Chemical activator and its preparation and application
An activator, chemical technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of toxic and side effects, use restrictions, and rarely reported anti-plant virus effects, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
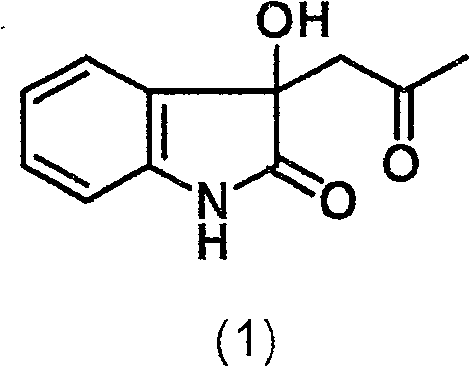
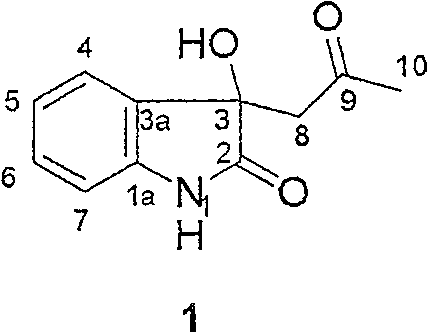
[0020] Preparation of 3-acetonyl-3-hydroxyoxindole (3-acetonyl-3-hydroxyoxindole, AHO) (1):
[0021] (1) 17 kg of dry weight plant Strobilanthesis cusia whole herb was extracted with 10% acetone-methanol, and after removing the solvent under reduced pressure, an extract was obtained. , Methanol, and water were dissolved, and the solubles were prepared into corresponding 5-part extracts after removing the solvent, dissolved in DMSO to form a solution with a concentration of 10 mg / ml, and the anti-TMV activity of each part was measured by ELISA. The ethyl acetate extract was used as an effective component, and was repeatedly separated by various column chromatography methods to obtain a single anti-TMV active compound 3-acetonyl-3-hydroxyoxindole (3-acetonyl-3-hydroxyoxindole, AHO) ( 1) 17 mg.
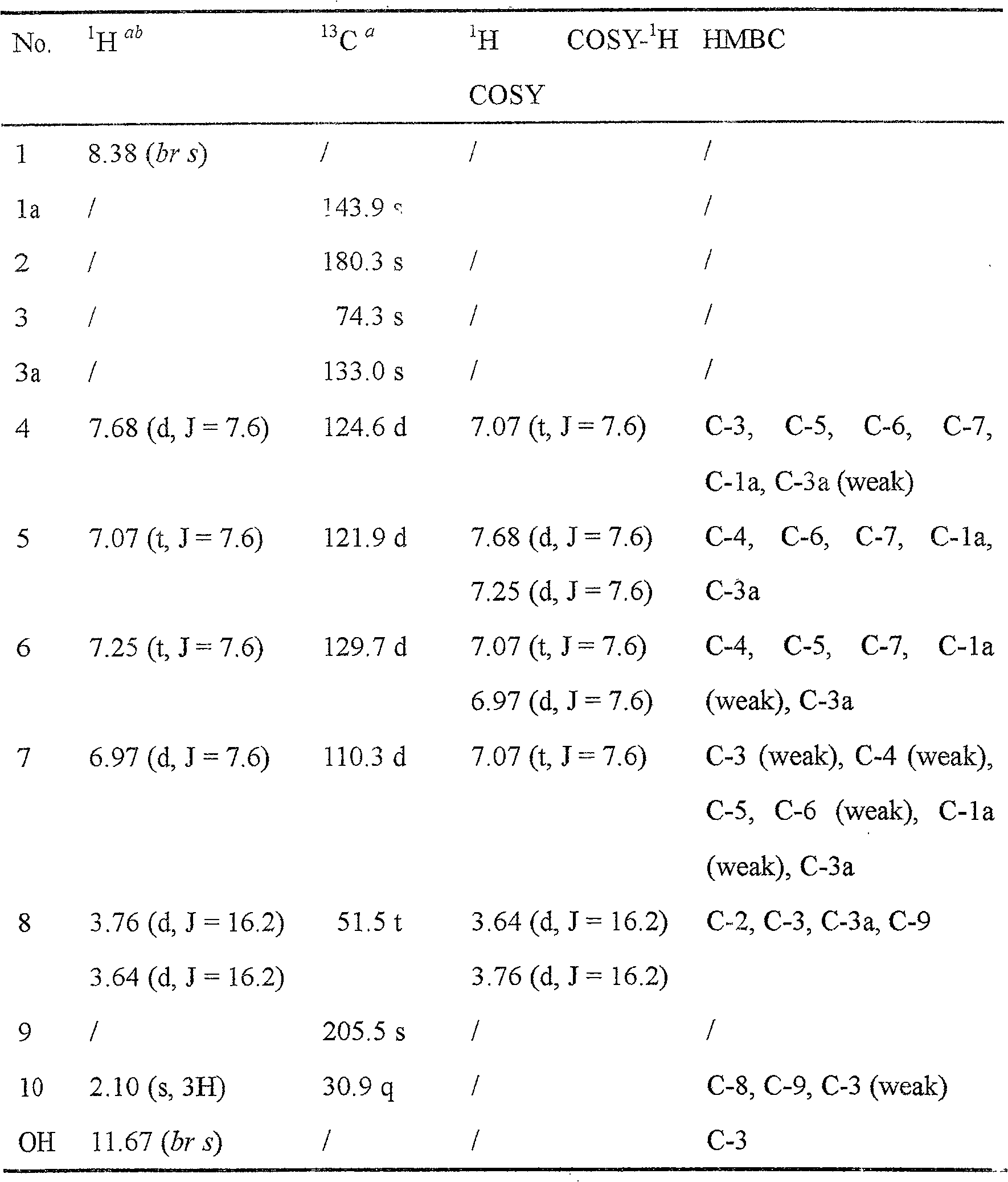
[0022] Table 1 Proton spectrum and carbon spectrum data of compound (1)
[0023]
[0024] 3-acetonyl-3-hydroxyoxindole (3-acetonyl-3-hydroxyoxindole, AHO) (1)
[0025]
[0026] ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The inhibitory rate test of compound (1) to TMV replication under different application conditions:
[0033] In order to explore the mechanism of action of the compound (1) against TMV, the present invention designs three drug testing methods: A) administering the drug first and then inoculating the virus, B) inoculating the virus first and then administering the drug, and C) mixing the drug and the virus for inoculation. The drug is divided into 5 concentrations, namely 100, 200, 300, 400, 500nM. Application method: apply the drug first and then inoculate the virus, or inoculate the virus first and then apply the drug, all are foliar application. The mixed inoculation of the drug and the virus is to mix different concentrations of compounds with TMV, place at 37°C for 15 minutes and then inoculate . Detection methods: scab detection, electron microscope detection, enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) detection. The experimental results show that the virus inhibition rat...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Under optimal reagent conditions, the impact of different concentrations of compound (1) on TMV proliferation:
[0038] Different concentrations of compound (1) were evenly sprayed on the leaves of the systemic host tobacco K326, and then inoculated with TMV. Three days after the inoculation, the proliferation of the virus was detected by ELISA. The results showed that as the compound concentration increased, the virus content gradually decreased, and when the compound concentration was 500 nM (125 μg / ml), no virus could be detected (Table 3).
[0039] Table 3. Determination of plant viruses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
[0040]
[0041] CK- is negative control, CK+ is positive control, greater than positive control is positive, negative control less than 2 times is negative.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com