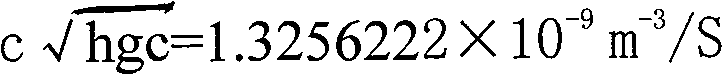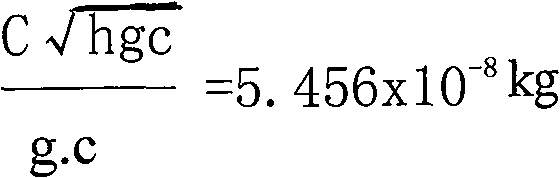Production of magnetic refrigerant material by ferro-manganese mixture
A technology for magnetic refrigeration materials and iron-manganese nodules, which can be applied in heat exchange materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low grade and no mining value, and achieve simple preparation process, widen possibilities and rich sources of raw materials. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0012] Take 10 kilograms of iron-manganese nodule secondary ore or ocean polymetallic nodule secondary ore, add dilute nitric acid to dissolve it, control the PH value of 3-4, and then add 10 kilograms of gadolinium gallium garnet powder, homogenize, and wait for the pH to rise After reaching a slightly acidic pH of about 6.5, the excess tartaric acid aqueous solution is thoroughly mixed and dehydrated by a centrifugal dehydrator. The dehydrated material is heated in the air at 900-1000℃. For example, it can be heated, dried and cooled by a constant temperature blast furnace. Serve as a magnetic refrigeration material. During the above-mentioned whole reaction process, some non-magnetic gallium ions are replaced by magnetic iron ions, and because of the super exchange between Fe ions and Gd ions, the local magnetic moments are ordered to form magnetic nanocluster materials. The effective working temperature range of magnetic refrigeration materials is 15k-40k.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com