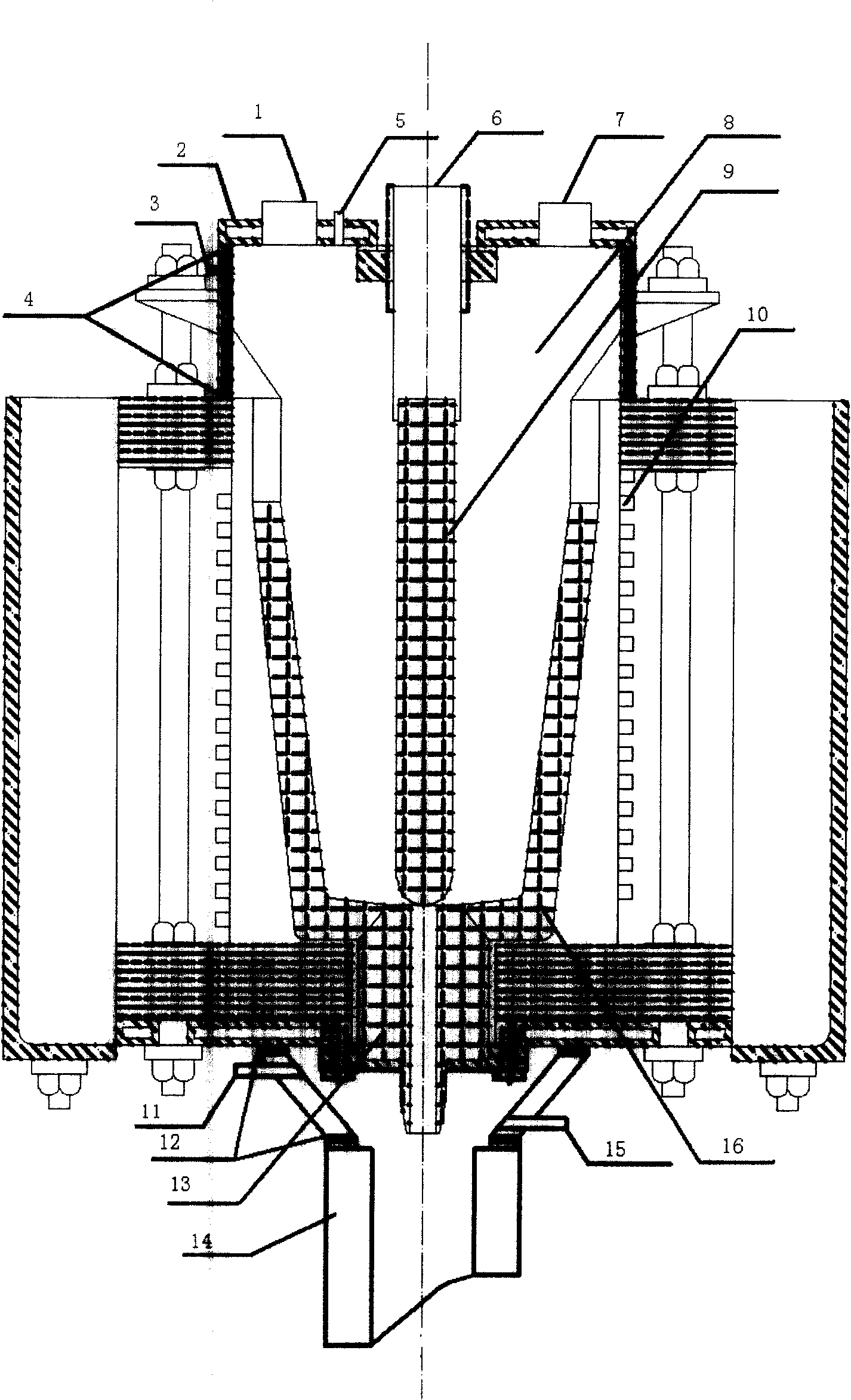
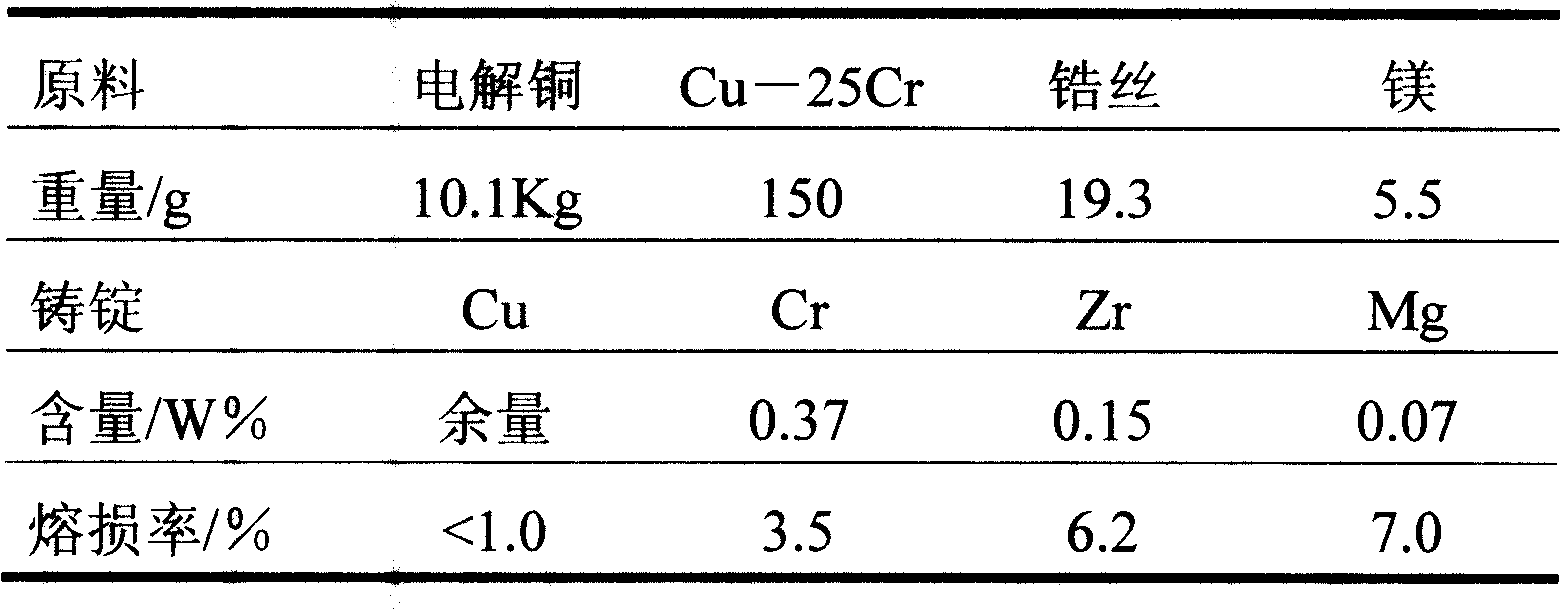
[0020] The raw materials of electrolytic copper, copper-chromium intermediate alloy and zinc are respectively taken, and the amount of materials taken is shown in Table 1, and loaded into the furnace 8 from the feeding port 7, so that it is contained in the crucible 16; the furnace cover 2 can also be opened to directly add raw materials. Cover the feeding port 7 and the observation window 1, open the protective gas valve, and pass in argon gas from the upper air inlet 3 until the air is discharged from the upper gas outlet 5, the protective gas is filled with the furnace 8, and the match will be lit at the upper gas outlet 5. Immediately extinguished. Turn on the induction heating device 10, the power is 10KW, the time is 10 minutes, the power adjustment is 50KW, and it is heated to melting. The whole heating process can be observed in the observation window 1. Add copper-clad zirconium and magnesium from the feeding port 7, smelt for 5 minutes, open the gas valve at the same...
