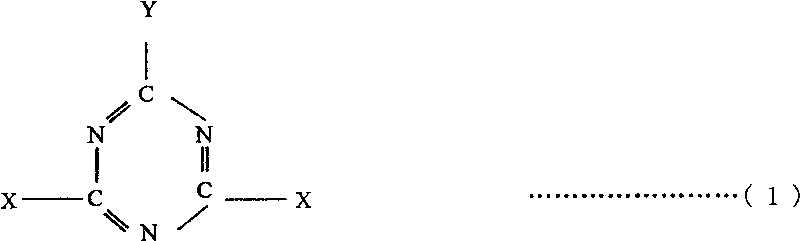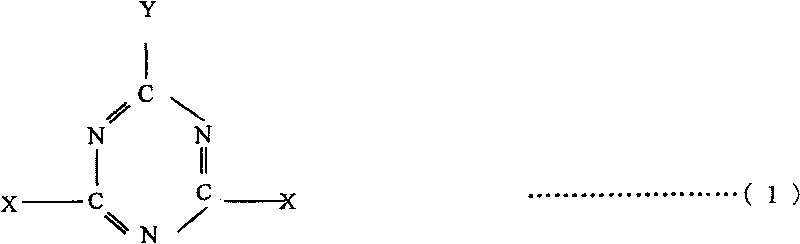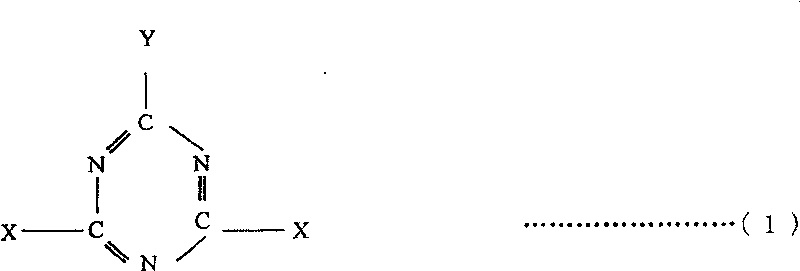Method for improving organic fiber structure performance and endowing hydrophobic function
An organic fiber and structure technology, applied in the field of organic fiber structures, can solve the problems of promoting the absorption capacity of dust, garbage and other substances, the negative impact of the organic fiber structure's pulling degree, and the rough and hardening of the fabric, so as to save money and reduce Carbon dioxide and oxychloride, the effect of energy saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] 100% silk dyed with acid dyes, EC / 72 counts, using the "exhaust in bath method". Water 360L in the dyeing machine, concentration 10% 2,6-dichloro-4-(3-sulfonic acid group)-S-triazine aqueous solution 3.6kg, acetic acid (4.8% concentration) 170g, sorbitol 360g, Adjust the liquid with the above raw materials. After that, the speed does not exceed 2°C per minute until the temperature rises to 50°C, and the machine runs for 20 minutes in this state. After that, the standard is not to exceed 2°C per minute, and it has been raised to 85°C. In this state, after 30 minutes of machine operation, the water is drained. Then wash with 85°C hot water for 10 minutes to make it hydrophobic. Wash again with ordinary water, and after dehydration, use 120°C dry heat to carry out the first stage of substantial drying process. Afterwards, mix 100L solution with hydrophobic function, calculate according to the water absorption rate of 70%, dehydrate the cloth after absorbing the correspo...
Embodiment 2
[0081] 100% cotton of navy blue 60 / 22 / 2 counts dyed with chlorotriazine reactive dyes, the cloth with a total weight of 24kg is injected with 360L of water in the dyeing machine, and dropped into 10% sodium chloride aqueous solution (o.w.f20%) 4.8 kg and 9kg of sodium bicarbonate, 1.8kg of sodium carbonate, 10.8kg of sodium sulfate, and 480 pieces of hydrolyzed silk components (o.w.f 2%). Put the above raw materials into water below 30°C for stirring. Gradually raise the temperature to 50°C at a speed exceeding 2°C, and run the machine for 20 minutes while maintaining this temperature. Gradually heat up to 85°C at a rate of no more than 2°C per minute. At this temperature, run for 30 minutes to drain water, then wash with hot water at 85°C. After the hydrophobic process, wash with water again, and after dehydration, Substantial drying treatment was carried out at a temperature of 120°C, and then, as the last process, a high-temperature heat treatment at 170°C was carried out a...
Embodiment 3
[0085] 2 / 1, 100% wool fabric dyed with chrome dyeing, weight 25kg. As the treatment of the first stage, need water 144L, the 2 of concentration 10% 2,6-dichloro-4-azulene-S-triazine sodium chloride aqueous solution (o.w.s20%) 36kg, add hydrolysis silk component 1.8kg ( o.w.s1%) acetic acid (48% concentration) 900g, the above several raw materials, as the first stage of treatment, after stirring at room temperature, o.w.s20% aqueous solution is poured into the liquid tank and calculated according to the water absorption rate of 60% , after soaking and dehydration, carry out the drying treatment in the first stage for 3 minutes at a temperature of 90°C, and then perform double boiling in a water temperature of 80°C for 10 minutes, followed by dehydration and drying treatment. Then soak in 100L solution with hydrophobic function, the water absorption rate is calculated as 58%, and then carry out substantial drying treatment in a dryer at 130°C, and finally carry out 30°C in a hig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com