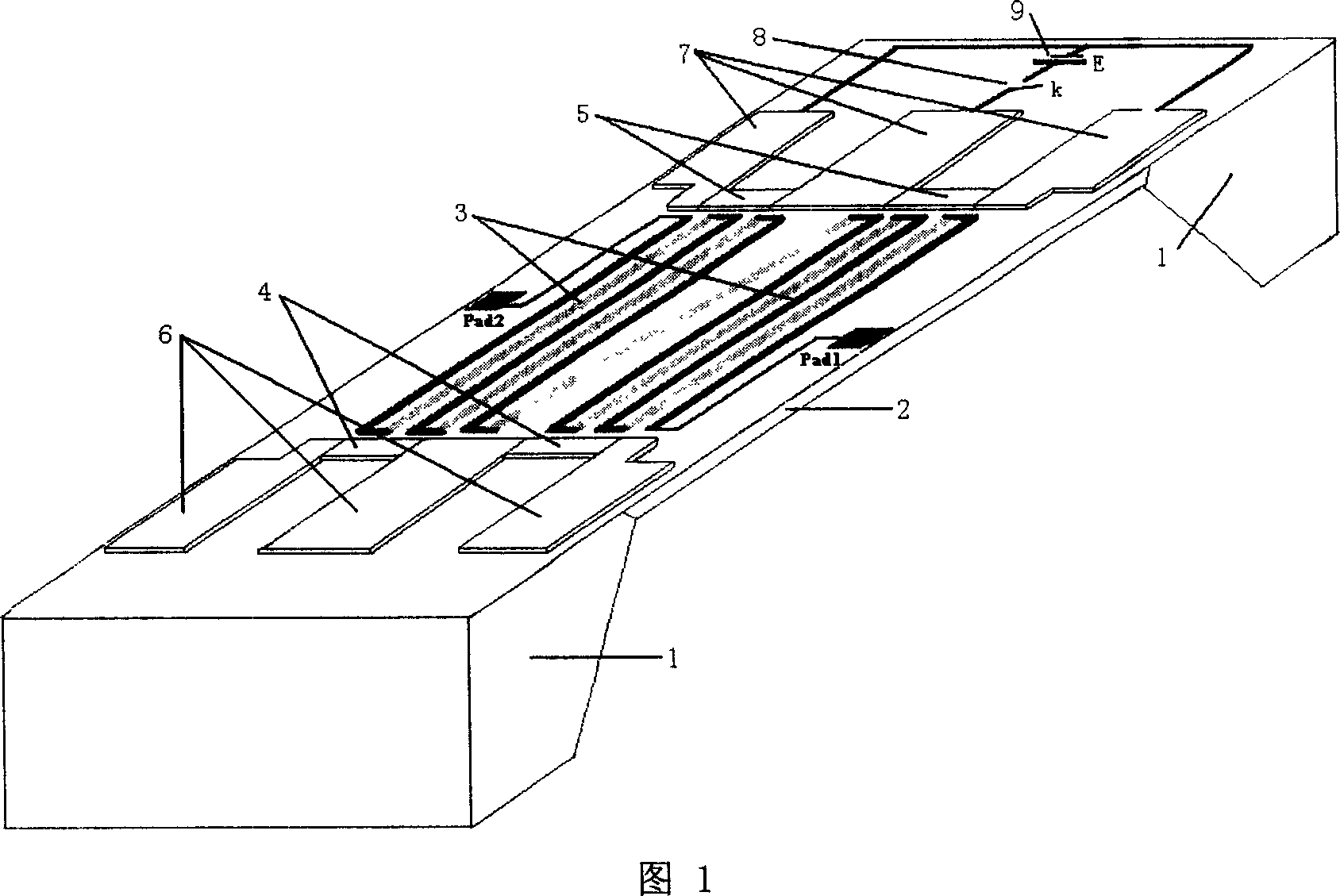
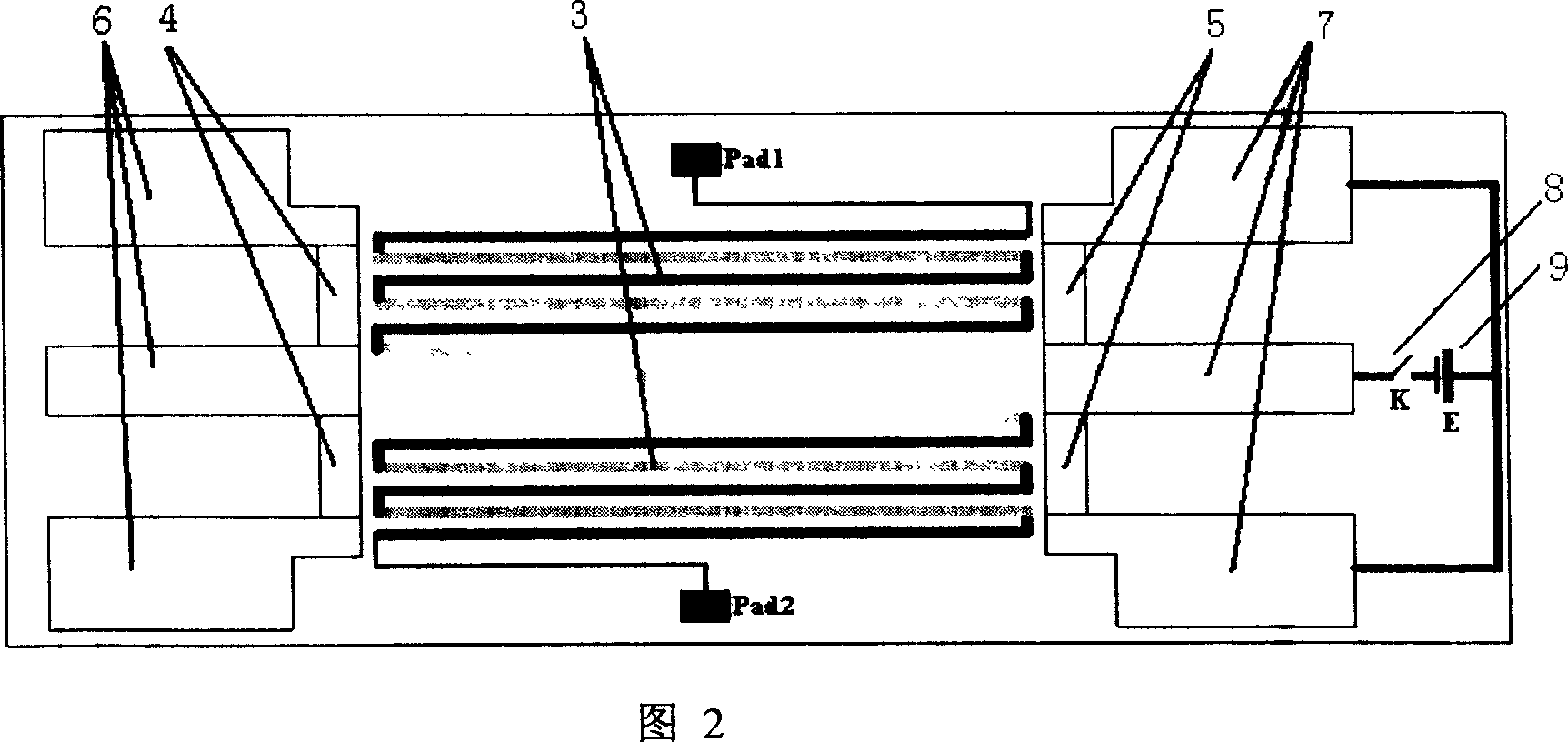
Two-end heated microwave power sensor
A microwave power and sensor technology, applied in the direction of electric power measurement by thermal method, can solve the problems of high cost, complex manufacturing process, inconvenient use, etc., to simplify the design process, improve the microwave performance, and increase the degree of freedom. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The double-terminal heating type microwave power sensor of the present invention uses the coplanar waveguide as a microwave transmission line to introduce the microwave signal to be measured, and uses two matching resistors at the end of the coplanar waveguide to convert the microwave signal into heat, and a group of heat piles ( Including two output pressure welding pads Pad1 and Pad2), symmetrically make the same DC transmission line as the microwave transmission line (coplanar waveguide) and microwave load resistance at the other end of the heat pile, and two parallel TaN DC heating resistors 5, TaN DC The circuit of the heating resistor 5 also includes a DC switch K and a DC adjustable power supply E. For the thermopile in the middle, the whole structure is thermally symmetrical from left to right. When the sensor is working, adjust the size of the DC power supply E so that the output voltage of the thermopile is zero, then the measured microwave power is equal to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com