Embodiment 2
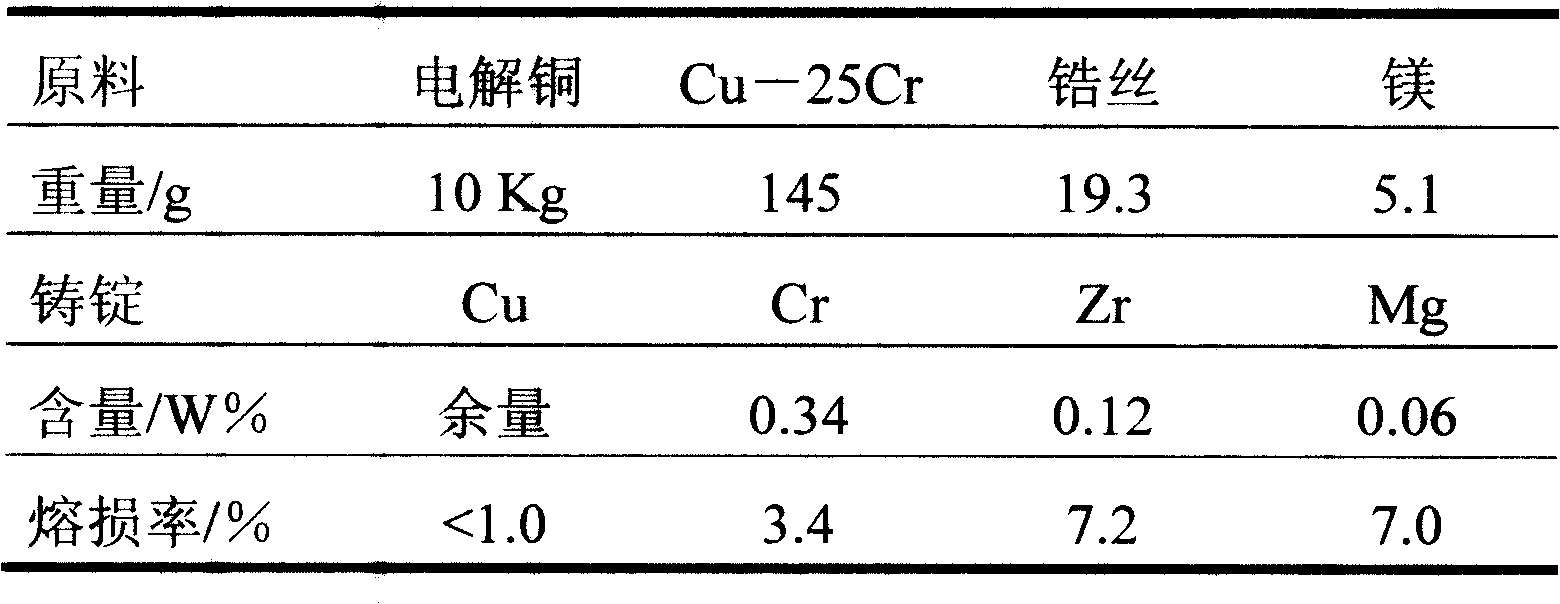
[0025] The present invention is carried out under the same conditions as in Example 1 by using zirconium wire instead of copper-clad zirconium. The chemical contents of raw materials and ingots are shown in Table 2. The loss rates of each metal during the smelting process are: Cu≤1.0%, Cr≤3.4% and Zr≤7.2%.
[0026] Table 2
[0027]
Embodiment 3
[0029] Adopt the same condition as embodiment 1, adopt N 2 In order to protect the gas, use a gas nozzle to extend into the melt from the feeding port 7 during the heat preservation process after smelting, and inject N 2 Pass into the melt for degassing. The chemical content of raw materials and ingots is shown in Table 3. According to the metallographic photos, it can be seen that the structure of the ingot is significantly improved, and the pores and inclusions are reduced. The loss rates of each metal during the smelting process are: Cu≤1.1%, Cr≤3.4% and Zr ≤7.1%.
[0030] table 3
[0031]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com