Process for producing molten iron and apparatus therefor
A manufacturing method and molten iron technology, applied in the field of molten iron manufacturing, can solve problems such as being unable to remain intact, and achieve the effects of prolonging life, high metallization, and reliable protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
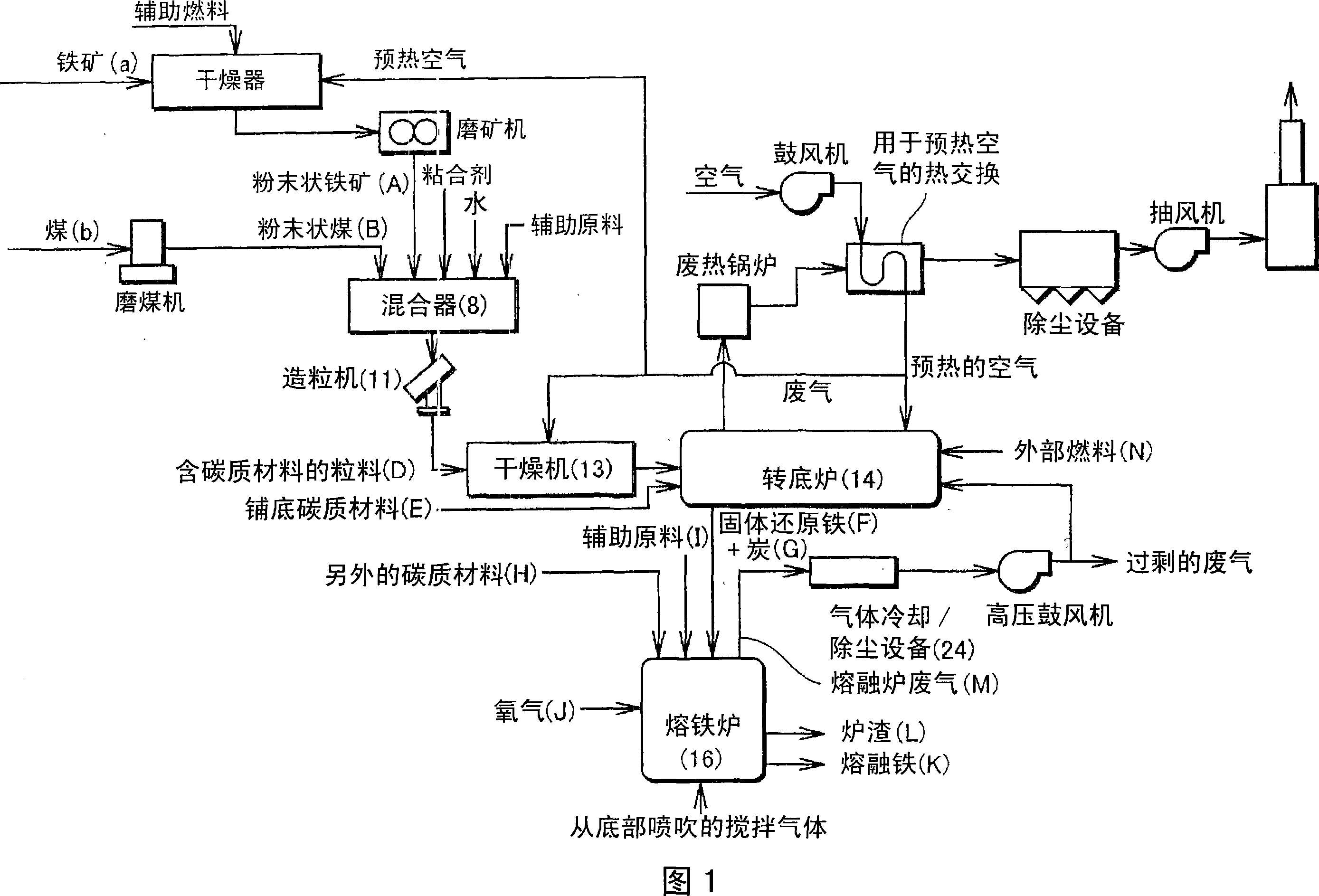
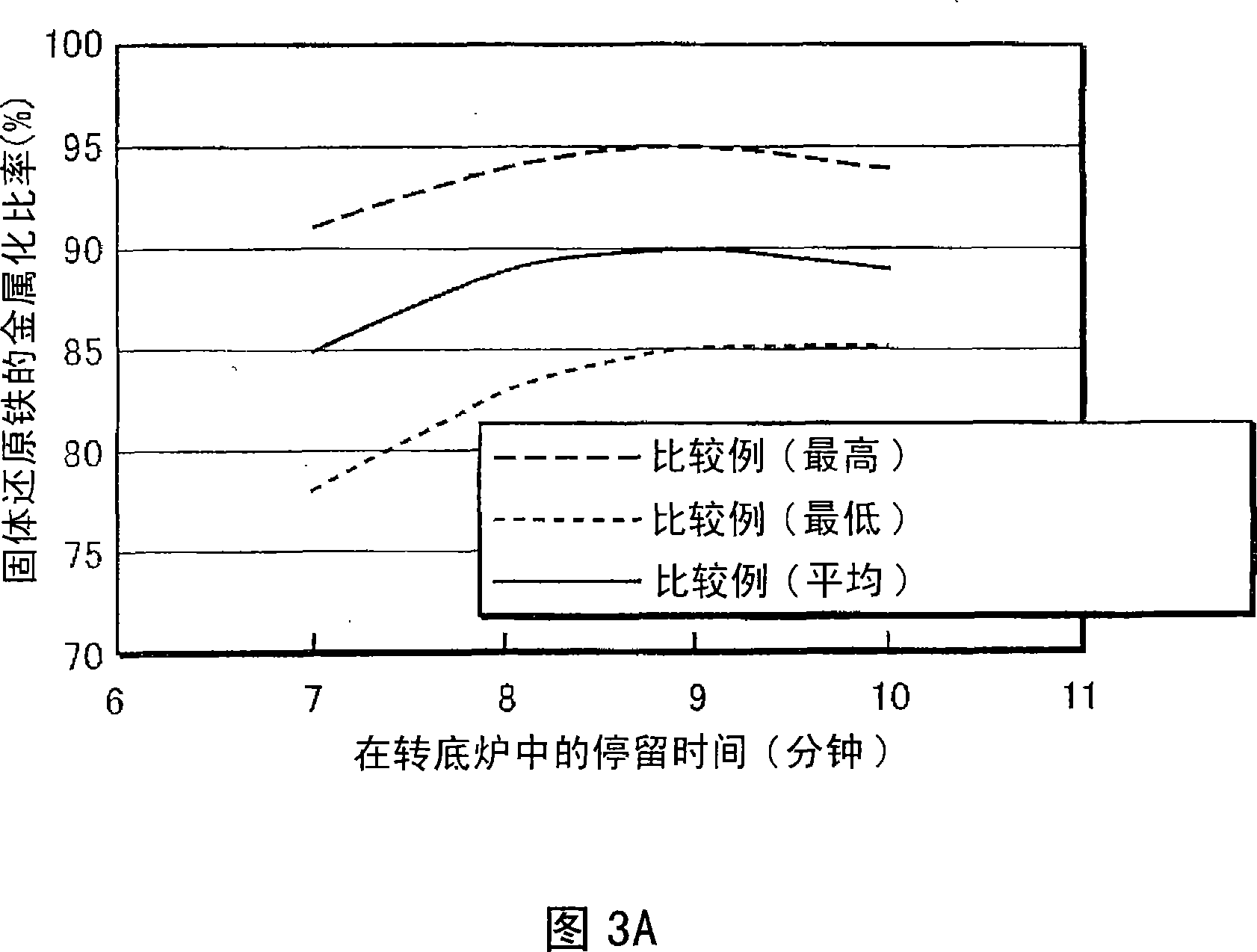
[0026] FIG. 1 is a flowchart showing a molten iron manufacturing process of one embodiment of the present invention, which is constructed by combining a rotary hearth furnace 14 and an iron melting furnace 16 as a live-bottom type reduction furnace.
[0027] When necessary, iron ore "a" as an iron oxide source and coal as a carbonaceous reducing agent are respectively pulverized into particles having a diameter of about less than 1 mm. The thus obtained powdered iron ore A as a source of powdered iron oxide and powdered coal B as a powdered carbonaceous reducing agent are mixed in a specified ratio, adding an appropriate amount of a binder and / or an appropriate amount of (In addition, all or part of the auxiliary raw material I can be added here, and the auxiliary raw material I is added to the iron melting furnace 16 as a slagging agent), and these are mixed by the mixer 8. After that, the mixed compound was granulated in the granulator 11 to have a particle diameter of about...
no. 2 approach
[0068] The following step (6) may be provided between the reduction step (the above step (2)) and the melting furnace charging step (the above step (3)).
[0069] (6) Step of thermoforming solid reduced iron F and char G together while they are hot
[0070] Specifically, solid reduced iron F and char G can be distributed together from, for example, a hopper 106 while hot, and press-formed into hot briquetted iron (HBI) by a thermoforming machine, and this HBI can be made Without cooling, it is dropped at a temperature of, for example, 500 to 1100° C. and charged into the melting furnace 16 .
[0071] This prevents fine particles from being scattered when charging into the iron melting furnace 16 and can significantly reduce the amount of dust in the exhaust gas from the iron melting furnace 16 . Therefore, iron yield and carbon yield can be significantly improved.
[0072] Since the purpose of shaping here is to eliminate fine particles, the shape of the compact is not limit...
no. 3 approach
[0074] The following steps (7) to (9) may be provided instead of the melting furnace charging step (the above-mentioned step (3)).
[0075] (7) After the solid reduced iron F and the char G are taken out together from the rotary hearth furnace 14, while they are hot or substantially without cooling, the solid reduced iron F and the char G are classified into coarse particles and thermal classification steps for fine particles;
[0076] (8) Utilize the coarse particle charging step that coarse particle is loaded in the melting iron furnace 16 by gravity;
[0077] (9) A fine particle spraying step of charging fine particles into the iron melting furnace 16 by spraying.
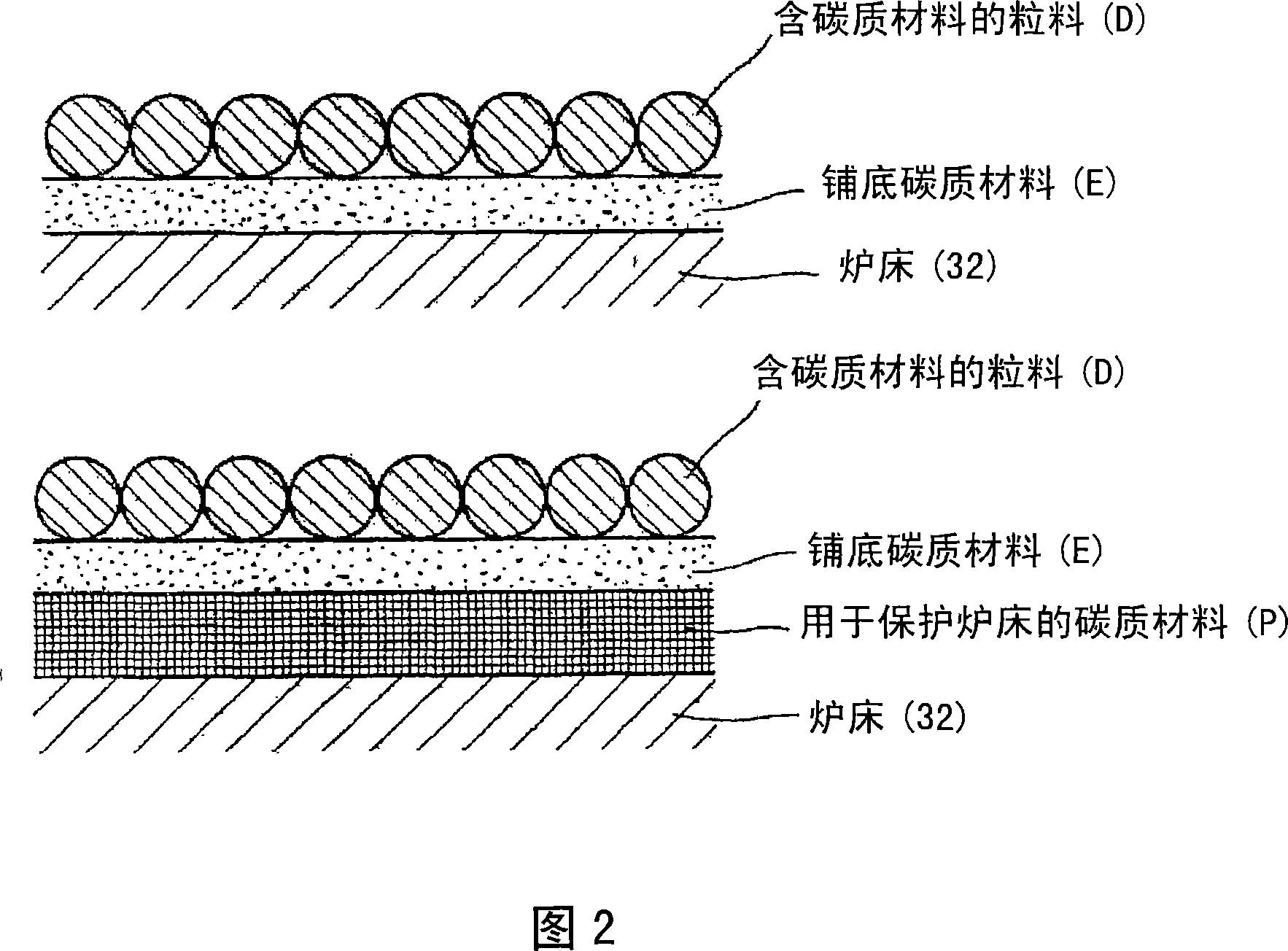
[0078] Specifically, devices having the following configurations can be used. A sieve having a mesh of about 2 to 5 mm is installed at the portion of the rotary hearth furnace 14 that discharges the solid reduced iron F and char G, and the solid reduced iron F and char G are screened while hot, wherein the coa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com